Hydraulic Ram Pump assisted river water lifting and application of stored water through drip irrigation for alley cropping [Paquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Hydram Pump
technologies_5740 - Paquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Maqsood Muhammad Mudassar
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Shrestha Arun Bhakta
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Raza Haider
WWF-Pakistan
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Dhakal Madhav
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Ali Ajaz
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Hassan Faizan-ul-
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Karim Fazal
WWF-Pakistan
Paquistão
Consultant:
Azeem-ullah
Azeemullah & Company Chartered Accountants
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Kundi Rehmat-ullah
GetGreen Tech
Paquistão
Especialista em GST:
Shah Ghulam Muhammad
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD)
Paquistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management for Improved Livelihood in the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan (UIB, Pakistan)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
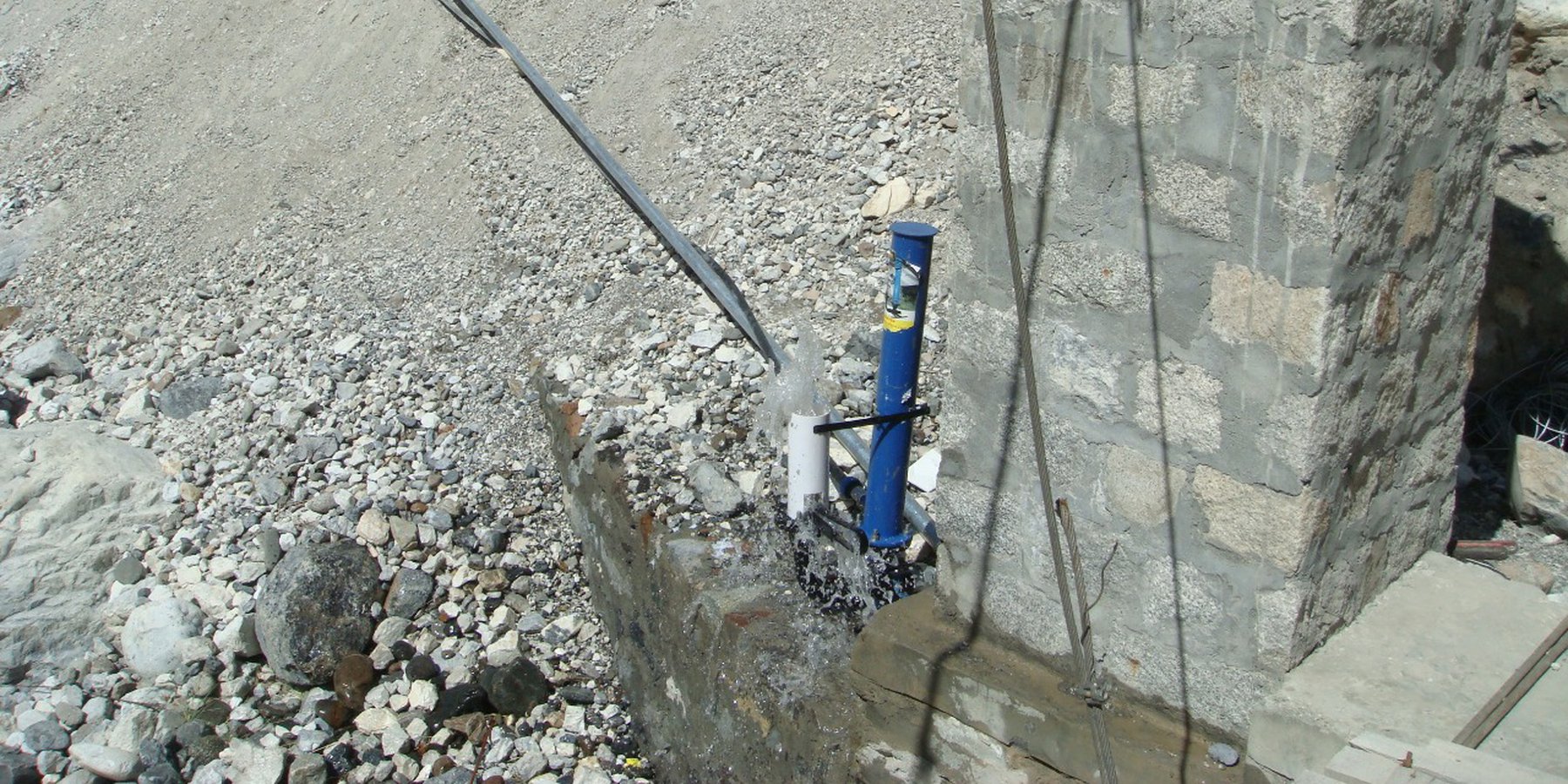
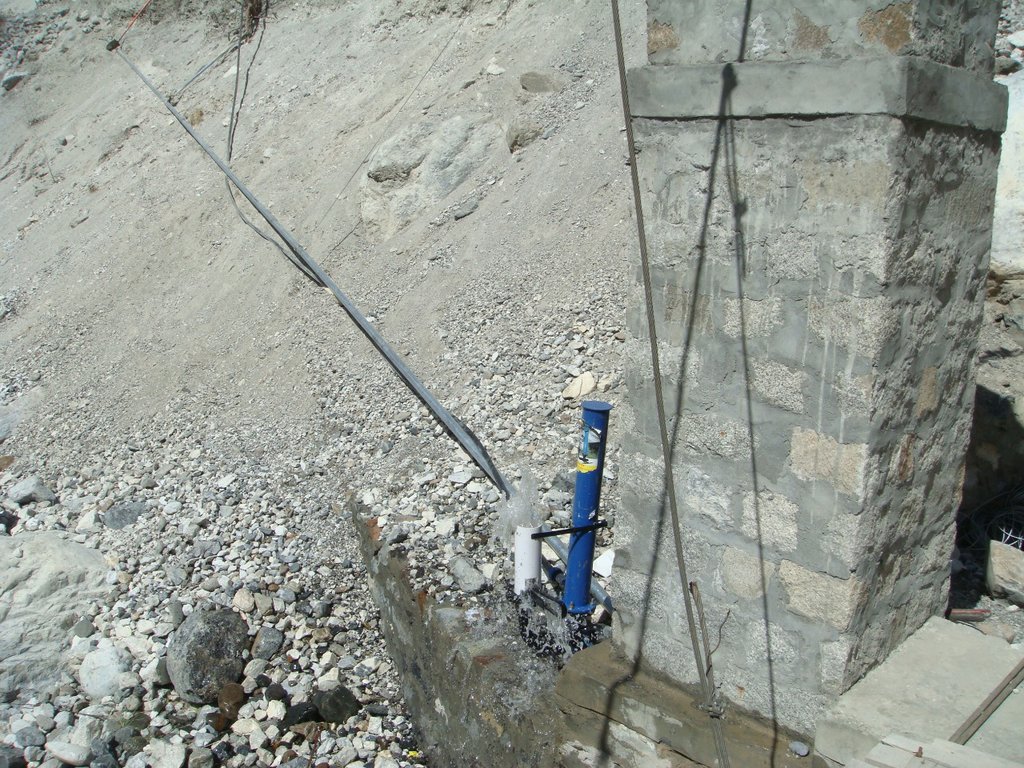
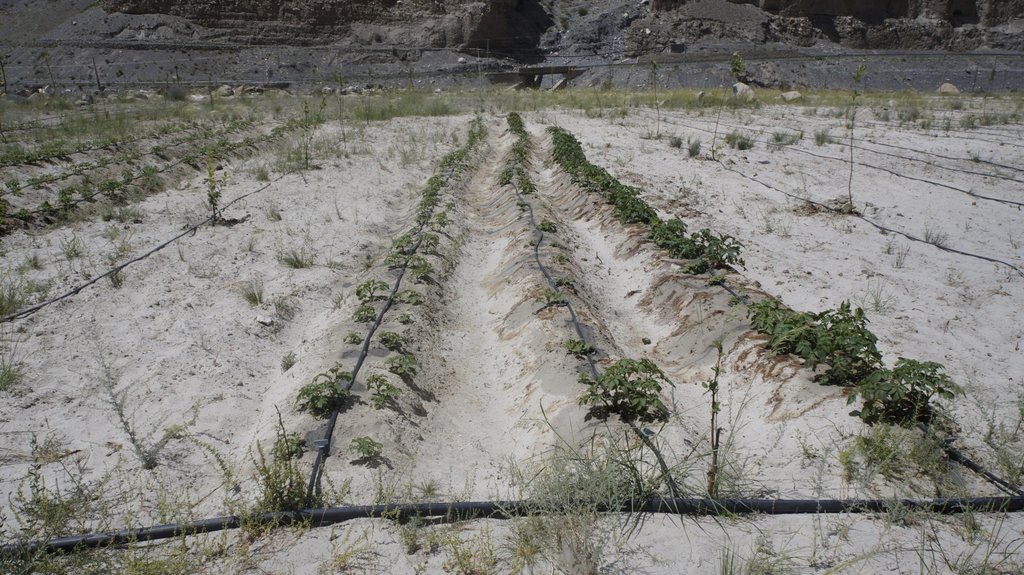
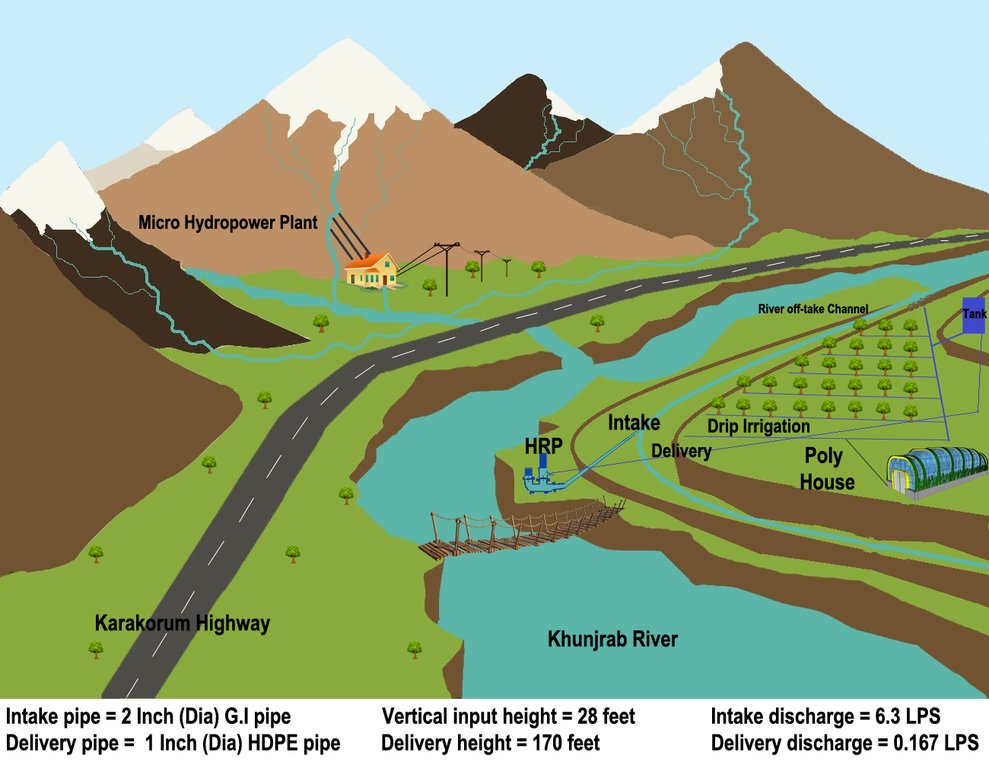
The water from a contour canal (off-taking from Khunjrab River) was lifted through hydro ram pump to uphill plastic storage and distributed to alley cropping (newly established orchard and vegetable rows) through drip irrigation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Agriculture, livestock herding and tourism are the major contributors to Gilgit Baltistan economy. The arable land in this region is limited (only 2%) and more than half of which is still barren due to unavailability of irrigation water supplies. The reported dependency of irrigated areas on glacier fed irrigation is more than 90 percent, which now have been fluctuating due to changing climate. This region has been experiencing drastic changes in climate which resulting into lowering of glacier and water related disasters leading towards discontinuity of irrigation water supplies. The electrical power energy options are limited as well as unreliable and in situ replacements are very expensive.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Khyber is located at 36.56o N latitude and 74.79o E longitude. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The population of Khyber village is 1200 residing in 150 houses. Almost 46 percent of population is salaried, 20 percent own business and roughly 19 percent engaged with farming to earn bread and butter for families. The average landholding per household is 3.8 acres out of which 1.25 acre is cultivable waste due to insufficient water supplies and local labor.
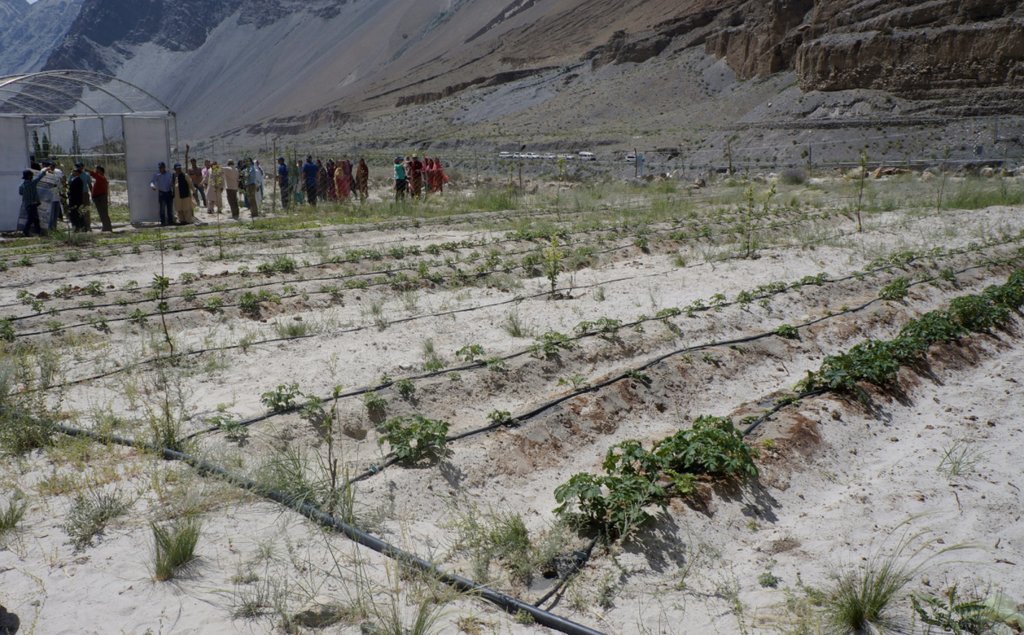
To address the above issues, the Indus Basin Initiative (IBI) of International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) through its a consortium of local partners including Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Mountain Agriculture Research Centre (MARC) and WWF-Pakistan has been demonstrating the alternative agricultural water management package of practices in lifting water for irrigation using Hydro ram pump. This study also presents the findings based on the experiment/demonstration and testing conducted in the pilot. The pilot site is located in Khyber village of Hunza, Gilgit Baltistan.
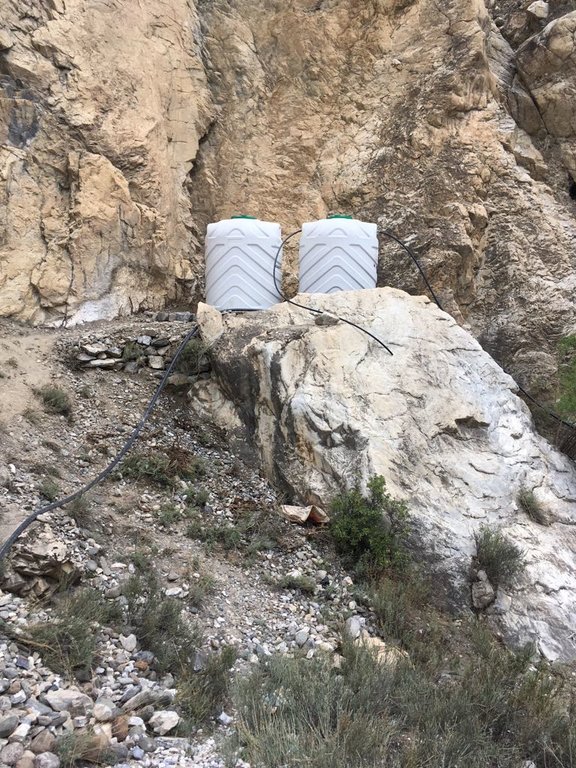
The pumping unit comprises a hydro ram pump (which is a zero carbon emission technology and needs no electricty to run, and it is locally customized having 1 inch/25mm out-take pipe) to lift water from a contour channel originating from the Khunjrab River and to carry the water to storage tanks (4000 liters) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 175 feet (53,3 m) vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was supplied to alley cropping (apple sapling rows and vegetables rows) through pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 10.2 liters/minute, which is irrigating around 350 apple plants and vegetable rows at 2.5 acre (1ha). The storage tank was kept 45 feet (13,5 m) vertical height from the orchard field. Plan to plant distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet (4,6 m) and 20 (6 m) feet respectively. Drip irrigation system was established for each apple plant, as well as vegetables rows. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they served also as water harvesting pits /check basins. Gilgit Baltistan chapter of WWF-Pakistan mobilized the local community, while PCRWR and MARC provided technical support to the Khyber Community in establishment of this pilot site. The community youth provided voluntary support during the land preparation, plantation and installation of hydro ram pump as well as drip irrigation system and the uphill storage tanks.
The cost of a complete package including hydro ram pump with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems, drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses for the site was US$ 25, 865 for 2.5 acre (1ha) of land. Women Organization of Khyber village takes care of the maintenance of technological package (fortnightly desilting of drip irrigation and storage tanks and annual repair of hydraulic ram pump). The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as soil fertility is still building up. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level. However, with higher yield in future, the total income from the farm produce (currenty vegetables only) would be divided equally among the participating 150 households of Khyber Village. A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would produce enough to the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
The community welcomed the new technology and is now planning to outscale it in other areas to bring more land under cultivation. The women organization in the pilot site are positive about the less labourous agricultural activities and foresee to extend the alley cropping under drip irrigation to the rest of 7.5 acres, too. This technology is being dessiminated to different stakeholders including practitioners, policy and decision makers, academia, researchers and local farming communities. For this purpose, exposure field visits and farmers' field days have been arranged by the implementation partners.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Paquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Gilgit Baltistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Khyber Village, Hunza District
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
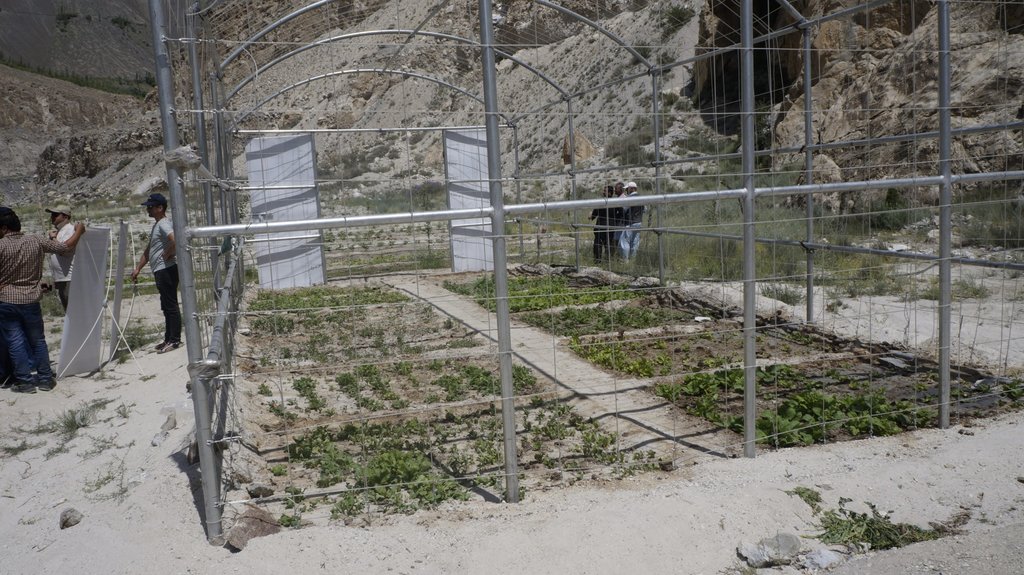
The community has protected the site with barbed wire with wooden posts.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The Indus Basin Initiative of ICIMOD, with support of Government of Australia under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio (SDIP), has been developing capacity (resilience to climate change) of vulnerable communities of Gilgit Baltistan through pioneer introduction of contextually new innovative technologies.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas, outros
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Only one crop is grown owing to the climate of this area
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
The seasonal vegetables are grown in between two successive apple orchard rows meaning Alley Cropping.
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
Barren land
Observações:
Due to unavailability of glacial-melt water, 50% of arable land in Gilgit Baltistan could never be cultivated. Before the interventions were implemented, this land was left barren.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Comentários:
River water is being lifted throuh hydro ram pump, stored in elevated storage tanks and distributed through drip irrigation
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
- Tecnologias de eficiência energética
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Damage and dysfunction of irrigation canal, due to water related disasters.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Due to water access cultivation of before barren land was possible and vegetation cover improved.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Hydro Ram Pump: Locally manufactured with pumping capacity of the pump: 10.2 litres/minute. The intake G.I pipe (2 inch/50mm diameter) of 83 feet (25 m) long is connected to water channel. The vertical difference between hydro ram pump and water channel is 28 feet (25m). The out-take HDPE pipe of (1 inch/25mm diameter) of 200 feet (61m) carries water from hydro ram pump to plastic storages. The vertical distance between hydro ram pump and plastic storage tanks is 175 feet (53 m).
The capacity of storage tank: 4000 litres, location of storage tank: 175 feet height (53m, vertical) from the river and 45 feet height (14m, vertical) from the orchard field.
Drip Irrigation: Surface and pressure compensating. The spacing of dripping points: 15 feet (4.6m). Plant to plant and row to row distance of apple 15 feet (4.6m) and 20 feet (6m) respectively.
Autor:
Muhammad Mudassar Maqsood
Data:
25/03/2020
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Technological package at pilot site covering 2.5 acre (1 ha)
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
US$ 14.5 for skilled person and US$ 7.5 for unskilled person
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site identification in consultation with the communities | March 2017 |
| 2. | Detailed feasibility surveys of the site | May 2017 |
| 3. | Implementation agreement with the community | January 2018 |
| 4. | Installation of hydro ram pump | June 2018 |
| 5. | Installation of storage (plastic tank) with a line filter attached to it for the operation of the drip system and avoid sediment entry into the tank | June 2018 |
| 6. | Digging of pits for plantation of the apple orchard | June 2018 |
| 7. | Laying of drip irrigation systems | June 2018 |
| 8. | Plantation of tubed apple (Kala Kolu variety) it is bought from the local nursery | June 2018 |
| 9. | Training to selected farmers as caretakers of the technologies for its days to day repair and maintenance | August 2018 |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Plumbing and technical workers | 1 | 1,0 | 775,0 | 775,0 | 33,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Installation charges | 1 | 1,0 | 968,0 | 968,0 | |
| Equipamento | Ram Pump & Accessories | 1 | 1,0 | 8526,0 | 8526,0 | |
| Equipamento | Drip Irrigation | 1 | 1,0 | 5813,0 | 5813,0 | |
| Equipamento | Off-seasonal vegetable tunnel | 1 | 1,0 | 4715,0 | 4715,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Apple tree saplings (lumb sum) | 1 | 1,0 | 3165,0 | 3165,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 250,0 | 0,12 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Feasibility study | 1 | 1,0 | 1873,0 | 1873,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 25865,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 25865,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
ICIMOD through fundings from Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade under Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio
Comentários:
The USD to PKR exchange rate while time of budget transfer was 1 USD=104.50 PKR
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of hydro ram pump | twice an year |
| 2. | Desiltation of plastic tanks | twice an year |
| 3. | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | once an year |
| 4. | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | once in 2 years |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2,0 | 3,75 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Desiltation of plastic tanks | 1 | 2,0 | 7,5 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Desiltation of drip irrigation system | 1 | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0,5 | 37,0 | 18,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Repair of hydro ram pump | 1 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Repair & maintenance of drip irrigation system | 1 | 0,5 | 100,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Vegetable seeds | 1 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Diammonium phosphate (DAP) | 1 | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost (250 kg) | 1 | 1,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 245,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 245,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Since the most of the material (drip irrigation etc) is imported thus cost varies with foreign currency exchange rates. Moreover, the costs are also higher in Gilgit Baltistan comparing to plains of Pakistan owning to expensive transportation.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
150,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
it varies from 150 mm to 200 mm
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Passu ghar
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Frequentemente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water is available in the river but fields are higher up than river
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
This pilot site has been handed over to women organization of Khyber village, so women are managing all agricultural activities at this site.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Comentários:
Most of the uncultivated land is communal, community decides uses of the land
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The fruit production has not yet started as it is a newly established farming site. However, seasonal vegetable farming has just started. The produce is small as the soil nutrition building is still in process. Currently, the grown vegetables are being sold or used in the village at household level.
Área de produção
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2.5 acres/1ha
Comentários/especificar:
Production area increased as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
14,688 litres per day
Comentários/especificar:
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages to previously barren land
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Automized irrigation has decreased labour
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Organic vegetables for household consumption
Impactos socioculturais
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Comentários/especificar:
Women have been allocated 10 acre arable land (pilot area) for their agricultural area. Out of this 10 acres, ICIMOD with its partners and community organization has brought 2.5 acres under cultivation.
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Soil cover improved due to vegetation
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
The intervention has introduced block orchard technology which will help to reduce the impacts of CO2 emmissions from vehicles along the China Pakistan Economic Corridor. Moreover, the water management interventions being used are also climate smart.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de neve local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de frio | bem |
| Condições de inverno extremo | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
| Inundação súbita | bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento alogado | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
A comprehensive cost benefit analysis study has been conducted. It has been envisioned that apple orchard would mature in 4 to 5 years in cold climate of Gojal. By the 6th year, the farm would enough produce the reach break-event point. The vegetable production has started now and the envisioned annual income is 15,000 PKR (almost 111 USD,, if 1 USD=135 PKR).
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
ICIMOD and its consortium of partners piloted the technology in this region at one village only in District Hunza, which was further out-scaled by WWF under UNDP project to six other districts (one site per district) and now federal government has awarded a project to Government of Gilgit Baltistan (National Programme for Enhancing Command Area of Small and Mini Dams in Barani Areas of Pakistan, Gilgit Baltistan Component) to upscale the piloted technology to all districts (atleast 5 sites per districts) which means 50 hydro ram pump cum drip irrigation models. This project will cost 2.6 million USD.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The hydro ram pump assisted river water lifting integrated with drip irrigation is the first of its kind in the upper Indus basin. The system is simple and anyone once trained can operate it. It will contribute to nearly 40% of the additional income of the Khyber Village |
| The technological package is environmentally friendly and are effective adaptation measures in the context of climate change. |
| Women are involved in agricultural activities and this intervention has provided them relief. Women are now generating seasonal income from growing seasonal and off-seasonal vegetables. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The first innovative technological package in Gilgit Baltistan that is climate-resilient as compare to traditional practices. |
| Water application through drip irrigation is very efficient as compared to flood irrigation. |
| The technological package can last more than 20 years. Maintenance cost is nominal. |
| As women are predominantly responsible for farming activities, improved water access and application through drip reduces their work-load and frees up time for other activities |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Drip irrigation and parts of solar panel may not be available locally. | A spare parts should be made available locally for immediate replacement as and when required. |
| The investment cost is high. | Explain cost-benefit analysis to aware farmers that the benefit is high in the long run. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Field visits was done several times as this was a part of the project activity. Cost benefit analysis was done in 2020.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Collaboration Strengthens Climate Resiliency of Upper Gojal Gilgit Mountain Villages in The Upper Indus Basin, CIMOD, 2017
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.icimod.org/collaboration-strengthens-climate-resiliency-of-upper-gojal-gilgit-mountain-villages-in-the-upper-indus-basin/
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Zero-carbon water pumps turn Pak barren mountains green, Syed Abu Bakar, 2020
URL:
https://www.thenews.com.pk/print/636825-zero-carbon-water-pumps-turn-pak-barren-mountains-green
7.4 Comentários gerais
The questionannaire is very comprehensive.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos