Tree windbreaks within irrigated agriculture in Central Asia [Quirguizistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Niels Thevs
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5861 - Quirguizistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Agroforestry extension [Costa Rica]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Compilador/a: Olman Quiros Madrigal
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
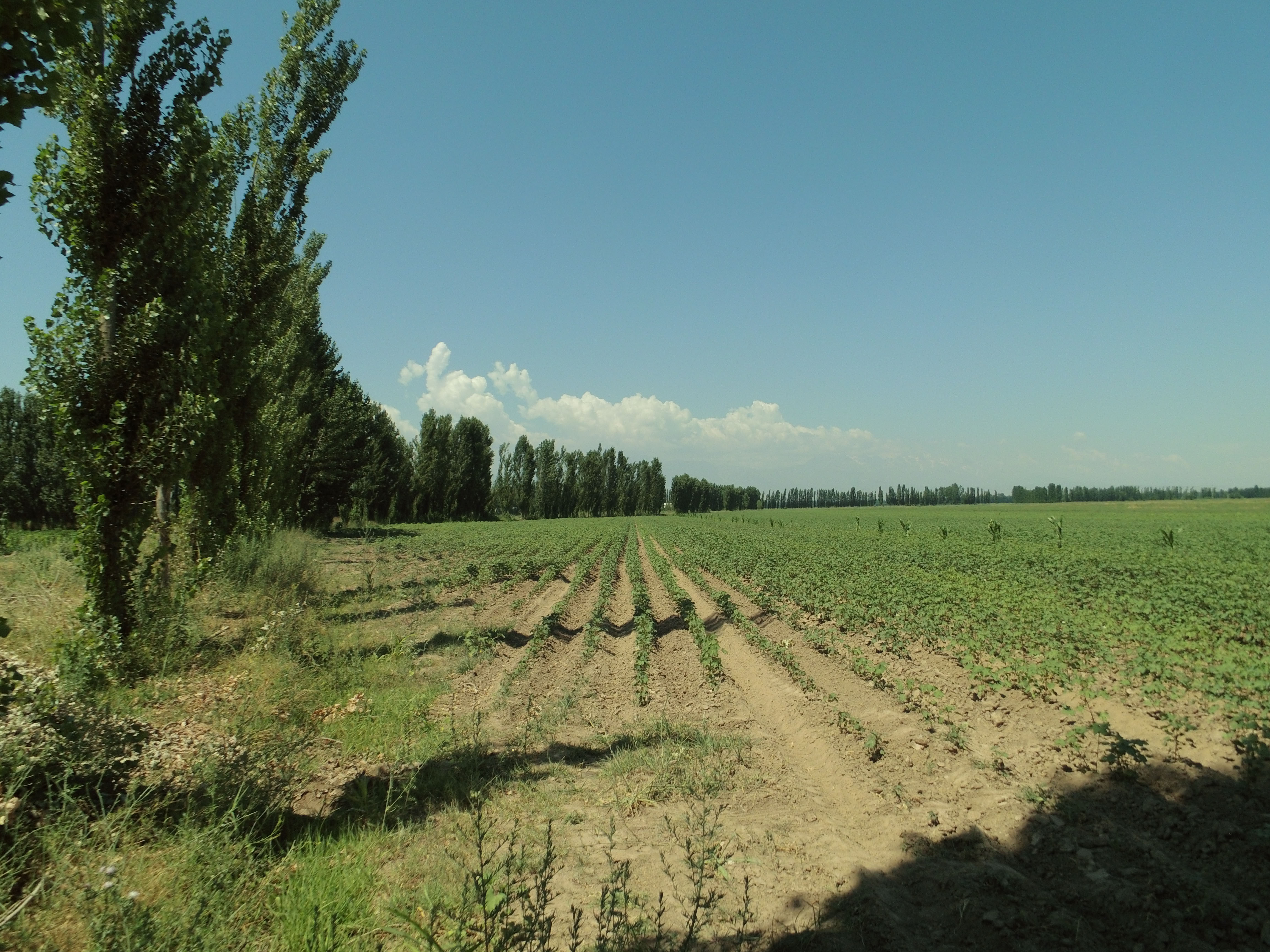
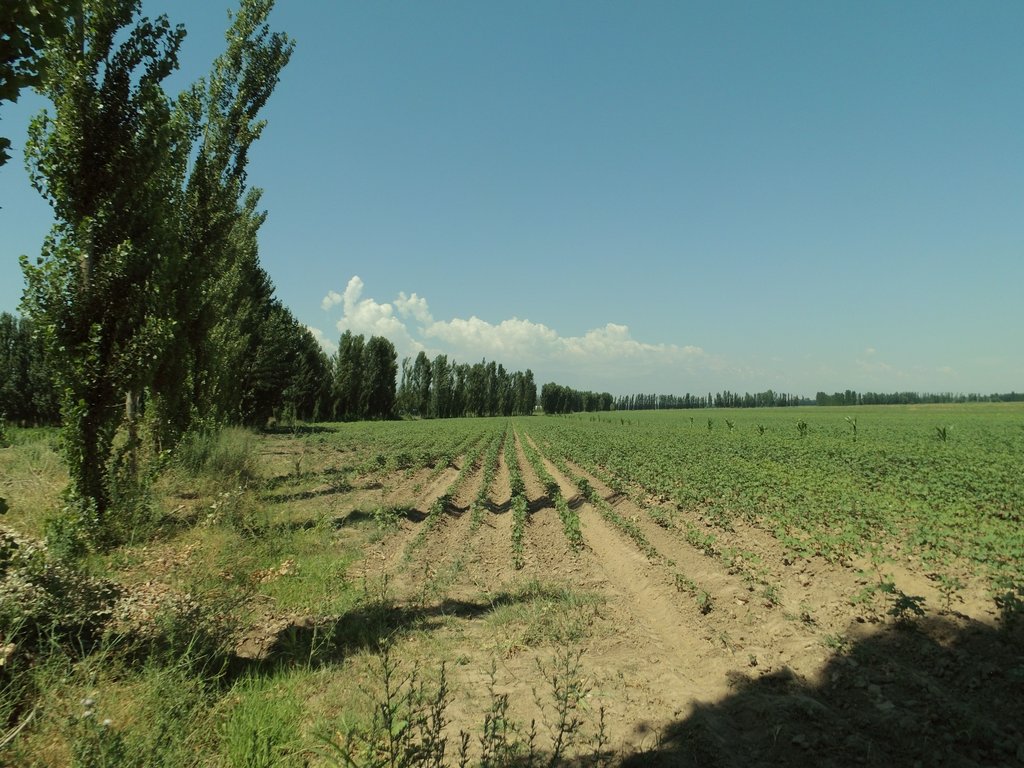
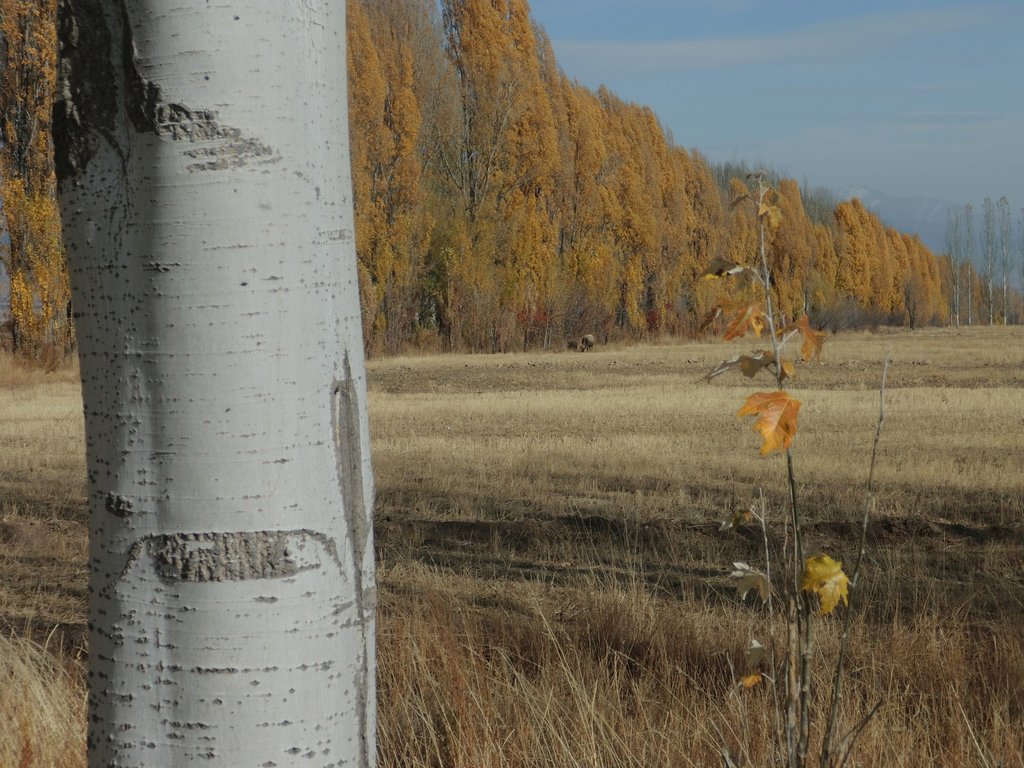
Windbreaks of poplar trees (Populus nigra pyramidalis) are a major agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture across Central Asia. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% and increase farm income by 10-15%.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
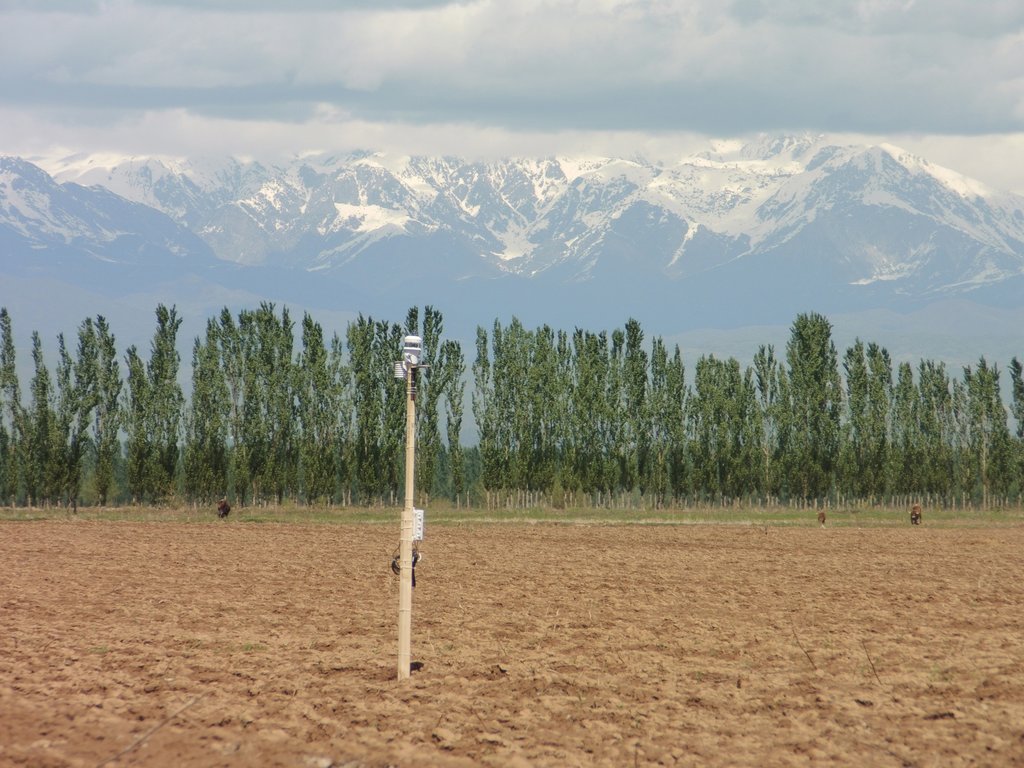
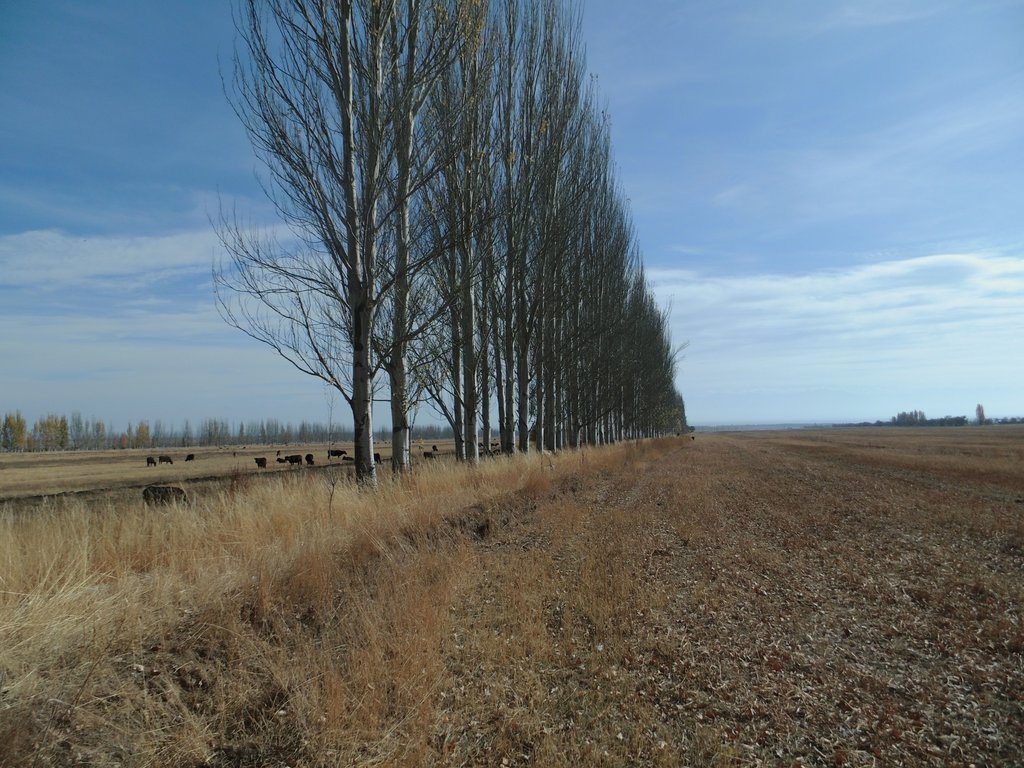
Windbreaks of trees are a major agroforestry system across Central Asia. The SLM technology presented here concentrates on windbreaks, chiefly of poplar trees (Populus nigra var. pyramidalis), within irrigated agriculture. These windbreaks of poplars have a long tradition as an agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture in the river basins of south and southeastern Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. In Kazakhstan and northern parts of Kyrgyzstan, poplars are partly replaced by Elm (Ulmus minor) windbreaks.
After those five countries had become independent, a large share of the windbreaks was cut down primarily for fuelwood and secondarily for timber, as the energy supply system had broken down in the course of the disintegration of the Soviet Union. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% compared to open field conditions, depending on crops and tree spacing (Thevs et al., 2019: doi:10.3390/land8110167). The trees serve as an additional source of income, chiefly from sustainable harvest of the trees for timber. Windbreaks also help to increase crop yields. In total, farm income is increased by 10-15% over the rotation period of the trees (Thevs and Aliev, 2021: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7). The rotation period of poplars is between 12 and 20 years, depending on the climatic conditions, e.g. poplars in the Ferghana Valles reach DBH (diametre at breast height) values of 22-27 cm and tree heights of 18 m after 13 years.
In this recent assessment, it was found that windbreaks of single tree rows with distances between trees of 1 m had the best effects on water saving and increasing farm income. The most suitable spacing between windbreaks was found to be around 200 m.
Windbreaks are perceived differently by land users depending on the region and knowledge (Ruppert et al., 2020: doi:10.3390/su12031093). For example, land users in the Ferghana Valley perceived windbreaks positively and were planting them primarily with the aim to have wood resources in the near future. In contrast, land users in the northern part of Kyrgyzstan were afraid firstly that windbreaks shaded their crops, consumed space, and competed for water and nutrients, and secondly that planting windbreaks may cause conflicts with neighbours due to those negative connotations. Farmers with larger field plots were more open towards them.
Windbreaks are planted with 2-year-old poplar saplings, which are locally available. The preferred place to plant is along irrigation ditches or other existing field boundaries. If windbreaks are planted along irrigation ditches, they simply tap water from the moist soil or elevated groundwater adjacent to those ditches. Otherwise, the trees need to be irrigated like the crops. As furrow irrigation is the dominant irrigation practice throughout Central Asia, poplars can be integrated without further adjustments in the field of irrigation. Alongside irrigation ditches poplars can withstand high water levels in those ditches as they occur during irrigation periods. If farmers switch to drip irrigation, and irrigation ditches are no longer present, the trees will need to be supplied with a dripline as well. The locally available poplar cultivars do not need additional fertilizer, but profit from the fertilizer applied to the crop. Only if high yielding modern cultivars were to be used, additional fertilizer application to the trees would be needed to unfold their full potential.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
Video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
This video provides a concise introduction into tree wind breaks, including their advantages with regards to water consumption, building resiliance against climate change, and income.
Data:
01/09/2019
Localização:
Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan
Nome do cinegrafista:
Gino Carlo Garcia
Comentários, breve descrição:
This video on Youtube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iv0VdPqBT9o, is part of a series on poplars. This part focusses on tree wind breaks with many statements of local acteurs. The other parts of this series introduce high yielding poplar cultivars and their options in agroforestry, woodlints, and value chains.
Data:
01/02/2020
Localização:
Kyrgyzstan
Nome do cinegrafista:
Lea Gerster and Stefanie Breunlich
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quirguizistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Jalalabad Region, Chui Region, and Issyk Kul Region
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
Windbreaks are spread over large areas, but the spatial distribution can be described as pockets of between 10 and 1000 ha. Within those pockets, tree wind breaks are sometimes interrupted. Also outside those pockets with more or less contiguous windbreaks systems there are remnants of those systems.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - milho
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- culturas de fibras - algodão
- culturas forrageiras - alfalfa
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- Poplars
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Comentários:
As the spatial distribution stretches over large parts of Central Asia, some locations where windbreaks are planted are rainfed and irrigated, but most parts need full irrigation.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários:
The main effect of windbreaks in the assessed areas is mainly reducing water consumption, and less wind erosion. Poplars could help to lower groundwater levels and thus contribute to combat salinization. But that did not play a role in the areas specifically assessed.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
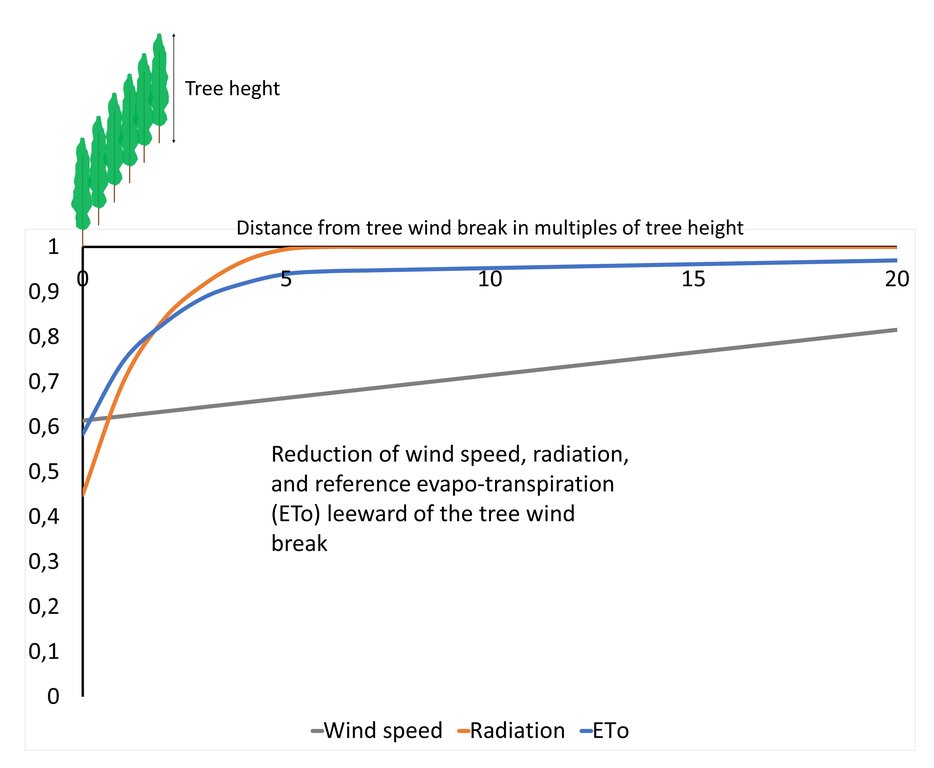
Windbreaks have their greatest impact when planted perpendicular to the main wind direction (or direction of the strongest winds). A whole grid of tree wind breaks running along all field plot borders will have a greater effect, as it prevents enhanced winds through a tunnel effect under changing wind directions. Tree wind breaks can be planted with distances of 50 m to 1000 m away from each other. The effect on the micro climate becomes less pronounced with increasing distance from tree wind breaks. Therefore, on a large field plot, say of 1000 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate averaged over the field plot will not differ much from the conditions without tree wind breaks. In contrast, on smaller field plots, say of 100 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate will differ significantly from open field conditions. This is also explained by the lines for temperature, air humidity, radiation, and in particular wind speed along an increasing distance from a given windbreak. Thereby, the distance from the windbreak is given in multiples of tree height.
In total, the best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption come with a spacing of 200 m between tree wind breaks.
The best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption were achieved with single tree lines. So, only one line of poplar trees is planted along the field borders. The planting distance between trees is 1 m to 1.20 m.
Poplar trees are locally available as trees with a length of 2 m to 2.50 m. Those trees are planted, best along the small irrigation ditches that run along the field borders. The local cultivar which is mainly used is a Populus nigra var. pyramidalis cultivar under the local name Mirza Terek. In principle, modern high yielding cultivars can be used as well; first research has shown a 2-3 times faster growth compared to the locally available cultivars at similar water and nutrient requirements.
Autor:
Niels Thevs
Data:
25/03/2021
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1 ha
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
KGS
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
68,87
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
750
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | March (first year) |
| 2. | Maintenance of trees | April to September (first and second year) |
| 3. | Harvest of trees | December to February (last year of tree rotation - after 15 years) |
Comentários:
These entries refer to a windbreak system of poplars to be harvested at tree age of 15 years combined with cotton. Thereby, the activities related to trees, including the harvest, are considered as activities to establish windbreaks into an agrarian landscape where irrigated agriculture is ongoing. The annual crop related activities are therefore listed under maintenance. If cotton is rotated with corn or rice, the timing of the crop-related activities is similar.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labor costs for tree planting and maintenance (first year) | man-days | 3,0 | 750,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labor costs for tree maintenance (second year) | man-days | 3,0 | 650,0 | 1950,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Labor costs to harvest trees (at tree age 15 years) | man-days | 3,0 | 70,0 | 210,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Poplar saplings | sapling | 116,0 | 20,0 | 2320,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Transport of saplings | 500,0 | 1,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 7230,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 104,98 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs had been retrieved for the year 2017. Costs that appear in the second year and later were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5% based on costs as of 2017.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation and sowing of annual crop (cotton) | March to April / every year |
| 2. | Irrigation, fertilizer application and other farm operations for the crop | April to August / every year |
| 3. | Harvest of the crop (cotton) | September to October / every year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labor costs for soil preparation | man-days | 6,81 | 750,0 | 5107,5 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labor costs for sowing | man-days | 2,5 | 750,0 | 1875,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Labor costs for irrigation | man-days | 23,64 | 750,0 | 17730,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Labor costs to apply fertilizer and plant protection | man-days | 3,34 | 750,0 | 2505,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Labor costs for harvest (cotton) | man-days | 32,78 | 554,0 | 18160,12 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine costs (rent) for soil preparation | ha | 1,0 | 10021,0 | 10021,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine costs (rent) for sowing | ha | 1,0 | 1316,0 | 1316,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine costs for fertilizer application | ha | 1,0 | 1200,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | kg | 50,0 | 101,0 | 5050,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 375,0 | 19,25 | 7218,75 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Plant protection | ha | 1,0 | 1517,0 | 1517,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Water fee | ha | 1,0 | 1014,0 | 1014,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 72714,37 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 1055,82 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour costs are the largest single cost item. In fact, in the cotton system a lot of labour is unpaid family labour or mutual help among neighbours. All labour was calculated in monetary terms, as the share of unpaid labour differed much between farms. This cotton tree wind break system is wide spread in the south of Kyrgyzstan. In the north of the country, tree wind breaks are combined with wheat, barley, corn, or alfalfa (lucerne). There, labour costs are lower as more machines are used (e.g. for harvest).
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Precipitation maximum during spring and dry summers, which makes irrigation necessary.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Bazarkorgon, Kara Balta, Kemin
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
hot continental and semi-arid
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Tree windbreaks can be applied in a wide range of topographical situations. Though this particular entry focusses on windbreaks in irrigated agriculture so that the whole SLM technique, i.e. trees and crops, is distributed on flat land. As irrigation is tied to rivers as water sources, this SLM technique is distributed on river plains.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Tree windbreaks per se are not limited to specific soil types. In the region considered here, the soils that are irrigated and therefore are sites for this SLM technique were mostly formed by riparian deposits. Those soils silty to loamy. On most of those areas, where irrigation takes place, soils are classified as Fluvisols. On few areas, the soils are classified as Gleysols.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Soil salinization and waterlogging do not play a role on the sites from where the information was collected for this introduction here. Though in parts of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, where this windbreak SLM technology is being applied and can be expanded as well, salinization and water logging do play a role.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
In Kyrgyzstan, the land users operate as households and can decide on their crops. Though, planting tree windbreaks does take place in agreement with neighbours. In Uzbekistan, where windbreaks are used as well, the freedom of farmers to chose their crops is limited, while tree windbreak planting partly follows governmental orders. In both countries as well as Tajikistan, labour migration is important for most rural families and remittances comprise a substantial share of the household income (off-farm income).
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
There is agreement in the scientific literature that tree windbreaks cause crop yield increases of 10-15%. Some references even claim crop yield increases of up to 40%.
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
The leaves of the trees are partly used as fodder. But that additional fodder only is a minor contribution to the overall fodder demand.
Produção de madeira
Quantidade anterior à GST:
none
Quantidade posterior à GST:
53 m³/ha after 15 years
Comentários/especificar:
Trees are harvested at an age of 15 years. Such trees have an average tree height and DBH of 19 m and 27 cm, respectively. Given a form factor of 0.42 one tree yields a stem volume of 0.457 m³. A number of 116 trees is assigned to 1 ha, which results in 53 m³/ha.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1 ha cropland
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0.9 ha cropland
Comentários/especificar:
Tree wind breaks occupy space so that the area available to the crop gets reduced. While the trees do not occupy substantial space during their first years of growth, they occupy about 10% of the cropland at and age of 10-15 years. This calculation was made for a spacing between tree wind breaks of 200 m.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Tree windbreaks at a spacing of 200 m do not impede farm operations, while narrower spacing may disturb farm operations, in particular with machines.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
904 mm over the cropping season
Quantidade posterior à GST:
777 mm over the cropping season
Comentários/especificar:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree windbreaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment below under evaporation)
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
There are expenses for tree planting material and labour associated to tree planting and maintenance during the first and second year.
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 214,000 KSG/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 232,000 KSG/ha
Comentários/especificar:
The accumulated NPV over 15 years for cotton versus cotton and tree wind breaks were compared to assess the financial gain from tree wind break systems. 15 years is the tree age at which the tree wind breaks are harvested. Costs and revenues were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5%.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Wood resources are added as additional income next to crops.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
904 mm over the cropping season
Quantidade posterior à GST:
777 mm over the cropping season
Comentários/especificar:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree win breaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment above under irrigation water demand)
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
As tree wind breaks reduce evapotranspiration, they help to maintain soil moisture.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Wind erosion did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia stronger winds prevail than in this very example. There, tree wind breaks do combat wind erosion.
Salinidade
Comentários/especificar:
Salinity did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia salinity does play a role. There, windbreaks, in particular poplar trees, help to lower the groundwater levels due to their high water consumption, which helps to combat soil salinization.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The leaves of the trees partly end up as litter on the soil surface. The trees' root systems add to the below ground biomass. Both contribute to the formation of soil organic matter. Though, this is limited to a small area adjacent to the tree wind breaks and does not translate into the area of the cropland.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
As the evapotranspiration (water consumption) and the demand for irrigation water are reduced, the general availability of water is increased.
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
Neighboring fields are partly shaded.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Glacier retreat which will result in reduced river flows and supply of water for irrigation |
Comentários:
There are two major effects of climate change on the region Central Asia: 1. Glacier retreat through rising temperatures and 2. increasing rainfall during winter and partly reduced snow. Currently, the melting glaciers cause elevated river flows so that there is more water available for irrigation. But, once the glaciers have reached a new equilibrium with smaller glacier volumes, they will deliver less water so that river flows are expected to drop during the second half of this century. Then, the supply of water for irrigation will become constrained. Tree windbreaks are one option to adapt to those conditions in the future.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
During the Soviet Union times, when tree windbreaks were promoted, multi-row tree windbreaks were planted. Today, farmers prefer single tree lines, in order not to sacrifice too much crop space.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks deliver wood resources for self consumption or to be sold on markets. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks provide additional income as they deliver wood resources. |
| Tree windbreaks reduce overall water consumption in irrigated agriculture. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Tree windbreaks shade the crop. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks compete with the crops for nutrients and water. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks disturb farm operations. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks cause conflict with neighbours, as neighbours may share those negative perceptions. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect and promote cooperation between neighbors to share benefits from tree wind breaks. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Financial resources are needed to establish tree windbreaks, while the revenue from the harvest of trees only can be realized in the future. | Access to suitable finance. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Regular field visits (every 14 days) on three sites to collect climate, crop, and tree data to, among others, calculate crop and tree water consumption.
Field visit to two additional sites to collect data on tree growth.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
62 household interviews to collect agro-economic numbers on crops and trees.
15 household interviews with wood traders and wood processors to collect information on markets and prices of wood from tree wind breaks.
80 semi-structured interviews on perception of tree wind breaks by farmers.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
compilation of literature on tree windbreaks, from Soviet Union and recent international literature.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/07/2017
Comentários:
July 2017 was the most busy time to collect the interviews on agro-economy and wood markets. The interviews on farmers' perceptions of tree windbreaks were collected during September and October 2018. Crop and tree data (growth, water consumption) were collected during 2017 and 2018.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K (2021): Agro-economy of tree windbreak systems in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia. Agroforestry Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Agroforestry Systems, EUR 37.40
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Ruppert D, Welp M, Spies M, Thevs N (2020): Farmers’ perceptions of tree shelterbelts on agricultural land in rural Kyrgyzstan. Sustainability 12:1093. doi:10.3390/su12031093
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/3/1093 - open access
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Thevs N, Gombert AJ, Strenge E, Lleshi R, Aliev K, Emileva B (2019): Tree wind breaks in Central Asia and their effects on agricultural water consumption. Land, 8: 167-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8110167
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/8/11/167 - open access
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Strenge E, Thevs N, Aliev K, Eraaliev M, Lang P, Baibagysov A (2018): Water consumption of Populus alba trees in tree shelterbelt systems in Central Asia. Central Asian Journal for Water Resources 4, 48-62
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.water-ca.org/api/v1/articles/5955-water-consumption-of-populus-alba-trees-in-tree-shelterbelt-systems-in-central-asia.pdf - open access
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K, Lleshi R (accepted): Water Productivity of Tree Wind Break Agroforestry Systems in Irrigated Agriculture – an example from Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan. Trees, Forests, and People
Disponível de onde? Custos?
will be open access
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
UNECE (2019): Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia – Challenges and Opportunities. Background paper for the Ministerial Roundtable on Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia (21-22 June 2018, Astana, Kazakhstan)
URL:
http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/timber/publications/DP-72-flr-cca-en.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Agroforestry and Central Asia
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
7.4 Comentários gerais
The questionaire guides the compiler through a number of questions through often standardized questions (ticking boxes). This is very helpful to avoid, possibly lengthy and not too concise descriptions. But with regard to agroforestry it should be made more clear where and how to address the trees.
In total it needs time to go through and fill in all sections, which surely is owed to the wish and need to collect information for a comprehensive description of each SLM technology. But, towards the end of projects, which have developed such technologies, the workload might be too high so that the entry into WOCAT is neglected. I guess one only can appeal to the motivation of projects or offer some sort of support for NGOs or so in need, but with very good SLM technologies to offer.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Agroforestry extension [Costa Rica]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Compilador/a: Olman Quiros Madrigal
Módulos
Não há módulos