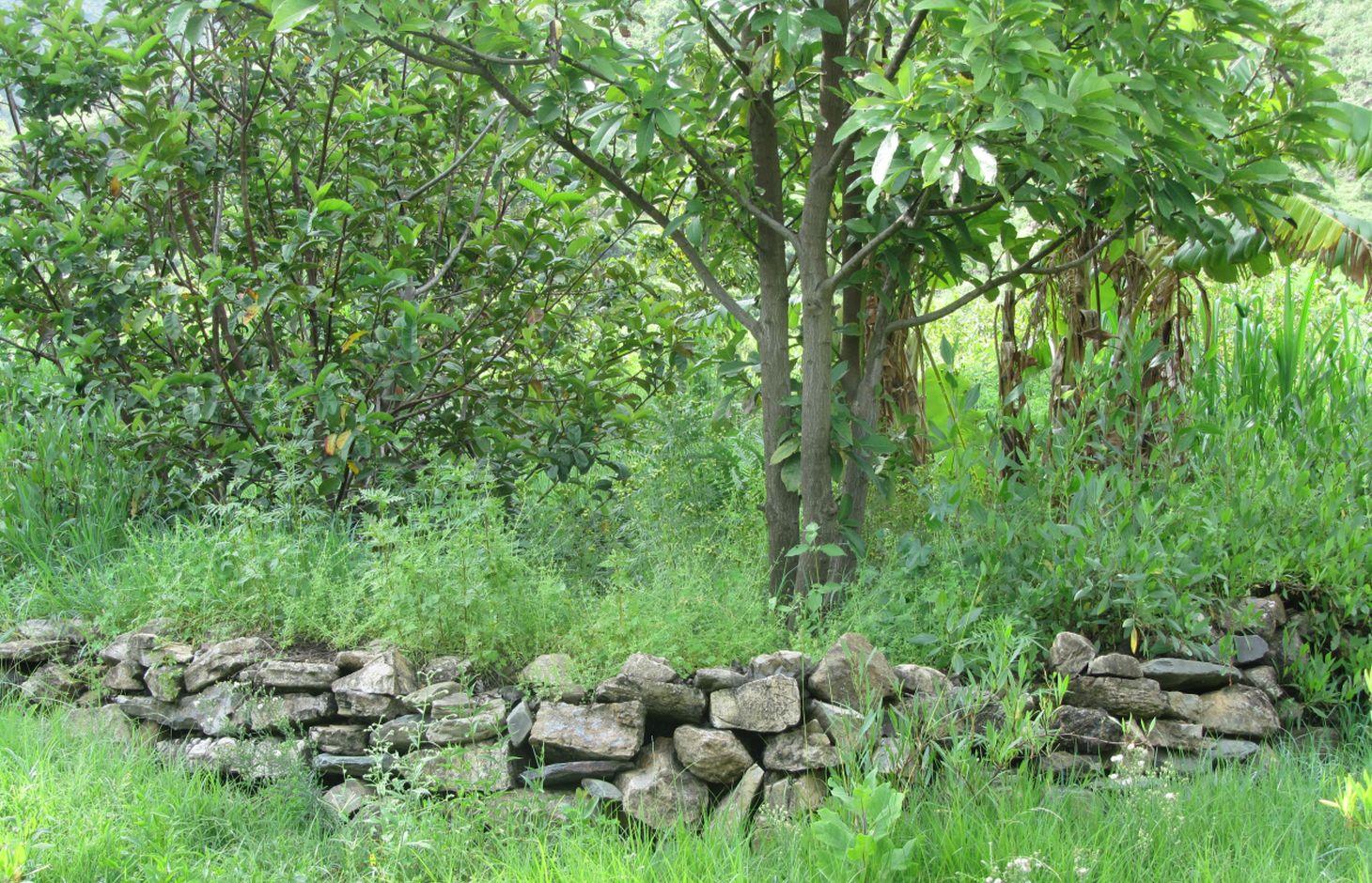
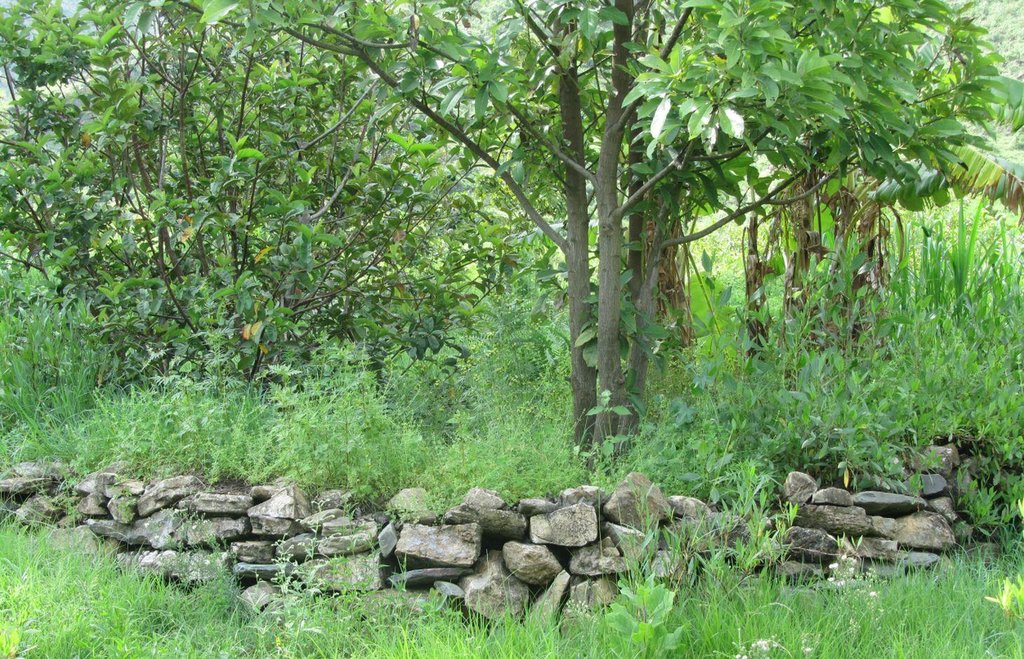
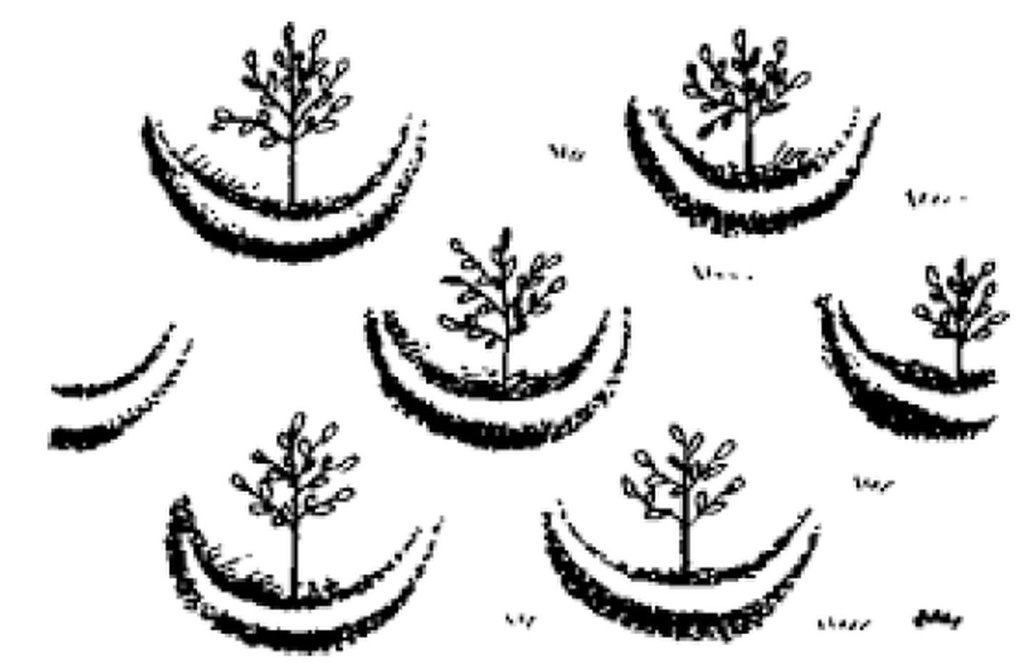
Large semi circular stone bunds [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Eyasu Yazew
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Abiy nay emni firki werhi
technologies_1546 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Hailemariam Mengisteab
Mekelle University
Etiópia
Especialista em GST:
Weldearegay Kifle
Mekelle University
Etiópia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Mekelle University (Mekelle University) - Etiópia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
These consist of stone embankments built in the shape of a semi circle with the tips of the bund on the contour and are arranged in staggered orientation in rows so that overflow from one row will run into the next downslope.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Large semi circular stone bunds are constructed by excavating a foundation of 0.1 - 0.2 m following the semi circle and building of the embankment using stones with a decreasing height at the tips to evacuate excess runoff. 1 - 3 pits are excavated within the semi circle for for planting trees.
Large semi circular stone bunds (Large half moons) are constructed with a diameter of 6 m and corresponding perimeter/length of 9.42 m. The spacing between the tips of adjacent bunds within a row and between the base bund and tip of adjacent rows is 3 m. The height of the embankment varies from 0.5 - 0.75 m at the base bund to 0.4 - 0.5 m at the tip while the corresponding width varies from 0.4 - 0.5 m to 0.2 - 0.3 m. The planting pit has a diameter and depth of 0.3 m.
Purpose of the Technology: Large semi circular stone bunds assist in decreasing slope length, runoff velocity and soil loss; and improving runoff harvesting, soil moisture and groundwater recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of large semi circular stone bunds involves collection of stones, alignment of a contour and the semi circle, excavation of foundation, construction of the embankment and digging of planting pits and runoff harvesting ditch. The maintenance includes re-enforcing the embankment and dredging sediment from runoff harvesting ditch during the dry season.
Natural / human environment: Large semi circular stone bunds are implemented in foot (5 - 8%) and hill (8 - 16%) slopes and in medium and light soil types of shallow to moderate depth (0.2 - 0.8 m). It reduces runoff amount and velocity thereby decreasing soil loss and desertification/land degradation. It also improves soil moisture availability and groundwater recharge.
It is mostly constructed using communal labour and there is a moderate trend of spontaneous adoption. The technology is witnessed to be increasing fruit and fodder production thereby improving the livelihood of the land users. It, however, demands high labour especially during establishment.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Tigray
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kilte Awlaelo
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- cítrico
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
- lemon, guava
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: June - November

Floresta/bosques
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
- Pastagem/Alimentação de folhas e brotos
- Conservação/proteção da natureza
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, soil erosion, overgrazing, decline of soil fertility and productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decrease soil moisture, drought, soil erosion, decrease fodder production and shortage of fuel wood.
Plantation forestry: Deforestation
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão do lençol freático
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep topography), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, land tenure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Large semi circular stone bunds are stone embankments built in the shape of a semi circle with the tips of the bund on the contour and are arranged in staggered orientation in rows so that overflow from one row will run into the next downslope.
Location: Tigray. Kilte Awlaelo
Date: 10/10/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.2 - 0.3
Spacing between structures (m): 3
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5 - 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4 - 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 9.42
Construction material (stone): The embankment of the semi circular bunds is constructed by the stones.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.5 and 12%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Autor:
Eyasu Yazew, P.O.Box 231, Mekelle University, Mekelle, Ethiopia
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Birr
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
18,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.50
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of stones, contour and semi circle alignment, excavation of foundation, construction of bunds and excavation of planting pits and water storage ditch. | January - May |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 3667,0 | 3667,0 | 60,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 3742,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 207,89 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replacement of displaced stones and dredging of planting pits and storage ditch | January - May |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 117,0 | 117,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 117,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 6,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Line level, tape meter, digging hoe, shovel, hammer
The cost was calculated for a semi circular bund of 6 m diameter, spacing between the tips of adjacent bunds within a row of 3 m and spacing between a base bund of one row and the tip of the next row of 3 m. This arrangement results in a construction of 2.5 bunds over 94.5 square meter area and a total of 264 bunds per ha.
The construction of one large semi circular stone bund and excavation of the planting pits and runoff harvesting ditch requires 5 person days during establishment while maintaining it needs 0.2 person days.The cost calculation rates apply to 2012. Accordingly, the daily labour wage is 40 Birr for light work such as sediment dredging and 50 Birr for medium work such as stone collection.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour, slope, stone availability and size.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average rainfall of 450-550 mm, Main rainy season from Mid-June to August
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: An average slope of 6.5% is taken for moderate/foot slope and 12% for hill slope.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1) and moderately deep (Fruit tree plantation on deeper soils, ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low (medium soils, ranked 1) and very low (Light soils, ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2, Drainage is restricted by the soil depth)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (Medium soils, ranked 1) and low (light soils, ranked 2)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 55% of the land (35 Birr/day/person).
30% of the land users are poor and own 35% of the land.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Cropland: Average land holding is 0.6 ha per household.
Forest land: Average land holding is 0.7 ha per household.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mobile communication:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Increased investment in health care as a result of increased income.
Instituições comunitárias
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
2820
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1880 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
940 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Increased vegetation coverage and fruit and fodder production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance of the structure. |
|
Reduced soil erosion and increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance of the structure. |
|
Increased spring discharges downstream How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance of the structure. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Decreased slope length, reduced runoff amount and velocity and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of bunds and runoff harvesting ditch. |
|
Increase in rainwater harvesting, soil moisture and groundwater recharge How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of bunds and runoff harvesting ditch. |
|
Increase in fruit and fodder production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper agronomic management |
|
Reduced maintenance requirement compared to bunds made of soils How can they be sustained / enhanced? No action needed, as is inherent to technology |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Damage to structures constructed at foot slopes if the hillside is not well conserved | Conserve the upper catchment first. |
| Increase labour requirement |
Mass mobilization and/or increased incentives to households. Reducing the size of the structure. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Poor design approach (the same diameter and spacing for different slope ranges) | Improve the design approach. |
| Increased labour demand | Mass mobilization and improving the design. |
| Reduced farm land | Increasing the spacing and reducing the dimension of bunds without compromising their effectiveness. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Staff members of the Kilte Awlaelo Wereda Office of Agriculture and Rural Development
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Carucci, V. (2000). Guidelines on Water Harvesting and Soil Conservation for Moisture Deficit Areas in Ethiopia:the productive use of water and soil. First draft manual for trainers, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Lakew, D., Carucci, V., Asrat, W. and Yitayew, A. (2005). Community Based Participatory Watershed Development: A guideline. Part I, first edition, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos