Gully Rehabilitation with Native Trees [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Selina Studer
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1543 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Mirsoiv Iskandar
Tajiquistão
usuário de terra:
Mirsoiv Avaz
Tajiquistão
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Boev Jahonbek
NCCR
Tajiquistão
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - QuirguizistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Vegetative and structural technology for the rehabilitation of an expanded gully
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
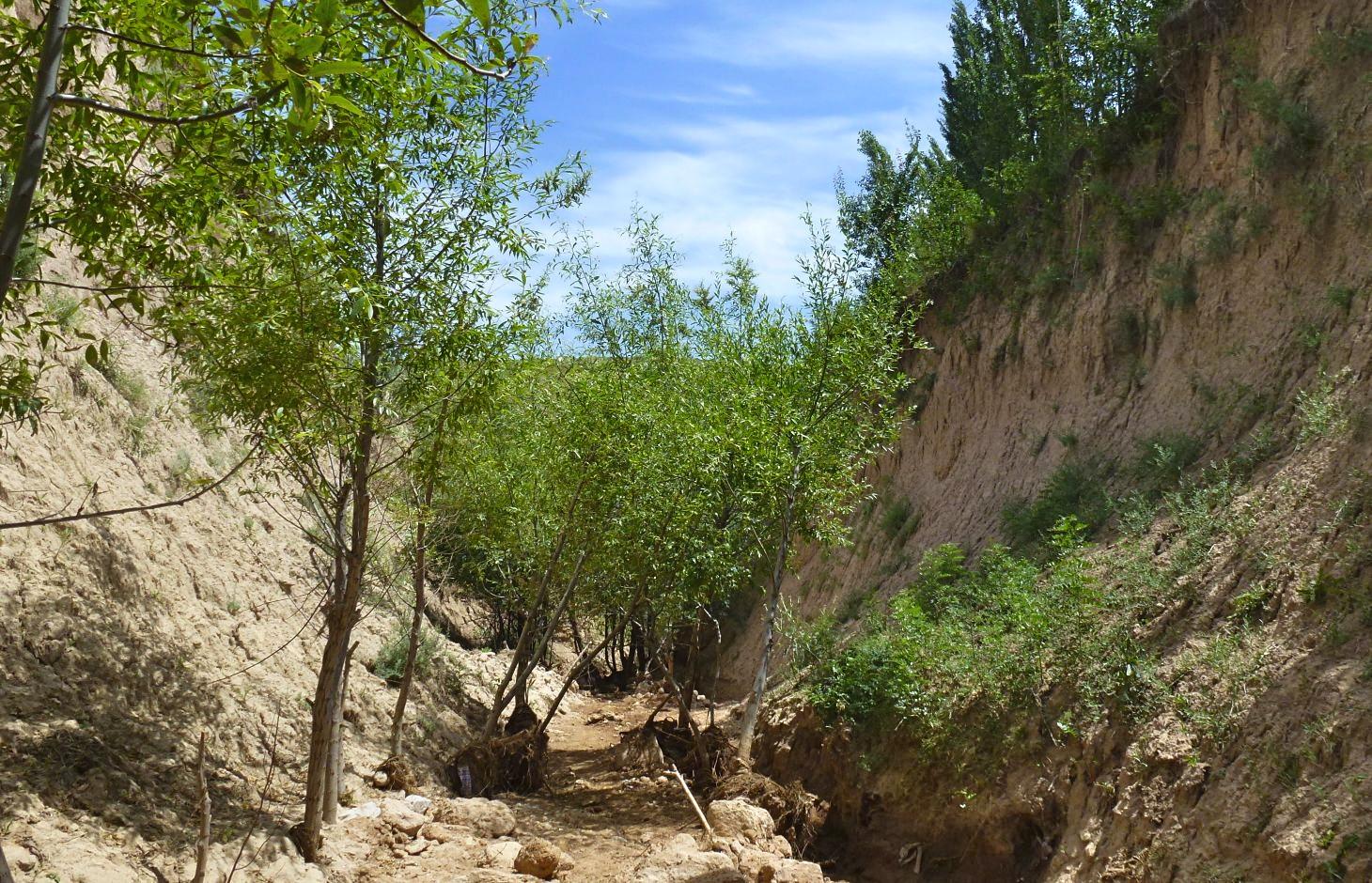
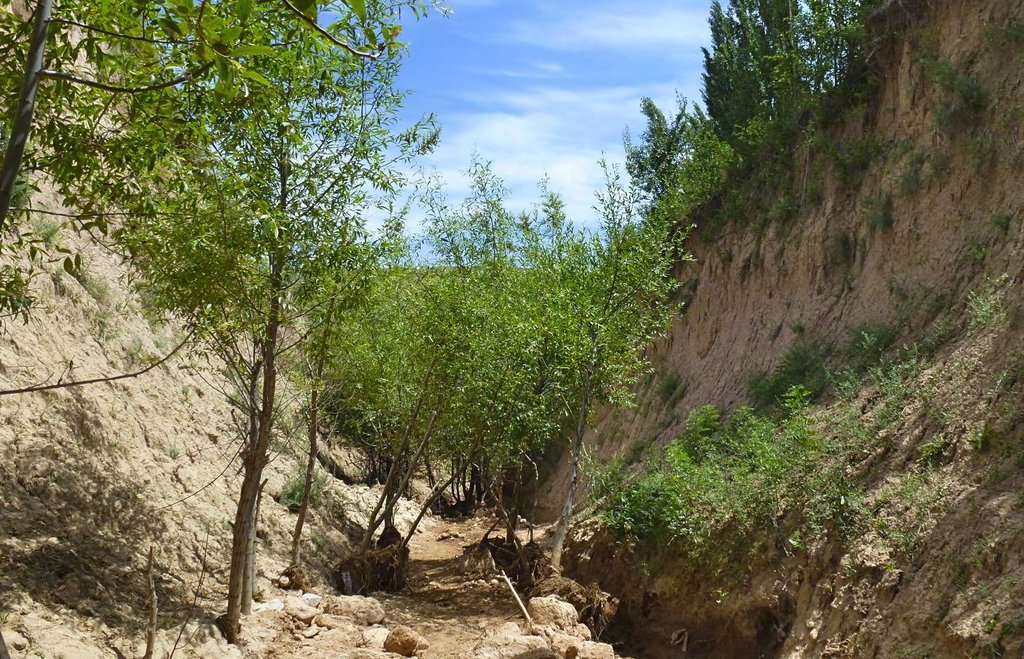
Descrição:
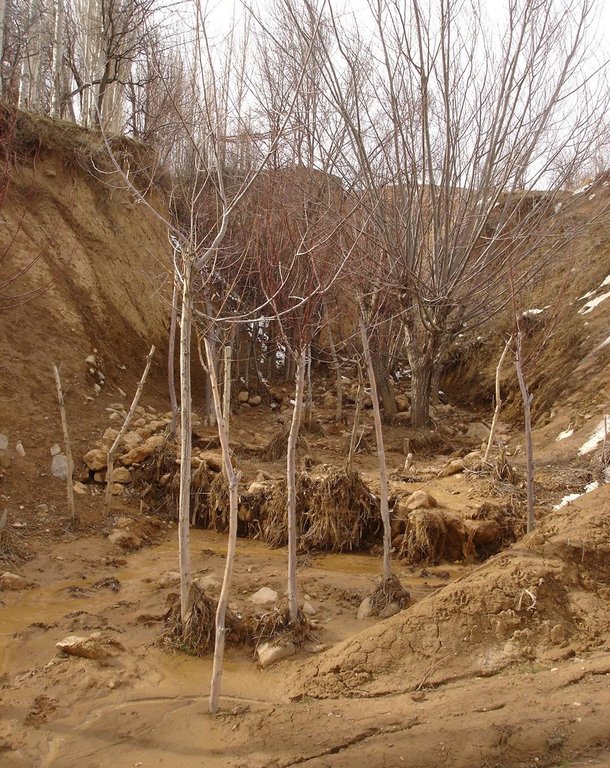
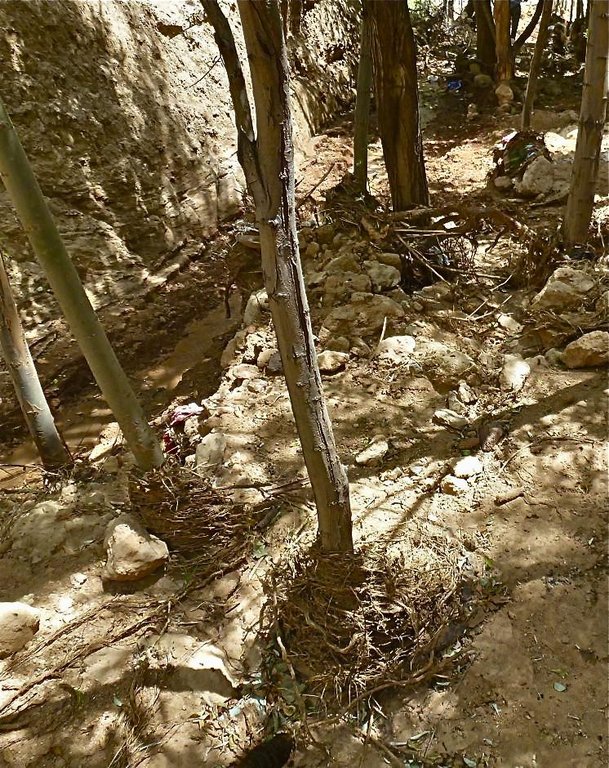
The extension of a deep incised gully, which borders a fertile orchard, is stopped and sediments are trapped by the help of vegetative and structural measures. The gully floor is vegetated with different trees inter alia willow, poplar, cherry, blackberry and walnut which are arranged in random groups. At the bottom of the gully where it intersects the road there is a stonewall, which collects the sediments that are washed down during heavy rainfalls mostly in spring. A dense bush line with Russian olives, apricots, cherries, walnuts, plums and buxus has been planted on the top of the side slopes of the gully, and roots of those bushes keep the soil stable and at the same time they prevent landslides and expansion of the gully. These tree lines are cut from time to time, otherwise they grow and become heavy and due to their weight the trees would possibly fall into the gully.
Purpose of the Technology: (1) The deep roots of willow trees on the bottom of the gully protect the soil and prevent it from being eroded during the heavy spring floods. Trees also help to collect sediment and to accumulate it in the gully. (2) The dense bush lines with its deep roots, on the top of the gully slope, stop the horizontal erosion, which endangers the fertile orchard close to the gully. (3) A stonewall at the lower end of the gully collects sediments which have been washed down. Once in a while a heightening of the stonewall has to be done. The technology with its three measures prevents from further gully expansion and supports its rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These three measures, the tree line, the bottom vegetation and the stonewall were developed and implemented by the farmer's own initiative. The farmer implemented the technology on his own and expands it every year. The entire technology doesn’t have to be established at once, which allows investing money and time whenever it is available. For maintenance new trees are planted both in the gully and in the tree line, which has to be cut and pruned from time to time. The technology is relatively affordable and facile to implement. At the beginning the farmer bought some seedlings. Meanwhile, the plants reproduce themselves and the farmer doesn't have to buy seedlings for further maintenance. The stones can be collected for free in the nearby riverbed. The work is done manually; no special tools are needed for the technology.
Natural / human environment: The farmer is proud of the outcome of his initiative. However he wishes that his neighbours would follow his lead, as for them it would be beneficial to implement the technology as well. He stated that usually people do not listen to a common farmer, but if the technology would be introduced by an official person it would spread out quickly.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Faizabad, Javonon, Chinoro
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: northernmost: 38°36'00.09"/69°23'58.93"
southernmost: 38°35'54.77"/69°24'03.18"
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002138 m2.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The farmer implemented the technology during the civil war and teached other farmers to do it. But it is not so easy for the farmer to convince other people to follow his example.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
gully
Observações:
The gully floor is vegetated with different trees inter alia willow, poplar, cherry, blackberry and walnut which are arranged in random groups.
A dense bush line with Russian olives, apricots, cherries, walnuts, plums and buxus has been planted on the top of the side slopes of the gully.
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Highly erodible loess soil, and heavy rainfalls which causes a lot of surface runoff and erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation, too few rain, steep slopes, infertile soils which make the use of fertilizers essential.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March to August
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos
- Wr: erosão das margens
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Wr: riverbank erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (lack of knowledge for soil treatement, e.g. people dig hollows which support gully formation, agronoms from soviet times are missing), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees were cut for domestic use), overgrazing, disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (land is not private property), poverty / wealth (no money for tractors, fertilizers, education, etc.,), education, access to knowledge and support services, war and conflicts (during the civil war the land was not cultivated sustainably), governance / institutional (land use rights)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), change in temperature (too hot and too cold temperatures dry out the soil, plants cannot survive), change of seasonal rainfall, population pressure, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (lack of machinery to treat the field properly)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
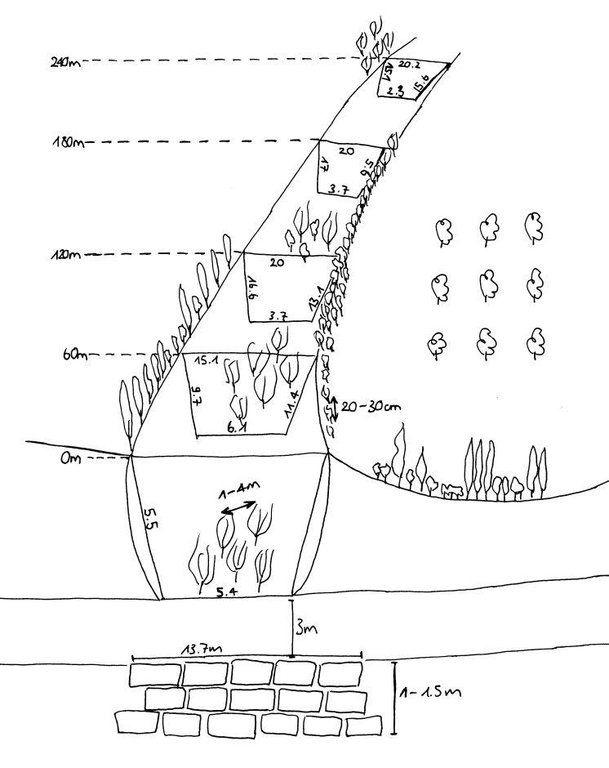
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The technology includes three different sketch information; 1) dense tree lines on the top of the side slopes, 2) stonewall at the end of the gully and 3) willow trees at the bottom of the gully.
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad/Javonon/Tajikistan
Date: 03.09.2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (People do not accept a suggestion if it is not from a good educated, accepted person.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m (1-2 Row(s))
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-4
Trees/ shrubs species: russian olive, willow tree, acacia, poplar, box
Fruit trees / shrubs species: walnut, apple, apricot, plum, cherries
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 0
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 13.7
Construction material (stone): Are taken from a nearby riverbed.
Autor:
Selina Studer
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tajik Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,7
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
12.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | plant trees in the gully | whole year |
| 2. | plant tree line | whole year |
| 3. | build wall |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Build wall | wall | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting trees | Persons/day | 3,0 | 12,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Tree seedlings | 1,0 | 166,0 | 166,0 | ||
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 327,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 69,57 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | add trees in the gully | spring |
| 2. | add trees in the tree line | spring |
| 3. | increase the height of the stonewall | once a while |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Add trees | Persons/day | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Increase the hight of the wall | - | ||||
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 12,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2,55 | |||||
Comentários:
The fact that the inputs for the technology are not evenly distributed throughout the area, the costs were calculated for the whole technology area.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The material is relatively affordable. Money intensive factor are the seedlings during establishment phase. Following years the trees reproduce themselves. The establishment of the technology, the planting of the trees and the building of the stonewall require a lot of labour input in the initial phase. As the whole technology does not have to be implemented at once, the work can be split-up over years.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: No soil in the gully
Soil fertility is medium for the treeline on top of the slopes of the gully (close to the orchard). but in the gully its very low because the soil was washed away.
Topsoil organic matter is medium at the treeline on top of the gully slope.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium and in the orchard, gully works as drainage
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology was directed by the farmer and implemented by the farmer's son. Only men were involved in the technology. In Tajikistan usually work for men and women is strictly divided. Women work in the household, take care for children and work on the field. The gully rehabilitation project was men's work.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich (trader which buy and sell products from the farmers).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: beneath the technology the farmer has an orchard with intercropping, a flax and a wheat plot.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Especially at the time of establishment.
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Land users acquired new knowledge.
security to have fertile land
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
Treeline
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
On the bottom of the gully willow trees should be planted which have strong roots to resist floods, especially if the gully is already deep. At the slopes Russian olives and wild cherries can be planted. The higher amount of trees makes gully even more stable.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Much more extra work comes up for the establishment, but for the farmer work is not a disadvantage.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Stopping the expansion (prevention) of the gully and filling up the gully (rehabilitation). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the vegetative measures, plant more seedlings and let them reproduce themselves. |
|
Firewood and construction material production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the vegetation with wood of good quality and use it in a sustainable manner (cut only as much as will be reproduced). |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Extensive use of the area and a relatively rich diversity of local vegetation. The maintained gully provides new habitat for natural flora and fauna. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep and promote the diversity of plants in the gully. |
|
Cheap and relatively less labor intensive work. Relatively little knowledge and no special tools are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make the technology public. |
| The entire technology doesn’t have to be established at once, which allows investing money and time whenever it is available. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The trees stop the water, sediments, branches etc. too effectively and this creates problems with too much water in the gully, which is washing out the sides of the gully. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| A disadvantage is the extra work the farmer have to spend on a little productive area. | In the land users view work is not a disadvantage, it is his job. Considering the fact that it is not that much extra work, it is not a big disadvantage. |
| For the establishment a first investment for the seedlings is required. | An establishment of the technology during a longer period allows to grow own seedlings from the plants which do not cost anything. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Integrated spatial assessment for Sustainable Land Management „SLM-planning“ in the loess hill of central Tajikistan using WOCAT mapping tools (working title), Selina Studer, 2013, Master Thesis, University of Bern, Bern.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
University of Bern
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
WOCAT technology movie: Orchard-Based Agroforestry
URL:
wocat@cde.ch
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos