Livestock Urine Collection and Use [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Kidist Yilma, Julia Doldt, Noel Templer
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Yeshint Madaberya
technologies_6623 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Shone Wachara
Farmer
Etiópia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology replaces the chemical fertilizer, urea, to restore soil fertility and improve vegetative growth and crop production. Also, it serves as a pesticide to manage insect pests.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [Etiópia]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [Etiópia]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- Compilador/a: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Collection of livestock urine allows resource-poor farmers to capture nutrient-rich livestock waste and use it to substitute urea fertilizer. It is a liquid organic product that restores soil fertility and pest management.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
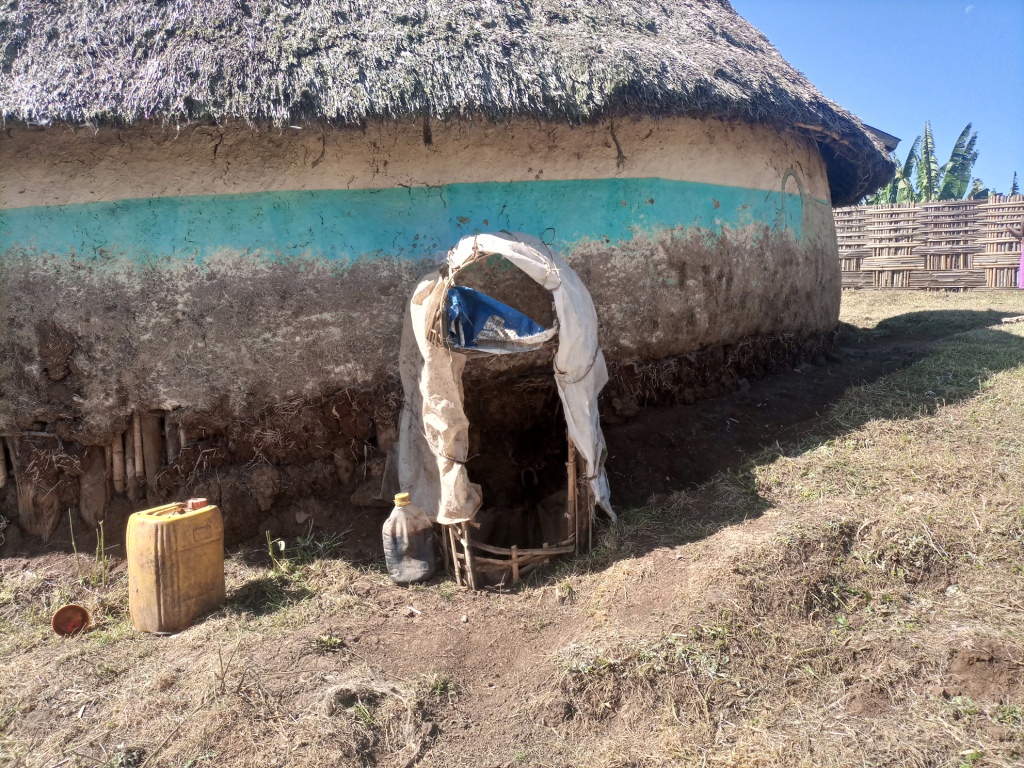
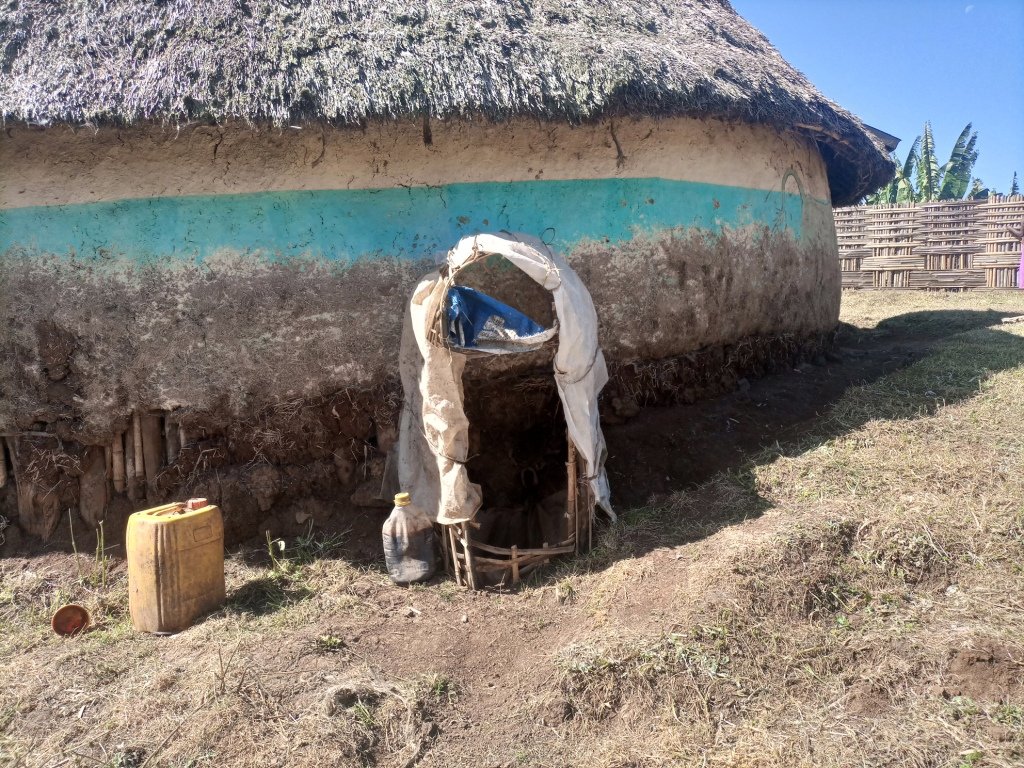
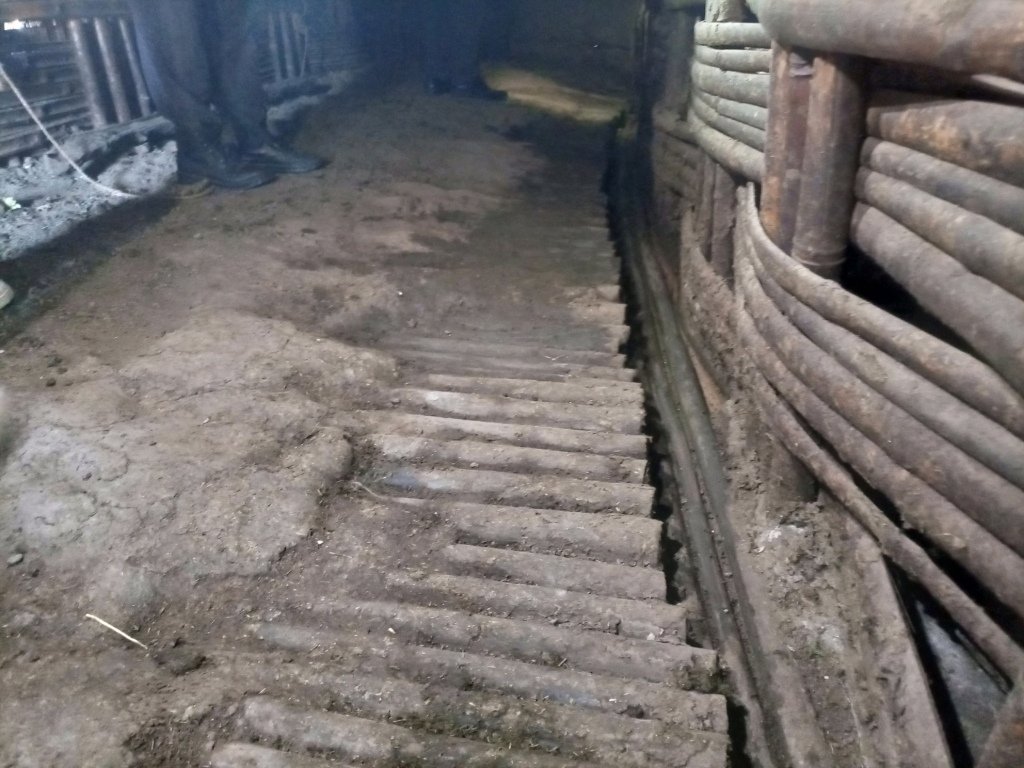
Enset, the “false banana”, is a perennial that grows well under the supply of organic fertilizers (farmyard manure, urine, compost and other household refuse). In the enset farming system, farmers traditionally shelter their livestock behind a partition within the main house. They construct a sloping floor in the livestock stall to allow the urine to drain into a narrow channel that leads to nearby enset and vegetable plots. However, construction of a collection chamber on the outlet side is an innovative approach which allows for better use of the urine. The collected urine fertilizes annual crops such as barley, maize, and vegetables - notably kale, carrots, and onions, via foliar and basal applications. Land users collect and preserve the urine for about 15 days before applying it to the target crops for the intended purposes. The urine is also used for pest management such as aphids and cutworms. According to the land user interviewed about 20 litres a day can be collected from six cattle. This implies the potential to collect about 7 cubic metres a year by a farmer: a considerable resource that should not be lost when there is an urgent need to restore soil fertility given ongoing and severe problems with land degradation. Therefore, urine collection and storage can be a way of reducing substantial investment in chemical fertilizers. To learn and showcase the benefits of urine as a replacement for urea fertilizer, a farmer sprayed 80 litres of urine twice onto 600 m2 of a ISFM+ barley demonstration plot. The sprayed amount replaced the equivalent of 6 kg urea that currently costs about 300 ETB.
Housing animals enables the collection of a reasonable quantity of urine to restore the soil fertility at the homestead and on the farm. Locally available bamboo helps to construct partitions and stall floors for the livestock as well as serving as a pipeline to drain the urine into a collection chamber. The benefits of applying urine goes beyond simply urea replacement, and its potential is merely limited by land users knowledge, skills, and motivation. These can be acquired via training, demonstration, exchange visit, and social learning. Land users like the role of urine in restoring soil fertility and boosting production. Furthermore, urine serves as integrated pest management via targeted application, deterring insects. However, the smell of the urine is unpleasant and may deter farmers from its use as they do not have safety clothes or masks to use when spraying the crop.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The photo portrays the floor orientation and the livestock partition/ stall drainage canal that leads urine to the collection chamber outside the house.
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Sidama
Especificação adicional de localização:
Tuticha Kebele 01
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2022
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Purely collecting and using urine for target application to the crop as a replacement for urea fertilizer was introduced by ISFM+ of the GIZ. However, land users used to drain slurry of manure and urine from livestock stall to the nearby enset farm. Land users forge spraying vessels and collection pits lined with plastic materials and temporary shade to urine collection points.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- culturas forrageiras - gramíneas
- legumes e leguminosas - ervilhas
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
- False banana (enset)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain).
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Cereals, like barley, rotate with legumes (such as field peas or faba beans).
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Bimodal rainfall is received twice yearly (short rain Mid-February to Mid-April, and prolonged rain from June to September).
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Crop protection: it plays the role of Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The nitrogen in urine stimulates the growth of various crops and non-crop wild species and restores degraded and potentially degradable lands.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
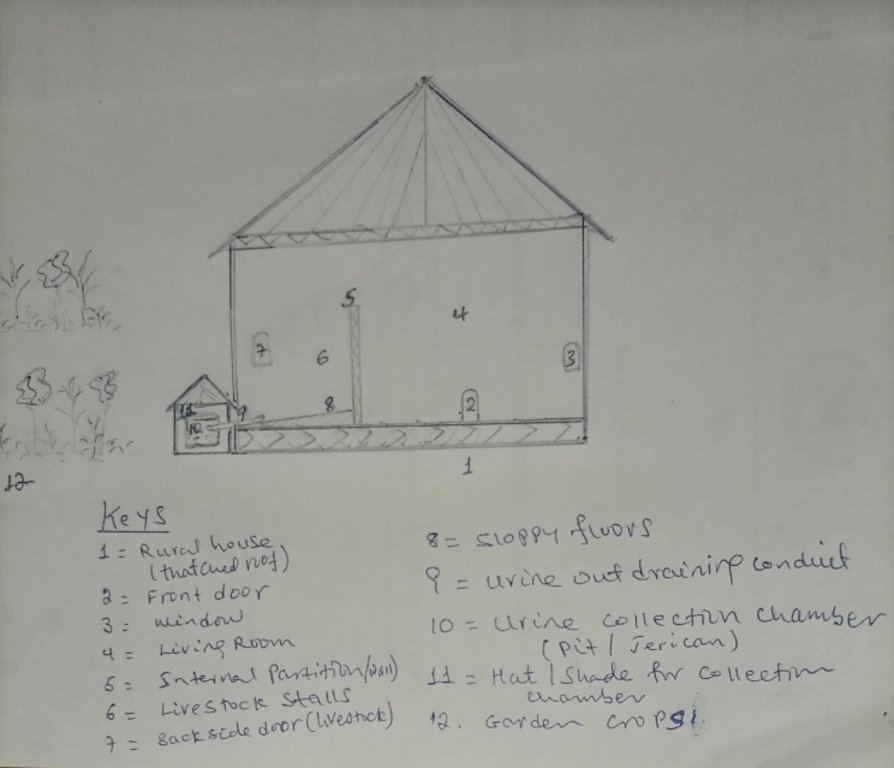
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The urine collection chamber is set up adjacent to the rural house on the side of livestock stalls. It receives urine that drains out of the sloping floor intentionally constructed using stone or bamboo to drain the liquid wastes through conduit directly to the collection chambers. A ditch that is placed adjacent to the outlet also takes the slurry to the nearby farm/garden. The dimension of the collection chamber and the types of materials used to establish the technology varies depending on resource availability or the number of livestock held by the land user. Other materials such as concrete pits or pits lined by google membranes can be used. Furthermore, jerrican or clay pots are the other alternative tools to collect urine. The different local materials replace the use of expensive materials. Small protective caps over the chamber is recommendable to protect the collected urine from rain and the heat of the sun that triggers the volatilization loss of urea. It is also possible to note additional information from the associated keys to describe the sketch.
Autor:
Gerba Leta
Data:
30/03/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
ETB
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
53,6283
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
500
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct collection chamber | Dry season |
| 2. | Construct hats or covering lid for the chamber/collection pit | Dry season |
| 3. | Lining drainage line heading to the pit with concrete | Dry season |
| 4. | Storage vessels/barrel | Anytime |
| 5. | Supplying safety clothes (wear, boots, gloves and mask) | In advance |
Comentários:
Urine collection chambers, lids or roofs, storage vessels, safety wears, and spraying tools are essential for collecting, storing, and further treating urine before use.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Casual labor | no. | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Carpentering | no. | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipamento | Safety wears (shirt & trousers, gloves, mask, boots) | Lump sum | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Equipamento | Watering cane | no. | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Effective Micro Organism | Litre | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Cement | kg | 100,0 | 20,0 | 2000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Stone | m3 | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Corrugated iron | pcs | 2,0 | 1000,0 | 2000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Posts and nails | Lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 50,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 13200,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 246,14 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
ISFM+ of the GIZ
Comentários:
For the model farmer who pilots livestock urine collection for soil amendment and management of pests, supporting the construction of a standard collection chamber and supplying associated kits helps to train and facilitate scaling of the technology in the best way. Effective Microorganisms (EMO) is an input being tested to investigate whether it has the property of changing the stink of the urine collected for storage and use on the farm.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Effective Microorganisms | Throughout collection and application |
Comentários:
The use of EMO to change the bad smell of urine, particularly during storage and application needs to be further investigated to prove and use it to reduce the abhorred side of collecting and applying urine for soil amendment and pest management.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | EMO | Litre | 6,0 | 100,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Family labor | no. | 52,0 | 100,0 | 5200,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 5800,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 108,15 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
NA
Comentários:
With the assumption that the land user can collect, treat and use about 140 liters of urine per week for different crops, family labor can be used at a lower rate as it is not a full-day operation. Despite our estimation, material and labour costs change in Ethiopia persistently because of market instability and economic crisis that is not uncommon since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Economic crisis, spiking inflation, and overall labour and material market cost instability.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Receive bimodal rainfall with a summer maximum.
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
The rainfall distribution is nearly consistent. The temperature is cold typical of highland weather conditions.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The topography is unremitting ups and downs.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Not available
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Surface and groundwater quality in the highland areas of Sidama region was not suggested as an issue. Rather, surface water can be polluted by soil erosion before the crops cover the ground.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The technology is piloted around the homestead. Agriculture is highly intensified in the area. Hence, only plantation forest or peripheral plants such as Eucalyptus species are the common tree species. This signals medium to lower species diversity that similarly applicable to habitat diversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The land user doesn't have off-farm income. He generates his livelihood from 2 hectares of land and a few livestock.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Farming is operationalized by hoes (hand-dug) to grow cereal crops. Otherwise, enset culture demands hand digging.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The land was inherited from the family line. However, the adopted national constitution declared land belongs to the state and the users. Thus, usufructs issued by the government to the land user.
Comentários:
In Ethiopia, the 1995 constitution declared the land as state property but the farmer has usufructs right. As a result, the certificate was issued except in the pastoralist areas of the country. Of course, most people inherited specific plots of land from their lineage, though there was frequent land redistribution during the Derg and early years of the EPRDF regime.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
Although they mentioned the quality of both ground and surface water is good in the preceding section, the level of sanitation is not significant as the resident use water from the springs for drink and other household activities.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
70 kg from 0.12 hectare of land.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
400 kg from the same land.
Comentários/especificar:
With the application of ISFM+ approach and urine as a replacement for Urea, a substantial yield increment was achieved.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
As the technology is at its early stage of implementation where documentation is not well organized, it was impossible to quantify the harvest and quality of the crop.
Gestão de terra
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
As urine complement urea fertilizer, other nutrients from Sulfur, Phosphorus and other micro nutrients remain important.
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Oportunidades culturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Crop response to urine application is an evidence based for adoption of the SLM technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Acumulação de solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Not practically measured and documented. Besides, the technology is at earlier phase to judge the real impacts.
Acidez
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade de habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
It has tangible impacts on managing pests.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
As a foliar application of urine to the target crops might be subjected to evaporation, if not good hours of the day are not identified, there is a likelihood of emission. However, its amount is very insignificant as the little amount used for foliar feeding.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
The on-site assessment is made based on conceptual knowledge of the beneficial effects of collecting and applying livestock urine as a replacement to urea fertilizer and the farmer and experts' knowledge on the fertilizer and pesticidal effects of liquid urine. Otherwise, careful documentation of various types of data is commendable to quantify and properly address such comprehensive questions included in the questionnaire.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
The impact has not yet measured.
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
As an optimum application of urine substitute urea fertilizer, it favors the growth of diverse plant species, positively contributing to the overall ecosystem services and reducing degradations. However, it has not been empirically measured.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento alogado | bem |
| Período de crescimento reduzido | moderadamente |
Comentários:
The technology has no direct influence on climate change/climate variability in the short term.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Post-establishment, the maintenance costs are believed to be very low. This shows the technology is cost-effective to resource-poor farmers.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Forty-four (44) farmers are currently piloting this technology. Of these, 30 farmers are innovative and adopted the technology on their own using locally available materials to collect and spray urine as a complement to urea fertilizer to the target crops.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 51-90%
Comentários:
Thirty farmers represent the most significant portion who spontaneously took up the technology.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
Unavailability of the right kits/materials
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Land users use locally available materials to collect, store and spray the urine on the target crops. Meaning the concept is introduced in a way it matches or complements conventional uses of livestock wastes to improve the fertility of soil on which Enset, a perennial crop is growing. Otherwise, standard designs or types of materials and safety precautions kits have not been associated with the technology. Despite the unavailability of the necessary kits for the establishment of the technology, farmers forge their mechanisms to collect and use urine. This indicates the innovativeness of the land/technology users.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Reduce costs spent on chemical fertilizer. |
| Increase yield per unit of land and land users' income in general. Furthermore, it increases the number of tillers per plant and overall biomass yield. |
| Manage insect pests such as cutworms and aphids. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| It seems a good substitute for chemical fertilizer, urea. It improves farmers' access to wasted resources without being used. |
| It restores the fertility of the soil and improves production and productivity, and species diversity which improves ecological benefits on top of the high return from the most minor investment in fertilizer. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Bad smell of the urine when sprayed on the target crops. | By ensuring access to necessary tools. Otherwise, they will not give up on using it since the benefit outweighs the loss. |
| Lack of spraying materials. | If not accessed spraying tools, the farmer committed to using locally forged ones. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Stinking of the urine while applying to the crop. | Try to test whether using Effective Micro Organism (EMO) can improve urine smell before using it in the field. |
| Lack of safety wear and associated necessary kits. | Improving access to the necessary materials, knowledge, and skills to use the available resources or materials effectively. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Four (4) persons, including a land user.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
A farmer
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Three (3) persons (district expert, regional SLM specialist, and ISFM+ regional advisor).
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/01/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Use of Cow Urine in the Field of Agriculture. Singh, R. 2022
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.pashudhanpraharee.com/use-of-cow-urine-in-the-field-of-agriculture/
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Utilization of urine waste to produce quality cauliflower. Khanal, A., Shakya , S. M., Shah, S. C., Sharma, M. D. 2011.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.nepjol.info (Free access)
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Nitrogen concentration in the urine of cattle, sheep and deer grazing a common ryegrass/cocksfoot/white clover pasture. Doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2010.499899
URL:
https://www.tandfonline.com
7.4 Comentários gerais
Not every question in the questionnaire is relevant to the Livestock urine collection for soil amendment and integrated pest management practices. Urine collection and use does not address every kind of land degradation stated in the questionnaire. However, it directly or indirectly addresses some of the SLM-related issues.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [Etiópia]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [Etiópia]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- Compilador/a: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
Módulos
Não há módulos