Mulching in rainfed vineyards on terraces in the loess hill zone [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Qobiljon Shokirov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Mulcha Sino
technologies_1111 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Boev Jahonbek
Tajik Soil Institute
Tajiquistão
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
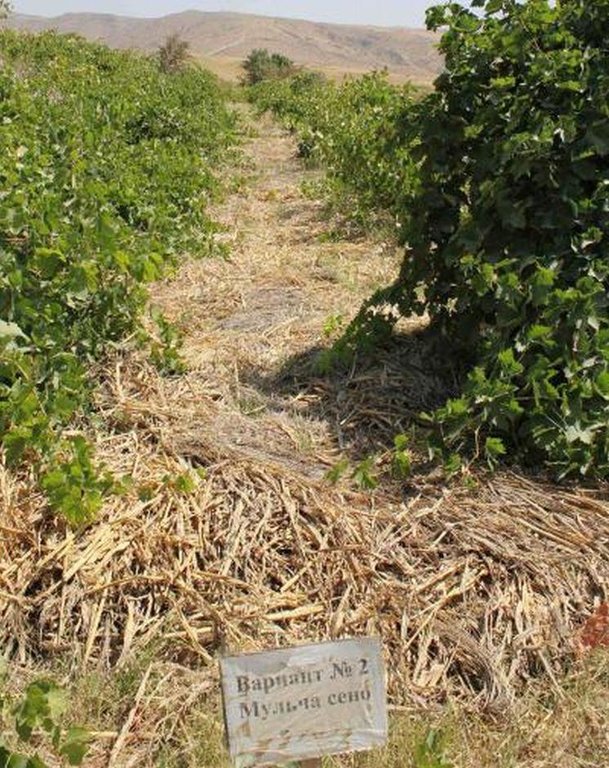
This technology consists of vineyards plots that are mulched with grass and established on terraced land in the loess hills of Tajikistan.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
On the terrain of the Tajik Soil Institut's research station in Karsang, Faizabad District, Tajikistan, a vineyard was established on forward sloping terraces with about 12° inclination on land formerly used as extensive pastures. This technology dates back to the times of the Soviet Union in 1968. Bulldozers were used to establish the terraces.
Before the planting of vines the soil was ploughed. Local vine sorts were used for the plantation and intercropping is done with wheat and fodder crops. About 1300 vine seedlings were planted per hectare.
Purpose of the Technology: Mulching treatment with grass was initiated to increase soil moisture in the soil, improve soil quality such as soil organic matter and other elements and protect soil from erosion by water and wind.
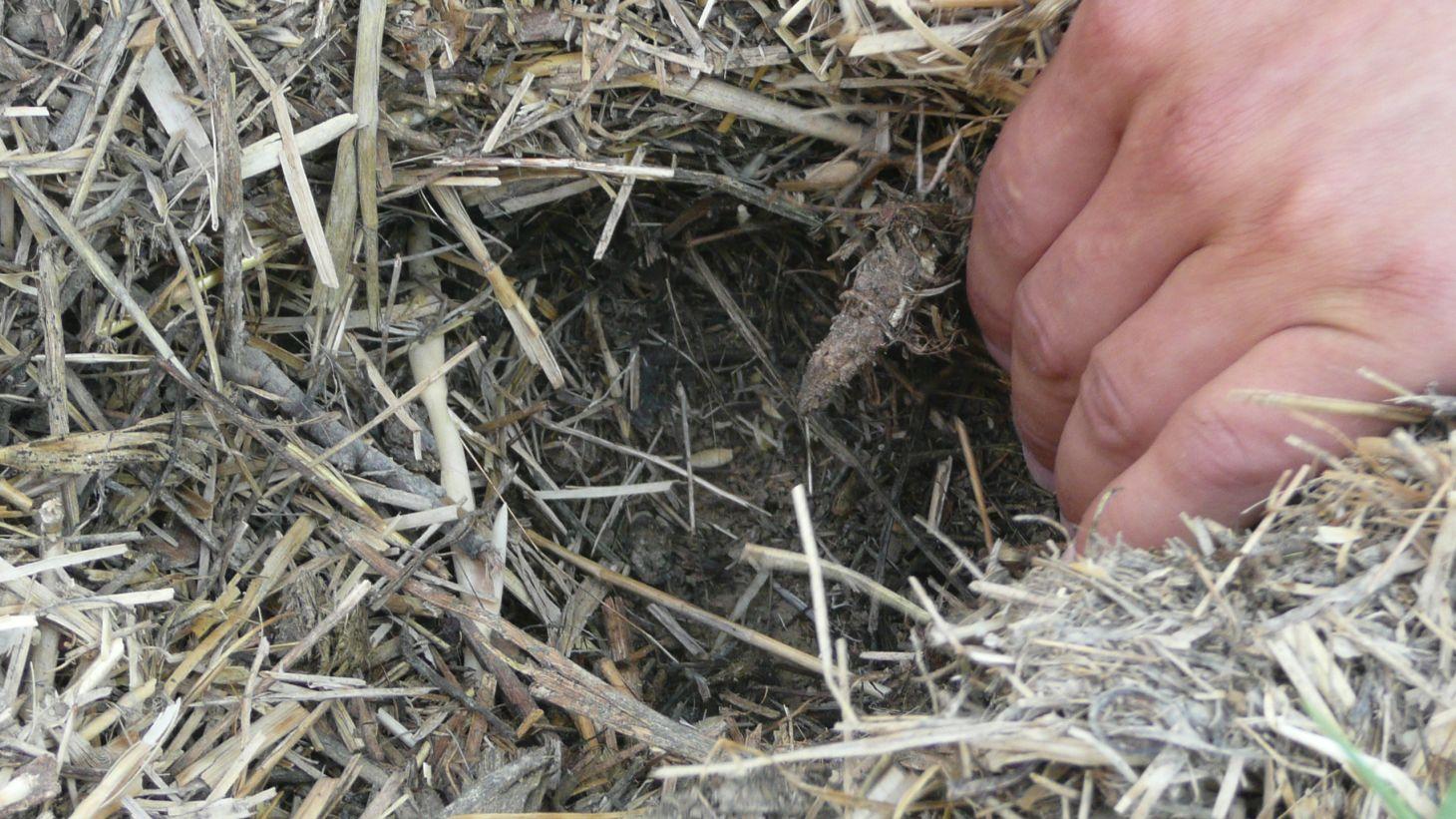
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Mulching with grass was set up by the Tajik Soil Institute and but has been maintained by the farmers who lease the land. Mulching with grass is relatively easy but can be very challenging; depending on the availability of resources. First, plots between the vineyard rows were ploughed by using animal power, in most cases horses. Natural grasses were cut from the property of the research station and applied as a mulch in between plots within the designated vineyard plots. Since then the experiment has been maintained by the farmers and over the last ten years layer of mulch with grass has been growing and building up the top soil layer. This layer of mulch prevents rainwater from eroding the top soil, improves soil organic carbon, provides shade to plant roots, and most importantly keeps soil moisture moderately in hot summer months, which is very essential in these rainfed areas.
Natural / human environment: The terraces have greatly helped to reduced soil erosion and the vines supported this effect in further stabilising the soil. Soil humidity has improved through increased soil moisture and reduced evaporation due to mulching throughout the year. As the vineyard was established on pasture land, a disadvantage is the reduced grazing land area. The disadvantage of mulching is that no inter cropping between the vines can take place for several years.
In summer of 2011, WOCAT questionnary was used to analyze and evaluate current conditions of the vineyard mulching treatment. At the same time proper soil samples were taken from the plots with mulch and control plots in 0-15 and 15-30cm for further comparison for soil organic carbon (SOC). All together 240 soil samples were taken from eight different plots and each have been analyzed for soil SOC content.
From this study it was revealed that plots with mulch has significantly higher SOC content than control plots. In average, plots with mulch consisted of 1.3% SOC and control plots in average contained 0.4% SOC within the 0-15cm depths. Average SOC content for plots with mulch and control plots were observed but there were no significant difference in 30cm depth, both contained 0.4-0.5% of SOC.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
RRS
Especificação adicional de localização:
Faizabad, Javonon, Karsang
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.07 km2.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The vineyard was originally set up 60 years ago but the mulching experiment within the vineyard was introduced around 2000-2003.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- uvas
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period from month to month: April to November

Pastagem

Floresta/bosques
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion through wind and water, soil moisture loss, soil nutrient mining
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil fertility and humidity decline, lack of technical equipment, low productivity of non-irrigated land on slopes when used in a conventional way as cropland of extensive pasture
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Pastagem
Comentários:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
A3: Diferenciar os sistemas de lavoura:
A 3.1: Sem lavoura

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, breaking compacted topsoil, zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Plowing), overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms, droughts, governance / institutional (common grazing land in the vicinity of the village regulated management)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
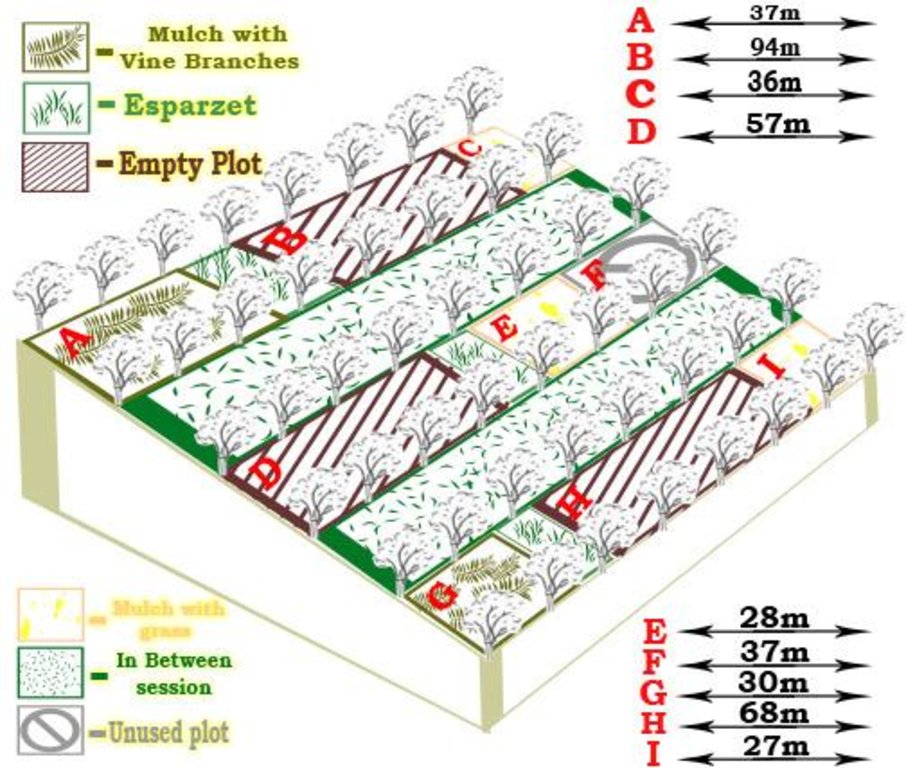
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
ocation: Faizabad, Tajikistan. RRS
Date: September, 2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Material: earth
Mulching
Material/ species: grass
Quantity/ density: 15-20cm
Remarks: mulch layer thickness (15-20cm)
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: loosing of soil around vines, yearly
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: zero tillage between the vines on the terraces
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1300
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Fruit trees / shrubs species: vineyards "rosevitaiti", improved local sorts
Terrace: bench level
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Ibrohimov Huseyn
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
-2,13
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
6.5
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting | |
| 2. | Terracing by bulldozer | late autumn / early spring |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting | Persons/day | 13,0 | 6,5 | 84,5 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Terracing by bulldozer | hours | 16,0 | 2,81222 | 45,0 | |
| Equipamento | Bulldozer rent | hours | 16,0 | 0,8125 | 13,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | Seeds/ha | 1300,0 | 0,5 | 650,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | |
| Material de construção | Grass | tons | 1,0 | 165,0 | 165,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 962,5 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | -451,88 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cutting of grass | spring/once a year |
| 2. | soil loosening around the trees | |
| 3. | Mulching | spring (end of April/beginning of May) |
| 4. | Cutting the grass | 1 |
| 5. | Protecting the vineyard from animals | autumn to spring |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Cutting of grass | Persons/day | 5,0 | 6,5 | 32,5 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Soil loosening | Persons/day | 2,0 | 6,5 | 13,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Cutting the grass 2nd time | Persons/day | 4,0 | 6,5 | 26,0 | |
| Equipamento | Mulching | tons | 1,0 | 86,0 | 86,0 | |
| Equipamento | Scissors | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 217,5 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | -102,11 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: scissors, hoes
The establishment of the vineyard took place in Soviet times and costs were born by the Soil Institute, which is a state institution. However, costs were calculated based on current costs (2011).
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Subsistence (self-supply) is supported by the local Institution.
All three levels of mechanization are existing.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- research
- research
Comentários:
harvest: 50% to state / 50% to land user
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
earthworms
Outros impactos ecológicos
Hazards towards adverse events
Comentários/especificar:
drought
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Comentários:
Different types of mulching are currently being tested to increase soil moisture storage, to build up soil organic matter and thus infiltration capacity and soil fertility properties.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Farmers have noted that usually change can be seen within few years after the technology has established.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
10 households (3 percent of stated area)
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Overall acreage of the all field are roughly 3 hectares.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Vineyards are adapted to climate and give consistently good harvest. |
| Between the rows there is an additional harvest thanks to intercropping. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Efficient soil protection. |
|
Very practical and easily adaptable in villages, where grass is available. How can they be sustained / enhanced? At the same time grass can become deficit in villages, because of high number of livestock. In that cases small scale mulching is recommended with rotation system. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Technology is very practical but so far it has not been taken seriously by the farmers. | Probably, few educational days for knowledge sharing would be very helpful. |
| Grass might be available for small scale mulching but usually not for a big scale, because everyone in the region has high number of livestock and automatically grass is used as fodder for animals. | Maybe mulching can be applied around the trees and not so much for covering entire plots. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos