Hedgerow establishment on an agro-pastoral farm for dairy cows [França]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Alan Radbourne
- Editores: David Robinson, David Norris, Sabine Reinsch
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bocage
technologies_5681 - França
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
co-compilador/a:
Joubioux Christiane
Chambre Regionale D'Agriculture De Bretagne, Regional Chamber of Agriculture of Brittany
França
usuário de terra:
Danilo Noël
Danilo Noel
França
Especialista em GST:
Senegas Isabelle
Chambre Regionale D'Agriculture De Bretagne, Regional Chamber of Agriculture of Brittany
França
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
European Interreg project FABulous FarmersNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - Reino UnidoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Association des Chambres d’agriculture de l’Arc Atlantique (AC3A) - França1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Low-maintenance hedgerows were established in 2003 at the ridges of an agro-pastoral farm common in Brittany to protect water quality, ensure animal well-being, maintain biodiversity, and for energy, timber and litter production.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Brittany is an area in the north-west of France. Brittany’s agriculture includes well-known products such as: fish, beef, pork, poultry, vegetables and milk. The technology is applied at Danilo Noël farm, located in the commune of Mauron in Morbihan. The region has an average annual rainfall of 650-700 mm and annual temperature of around 11°C. The climate of Mauron is warm and temperate, with the farm located in the basin known as Ploërmel. ‘Bocages’ in France refer to small forests and decorative elements such as hedgerows or ornamental garden structures that border agricultural fields .
The fields of the Danilo Noël farm are grouped together in a rotational system of fodder crop and short-term pastoral leys, divided into fenced paddocks. They are located between two ‘talwegs’, with slopes of 5 or 6 %. An analysis carried out in 2000 by the water management organization ‘Grand Bassin de l'Oust’, shows that 85% of the plots are at high and medium risk of plant protection product runoff due to the slope and water run-off.
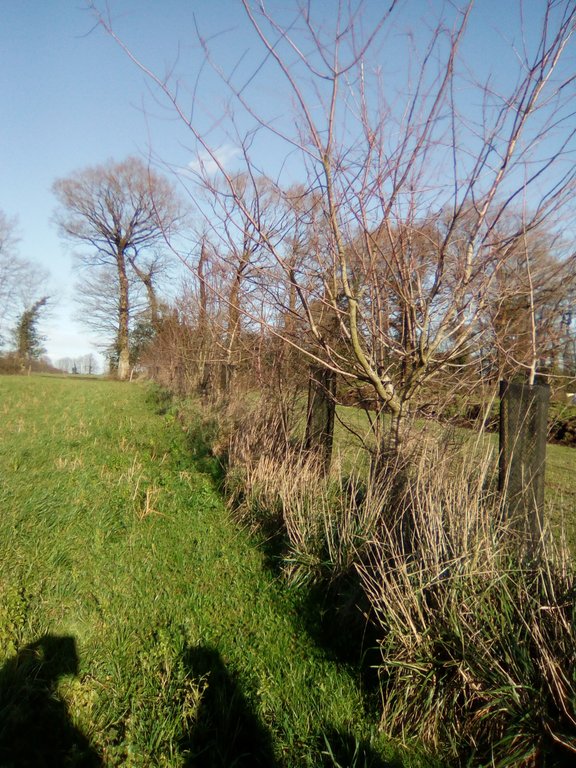
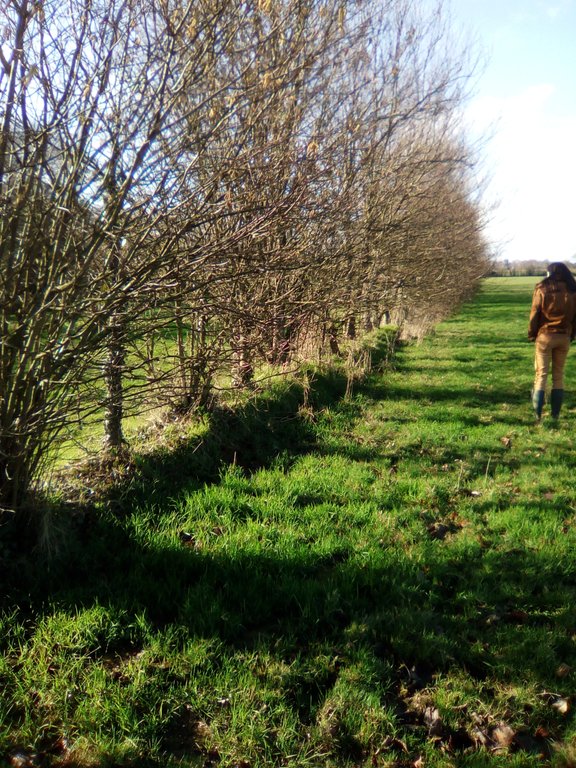
Following this evaluation of the farm, the ‘Bocage’ (small hedged pasturelands) was developed starting during the winter of 2003/2004, with the planting of 800 meters of woody features (hedges and trees) along the slopes of the talweg. Other slope plantings were carried out on the edge of the paddock in 2014/2015 (1500 meters) and 2018/2019 (1650 meters).
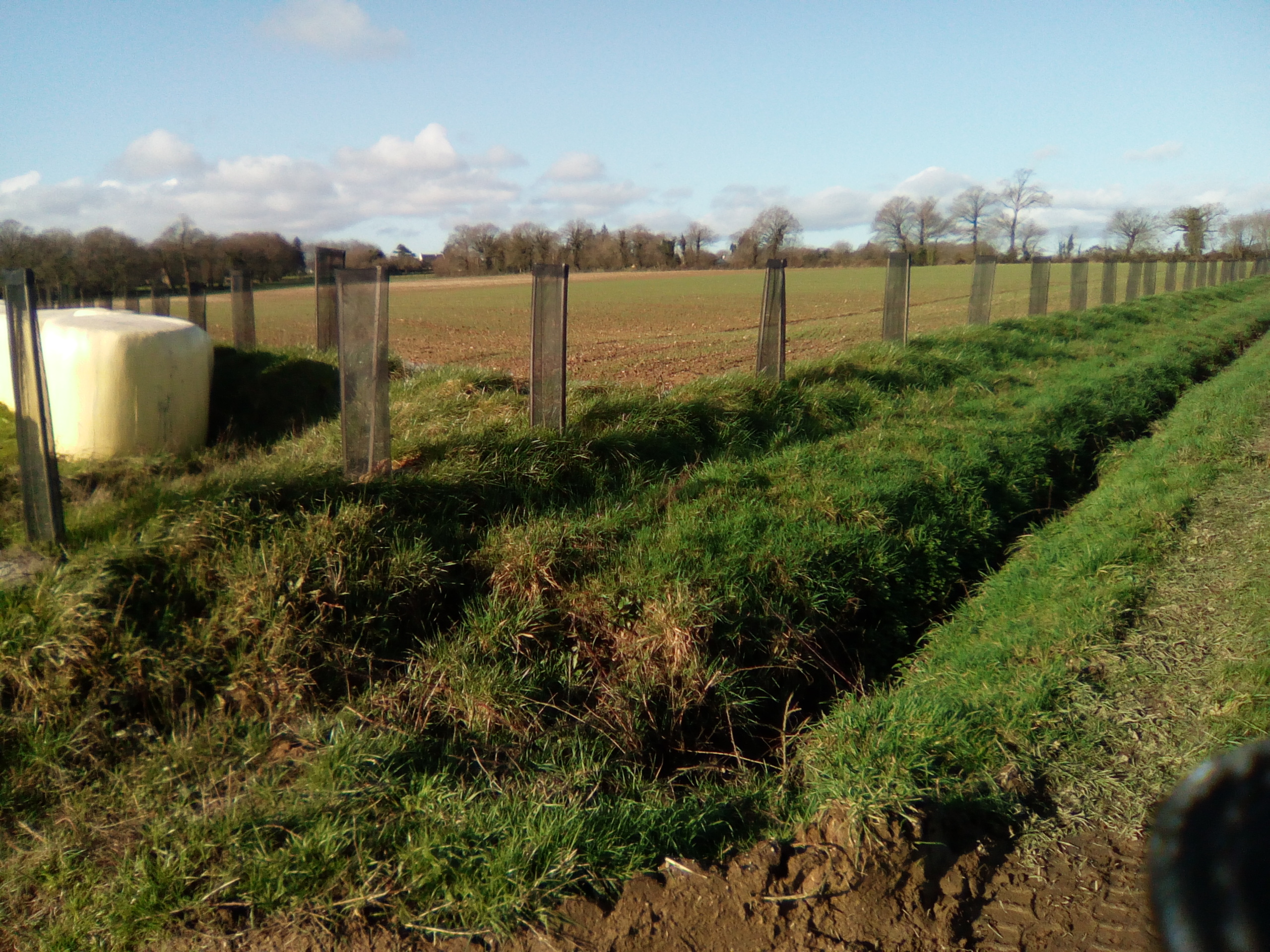
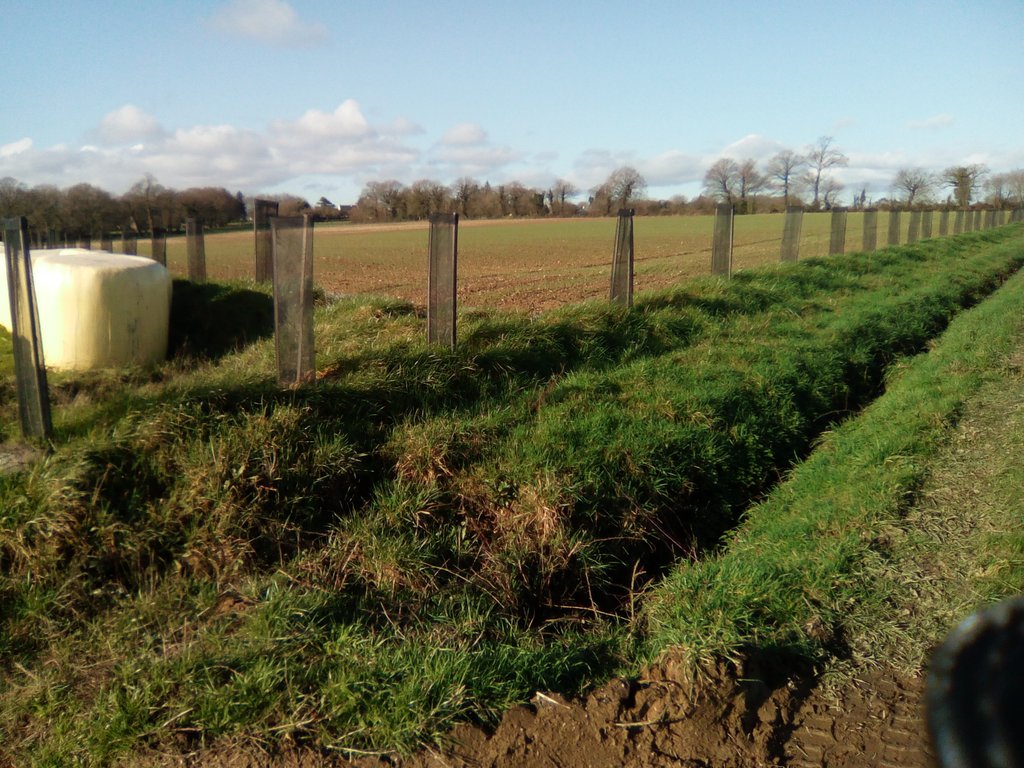
Earth bunds were established along the contour, either with a shovel (in 2003 and 2014) or with a forest plough (in November 2018), with hedge and tree whips (1-2 year old growth) planted 1 meter apart in single rows diectly into the shovel or plough furrow and a small amount of fertiliser and wire tree guards added. There was no irregation installed.
The technology was applied in three differnt phases combining to form one overall long-term plan. The tree species chosen for the hedgerow are local species (oak, beech, cherry, birch, myrobolan plum, chestnut, hazelnut, etc.). For the last two phases of the programs (2014 & 2018), emphasis was placed on the presence of melliferous species (for honey production) and the spread of flowering species (fruit trees, burdock, blood dogwood, medlar, etc.).
Buffering of fields with hedgerows aims to protect surface water quality and prevent land degradation by slowing surface water runoff and hence reducing soil erosion, nutrient and plant-protection product (pesticide) export and improving water infiltration into the soil and groundwater recharge. The reduction of soil erosion in turn improves productivity with a better surface cover and nutrient retention for improved plant establishment and growth. Additionally, maintenance and/or improvement of biodiverstiy can be attained as well as providing shelter for animals supports their well-being.
Major activities of the technology include: Tipping of trees (old and new) in spring/summer, soil preparation at the site of the future hedge in autumn and creation of the embankment (earth bund along the contour), tree planting over winter and laying of mulch and installation of game guards.
Benefits of the hedgerows/ shelter belts are reorganization and improvement of the field to reduce flooding, protect water quality , improve welfare of the livestock, Increase biodiversity of wildlife, including insects, birds and game. Additional honey bee forage supported the installation of an apiary (18 colonies) by a professional beekeeper in May 2019.
The only weakness of the technology in the eyes of the land owner was the extra cost/workload associated with the maintenance of the hedgerows.
The compilation of this SLM is a part of the European Interreg project FABulous Farmers which aims to reduce the reliance on external inputs by encouraging the use of methods and interventions that increase the farm’s Functional AgroBiodiversity (FAB). Visit www.fabulousfarmers.eu and www.nweurope.eu/Fabulous-Farmers for more information.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
França
Região/Estado/Província:
Brittany
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2003
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The farmer since 2000 has implemented various measures aimed at sustainable agriculture on the farm, and more recently (since 2018) the farm has become a 'pilot farm' in what is now the FABulous Farmers project aiming to improve biodiversity by enhancing the production system.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Hedge plantation
- wheat, corn
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Rotation of 1 year wheat, 1 year corn, 1 year fallow.

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- gado - lácteo
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Manure intentionally used to improve crop production & crop residues are fed to animals.
Produtos e serviços:
- leite
- grassland, corn silage, wheat
Espécie:
gado - lácteo
Contagem:
62
Comentários:
The hedges are planted on the periphery of the plot on embankments without interfering with the original land use.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
- S9: Abrigo para plantas e animais
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação biológica
- Bh: perda dos habitats

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
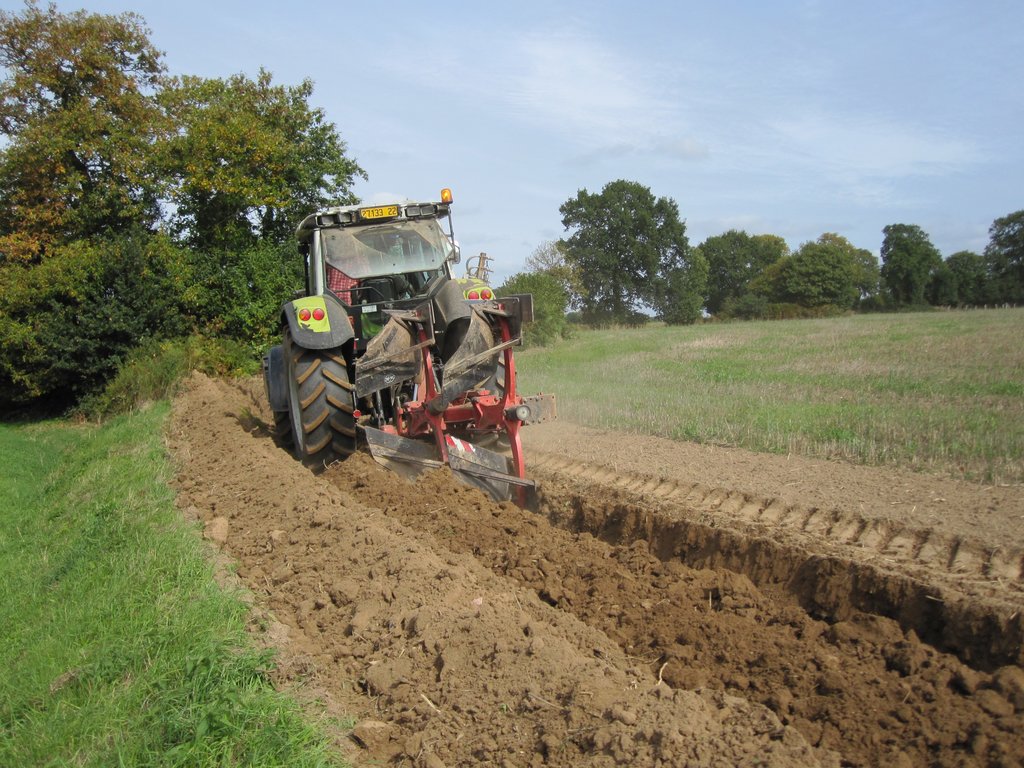
Creation of the embankment
- Use of the backhoe or excavator (2003/2004 and 2014/2015 developments)
- Earth removed from the field over a few metres wide - implementation by vertical compaction as the slope rises - shaping of the sides by slicing.
- Use of the forestry plough (2018/2019 development)
- 5 to 7 passes of the forestry plough to lift a 0.6 to 0.8 cm high ridge - bucket finishing for levelling .
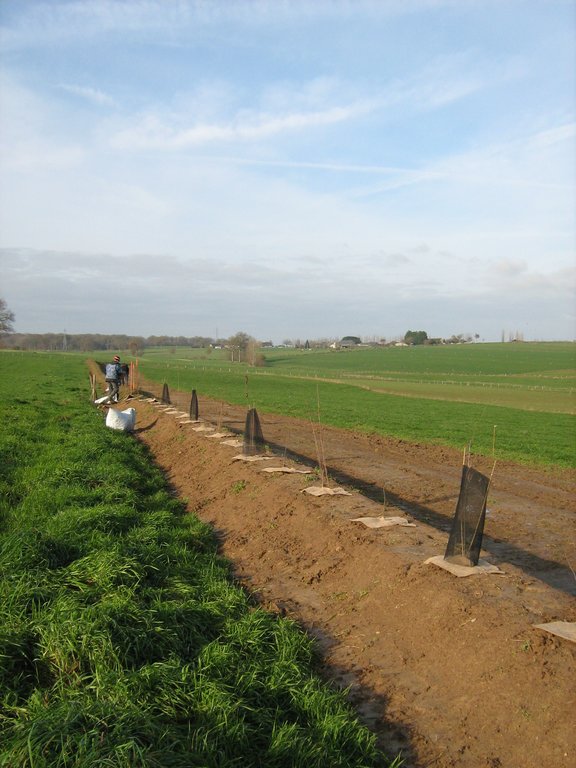
Planting
- Choose deciduous species adapted to the environmental conditions (soil, climate) and combine several species in a hedge.
- For a honey hedge (source of pollen and nectar for bees), aim to spread out the flowering with species accessible to bees (hazelnut, burdock, black elder, blood dogwood, obier viorne, country maple, small-leaved linden, cherry, chestnut, black alder, willow...).
- Install biodegradable mulch at the foot of each plant and protection against wildlife (deer, hare, rabbit).
Autor:
Isabelle Senegas
Data:
03/02/2020
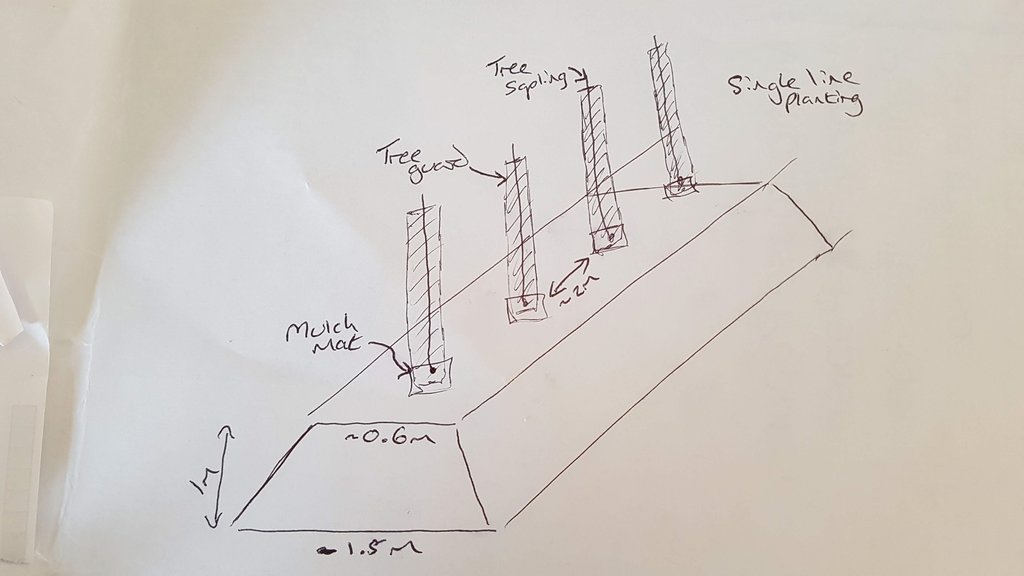
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
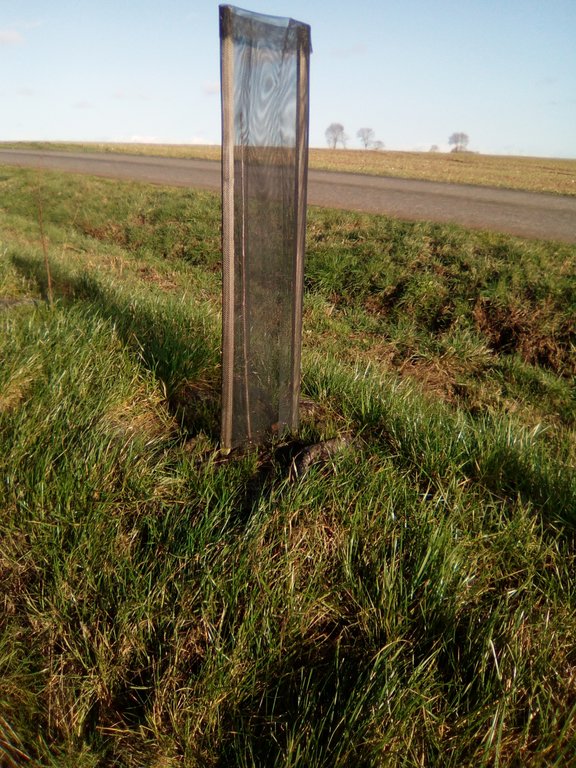
Example section of planting on embankment. Single line planting of tree saplings on top of embankment, mulch mat around foot of plant, tree guard installed.
Autor:
Alan Radbourne
Data:
12/02/2021
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
meter
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
1650
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
€
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
0,9
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
€10.15 on 1 January 2020, i.e. €1,539.42 monthly on the basis of the legal working week of 35 hours.
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tip saplings to form seedling transplants for new plants | spring-summer year 0 |
| 2. | Soil preparation at the site of the future hedge | September to October year 0 |
| 3. | Creation of the embankment using excavator or forestry plough to establish soil bunds. Vertical compaction of slopes and shaping. | September to October year 0 |
| 4. | Tree planting using several deciduous species adapted to the envionmental conditions. | December to March (year 0-1) |
| 5. | Laying of biodegradable mulch at the foot of each plant to provide nutrients and moisture retention | December to March (year 0-1) |
| 6. | Installation of game guards to protect againt wildlife (deer, hare, rabbit). | December to March (year 0-1) |
| 7. | Creation of grass strips at the foot of the slope to stabilise embankment | December to March (year 0-1) |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Tip saplings | metre | 1650,0 | 0,35 | 577,5 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Soil preparation | metre | 1650,0 | 0,8 | 1320,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Creation of the embankment & grass strips | metre | 1650,0 | 1,8 | 2970,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting, mulching & protection | metre | 1650,0 | 2,0 | 3300,0 | |
| Equipamento | Excavator / Forest plough | metre | 1650,0 | 0,5 | 825,0 | |
| Equipamento | Biodegradable mulch | metre | 1650,0 | 0,3 | 495,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tree guards | metre | 1650,0 | 0,7 | 1155,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 10642,5 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 11825,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The bocage development programme is carried out by the Great Oust basin with the following financial partners: Europe, the Loire-Brittany Water Agency, the Brittany Region, the Morbihan Department. The operator will have to pay €1 (excluding tax) per linear metre.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hedge pruning and training | Winters for 10-15 years |
| 2. | Lateral pruning of the flower part of the hedges | as required between two wood harvests (with a chainsaw) |
| 3. | Slope maintenance (brush clearing and grazing) | once a year |
| 4. | Wood harvest: re-growing of out-sticking branches (Coppice and shrubs) | 15 years after planting, then every 10-15 years |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Hedge pruning and training | meter | 1650,0 | 0,25 | 412,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Mechanical intervention: annual clearing | meter | 1650,0 | 0,35 | 577,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Thermal brushcutter for landscaping and forestry work (investment to be amortized) | meter | 1650,0 | 0,6 | 990,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Maintenance of the embankment | meter | 1650,0 | 0,15 | 247,5 | 100,0 |
| Outros | od storage, chipping, transport of chips | meter | 1650,0 | 0,25 | 412,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2640,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2933,33 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
- consistency of management
- hedge width
- Existence of outlets for wood (self-consumption, local industries, etc.)
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
700,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The farm is situated in the commune of Ploërmel in the Morbihan which lies in the early pedoclimatic zone.
The average annual rainfall is between 650-750 mm over the period 1971-2000.
The average annual temperature is around 11.5°C over the period 1971-2000.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Ploermel
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
The Ploërmel basin is the most continental of the Morbihan with colder winters, warmer summers and rainfall between 650 and 750 mm/year.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The farm is located between two talwegs. Altitudes vary between 75 and 100 m. The steepest slopes (on the southern slope) are about 6%.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
The farm is located in the commune of Ploërmel in Morbihan is in the geological zone of the Briovian Shale:
- Soil mapping unit (UCS (soil map units) n°4034): Brown soils gradually leached from the plains and plateaux from locally sandstone soft shale (including deep valley bottom soils, hydromorphic from the surface, with colluvio-alluvial or alluvial input).
- Soil mapping unit (UCS (soil map units) n°4040): Mainly well-drained and poorly leached soils of cultivated plateaus from soft shale.
Source Sols de Bretagne (http://www.sols-de-bretagne.fr/)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Medium habitat diversity due to still young age of the hedges)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
The farm covers an area of 66 ha, 60 ha of which are accessible for grazing and some of which are wet.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
diversification of production
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
remained same
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Shelter belts protection of crops
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
remained same
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
Well-being improves production
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
New output product on land
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Wood produced
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Increased labour but more sustainable water and land management
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
New machinery and labour costs associated with diversified management
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Increased output production
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Addition of woody crop output
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Increased workload with hedgerow management
Impactos socioculturais
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
quality of life
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Improved water quality in streams due to reduced surface run-off with hedgerow buffer strips
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Decreased run-off with hedgerow buffering
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Rooting system reducing flooding
Solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced soil erosion from buffered strips
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Hedgerow inceasing below ground C
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
longer cover of vegetation with hedgerows
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
hedgerows increase above ground C
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Woody crops added
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Biodiversity increases with hedgerow habitat creation
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
Bees, insects and birds as predators of pests
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Habitat creation in hedgerows
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
cultivation aids
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
Buffer strips & rooting systems improving infiltration
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
Buffer strips slowing suface water flow and soil erosion
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Buffer strips limit water loss in drought
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
buffer strips provide crop and animal shelter
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
regulation of belt slope eriosion
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced soil, nutrient and plant protection run-off polluting watercourses
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
hedges slow flow as a buffer
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
shelter and sedimant capture
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Intake from hedges
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | muito bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | bem |
| Onde de frio | moderadamente |
| Seca | moderadamente |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | moderadamente |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento alogado | não conhecido |
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
| Elevação do nível do mar | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Several Breton regional programmes that aimed at improving water quality have made it possible to support bocage developments thanks to the involvement of financial partners from 2008 to 2020, as part of the wider "Breizh Bocage" programme. The remaining amount to be paid by the operator is 1€ per linear meter in the current programme.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
economic concern of operating system
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Due to a concern the maintenence costs would outweigh the benefit return the parcels of land have been rearranged to suit a more efficient system.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Improvement and reorganisation of the plot with a reduction of wetlands. |
| Protection of the animals against bad weather and welfare of the herd. |
| Protection of water quality. |
| Increase in wildlife: insects, birds, game, etc. |
| Additional benefits of the hedges are the possibility of installing apiary (18 colonies) by a professional beekeeper in May 2019. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Hydraulic and water chemical control with combination of hedge and embankment. |
| Improvement of the landscape and the living environment favourable to the preservation of heritage and the development of tourism: hiking circuits. |
| Ecological functions with the preservation of biological diversity: "ecological corridors". |
| Economic functions with multiple outputs, such as firewood, timber, hederow crop (i.e. berries) and increased pollen source for bees |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Hedge maintenance: extra cost and workload | Delegation to a specialised company. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Time intensive upkeep (i.e. training of saplings) that maybe overlooked and thus not produce highest quality output | Outsource labour work (yet additional expense) |
| Lack of outlets for wood from hedgerows |
- self-consumption of wood: installation of plate boilers on farms, or heating networks, use of wood for animal bedding - developing territorial channels for the valorisation of wood from hedgerows |
| Need for training and support for operators | Sustainable management plan for hedges and trees on the farm, and monitoring. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
At the farm Noël Danilo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
At the farm Noël Danilo
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Breih Bocage Programme (2015-2020): diagnosis actions
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Le guide du conseiller pour accompagner des projets agroforestiers - 2020
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Agricultures & Territoires Chambre d’Agriculture APCA
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Le programme de plantations des haies dans la Manche - 2017
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture de la Manche
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Réussir une haie bocagère
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture de la Manche
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Guide pour des haies propices aux insectes entomophages - 2017
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture Pays de la Loire
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Guide pratique : produire du bois d’œuvre dans le bocage - 2015
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture d’Ille et Vilaine
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
La haie : réservoir d’énergie - 2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture de Bretagne
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Guide technique des pratiques favorables à la biodiversité en agriculture - 2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Chambre d’agriculture de l’Hérault
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Le guide du conseiller pour accompagner des projets agroforestiers - 2020
URL:
https://opera-connaissances.chambres-agriculture.fr/doc_num.php?explnum_id=152429
Título/ descrição:
Le programme de plantations des haies dans la Manche - 2017
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwi3wNP-5r_nAhXBxoUKHS0AC6AQFjAAegQIAxAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fagriculture.gouv.fr%2Ftelecharger%2F84451%3Ftoken%3D72db2767fffa8628090ba53ae5b23133&usg=AOvVaw2WekHpjyhNMwQLToNVlfxk
Título/ descrição:
Réussir une haie bocagère
URL:
https://manche.chambres-agriculture.fr/environnement/reussir-une-haie-bocagere/
Título/ descrição:
Guide pour des haies propices aux insectes entomophages - 2017
URL:
https://pays-de-la-loire.chambres-agriculture.fr/publications/publications-des-pays-de-la-loire/detail-de-la-publication/actualites/guide-pour-des-haies-propices-aux-insectes-entomophages-grandes-cultures/
Título/ descrição:
Produire du bois d’œuvre dans le bocage -2015
URL:
https://afac-agroforesteries.fr/guide-pratique-produire-du-bois-doeuvre-dans-le-bocage/
Título/ descrição:
La haie : réservoir d’énergie - 2009
URL:
https://www.bioenergie-promotion.fr/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/La-haie-réservoir-énergie-Pôle-agronomie-Bretagne-2009.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Guide technique des pratiques favorables à la biodiversité en agriculture - 2009
URL:
https://www.chasse-nature-occitanie.fr/agriculture-et-territoire/documents/Agrifaune-guide-tech-biodivers.pdf
7.4 Comentários gerais
none
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos