Firebreaks/ Greenbreaks [Filipinas]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1705 - Filipinas
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Padilla Alberto
Danao Municipality, Local Government Unit
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Dacumos Evangeline
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Espanto Patrick Benson
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Castillo Forester Emma
Department of Environment and Natural Resources-Forest Management Bureau
Filipinas
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - FilipinasNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Danao Municipality - FilipinasNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Forest Management Bureau (Forest Management Bureau) - Filipinas1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) [Filipinas]
A process of rehabilitating degraded forest lands by taking advantage of trees already growing in the area.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
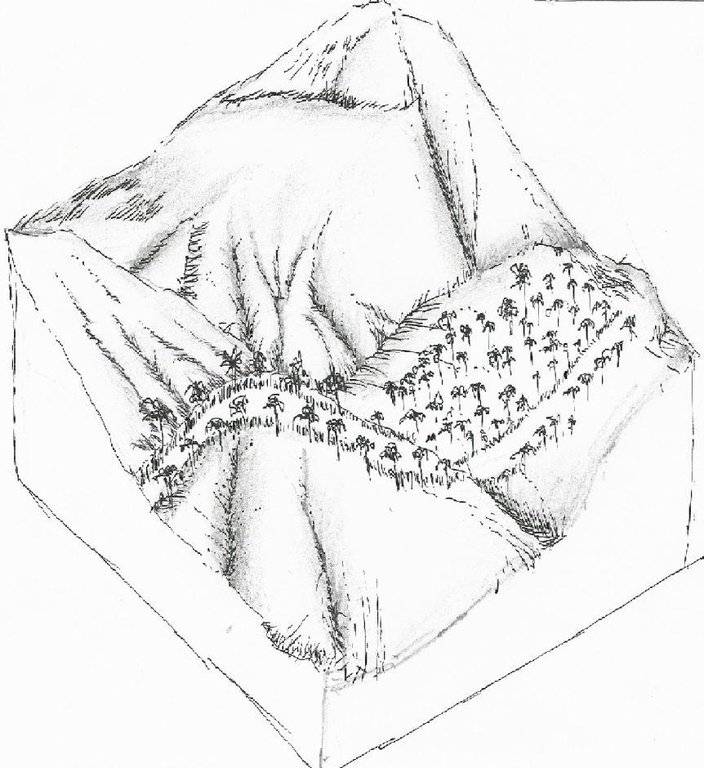
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
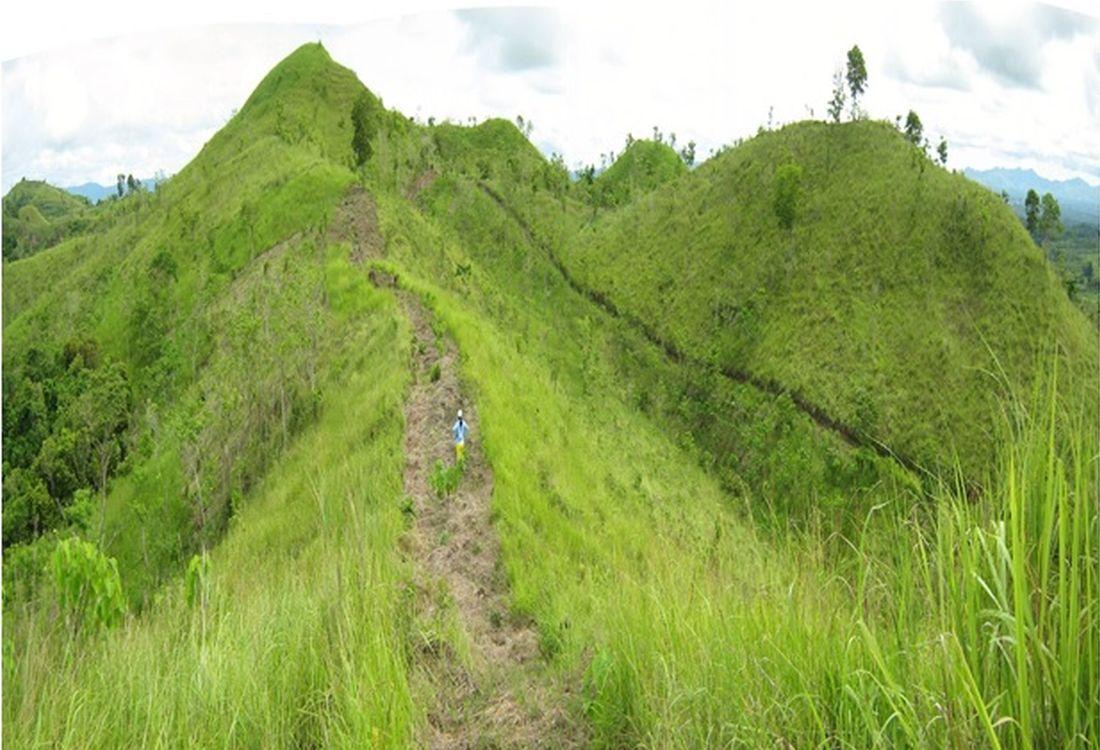
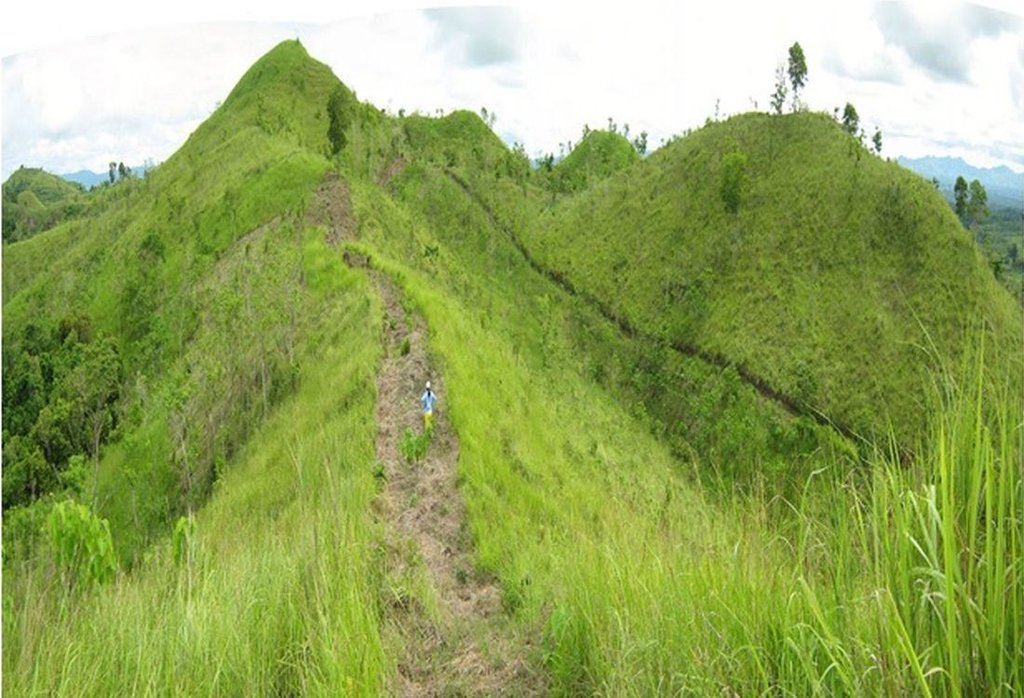
Firebreaks are 1,000-meter long, ten meters wide, located in the periphery/boundary and/or top of the ridge as barriers to slow or stop the progress of a fire. Greenbreaks are formed within the firebreaks by planting fire-resistant species in the gap portions such as kakawate (Gliricidia sepium), banana (Musa) abaca (Musa textilis), malunggay (Moringa oleifera), and cassava (Manihot esculenta). As a practice, fire breaks are established in every ten hectares to form a block, but it can vary depending on the slope of the area. Fires tend to spread quickly in higher slopes compared to flat areas, thus, more firebreaks are recommended.
Purpose of the Technology: Firebreaks/greenbreaks are established to protect the forest trees and wildlings from disturbances and wildfire. In case of forest fire, firebreaks/green breaks prevent the spread of fire from one block to another. Wildlings are seedlings derived from seeds scattered by birds, insects, animals and wind without human intervention, and allowed to grow naturally in the forest. The green breaks are planted with cash crops as immediate source of food and additional income for the land users.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The first step in creating fire breaks is the removal of all combustible materials such as deadwoods and cogon grasses (Imperata cylindrica) by using hoe or plow. Then, fire-resistant plant species such as kakawate (Gliricidia sepium) cuttings (i.e. 1-meter high) are staked at 1.5- meter spacing on both sides of the 10-meter wide firebreak. Kakawate is the preferred plant species because the leaves have high Nitrogen content and resistant to fire and drought. Maintenance of firebreaks/green breaks is done before the onset of the dry season. It is done through brushing of invasive weeds and plating of root crops. The pruning of kakawate is done every three years." Bayanihan" (rotational schedule of labour), a traditional communal concept of voluntary work is practiced during the establishment of the technology.
Natural / human environment: The area is part of the forest reserve in Danao, Bohol primarily intended for nature conservation and protection. It is about 100-500 m.a.s.l with moderately rolling to hilly slopes. It is under humid tropics climate with an average annual rainfall of 1500-2000 mm per year. The soil is loam, shallow depth, low fertility, with good drainage and medium water storage capacity. The area has high biodiversity as indicated by the presence of different indigenous trees and plants species, and wild animals and birds. The land users who apply the technology are small-holder farmers.These are members of a local cooperative. The population density is about 10-50 persons per sq. km. Since extraction of resources from the forest is prohibited, off-farm income is very important to the land users. Access to basic services and infrastructures are low.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Filipinas
Região/Estado/Província:
Brgy. San Miguel
Especificação adicional de localização:
Danao, Bohol
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
3,6
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.6 km2.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
- DENR (Department of Environment and Natural Resources) protocol on reforestration
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Floresta/bosques
- Tree regeneration
Produtos e serviços:
- Frutas e nozes
- Outros produtos florestais
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Forest fire, competition with weedy species
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): spread of invasive alien species
Other type of forest: tree regeneration
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Increase of biodiversity (Wildlife)
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão natural e seminatural de floresta
- Firebreak
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V3: Limpeza da vegetação
- V5: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: Pruning of kakawate, root crop planting
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bf: efeitos prejudiciais de incêndios
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
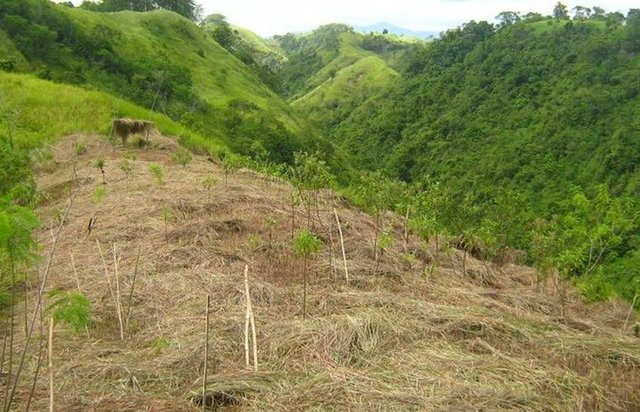
Firelines established in the ANR site.
Location: Barangay San Miguel. Danao, Bohol
Date: June 10, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), perimeter dirt road
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Trees/ shrubs species: Kakawate trees
Autor:
Mr. Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing of cogon grass in the firelines | February |
| 2. | Planting of kakawate cuttings | on set of rainy season |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | clearing of cogon grass in the firelines and Planting of kakawate cuttings | ha | 1,0 | 26,66 | 26,66 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 26,66 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 26,66 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | brushing/clearing | Every after 4 months |
| 2. | Pruning of kakawate/per year | every 3 years |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | brushing/clearing as well as pruning of kakawate/per year | ha | 1,0 | 31,1 | 31,1 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 31,1 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 31,1 | |||||
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (220m)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil vertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
100% of the land users are poor and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Forest conservation and self subsistence ( Green breaks planted as cash crop )
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Average: 75 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Produção de madeira
Renda e custos
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Atenuação de conflitos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Through the technology, People's Organization (PO) members were encouraged to plant cash crops as greenbreaks as an immediate source of food and additional income.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade de habitat
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Risco de incêndio
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) provided financial and technical support in the establishment of the technology.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No spontaneous adoption was recorded without the support of the government (DENR) or private agencies.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The technology does not require heavy equipment and instrument during the establishment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of indigenous tools during establishment such as hoe and plows |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Relative small financial input in the establishment of the technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular clearing of firebreaks |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Fires could cross on the firebreaks because of big and overlapping canopies. | Regular trimming on the canopies of trees near the firelines and brushing of weeds/grasses. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) [Filipinas]
A process of rehabilitating degraded forest lands by taking advantage of trees already growing in the area.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Módulos
Não há módulos