Polypit nursery [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Plastic-Khalte nursery - Nepali
technologies_1498 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A simple, inexpensive and practical method for raising healthy plant seedlings
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
During the winter in Nepal’s middle mountains, the soil temperature generally remains at 5-10 degree celsius above the ambient air temperature. This principle was used to design a simple, inexpensive, and effective nursery technology for raising vegetable and horticulture seedlings in colder regions. The polypit technology allows seedlings to be raised by protecting them from the freezing temperatures that occur mostly at night.
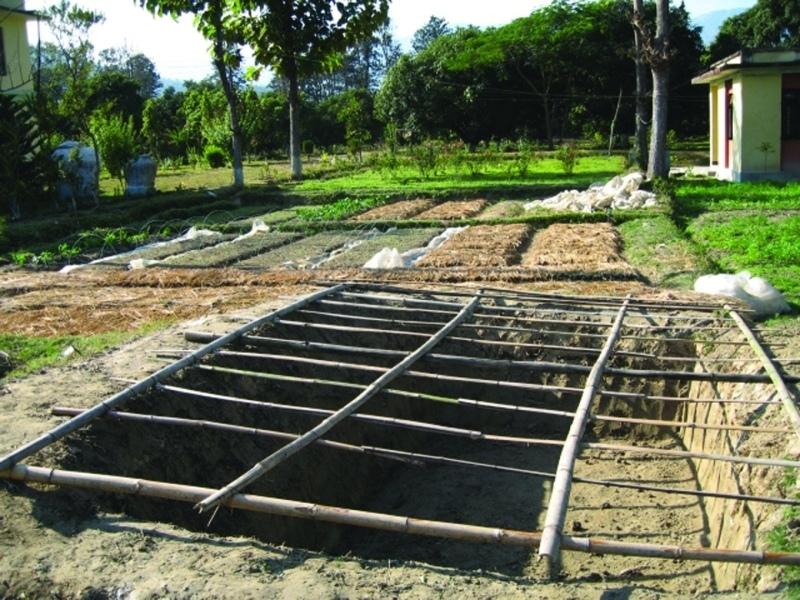
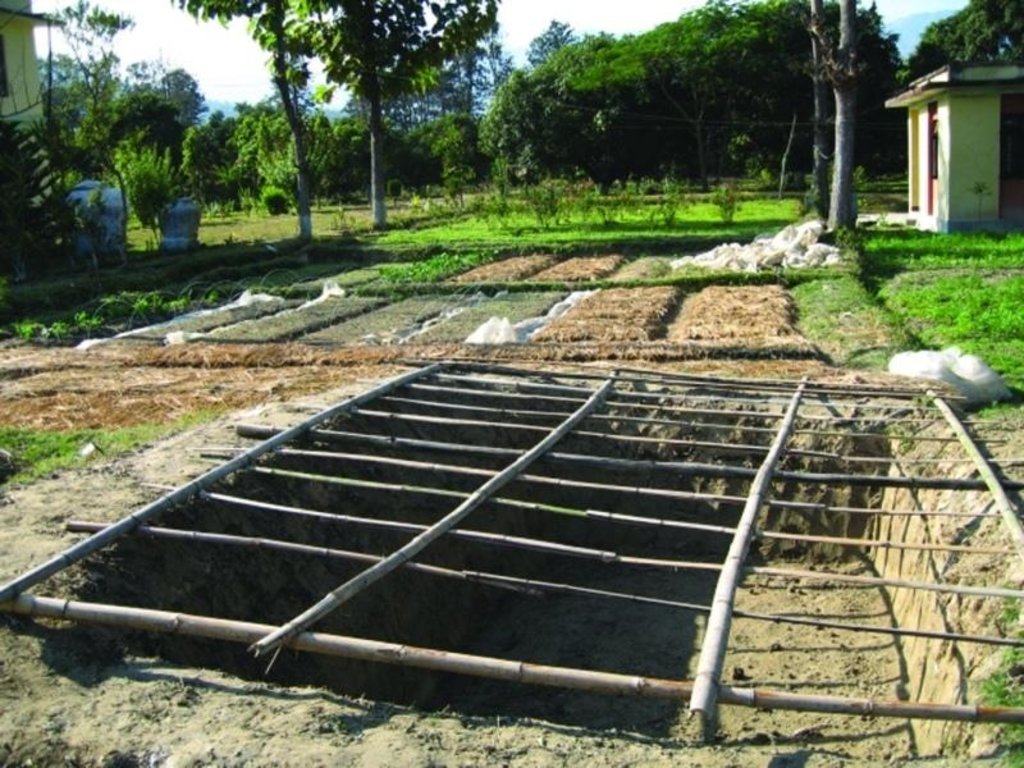
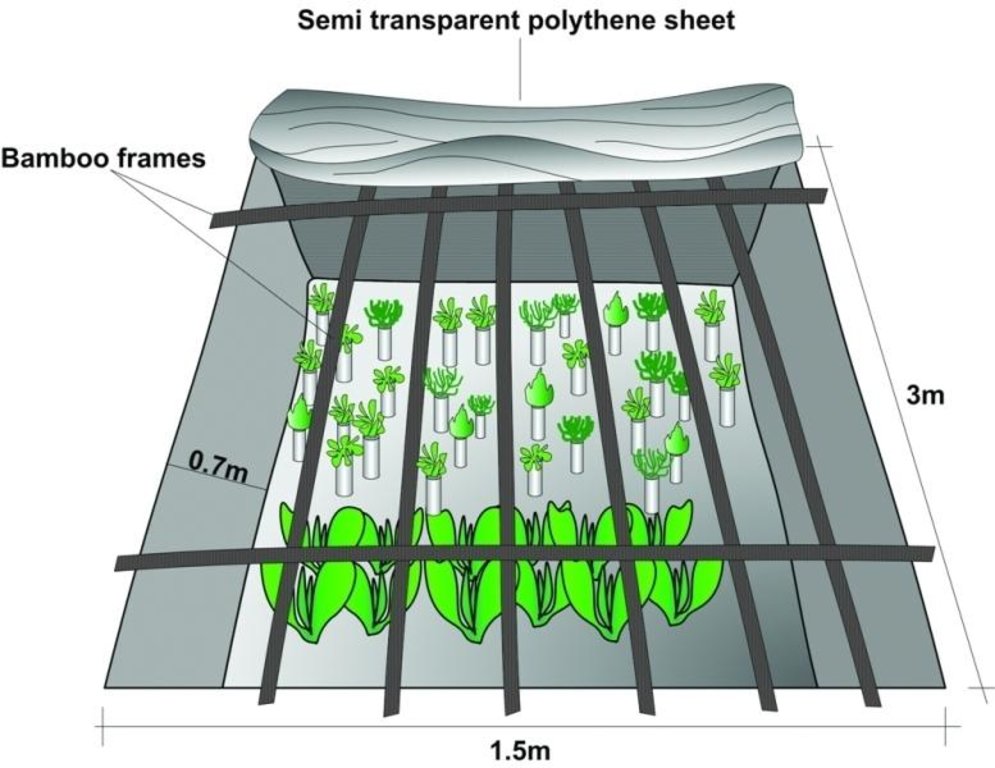
Polypits are about 1m deep pits dug into the ground and covered with semitransparent polythene sheets, preferably UV stabilised and supported on bamboo frames. A 30 cm high mud wall is built across the slope on the upper side of the pit. The polythene sheet is sealed on the upper side of the pit, leaving three sides unsealed but held down with stones that can be lifted to access the pit. The base and sides of the polypit are left as they are with no form of plastering.
The polythene sheet covering the pit reduces the photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) by around 30% inside the pit, still allowing sufficient sunlight to reach the plants inside. The polythene is usually removed during the day from 11 am to 4 pm to allow full sunlight to reach the plants except on rainy and very cold days. A modified version of these polypits - only 70 cm deep - were used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed to grow vegetable seedlings during the winter. The pits can be made of any reasonable size depending on the number of seedlings to be grown and the layout of the land. The Jhikhu Khola pits were about 3m long, 1.5m wide, and 0.7m deep.
Since the polypits are closed at night, the CO2 released by the plants and soil microbes accumulates and increases to well above levels outside the pit. In a completely sealed polypit, the CO2 concentration could reach up to 3000 ppm during the night which would be harmful for plants. Thus the polythene cover is only loosely sealed along the edges at night to regulate and maintain the concentration of CO2 at about two to four times the ambient concentration.
The warmer protected conditions and CO2 enrichment leads to extra growth and biomass gain for plants grown inside the pits during the winter. This technology is easy to maintain with the only maintenance costs being to repair damaged polythene sheets and frames.
The polypit technology is useful for mountain farmers where water scarcity and low temperatures limit the potential to raise quality seedlings. The technology is being promoted in the northwest Indian state of Uttarakhand, although only a few farmers have adopted it so far. It is a very promising technology and its use should be encouraged by hill farmers and research and development organisations engaged in raising seedlings. The technology needs more participatory action research to improve it and to encourage more farmers to adopt it spontaneously.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kavrepalanchowk district/Jhikhu Khola watershed
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
The technology was tested in the farmers field at Lamdihi and Spice Crop Development Centre. atTamaghat.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology is developed by G.B Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment and Development (GBPIHED) in Almora (India) for raising healthy plant saplings, named as polypit (Palni et al. 1994).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- Legumes e leguminosas - outras
- culturas oleaginosas - girassol, colza, outros
- legumes - outros
- rice, wheat
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Production is limited due to insufficient water during winter and the pre-monsoon season (from Nov-May); insufficient
farm income due to small landholdings; increased inputs of chemical fertilisers
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Irrigation shortage during pre-monsoon and monsoon months.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize -vegetables/wheat-vegetables
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- full year planting
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S4: Valas de nível, fossos
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Poly pit covered with semi transparent plastic sheet which is supported on a bamboo farme.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: protecting seedlings from frost, reduction of water loss, carbon dioxide enrichment
Structural measure: pit
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5 m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3 m
Construction material (earth): a mud wall is made about 30 cm high from the ground, sloping on the two sides.
Construction material (wood): to place semi transparent plastic on a frame.
Construction material (other): plastic sheet: to cover the pit, rope, wire: frame preparation
Autor:
Madhav Dhakal, A.K. Thaku
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Polypit nursery
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.10
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine the appropriate size (length, width and depth) of the pit | beginning of the winter season |
| 2. | Mark the area for soil excavation | beginning of the winter season |
| 3. | Excavate soil from the marked area | beginning of the winter season |
| 4. | Make a mud wall (~30 cm high) from the ground, sloping on two sides | beginning of the winter season |
| 5. | Make a bamboo fram of an appropriate size | beginning of the winter season |
| 6. | Lay the frame over the pit with one end resting on the mud wall | beginning of the winter season |
| 7. | Lay the plastic sheet over the frame | beginning of the winter season |
| 8. | Seal the polythene sheet on the higher side of the mud wall and leave three sides unsealed | beginning of the winter season |
| 9. | Lay the other three sides of the polythene sheet normally at ground level and weigh down with stones that can be removed to access the pit | beginning of the winter season |
| 10. | The base and sidesof the polypit do not need any form of plastering (even with mud) | beginning of the winter season |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of polypit nursery | Persons/unit | 1,0 | 2,1 | 2,1 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Plastic | unit | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| Material de construção | Bamboo | unit | 1,0 | 1,3 | 1,3 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Rope | unit | 1,0 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 7,6 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 7,6 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The polythene cover is opened to acclimatized the plants to the outside environment | 11:00- 16:00/Every day |
| 2. | Cleaning the pit | After trasplanting the seedlings/ once or twice in |
| 3. | Replacing the frame and polythene sheet if it gets damaged. | before raising nursery/In case of damage |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Maintaining the pit | Persons/unit | 1,0 | 2,1 | 2,1 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2,1 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2,1 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: wooden/iron peg, spade, shovel ,knife, and saw
The cost was calculated only for unit technology , and it can not be extrapolated on hectare basis as in 2006.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The plastic sheet , but it is easily affordable by the land users.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1200,00
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 850 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Variable
Soil texture: Fine/ heavy (clay) is red soil with high clay content but medium (loamy, silty) is non red soil
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water quality (untreated): Also good, but more in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: natural spring.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: About 50 percent of the product , especially vegetables are grown commercially.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for planting, irrigation, harvesting; Animals are used for field preparation and in valley bottom machines can be used for field preparation
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
the pit interrupted land preparation
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
About the polypit and their advantages
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Inside the polypit high relative humidity is maintained.
Outros impactos ecológicos
Protection of seedlings against frost
Quality of seedlings
Comentários/especificar:
customers prefer to buy seedlings grown in polypits compared to those grown outside
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The investment costs can be recouped within one season leading to positive results due to higher production.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
2 households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There were not enough dissemination and awareness raising activities to inform farmers of the benefits of the technology and convince them to use it.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The survival rate for vegetable seedlings is higher and seedlings mature about two weeks earlier than if grown outside where they take about one month to be ready, leading to additional income for farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Polypits are a simple, inexpensive, practical and effective technique for raising and protecting plant seedlings from severe winter temperatures.They can be called ‘poor farmers greenhouses’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? More dissemination and awareness raising activities are needed to inform more farmers about the benefits of this technology |
|
The high relative humidity in polypits means that watering only needs to be carried out once or twice a month in comparison to fi ve to six times for open nursery beds, thus saving labour and water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
|
The more physical conditions and CO2 enrichment in the pits during the winter months are refl ected in the extra growth and biomass gain of plants grown inside the pits How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| In the demonstration, the bamboo frame to hold the sheet was too heavy making it diffi cult for the farmer to remove the frame and work inside. | Use a modifi ed frame with a space built in to allow a person to enter the pit easily without having to remove the frame. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| In completely sealed polypits, the CO2 concentration can become so high during the night that it harms the plants | Only loosely seal the sheet at night to regulate and maintain the CO2 concentration |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Bhuchar, S. (2004) Polypit: a Green-chamber for Poor Farmers, an article prepared for PARDYP Quarterly e-Newsletter-8, ICIMOD, Kathmandu
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ICIMOD
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Palni, L.M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Kothyari, B.P. (1994) ‘A Simple Polypit can Greatly Reduce Nursery Time of Tree Seedlings”. In Journal of HIMA-PARYAVARAN, 6(2):10-11
Disponível de onde? Custos?
GBPIHED- Almora
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Vyas, P.; Bisht, M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Sharma, S.; Palni, L.M.S. (1999) ‘Polypit: An Improved Technique for Raising Nursery Plants’. In Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 8(1): 43-59
Disponível de onde? Custos?
GBPIHED- Almora
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos