Cascading Rock Irrigation Channel [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Davlatbek Davlatov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Boloi Dasht (Tajik)
technologies_1454 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
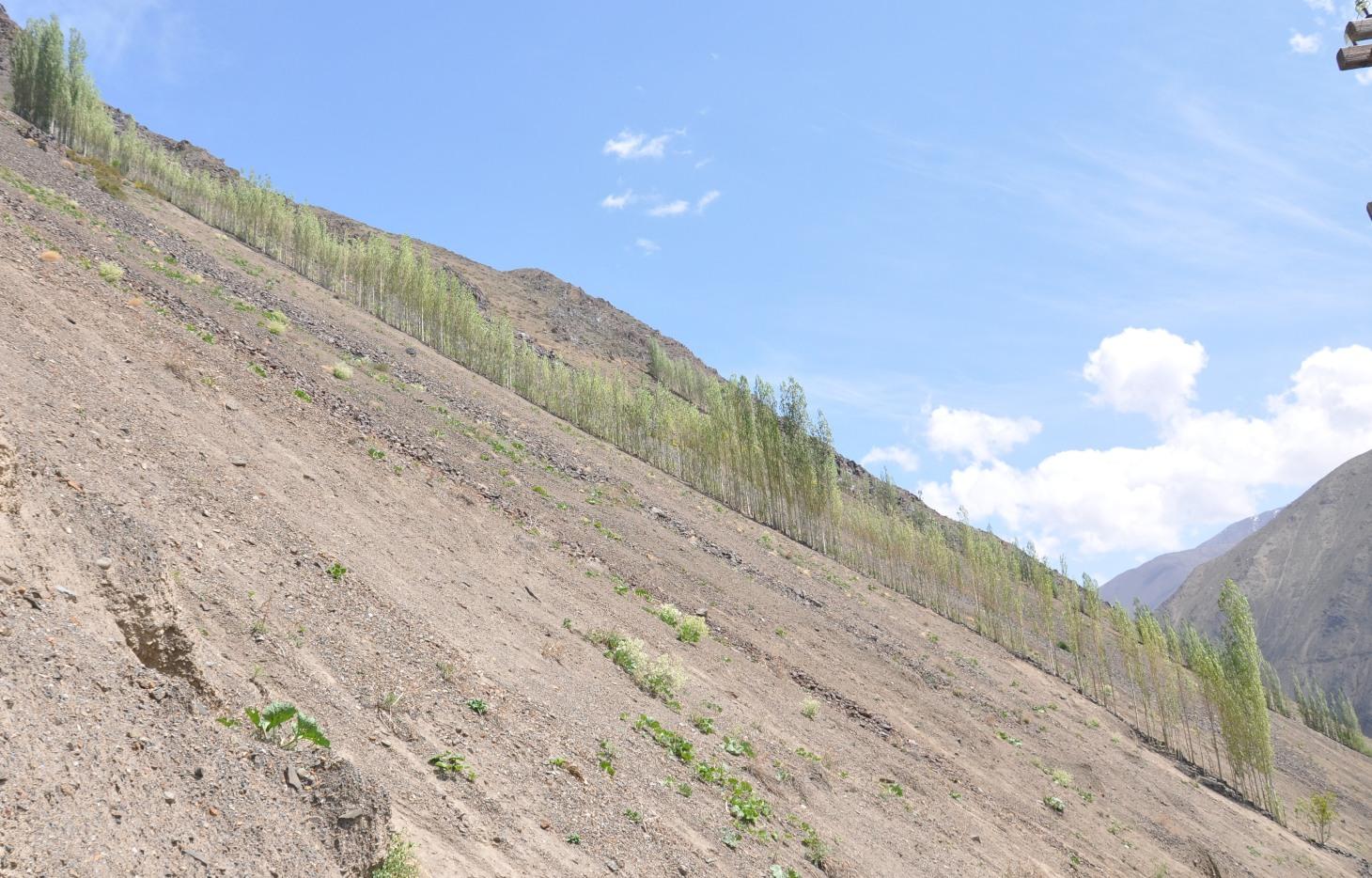
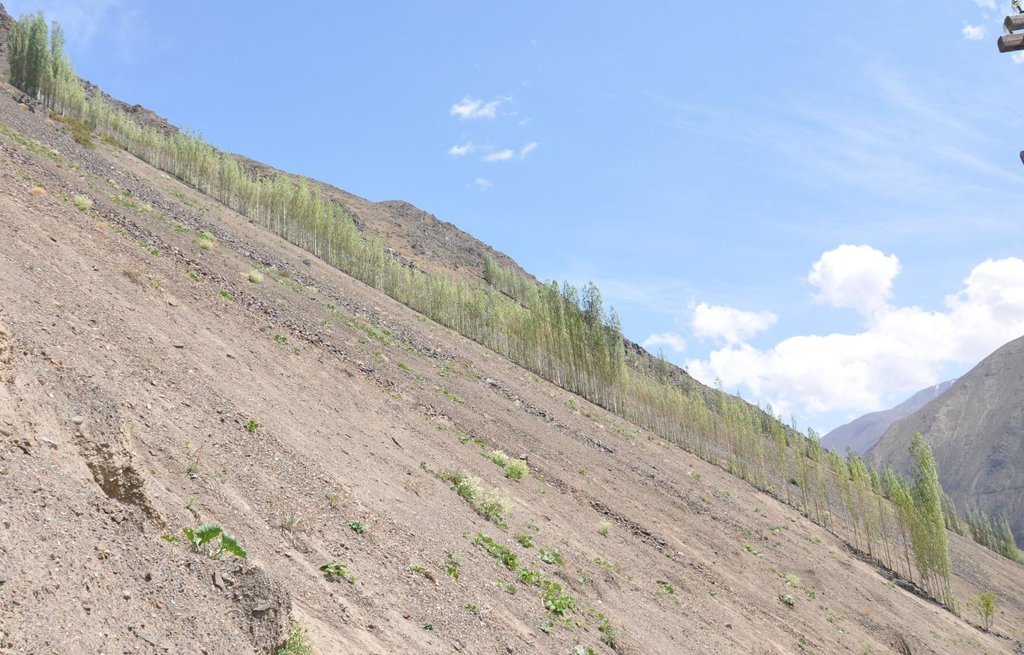
A cascading rock irrigation channel lined with fast growing poplar trees, constructed on rocky slopes to channel water runoff from the high mountains for human use at the valley floor.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
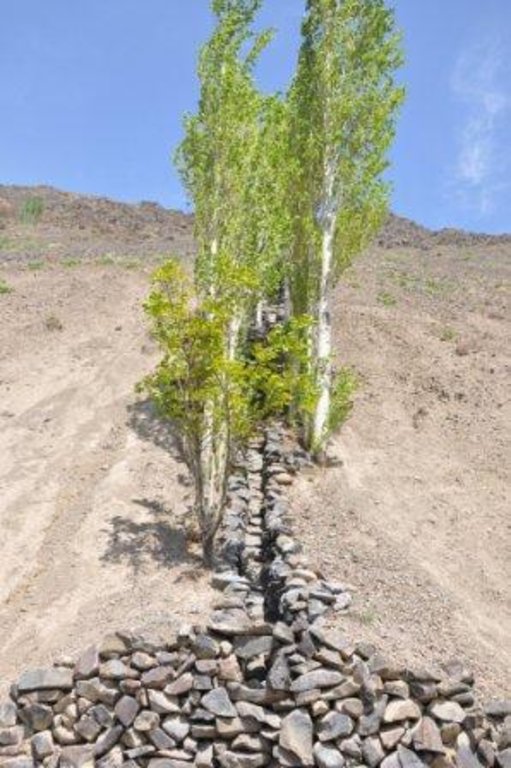
A one metre wide, 300m long, irrigation channel constructed of stones, that is built into the steep slope of a mountain gorge. The channel is 0.5m deep and is lined with poplar trees that help stabilise the structure. The water runs down the channel from the top mountains, with water splashing onto the poplar trees. At the foot of the channel the water is used to irrigated cultivated land and provide drinking water.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the cascading rock irrigation structure is to capture surface water run-off from the top of the mountain and channel it to where it can be utilised for human use such as drinking water, sanitation, and irrigation. The uneven surface of the rock channel slows the pace of the water thus preventing scouring at the foot of the channel. The channel also provides a suitable environment for the cultivation of poplar trees which in turn can help reduce water and wind erosion on the slopes, thus preventing rock and debris movement down onto the cultivated lands on the valley floor.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The channel is dug perpendicular to the steep slope and lined with stones gathered from the mountainous slopes. This activity is labour intensive, but can be more efficient with the use of donkeys. The stones are placed upon/on top of each other in the base of the channel, and used to line the sides of the channel to retain the water. The soil along the edge of the channel is cleared of debris and stone until it is suitable for the planting of poplar cuttings. The cutting are supplemented with organic fertiliser. The channel is financed by the land owner, with voluntary support from the community.
Natural / human environment: The cascading rock irrigation channel is located in a remote steep mountainous gorge where there is a shortage of land for cultivation. Water is in short supply, especially during the hot summer months. Subsequently the inhabitants have a high dependency on irrigated water from the top of the mountain range. The majority of the residents have a semi-subsistence living and are highly reliant upon the cultivated land where they grow a range of crops (e.g. wheat, potatoes. etc), fruits (e.g. apricots) and poplar trees for selling and construction purposes.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Sogd region
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ayni
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Long and narrow geographical areas were chosen for implementation of the technology. The technology was replicated ten times in this community area.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was constructed in 1992 and 1997 based upon ideas generated from the local inhabitants.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- improved access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
Plantação de árvores, florestamento: Especificar a origem e composição das espécies:
- Monocultura de variedade local
Produtos e serviços:
- Proteção contra desastres naturais
- construction

Outros
Especifique:
Wasteland: The mountain slopes are mainly devoid of vegetation.
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water and wind erosion, rockfalls and debris movement.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Debris movement due to excessive rains damaging crops and infrastructure.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Infrequent felling of poplars.
Forest products and services: timber, protection against natural hazards
Other forest products and services: construction
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)

Floresta/bosques
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March-October
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Ed: deflação e deposição
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ed: deflation and deposition
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Removal of forest vegetation many years before.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Extreme events lead to debris movement covering fertile lands.)
Secondary causes of degradation: war and conflicts (Lack of natural resources during civil war led to the cutting of many of the trees preventing slope movement.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
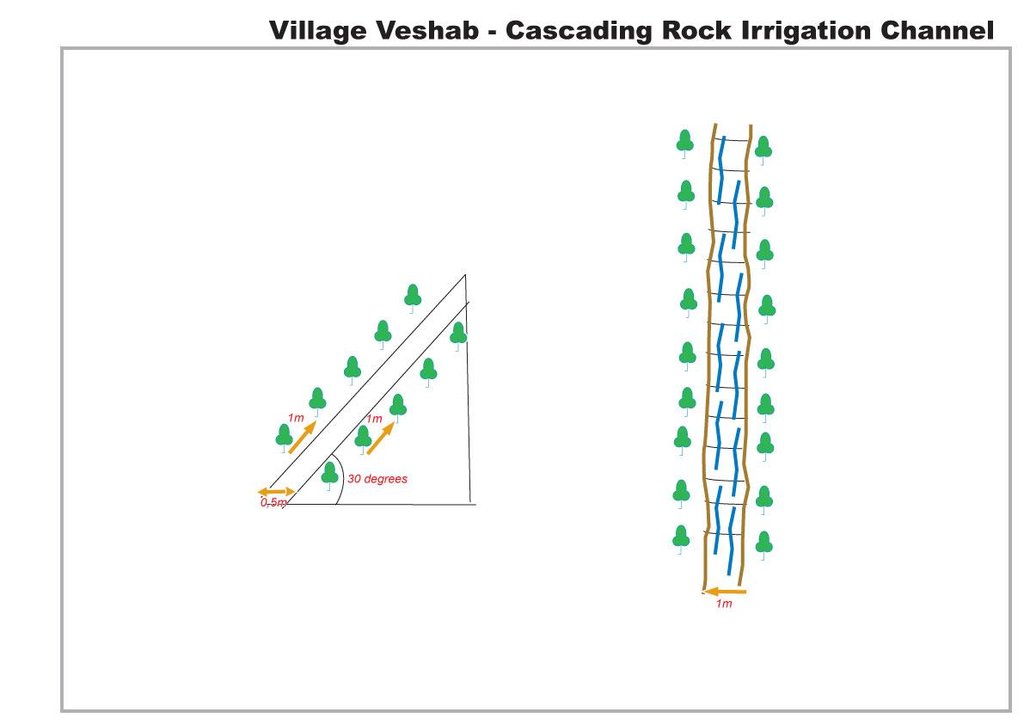
The drawing shows in plan and profile the cascading rock channel. The slope of the mountain is 30 degrees, a one metre wide channel, 0.5 m deep, is dug into the slope. The channel is lined with stones. The soil either side of the channel is cleared of rocks, and poplar branches are planted at 1m intervals lining the channel.
Location: Veshab Boloi Dasht. Ayni Sughd Region Tajikistan
Date: 2011-05-04
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (An understanding of how to build the basic structure without it collapsing and able to meet the discharge capacity of the water.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water harvesting / increase water supply, Prevent off site damage to cultivated land at the foot of the slope.
Secondary technical functions: Stabilisation of soil along the channel.
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 600
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: Poplars (safedor) are planted in vertical rows, 1m apart, on both sides of the 1m wide channel.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300
Construction material (stone): local stones and rocks
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Davlatov Davlatbek, Dushanbe City,Rudaki str.131,fl.19
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.50
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting Poplars | Spring, March |
| 2. | Composting | spring |
| 3. | Construction of rock irrigation channel | spring |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting Poplars | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of rock irrigation channel | Persons/day | 60,0 | 25,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | Pieces | 3,0 | 20,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Donkey | Donkey/day | 20,0 | 22,5 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | Unit | 1,0 | 266,0 | 266,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Composte | per tree | 250,0 | 1,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Stone | tons | 50,0 | 20,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 3776,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 839,11 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tree tending | every year |
| 2. | Maintenance of channel | Spring |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Tree tending | Persons/day | 7,0 | 25,0 | 175,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance of channel | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 425,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 94,44 | |||||
Comentários:
The indicative cost of the technology was calculated based on 2010 prices.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
There was no real cost in construction of the rock irrigation channel. All labour, animal traction and materials were sourced locally for no cost, poplar seedlings are cuttings from local poplars, and organic compost for the trees was collected from local livestock.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Heavy Spring and Autumn Rain
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. 4 months of snowing during the winter period.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: This area is located at 1500m
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture is rocky, shale.
Soil fertility is very low and nothing is growing on the adjacent slopes.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
No natural propogation/reproduction on the slope and slow growth rate without irrigation.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the incomes come from driving, teaching etc
Market orientation of production system: Poplars are used for personal construction projects but can be sold for $300 per tree.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
This includes wood for construction, improved water supply for irrigation and improved water quality for drinking and sanitation.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Perda de solo
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| mass soil movement | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Low initial expense due to inputs easily available.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
400 households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
400 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Minimal replication in small areas of land, but no replication in recent years. (It appears in this area the implementation of the technology may have been optimised).
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Improved livelihoods and the variety and yield of crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the water was not available through the channel then the land would have to be abandoned. |
| The poplar trees provide a good source of secondary income. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It reduces soil and wind erosion from the mountain slopes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further planting of trees. |
| It reduces rockfalls and debris movement, thus protecting the land down slope that is used for cultivation. |
|
It provides water for irrigation and hence leads to an increase in crops yields and crop diversification down slope of the channel. These crops include wheat, potatoes, onions and some fruit trees mainly apricot. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pipes form the channel to other areas. |
|
Increased access to clean running water has improved sanitation and hygiene conditions for the inhabitants. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further training on hygiene and sanitation. |
| The use of uneven rocks slows down the speed of the water in the channel and prevents water erosion at the base of the slope. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The channel can become severely damaged after a harsh winter. | The rock lining could be cemented in but that would increase the cost, and the trees would not be able to use the water that soaks through the channel. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology is a major construction activity that needs to be strategically positioned. | The location should be carefully considered with help of specialists. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos