Zero grazing [Uganda]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Wilson Bamwerinde
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okurisiza hamwe
technologies_1188 - Uganda
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItáliaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - Uganda1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Stall-fed livestock production is an efficient method to produce organic fertilizers (manure) for the conservation and improvement of soil fertility.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
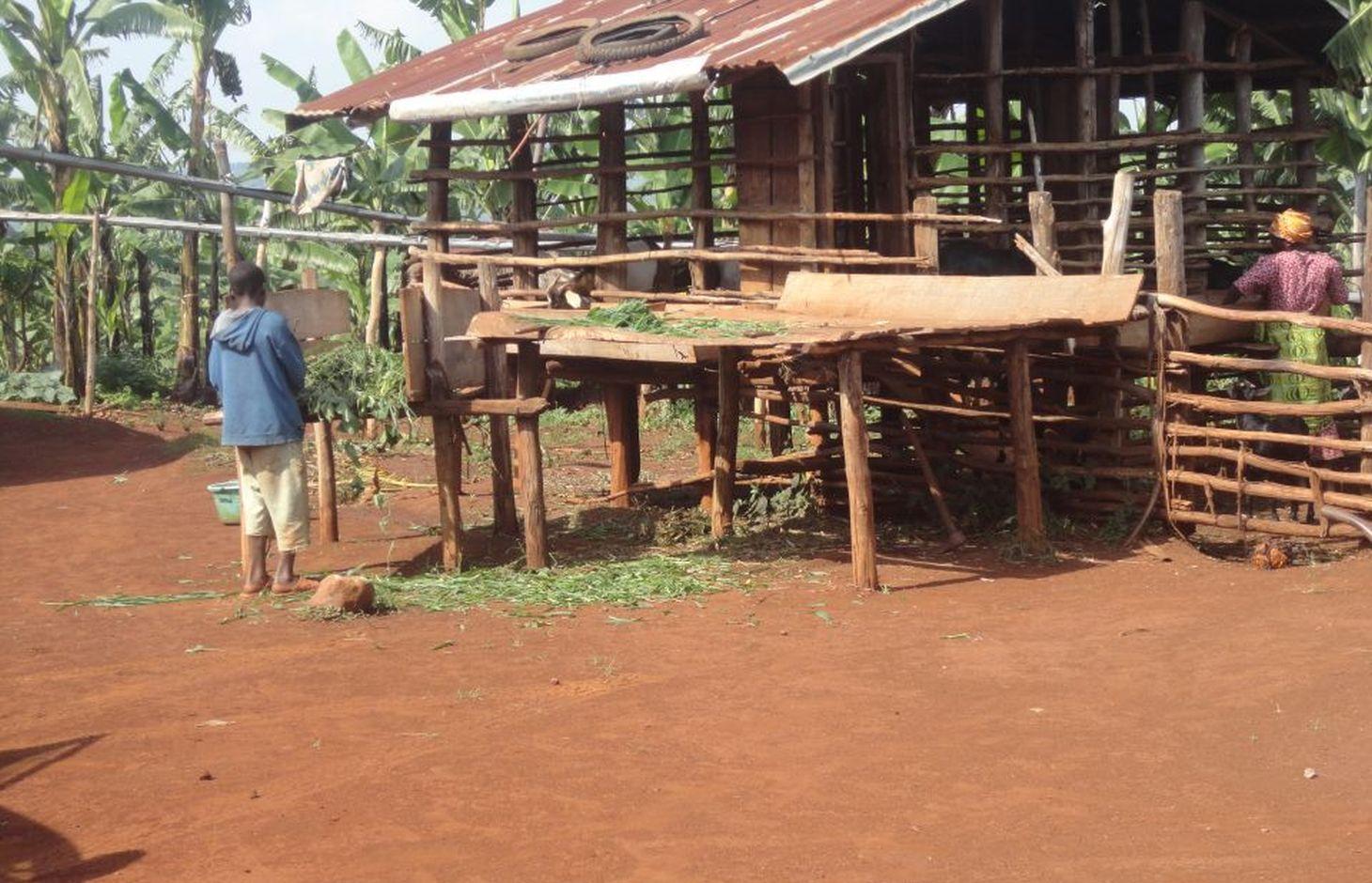
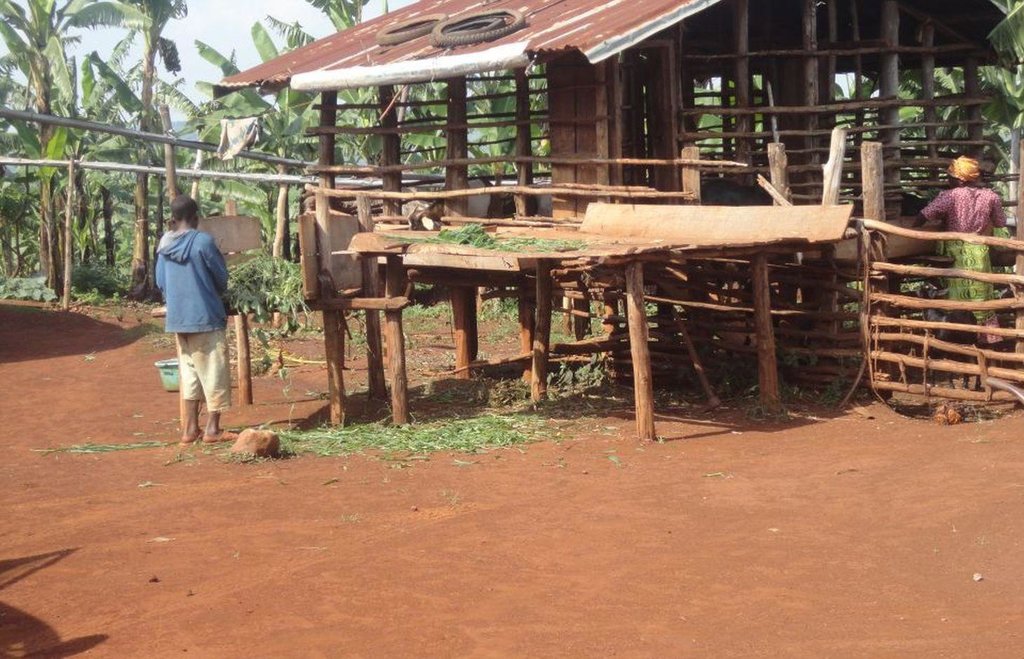
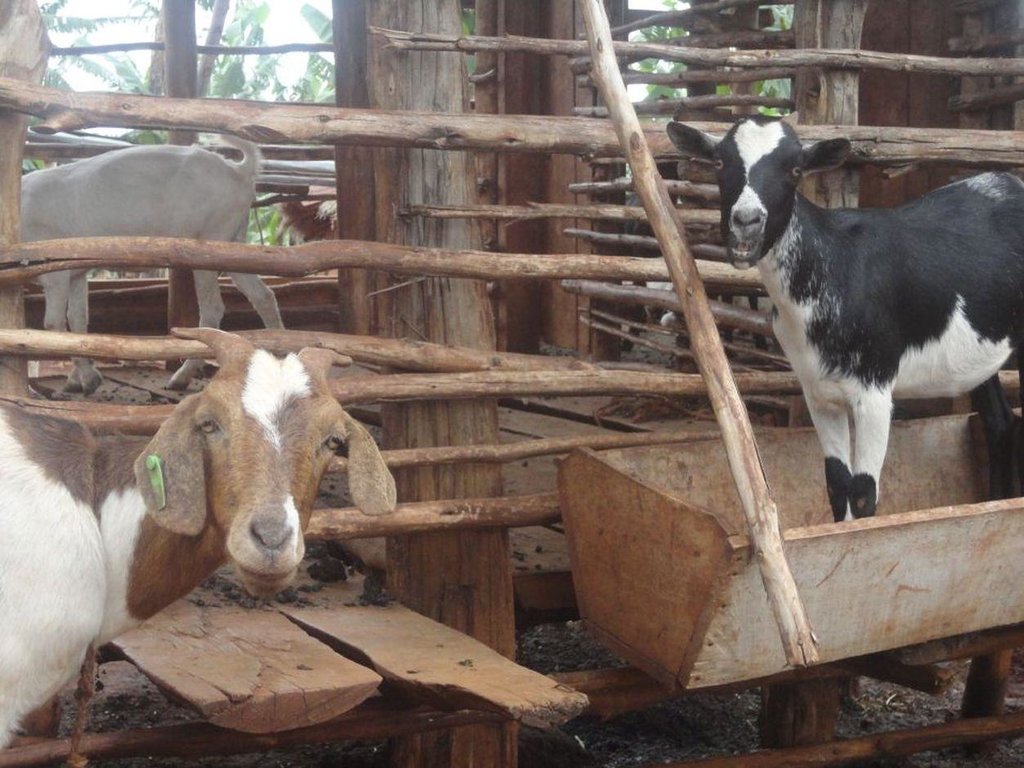
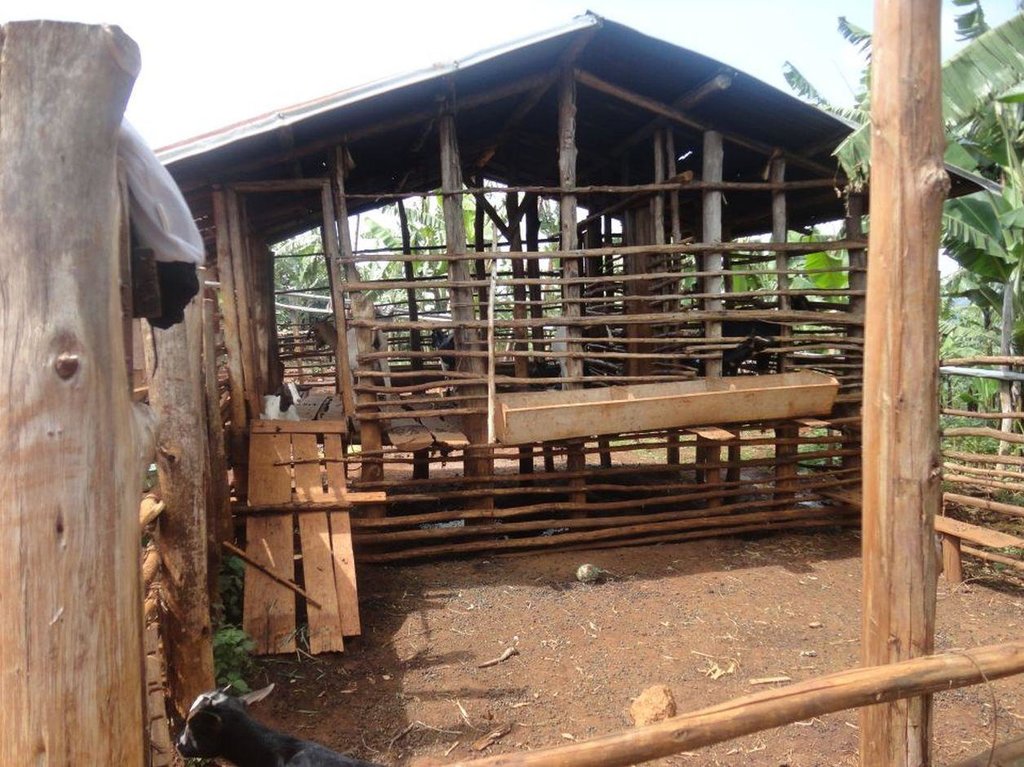
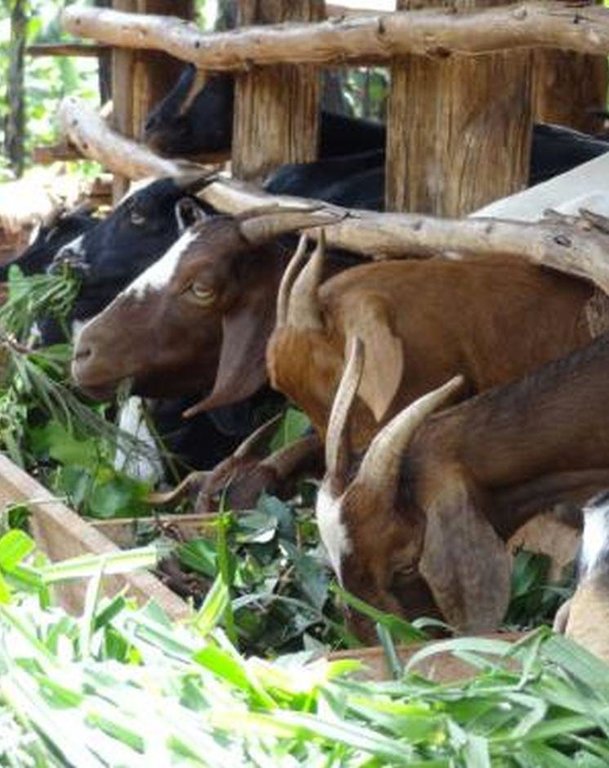
Zero-grazing has been a common livestock (cattle and pigs) management practice in most areas of south-western Uganda due to reduced communal grazing land. In the predominantly annual cropping system communities, free grazing livestock often damage crops and are a major cause of conflict. On the other hand, farmers observe that crop yields have declined season after season. For example, the bunch of bananas has grown smaller, it has smaller fingers, and many banana stands have no fruit during much of the year. The most important ways through which croplands in Rubagano are degraded include nutrient transfer through harvest and crop residue movement and use; nutrient mining whereby continuous cultivation is done with little or no replenishment; and soil and water runoff on steep slopes. Farmers know that one of the most important ways to reverse declining soil fertility is to apply manure, but it is expensive. Therefore farmers acquired goats or pigs primarily for the provision of manure for their cropland, but also as a household income generating enterprise. In stall-fed goat or pig production, The zero-grazing unit is designed in such a way that it is well ventilated and protected from wind, rain and constant direct sunshine to avoid livestock developing coughs, colds and stress. The unit has 3 major parts: the feeding and rest area, the exercise area and the manure collection area. The feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground. Below it is the manure collection area and above it, a corrugated iron roof. There is a feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area in which mixed fodder is fed to the livestock. A wooden food preparation slab for cutting and mixing fodder is in front of the feeding/rest area. The unit for housing 12 goats is 4 m by 8 m on the ground and 3 m high at the feeding area.
Purpose of the Technology: The major objective of stall-feeding is to maximize manure collection for sustaining soil fertility in cropland. Other goals are to improve household income, reduce expenditure on pests and disease management through livestock isolation from other animals and to reduce labor by cutting and storing fodder for use over a period instead of grazing in distant pastures daily.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The materials required for establishment of the zero-grazing unit for goats are wooden posts or poles, cut-off planks, wooden slats/timber, iron sheets and nails. The 4 m by 4 m feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground on strong Eucalyptus or pine posts of diameter 5-10 cm. Its wall is 2 m high and is made of widely spaced cut-off planks or light wooden poles not more than 3 cm diameter nailed to strong upright posts. The floor is made of wooden slats placed 2 cm apart, big enough to allow livestock droppings to fall through but too small for adult goats’ or kids’ hooves pass, in order to avoid injury to livestock. There is a 1.5 m by 0.5 m feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area and a 1 m by 1 m fodder mixing wooden slab at the front. On the ground to one side of the feeding/rest area is the 4m by 4m exercise area. The unit can be constructed at any time of the year.
Natural / human environment: Regular maintenance of the unit is done to ensure the floor does not develop holes that can lead to injury of the livestock, and the roof does not leak when it rains. Increased manure collection and application increases crop yields and supports crop diversification.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Uganda
Região/Estado/Província:
Uganda
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mbarara District
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86313 30.62564; -0.86314 30.62561; -0.86316 30.62569; -0.86319 30.62567
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002 km2.
There are 20 zero grazing units (goats and pigs) in the area and with a total area of about 2 hectares. The technology is being adopted slowly throughout the community.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
This technology was introduced in 2008 by NAADS and later by Africa2000 with aim to improve manure and compost production in Kagera region. Recently, Kagera TAMP project provided additional support to introduce exotic breeds of the goats and increase livestock productivity.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Tipo de animal:
- gado - lácteo
- caprinos
- pigs
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Reduction of soil organic matter content
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decline of soil fertility and decreased crop yields
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: other crops like peas, millet, maize and sorghum are also grown.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Pastagem
Comentários:
Extensive grazing land
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor methods of cultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor agronomic practices), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Vegetation destroyed for domestic use (firewood and thatch).)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Details of zero grazing shed structure : A. Overview of the livestock shed with manure colelction area (below) B. View on the feeding arrangement with the fodder vats abouve ground level C. Deatils of the fodder vat D. Overview of the fodder preparation structures
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 29-DEC-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Manure (Pigs or goats)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 900
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Grass species: Pennisetum purpereum (napier grass), Calliandra Spp.)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25-30%
Change of land use type: Mixed crop and livestock husbandry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Planting fodder in addition to traditional annual and perennial crops
Autor:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabala
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
UGX
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
2600,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.85
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of tools | Wet season |
| 2. | Purchase of construction materials | |
| 3. | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | |
| 4. | Purchase of livestock | |
| 5. | Grass seed procurement and sowing | Wet season |
| 6. | Converting part of the cropland (annual and perrenial crops) into fodder production |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | ha | 1,0 | 115,4 | 115,4 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | Set | 1,0 | 115,4 | 115,4 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1,0 | 38,46 | 38,46 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1,0 | 173,1 | 173,1 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 692,36 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 0,27 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
Lifespan of:
Tools - 1 year
Construction material - 10 years
Zero grazing shed - 1 year
Livestock - 20 years
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and carrying and application of fodder | Daily |
| 2. | Collection, composting and application of manure | Daily |
| 3. | Purchase of tools and materials for reconstruction/repairs of the shed structure | annual |
| 4. | Weeding and gapping | Seasonal |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 38,46 | 38,46 | |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 11,54 | 11,54 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1,0 | 3,85 | 3,85 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1,0 | |||
| Outros | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 71,85 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 0,03 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Panga, hoe, tree poles nails, soka jembe, spade, and wheel barrow., Hand hoe, panga.
The costs were calculated for the construction of the shed, acquisition of 3 does and establishment of fodder crops on part of cropland formerly used for annual and perrenial crops. The calculations were done for the technology in August 2011.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most determinate factors in the establishment of the technology are: labour for planting, maintaining and cutting grass and other pastures and carrying the fodder to the zero-grazing unit; labour for fetching water for the animals; and labour for removing and composting manure and spreading into the garden.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1041,00
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C.
Rubagano receives at least 6 months of rain in 2 seasons, February to May and September to November
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1740 m.a.s.l)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Fairly steep slopes in places)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (Mother rock easily reached on pitting)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Sand and stones)
Soil fertility: Low (Fertility depleted; being slowly replenished by application of technology)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (Water easily penetrates into the soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (Crops easily dry during the dry spell)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: >50m (Not possible to reach water table)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (No surface water except when it rains)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, muddy water collected by damming runoff in natural rock depressions)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Low, noticed improvements after application of the technology
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No difference in involvement of men and women.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
14% of the land users are rich and own 37% of the land.
48% of the land users are average wealthy and own 42% of the land.
21% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land.
17% of the land users are poor and own 7% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is increased yield where the technology has been applied, increasing the income generated on-site thereby reducing off-farm percentage.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (use hand hoes)
Market orientation: Mixed (Some crops are sold to generate household income. Goats will be mainly for sale)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Some households have more while others have less land.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Individual land ownership. Recent introduction of the water harvesting measures provided land owners with access to own water sources
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10kg
Quantidade posterior à GST:
60kg
Comentários/especificar:
increased yields for beans realised.
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
23dollars per yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
92 dollars per yr.
Comentários/especificar:
yields increased from sell of goats
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
As there is now a lot more activity on-farm
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation cover has been improved.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Food security and household income have improved. This has resulted in children in these households having more time for school and in case of illness, there in some money for accessing treatment.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
livestock is confined
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Comentários:
Forage and fodder usually become scorched during seasons of long drought and livestock may die from lack of food. Grass is cut in the wet season while it is plentiful and turned into hay for the time of scarcity. For this, a barn unit needs to be constructed.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The benefits far outweigh the establishment and maintenance costs. The negative on short-term returns is due to the cost of the technology (construction and procuring livestock) which is a little high for the farmers in this area.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
20 on 2 hectares
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The does were supplied to farmers using project funds.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: these farmers are rich and procured the technology without support from the project
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: 20 households in one village have adopted the technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Technology easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the livestock |
|
Helps in soil fertility management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good manure management |
|
Imporove soil cover and reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? using the manure in a proper /recommended way i.e. using it when planting or putting it in the plot before primary cultivation |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Animals are fed on selected pasture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the growing of that pasture |
|
The technology promotes us of organic manure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of compost pits to recycle the wastes into manure |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology may contribute to loss of vegetation | Planting pasture & other grass for feeding the animals |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos