Maize strip tillage [Suíça]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Streifenfrässaat (German)
technologies_1006 - Suíça
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Wyler Roman
Center for Development and Environment, University of Berne
Suíça
usuário de terra:
Wyss Beat
Suíça
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Soil support program for conservation agriculture [Suíça]
Through the soil support program land users get subsidies for applying conservation technologies on their fields during a period of 6 years.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli

Direktzahlungssystem [Suíça]
Finanzielle Leistungen des Bundes um den Ertragsverlust, den eine Kultur für den Bauern bringt, auszugleichen. Das Direktzahlungssystem führt gewissermassen zu einer 'Vergünstigung des Produkts' für den Konsumenten.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli

Förderprogramm Boden [Suíça]
Mit dem Förderprogramm Boden des Kantons Bern erhalten beteiligte Landnutzer Direktzahlungen für die Anwendung von bodenkonservierenden Anbauverfahren auf ihren landwirtschaftlichen Feldern. Das Projekt hat eine Dauer von 6 Jahren.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A cropping system for maize which reduces the reworking of the soil to the stripes, in which the seeds are planted.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
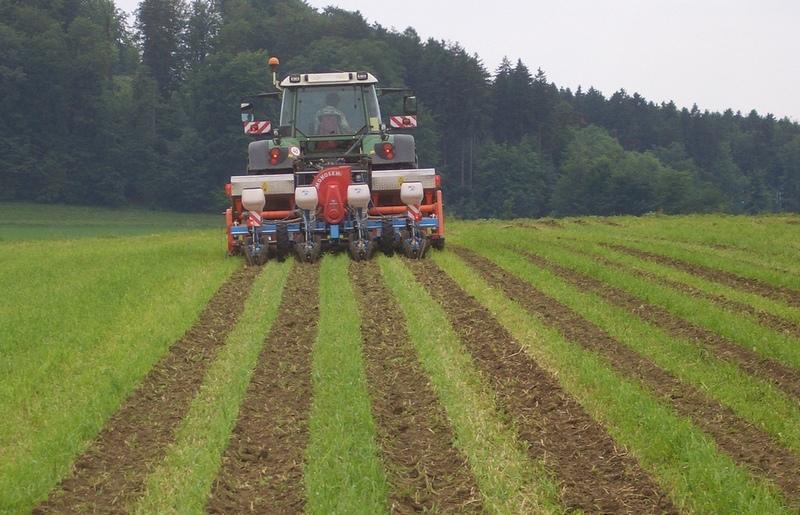
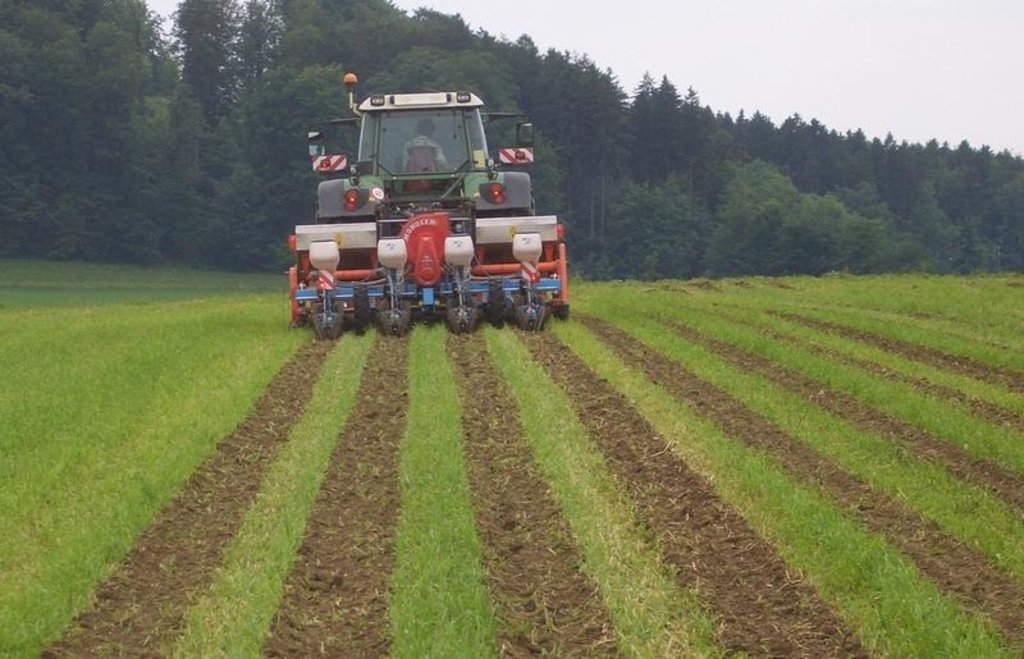
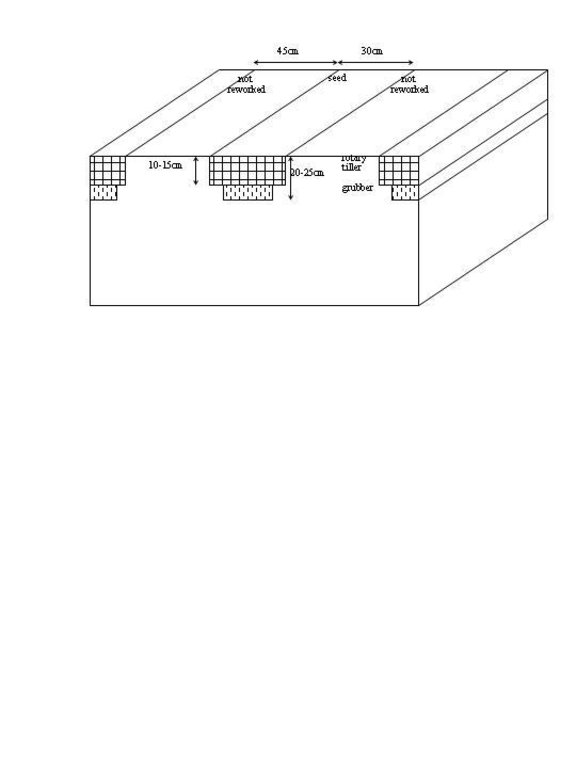
Maize strip tillage is a mixture between no tillage and conventional agriculture. The reworking of the soil greatly reduced. Instead of ploughing and harrowing a special rotary tiller including a grubber is being used. The working depht of the rotary tiller is 10-15cm, the grubber reaches to 20-25cm depht. The machine reworks the soil on stripes of 30cm width. This is where the seeds are planted. In between there are stripes of 45cm width, which are left untouched.
In Switzerland farms usually are small. A major part of the arable land is used to produce fodder. (For example maize, grain, fodder beet)
Usually maize strip tillage is being used to avoid soil erosion or for economical reasons. Compared to conventional agriculture several working steps can be saved. The reworking of the soil, manuring, seeding and applying of herbicides can be done at once.
Since the machine is expensive and a strong tractor is needed, farmers usually don’t buy it on their own. In most cases a contractor will be tasked to do this work. Of course this is not for free. But since several working step are saved, there is more time left to do other work (6.5h/ha).
The reduced reworking of the soil holds remarkable ecological advantages. Occurrence of erosion is very seldom, because the stripes covered by plant residual significantly reduce the speed of surface water. To increase this effect, the stripes are laid along the height countours, if possible. Since the soil structure is not disturbed in the stripes between the seeds, the risk of compaction is reduced there. For that reason maize strip tillage is often used before potatoes in a crop rotation. This is a crop that is very sensitive to soil compaction.
The technique brings along an ecological disadvantage, too. Before sowings the precedent crop needs to be treated with a total herbicide (glyphosat) to avoid unwanted competition. Only in wet areas, where there is enough water available it is possible to not use glyphosat. Also in long time studies, residues of glyphosat could not be detected in the soil. But if ever weeds will develop a resitance against it, that would certainly be a major problem.
The enhanced risk of crop loss is another disadvantage of the technology. In conventional agriculture the soil is left to dry for a few days after ploughing. maize strip tillage does not hold that possibility. If the conditions are wet, risk of crop failure can be a problem. However, if conditions are good (dry enough), both quality and crop yield are similar to conventional agriculture.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
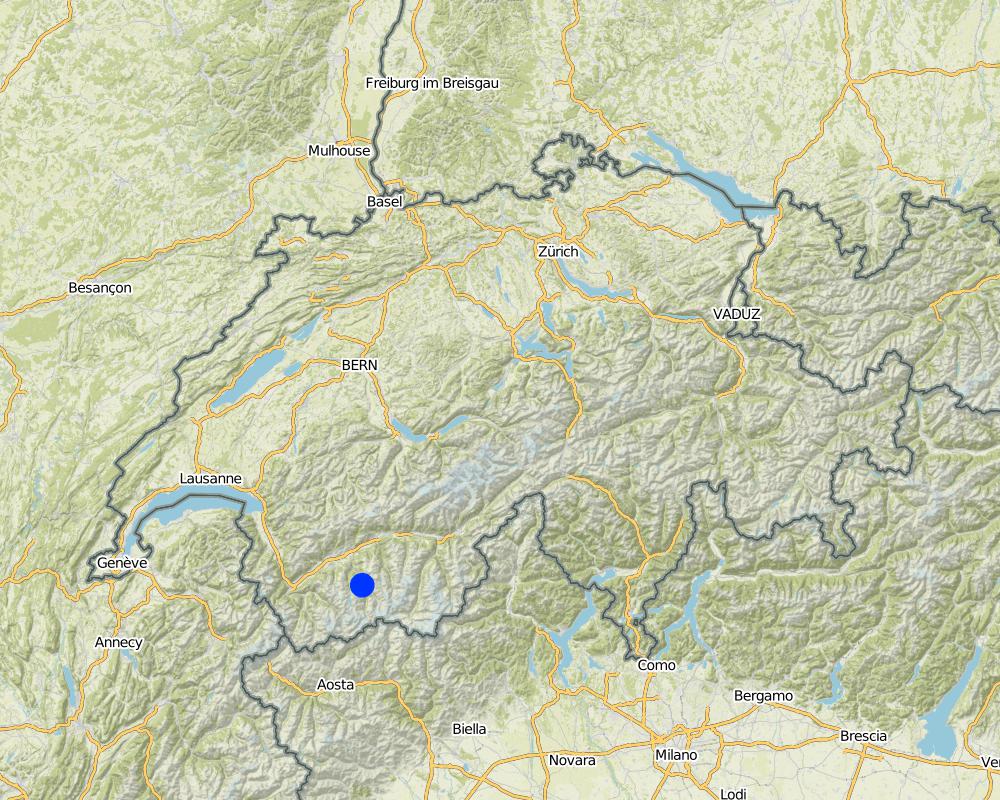
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Suíça
Região/Estado/Província:
Kanton Solothurn
Especificação adicional de localização:
Oberramsern
Comentários:
The portraited farmer is working as a contractor and is applying the technology on about 0.8km2. Currently only 1ha of his own land is used for maize.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was developed some 12years ago by the designer and contractor Walter Witzig supported by researchers from Forschungsanstalt Reckenholz-Tänikon.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- hay
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct
Comentários:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water and soil compaction.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping, minimum tillage
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (too deep and too intensive reworking of the soil.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), education, access to knowledge and support services (Tradition. Most people do not question tillage.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree / shrub) (too heavy machinery used under wet conditions.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
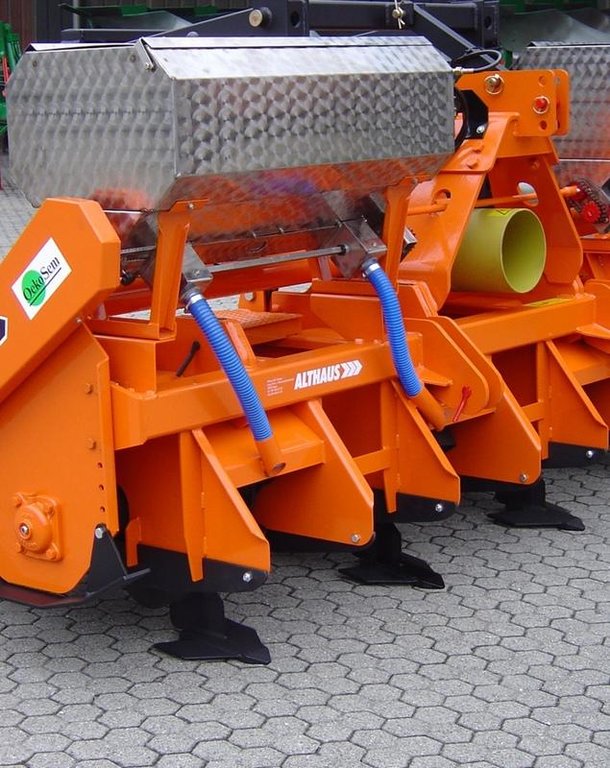
The rotary tillers working depth is 10-15cm. The grubber reaches to 20-25cm depth. This is to obtain a loose soil structure. Manure is brought into the soil while tilling.
Immediately after that the seeds are brought into the soil. Finally a selective herbicide can be sprayed. Stripes of 45cm width are not reworked and help to avoid soil erosion and compaction.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Maize
Minimum tillage
Remarks: The stripes are laid along the contours
Autor:
Roman Wyler, Bern, Switzerland
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Swiss Franc
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
1,13
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a "Streifenfräse" | |
| 2. | Buy a tractor |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Streifenfräse | Machine | 1,0 | 42000,0 | 42000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tractor | Machine | 1,0 | 115000,0 | 115000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 157000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 138938,05 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | application of glyphosat (total herbicide) | 1 per growing period |
| 2. | tillage of stripes including seeding, manuring, spraying of herbicide | 1 per growing period |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | tillage of stripes, seeding, | ha | 1,0 | 393,0 | 393,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | appliance of total herbicide | ha | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 53,0 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 534,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 472,57 | |||||
Comentários:
Crop yield is about the same as in conventional cropping systems. The cost to apply the technology are about $410 per ha. It takes about 2 working hours per ha. In addition the glyphosat needs to be applied, which accounts for $150 or 0.75h of work. The following worksteps are not needed anymore (working hours, costs when tasking a contractor excl. material): Ploughing (1.25h, $260), harrowing (1.25h, $180), conventional seeding (1h, $100), manuring (1h, $50), applying of herbicides (0.75h, $90). In total about $130 and 4 hours of work can be saved per ha. In some cantons Streifenfrässaat is also subsidised. In the canton of bern this accounts for $420 per ha and year for the first 5 years of appliance. The costs for manure, herbicides, seeds are not included since they are the same as in conventional agriculture.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The machine is very expensive. In addition a strong tractor is needed (ca. 150hp). Thats why most farmer task a contractor with the seeding. In this case no initial investment needs to be done. The machine in this case study is used for about 60ha per year. A bigger workload would be possible.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: good, medium ( precipitation maximum in summer )
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Ist mostly men that get in touch with the technology since it is mostly them who are using the machines. But decisions about which technology should be used are taken at the household level including both women and men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer interviewed is working for other farmers, too. In general off-farm income is significantly lower.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
The farmer portraited owns not more than 10ha, he is working for others as a contractor
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
steeper hills can be cultivated since the risk for erosion is reduced
Qualidade da forragem
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
droughts: less water scarcity, intense rain: less erosion but the weather needs to be dryer in spring, since the soil cannot be left to dry between ploughing and seeding
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Less worksteps need to be done, income remains the same. But a total herbicide and sometimes a little more manure is needed
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Since the work is usually outsourced to a contractor, the farmer can use his time for other activities
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
less worksteps need to be done
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced independence if contractors are tasked
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
more earthworms
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The farmer portaited bought a machine on his own. If a contractor were tasked short-returns would be positive too.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: There is the possibility to get subsidies. But resources are limited and therefore not everybody gets them. (See Approach)
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is not spreading homogenously. Adoption and acceptance varies very much in different regions. Pioneers play an important role.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The number of worksteps is greatly reduced. Thats why money and time can be saved. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Since less work needs to be done, the farmer can concentrate on other activities to enhance income. |
|
Soil structure is improved. Risk of compaction is reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Still heavy machinery should not be used under wet conditions. |
|
Soil erosion is reduced very much. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology applies for maize only. Other conservation techniques should be used for other crops. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Steeper hills can be cultivated without risking erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? the stripes should in general be laid along the contours. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Risk of crop failure is enhanced if seeding under too wet conditions. | The time of seeding is critical and should be chosen carefully. If conditions are too wet, ploughing might be a better choice. |
| The machine is very expensive. Single farmers usually cannot afford it. | Cost can be shared with other parties or a contractor can be tasked. |
| In general a total herbicide must be applied before sowing. | The amount of glyphosat should be adapted to the number of weeds. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Reworking of the soil is still intense. | |
| A powerful tractor is needed. Fuel consumption is still high. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
report on DVD: von Bauern für Bauern
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www.vonbauernfuerbauern.ch CHF 20.-
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Soil support program for conservation agriculture [Suíça]
Through the soil support program land users get subsidies for applying conservation technologies on their fields during a period of 6 years.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli

Direktzahlungssystem [Suíça]
Finanzielle Leistungen des Bundes um den Ertragsverlust, den eine Kultur für den Bauern bringt, auszugleichen. Das Direktzahlungssystem führt gewissermassen zu einer 'Vergünstigung des Produkts' für den Konsumenten.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli

Förderprogramm Boden [Suíça]
Mit dem Förderprogramm Boden des Kantons Bern erhalten beteiligte Landnutzer Direktzahlungen für die Anwendung von bodenkonservierenden Anbauverfahren auf ihren landwirtschaftlichen Feldern. Das Projekt hat eine Dauer von 6 Jahren.
- Compilador/a: Deborah Niggli
Módulos
Não há módulos