Low-Cost Plastic-Lined Water Harvesting Pond [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Nima Dolma Tamang
- Editor: Kuenzang Nima
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Chhu-zing
technologies_6821 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Sangay
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Climate-Smart Village Approach [Butão]
Climate change has become inevitable, and there is a need to address this impending danger. In the Climate-Smart Village (CSV) approach, land users in Ngaru-Pongtang have implemented several technologies and innovations to address climate change impacts, and the programme has worked with 50 households on a total area of 137 …
- Compilador/a: ONGPO LEPCHA
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
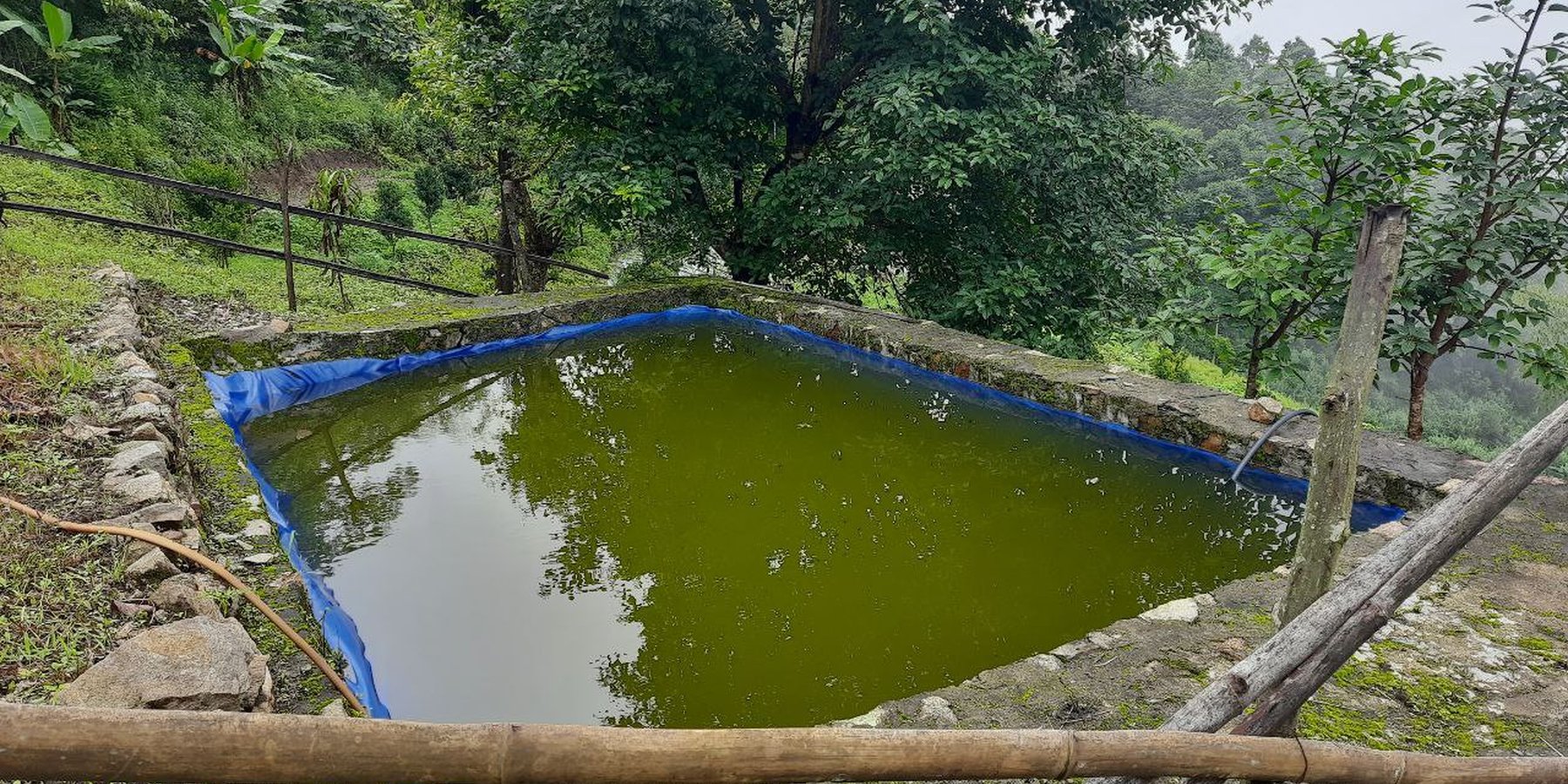
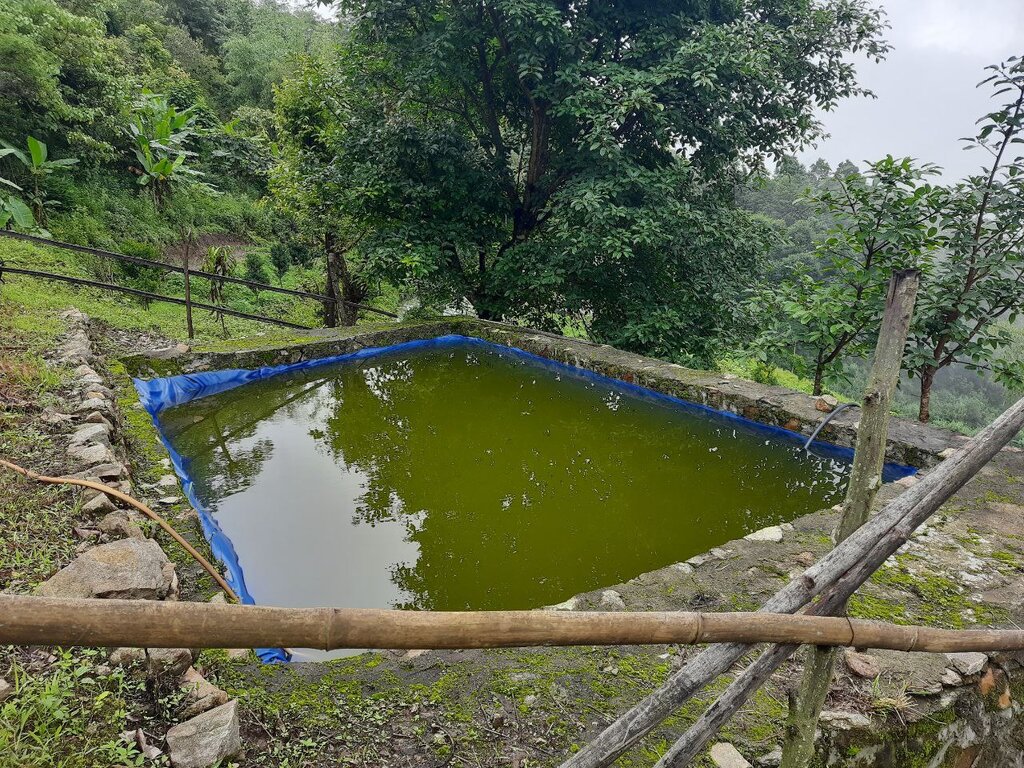
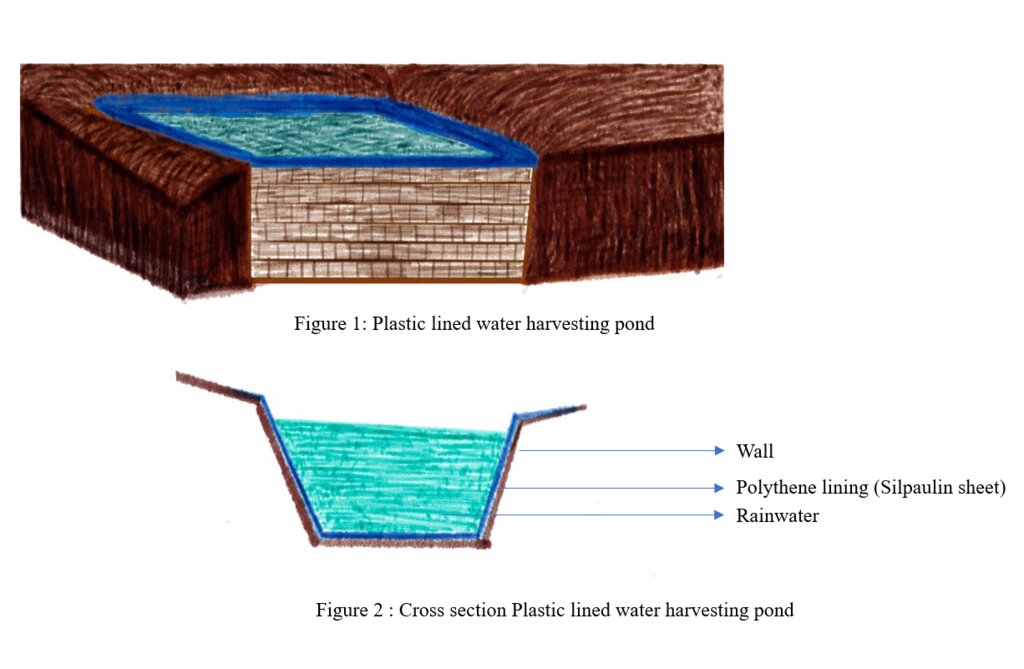
Low-cost plastic-lined water harvesting ponds collect and store rain and overland flow water for agricultural and domestic purposes in the dry season. They are both economic and efficient.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Low-cost plastic-lined water harvesting pond are used to collect and store rain or overland flow water for agricultural purposes in the dry season. They are economic and efficient. These ponds are required in the context of irrigation water shortages. Although rainfall has been projected to be increasing (NCHM, 2017), irrigation water shortage was - and continues to be - one of the major constraints in crop production (IHPP, 2017).
Water from precipitation and surface water sources is lost due to inadequate collection and storage. Villages at the top of the hills, in particular, suffer from acute irrigation as well as drinking water shortages. To tap and collect wastewater, rainwater, and water from other perennial and non-perennial sources, low-cost plastic lined water harvesting ponds are proposed. This water can be used during the dry or “lean” season for agricultural as well as household purposes.
The proposed model pond (plastic sheet size; 9m * 7m) costs less than Nu. 25, 000 (USD 315) for construction but can hold more than 27, 000 litre of water. The same dimension of pond if constructed using concrete, would cost more than Nu. 1, 19, 000 (USD 1500). Furthermore a 10, 000 litre synthetic tank available on the market costs more than Nu.35, 000.
Irrigation water shortage results in fallow lands. It is reported that 6,400 acres (2,600 ha) of irrigable land was left fallow in 2016 and 26 % of the total households surveyed were affected by irrigation water shortages (DoA, 2016). By reducing fallow land and increasing crop production, this technology could be a stepping stone towards food self-sufficiency – as well as providing water for consumption by people and livestock.
Though a similar technology is said to have introduced in the country many years ago, the present form of the technology was introduced to Barshong gewog in Tsirang Dzongkhag by the ‘Himalica’ pilot project in 2014. However, the proposed technology has been modified and improved to suit to the topography and needs of farmers in Bhutan. The proposed pond design is a reverse truncated square pyramid shape unlike the cuboid shape ponds of ICIMOD’s. The pond is designed in such way as to increase pond stability and ease of construction.
Concrete tanks require specific construction methods and faults can develop with ice freezing and expanding in cracks in tank walls during the winter (Slater, 2011). Plastic (silpaulin) sheet lined ponds are leak-proof and primarily depend on the longevity of the plastic sheet unlike concrete tanks. Concrete water tanks, (especially elevated tanks) are also prone to damage due seismic activities (Housner, 1963).
The low-cost plastic lined water harvesting pond adopted is cheap, environmentally friendly, and has positive social impacts. It reduces irrigation water constraints, addresses fallow land problems, and supplements water for domestic purposes. The technology is a tool for reducing poverty, expanding cultivated land and increasing food self-sufficiency resulting in a healthier and happier society.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Dagana Dzongkhag
Especificação adicional de localização:
Pangserpo Chiwog, Drujeygang Gewog
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is located in the land users field.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2019
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was initiated by Agriculture Research and Development Centre Bajo through fund support of Food Security and Agriculture Productivity Project of the World Bank. Drujegang, Kana and three blocks of Lhamoidzingkha sub-district of Dagana districts were selected as the project sites.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
- legumes - outros
- legumes - raízes (cenouras, cebolas, beterraba, outros)
- chilli, onion
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- cítrico
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Vegetables intercropped within citrus orchard
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
The land users grow different crops in the same area. For example, if they plant potatoes this year, they plant beans next year.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Site selection for pond construction:
Choose a site for the pond at the top of the farm for easy flow/use of water to the agricultural fields. Select the site only at the stable soils to avoid collapse, and bursting of the pond. Water sources for the pond may be perennial water sources, rainwater gutter systems, water from tap stand, and waste water from farm house or a combination of the different sources.
Materials required: The materials required for making the pond are:
1.Plastic sheet of desired length and breadth
a.250-300 GSM (gram per square meter)]
b.UV stabilized
2.Measuring tape (30m)
3.Shovel, spade, and crowbar
4.Mosquito net or similar ones
5.HDPE pipes, gates valves
6.Fencing materials (bamboo poles, wooden poles, barbed wire, nails, wire mesh, binding wire)
Procedure to dig the pond:
1.Clear the vegetation and level the ground to construct the harvesting pond.
2.Measure the base length (l), and the base breadth (b) on the leveled ground. These length and breadth will be the length and breadth of the pond floor. Dig out the soil till 1.2 m height (h) to construct a cuboidal pond.
3.From the top edges of the cuboidal pond, measure distance ‘g’ in all four sides. Make slanting cuts from the top to the base on all four sides. Scrap off soils on all sides to obtain slope of 700. The gradient is made for slope stabilization and convenience to lay out plastic sheet.
4.Make the cut surfaces including the floor smooth by using mud and cow dung paste or mud paste in order to avoid damages to the plastic sheet while laying out and when filled with water. The pit ready to lay out plastic sheets should have the dimensions.
5.Carefully lay out the plastic sheet over the pit. Keep an anchor length (overlap) of 0.5m on all sides of the pit. Fix wooden or bamboo pegs or iron rod through the eyelets of the plastic sheet and or cover the overlapping plastic edges by at least 10cm of mud or soil to strongly anchor the plastic sheet.
6.Construct a drain with 30cm width and 30cm depth around the edges of the plastic sheet which was covered with soil or mud. The drainage should slope towards a suitable drain out area.
7.Fence the pond using wire mesh/bamboo/wooden poles/timber to prevent mishaps or accidents. Fill the pond with water only after fencing. Galvanized wire mesh is preferable.
Using water:
Water from the pond can be used in the following ways:
Directly siphoning off with a pipe
Pumping up with a small motor pump
Taking out with suitable containers
Inserting a drain out pipe at one of the base corners.
The insertion of the drain out pipe should be done during the construction of the pond.
Note: The stone wall may be required in specific situations if built in a slope like this one but not generally needed. Technical drawing of the water harvesting pond without the cement structure is available at http://rcbajo.gov.bt/leaflet/ also shared under section 7 of this document.
Autor:
Ongpo Lepcha
Data:
08/12/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
water harvesting pond
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
41.6 cubic metre
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum (Nu.)
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
Ngultrum 350
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveying and site selection | Anytime |
| 2. | Procuring materials | Anytime after surveying |
| 3. | Construction of pond | Dry season |
| 4. | Fencing | After completion of water harvesting pond |
| 5. | Monitor | Checking water level, infestation of mosquitoes and checking safety measures like fencing and leakages |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of pond | Person-days | 8,0 | 500,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | HDPE pipe | Metre | 100,0 | 40,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wire mesh | Pieces | 2,0 | 3500,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Silpaulin plastic sheet | Pieces | 1,0 | 7500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Material de construção | Wooden post | Pieces | 14,0 | 60,0 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 23340,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 291,75 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The cost were for plastic sheet and wire mesh and were funded by Food Security and Agriculture Productivity project and Green Climate Fund project.
Comentários:
Pit digging and laying of plastic sheets were all done manually by the land users. Bamboo used for fencing purposes was available locally. The labour cost was not borne by the land users as they implemented a system of labour-sharing where land users reciprocate by working for an equal number of days at other land users' households as compensation.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of concrete wall | Dry season |
| 2. | Monitor | Throughout the year |
| 3. | Maintenance of fence | Annually |
Comentários:
Due to the unpredictable rainfall patterns and the associated risk of landslides as the pond is located on steep slopes, the farmer was required to reconstruct and reinforce the pond by utilizing cement to provide additional support. Ponds located in the plain or lower gradient do not require support using concrete walls.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Reconstruction of pond | Person-days | 15,0 | 500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Material de construção | Cement (50 kg per bag) | Bag | 10,0 | 400,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 11500,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 143,75 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The cement was supported by the government.
Comentários:
Boulders and stones used were collected from the land users' field.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most important factors that affect the cost are the construction materials and labour. In this particular situation, cement wall is also one of the major factors affecting the cost although it is not usually required.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
2000,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
It has an annual rainfall range of 1200-2500 mm
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
National Centre of Hydrology and Meteorology
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Falls under humid subtropical and dry subtropical zones from the six Agro-ecological zones of Bhutan.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Moisture content 3.38%, organic matter 4.19%, Organic carbon 2.44%, pH 6.31, electrical conductivity 93.30 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.12%, phosphorus 0.36 ppm, Potassium 301.07 mg/100ml, texture Loamy sand.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The total area of the farm is 1.8 acres or 0.72 hectares. The average land holding of Bhutan is 3.4 acres, therefore the land users owning less than 3.4 acres are categorized as small-scale.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The land users mentioned that there has been an increase in production due to the availability of irrigation water during the dry season.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Improved irrigation water leads to better quality of crops. For example, the leafy vegetables will be flaccid with a reduced total leaf area in the absence of irrigation.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The availability of water during the critical periods of crop development in dry seasons reduces the risk of production failure.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
The harvested and stored water from the tank is used to feed the livestock. It is also used to maintain the sanitation of the cattle shed.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The spring water dries in the winter. Therefore, the stored water in the water harvesting tank is available during dry seasons for irrigation.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Trapping the rainwater prevents the utilization of scarce spring water. Therefore, reducing the demand for irrigation from the spring water source.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Irrigation plays a significant role in crop cultivation. Therefore, with adequate irrigation water crop production and productivity increase leading to increased farm income.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
With sustainable sources of irrigation, land users produce enough food for self-consumption increasing food security. Further, the land users sell the produce and generate income with which they can purchase nutritious foods that are not available on the farm.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Water is important to keep the surroundings clean. Therefore, the technology improves the health of the farm household and livestock.
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Using drinking water for irrigation leads to social conflict. However, the issue is resolved with the low-cost plastic-lined water harvesting technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
The amount of water available for farm activities is increased as the technology traps overflow and rainwater preventing water wastage.
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
The rainwater and overflow water are harvested efficiently preventing runoff and surface erosion.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Water harvesting pond acts as a suitable habitat for mosquitoes therefore increasing the risk of malaria.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
The impact of drought on agricultural activity is significantly reduced as the tank increases water availability.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced spring water requirement in the field is diverted to water availability for other farming communities and wildlife.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | muito bem |
Comentários:
The technology copes well with the decreasing rainfall as it captures the limited rainwater and makes it available for agricultural use.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
All the farmers who have adopted the technology were partially funded (external support).
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mudança climática/extremo
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
The location of the water harvesting technology on slopes presents a risk of potential landslides caused due to climate change effects such as heavy rainfall. Therefore, the structure of the technology was modified to address this issue by providing support using the cemented wall. The modification is suitable for the steep slopes and is not required on the plain areas.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Increased crop production. The technology enables land users to cultivate crops during dry seasons. |
| Increased water availability. The water harvesting pond provides adequate water for livestock rearing, household use and agricultural purposes. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| It is cost-effective compared to a cemented tank. |
| The water harvesting tank constructed using high-quality plastic is durable providing economical benefits. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Risk of accidents leading to the drowning of small children and domestic animals such as dogs. | Constructing a fence around the pond and creating awareness. |
| The technology acts as a habitat for mosquitoes leading to increased malaria infection in the household. | Regular cleaning and removal of sediments, vegetation, algal and plankton growth (serves as a food source for mosquitoes). |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
one
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
one
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
07/07/2023
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Low cost plastic lined water harvesting pond
URL:
http://rcbajo.gov.bt/leaflet/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Climate-Smart Village Approach [Butão]
Climate change has become inevitable, and there is a need to address this impending danger. In the Climate-Smart Village (CSV) approach, land users in Ngaru-Pongtang have implemented several technologies and innovations to address climate change impacts, and the programme has worked with 50 households on a total area of 137 …
- Compilador/a: ONGPO LEPCHA
Módulos
Não há módulos