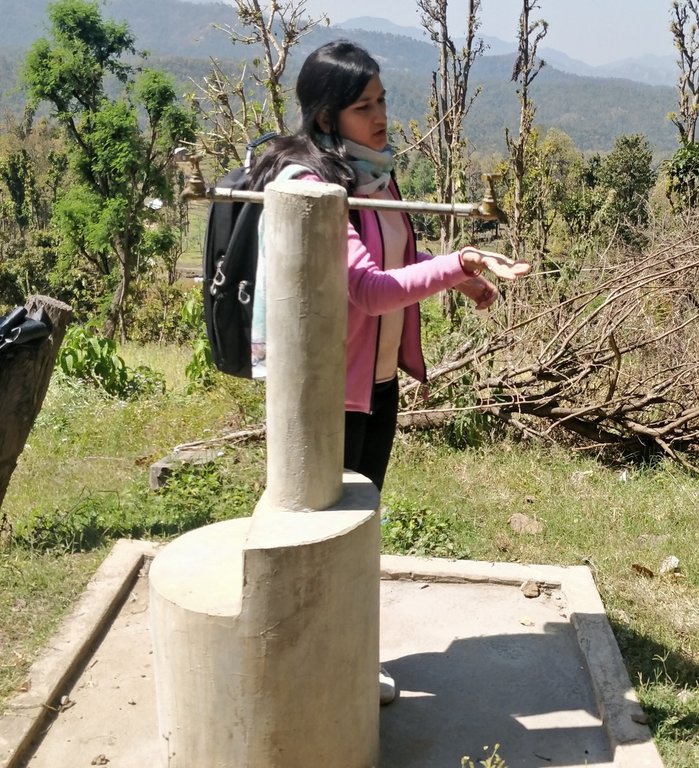
Gravity-Fed Multiple Use Water System (MUWS) : Odaltaal [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Jhuna Kattel
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Renate Fleiner
Odaltaal Ghaito
technologies_5182 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Water User:
Sunar Kopila
Nepal
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Prospects and challenges of water use systems as climate adaptive option for sustainable water management in Himalayan RegionNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology used serves as a source of providing water for drinking and other multiple uses; such that it acts as a means to conserve and manage water resources rather than degrade them.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
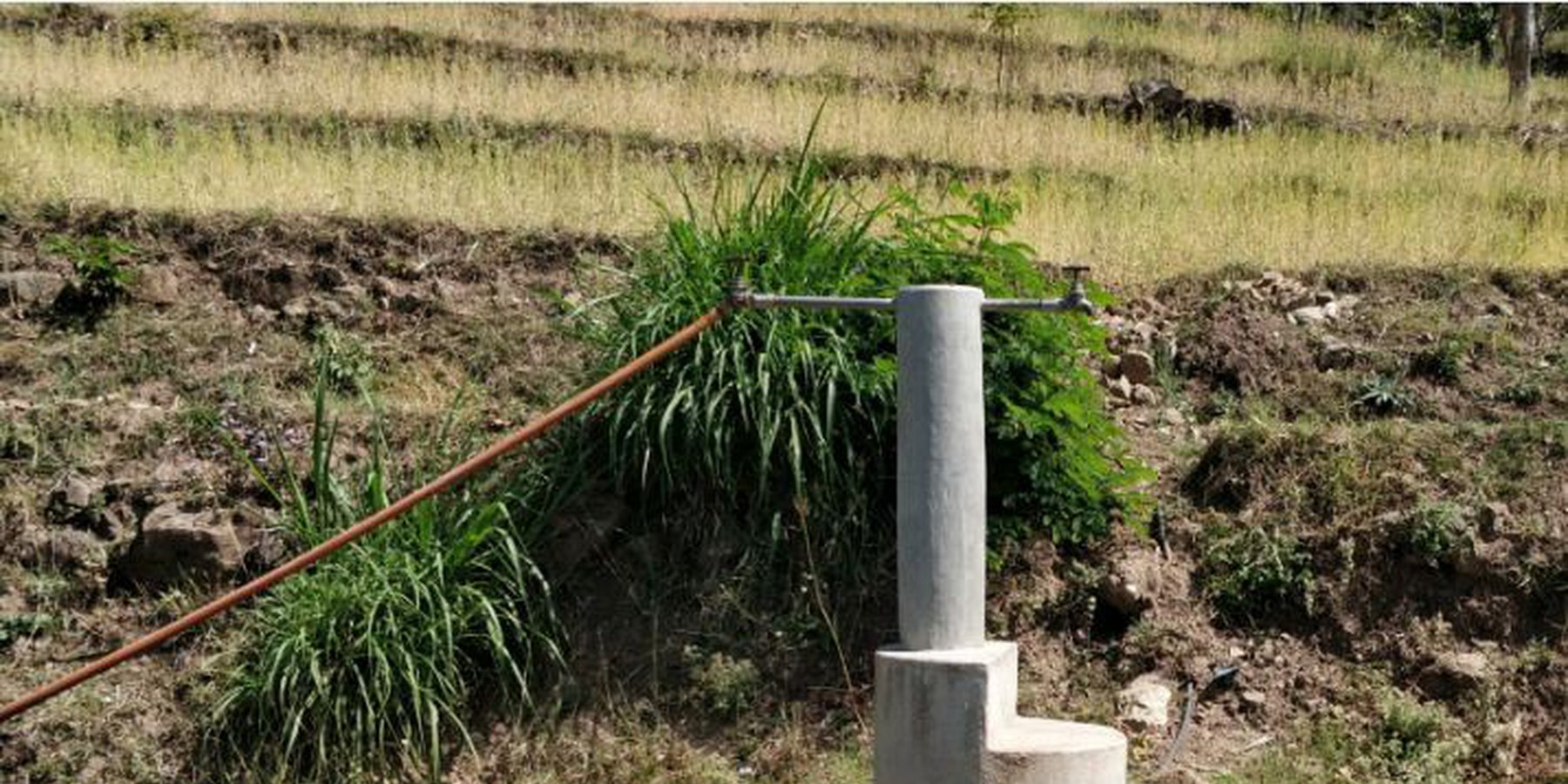
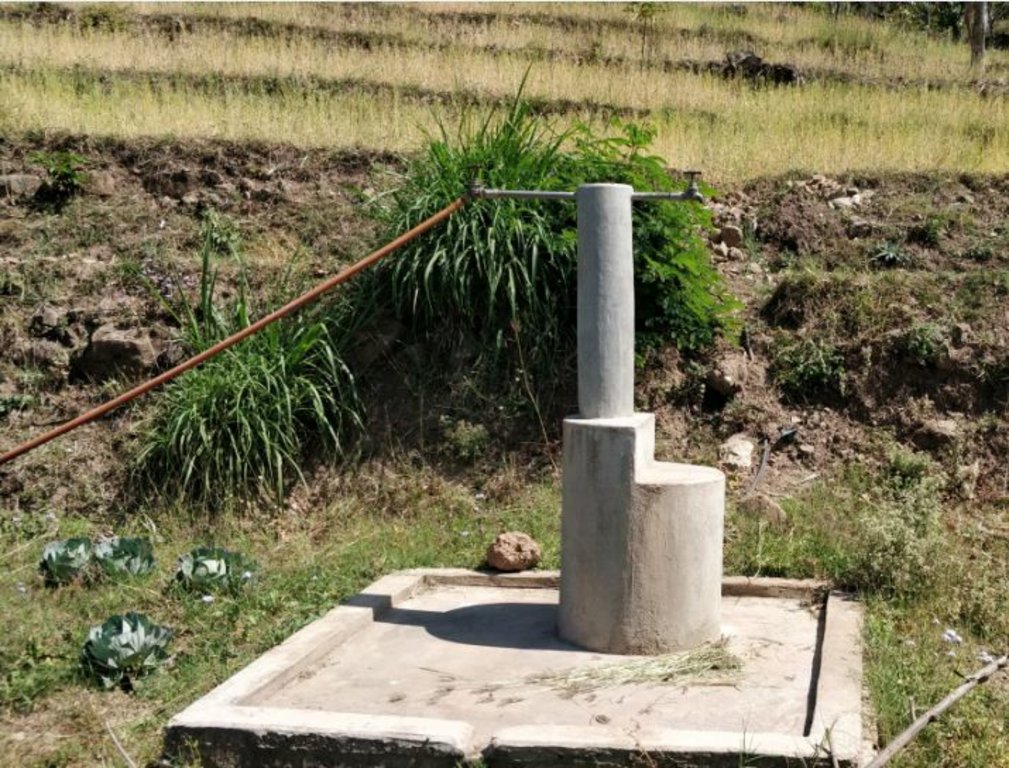
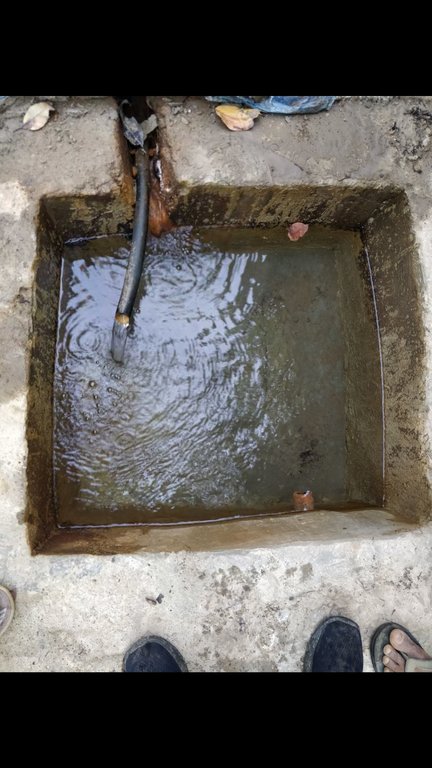
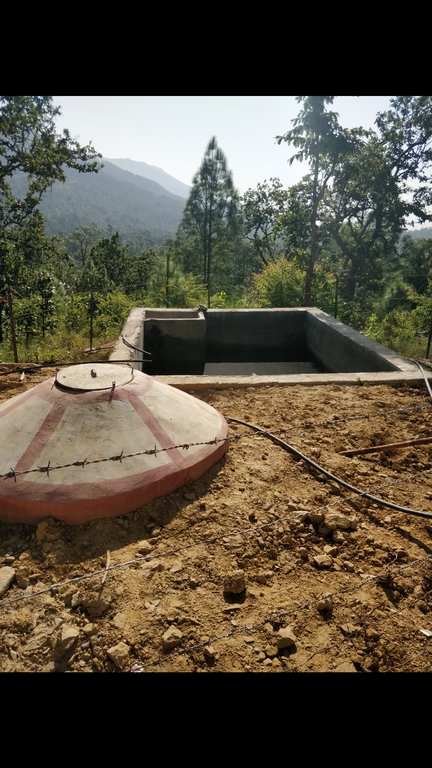
Water from source in hill top is collected in a small reservoir (to preserve natural source), then passes onto a Reservoir Tank (RVT) / Ferro-Cement Tank / "Ghaito" for drinking water with a capacity of 4000L. When the RVT gets filled, water overflows, is collected in another concrete irrigation pond (10,000L) for irrigation. From the ferro-cement tank (Ghaito) and concrete irrigation pond, two pipelines are fed and water supplied into individual tap-system or MUWS tap towers for multiple purposes.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The technology is applied in a natural environment, i.e. natural water source. The source of water is a natural source of water that sits atop a small hill which is owned by the government. From the source, water is collected in RVT ( for drinking water) and concrete irrigation pond ( for irrigation). PVC pipes are fed onto the tanks to distribute the water for multiple purposes to 4 MUWS tap towers or tap systems or "Thaado". These MUWS tap towers consist of two faucets each- one for drinking and the other for irrigation and other purposes.The major purposes of this technology are to supply clean water for drinking and other multiple purposes through a cheap, effective and simple system. The natural source of water is locally maintained. Operation and maintenance works are not mandatory, however the locals are responsible for maintaining it should the need arise. The system was financed through a public-private-partnership (PPP) program; out of which some amount was funded by a Non-Governmental Organization (NGO)- Sundar Nepal ( NPR. 2,77,000 ), some amount by the Village Development Committee (VDC)- (NPR. 2,63,000), and the remaining amount was collected by a locals’ group (NPR. 60,000). For establishing the system, labor and construction materials were needed for building the tanks and pipeline systems. For the maintenance, manual labor is necessary. The quality of the water that is supplied to the households is good and the quantity seems sufficient for the 19 households. Sustainable use of water resources through a MUWS system, cheap and effective way to conserve water resources, ensuring availability of clean water even through dry seasons are some of the technology's advantages. Similarly, clean water, more water for irrigation for vegetable farming, simplifying day-to-day life are some of the strengths of the technology. Dislikes could be the limited availability of water during the dry season and that out of 4 systems only 2 are in operation and the other ones are in a non-working condition.
Management system in place for MUWS:
A separate committee is set up for the smooth operation of the system, which consists of 20 members- 10 males and 10 females. The head of the committee is Mrs. Kopila Sunar. The committee conducts a monthly meeting to discuss the problems and need of maintenance. During the initial setup, the connection of pipelines from the tap systems to the reservoir tanks was, however, done with the contribution of the locals. Every month, each family from the 19 households contributes NPR. 100 ( One Hundred Rupees) , which goes to a fund that is set up for the times of need. The labor contribution by the people of the VDC was dependent upon the number and availability of family members in the household. Similarly, the use of the MUWS system and water from it is also dependent upon the availability of family members. Little to no maintenance was done to the system till now from 2075 B.S. ( 1 years) . Equal number of male and female members are in the committee dedicated to the MUWS system.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Região/Estado/Província:
Province-6, Mid-Western Development Region
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kunathari VDC-10, Odaltaal
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Sundar Nepal- a non-governmental organization (NGO) helped with Odaltaal Multiple Use Water Systems
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- improve water security and increase efficient use at a household level
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - milho
- cereais - arroz (planalto)
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- areca
- banana/planta/abacá
- cana-de-açúcar
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
The water used for irrigation is used in fields for 2-3 cycles of crop growing (annual) like rice, maize and barley and into kitchen-farming/tunnel farming (perennial) where vegetables grown are cucumber, tomatoes, chilli, bitterguard, peas, etc.
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Rice, Maize and Wheat are cycled according to the seasons.

Outros
Especifique:
Drinking Water
Observações:
Drinking water used directly from the tap systems. Some boil it but most of them use it straight from the tap systems and consume without filtration.
Comentários:
Irrigation and Multiple Uses: The locals use the technology in order to irrigate their cropland so that the plant productivity is increased. As well, the introduction of this technology has opened up doors to new possibilities like construction of tunnels ( green houses) so that the locals can grow seasonal and off-seasonal vegetables in their backyards. Animal husbandry has also been an increasing practice. Human uses like washing, cooking, cleaning, bathing, etc are amply sufficient due to adequacy of water from this technology.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - milho
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
Comentários:
Before the introduction of the technology, the land productivity was minimal. Water for human uses like bathing, cleaning, washing, cooking, etc. were scarce; especially during the dry seasons. No green houses were constructed. They used to rear very few cattle.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Outros (p. ex. pós-inundação):
- Natural source (Mool) of water in foliage atop a hill
Comentários:
The supply of water comes from a natural source ( 'mool' in local language) , where a small enclosure is constructed so that the source is preserved and water is amply supplied to the ferrocement RVT for drinking purposes ( 'Ghaito' in local language) and concrete irrigation pond for irrigation purposes.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão do lençol freático
- Gravity Fed Multiple Use Water System (MUWS) , New Scheme
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
The technology is comprised of structural measures, barbed wire fences to surround natural water source, iron lid top, cement enclosure for water source, pipes feeding onto the source, ferro-cement RVT, tap towers, faucets, concrete irrigation pond, etc.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Before setting up the technology, much of the water during dry seasons would evaporate from the natural source ( mool) and there would be scarcity of water during dry seasons. This has been addressed by the technology, where securing the natural source of water prevented evaporation and storing water in enclosed tanks helped supply water during dry seasons.
Similarly, due to no preservation of the source and no storage tanks, the water would be soiled by sediments, wastes and insects' larvae. After setting technology up, the quality of water has vastly improved as well.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
Comentários:
The technology prevents water source degradation, improves perennial water availability, helps tackle with the effects of natural calamities like drought, etc.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Source: Natural (mool) atop a small hill, secured by wire fences and preserved with concrete and metal lid ( to prevent evaporation).
Water from source collected in Ferro-Cement Tank (RVT) / "Ghaito" in local language, with capacity 4000Ltrs.
Water overflows from RVT into an Irrigation Pond (Open Top, Concrete) with capacity 10,000Ltrs.
PVC Pipes leave the RVT and Pond into 4 MUWS Towers ("Thaado" in local language) to serve 19 households.
One faucet supplies drinking water from RVT and next faucet supplies water for irrigation and other multiple purposes (drip irrigation, tunnel farming, etc.).
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
5-6 dhurs
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha = 590 dhurs
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
NPR
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
110,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
N/A ( voluntary labour from each household)
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Enclosement for the groundwater source | Before rainy season |
| 2. | Construction of Ferro-cement tank for Drinking Water | Before rainy season |
| 3. | Construction of Concrete pond for Irrigation | Before rainy season |
| 4. | Securing the perimeter for the tanks | Before rainy season |
| 5. | Laying down the PVC pipework | Before rainy season |
| 6. | Construction of 4 individual MUWS tap towers ( Thaado in Nepalese language) | During rainy season |
| 7. | Final touch-ups, Setting up faucets, Preliminary checking | During rainy season |
Comentários:
A total of 3 months ( roughly 90 days ) was required for the construction of the technology to be complete.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Voluntary by locals | 100,0 | ||||
| Equipamento | Irrigation Pond | 1,0 | 275000,0 | 275000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | Ferrocement Tank ( Ghaito) | 1,0 | 225000,0 | 225000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | Securing fences, Perimeter securing for tanks and water source | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | Setting up MUWS tap towers ( Thaado in local tongue) | 4,0 | 12500,0 | 50000,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | PVC Pipes | 100,0 | ||||
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 600000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 5454,55 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
1.Village Developmment Committee:NPR. 2,63,000 2.Sundar Nepal NGO: ~ NPR. 2,77,000 3.Water – Users : NPR. 60,000
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plan on Changing PVC pipework for a Galvanized-Iron (GI) pipe | 1 time after PVC pipes damaged by wear and tear, lime, etc |
| 2. | Plan on Construction of another Drinking Water Tank | When the one tank is not sufficient for providing enough water |
Comentários:
Construction has been completed and technology is in use since a year only, so no maintenance works till now. However, construction of another drinking water tank and changing the PVC pipes for GI pipes is imminent in near future.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Voluntary | 100,0 | ||||
| Equipamento | Drinking water tank construction | 1 | 1,0 | 75000,0 | 75000,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipamento | Laying down GI pipesinstead of PVC Pipes | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 25,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 125000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 1136,36 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The non-governmental organizations and government offices (Village Development Committee) have expressed an interest to help financially in the construction of another drinking water tank and GI pipes laying should the need arise.
Comentários:
These are the expected costs should the need of such arise.
The water users' committee, along with NGO's and governmental bodies shall bear the costs in the said maintenance works.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The construction materials- rods, concrete, cement, bricks and Galvanized Iron (GI) pipes would cost the most
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Monsoon/ Rainy Season 2-3 months ( June-August)
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Meteorological Forecasting Division, Nepal ( www.mfd.gov.np)
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Before the introduction of MUWS technology, the water used to be a problem during the dry seasons. However, after the technology was applied, the natural ground water source is conserved, people have been monitoring the water levels cautiously and nowadays, the water sustains the locals during the dry seasons as well.
Salinity is not a problem, but the presence of lime in the water is a problem.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Birds are abundant, new fowls are sighted regularly.Lampuchhre ( Long-tailed widowbird),Ravens,Hawks,Peacocks and peafowls,Peasants,Guinea fowls and other fowls; rarely seen before are common after setting up the technology.
Animal sighting is rare. Forests, although consisting of a few varieties of trees, like Saal ( shorea robusta), Sadhana ( Moringa) , Belauti ( Guava), Sallo ( pine tree), Aap ( Mango). very few species are abundant in a given stretch of land.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Crianças
- meia-idade
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Members of the community: 1:1 ratio of males to females
Age : mostly middle-aged, a few children and few elderly
Caste/ Ethnicity: Thakuri, Dalit and Janajati
Literacy: 1 person completed High – School level (+2), rest are literate ( Class 5)
Total Land Holding: < 10 ropanis of land, Human Settlement since 2040 B.S. ( since last 36+ years) in search of better opportunities and access to better services of water, roads, etc.
Total households: 19
Jobs: Males : bread- earners, construction workers, labour, farming
Females: Housewives, Farming. Most of the males in the village have been to foreign country ( India specially) for manual labour and mostly females are present in the village.
Ethnicity: Few families are of Upper- Caste: Thakuris ( as per Nepalese traditions) and most are Dalits and Janajatis, who were considered low-caste previously. The term "lower-caste" has been abolished now.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
19 households occupying less than 10 ropanis of land.
(1 Hectare = 19.66 ropanis)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- The source, tanks fall under community forest area- owned by the Government
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Especifique:
Previously, the society had a caste system in which the higher and lower caste discrimination was done and the water tainted by the lower caste ( Dalits, Janajatis) were deemed “unfit” by the upper caste ( Thakuris, Brahmins, Chhetris). However, after the abolishment of the caste system, everyone enjoys equal rights to the access to water.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
The access to health, education and markets along with other facilities is only accessible after a 15 minute journey to the ‘bazaar’ or market area from the village.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Qualidade da safra
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Qualidade da floresta/do bosque
Produção florestal não madeireira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Geração de energia
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Qualidade da água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Disparidades econômicas
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Knowledge about the technology (MUWS) improved
Atenuação de conflitos
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
evaporation of water decreased after the construction of enclosures / tanks.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Acumulação de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Salinidade
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Acidez
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
As per water users, effects of drought were imminent in the dry seasons, leading to less water available for drinking and irrigation. However, after the MUWS was installed, the effects of drought could be tackled; mainly due to the availability of water for drinking and drip irrigation, even during the dry and arid winter seasons.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
MUWS focuses mainly on the preservation of water resources through its sustainable use.
Similarly, this technology also addresses the water shortage issues (especially in dry seasons), tackles effects of climate change, ensures water availability in geographically challenged areas, uses minimal modern technologies (relies on gravity for water supply) , is cost-effective ( little to no maintenance costs) and also ensures the social and economic well-being of water users through off-farm and farm incomes ( with the help of drip irrigation).
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
Since this technology is adapted in a small area, without any significant construction, there is virtually no off-site impact at the moment.
However, beneficial off-site impacts can be expected in the long run.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | moderadamente |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The system has been in operation since a year only. Thus, long term effects are yet to be visible. Evident from the cost of operation and maintenance with the benefits of the technology, there is a positive impact evident.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Substantially less amount of lime present in water than what was previously found. |
| Availability of water even during the dry seasons. |
| Increase in the productivity of perennial vegetables in kitchen garden, construction of tunnels for farming vegetables possible |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Water quality vastly improved, no lime and/or saltiness present in water |
| Need of alternative sources of water during dry seasons not present after construction of MUWS system |
| Overall productivity of land improved through effective irrigation of water |
| Self-sufficiency in the aspect of water and crops, as well as alternative sources of income increased leading to improved quality of the lives of the water users. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Water levels not rising in two tap systems of the four | Technician could oversee the problem of elevation and give a viable solution so that 4 out of 4 tap systems could be functional again |
| Pipes’ diameter and quality could be improved | If the government and/or NGO could add to the savings of the group, good quality of GI pipes could be installed instead of the PVC pipes used |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The tank for irrigation is left open at the top | Closing the top of the tank |
| The pipes used are not sustainable | The use of heavier PVC pipes and/or hybrid GI pipes could result in less chances of system failure due to lime in the water |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
> 10
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
> 1
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
26/05/2019
Comentários:
Data collection, compilation done through field visits ( 3 times).
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos