Geocoding of Million Fruit Trees for Monitoring and Tracking [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Nima Dolma Tamang
- Editor: Haka Drukpa
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Not Applicable (NA)
technologies_6829 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Agriculture Extension Officer:
Penjor Thuji
Geog Renewable Natural Resources (RNR) Center, Agriculture Office, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
Butão
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology enables remote monitoring of the growth and development of fruit trees ensuring the sustainable use of land and its resources. Further, the technology aids in the success of the Million Fruit Tree Plantation Project reducing the risk of converting cultivable land to fallow.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Geocoding of fruit trees allows remote monitoring and progress tracking of the growth of seedlings. The Smart App MoDA (Mobile Operation and Data Acquisition) is used in geocoding.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The Photo does not directly depicts the technology described here.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Thimphu Dzongkhag
Especificação adicional de localização:
Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The geocoding of fruits are in the land users field. Therefore, the area does not fall under any of the protected area or national parks.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2022
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The geocoding of the million fruit trees in the country was initiated as per the directives of His Majesty the 5th King of Bhutan where all the saplings are funded by the Royal Government of Bhutan. Plantation and geocoding were done by the Desuups (Desuup is the highest form of the voluntary act in Bhutan. They wear orange uniforms and are also known as the Guardians of Peace).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (planalto)
Sistema de cultivo anual:
Arroz de manguezal - trigo
- Apple
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Paddy in summer is followed by winter wheat or vegetables
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
They intercrop vegetables with lugumes.
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
The land used for paddy cultivation is used for planting vegetables such as potatoes.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
The technology aids in maintaining land cover by ensuring vegetative coverage of the land in which geocoding enhances easy management and improved health of the fruit trees such as apples, dragon fruit, banana, areca nut, kiwi, avocado and others.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Fruit tree plantations will potentially prevent land degradation in the long term by giving cover and strengthening soil structure by its roots.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
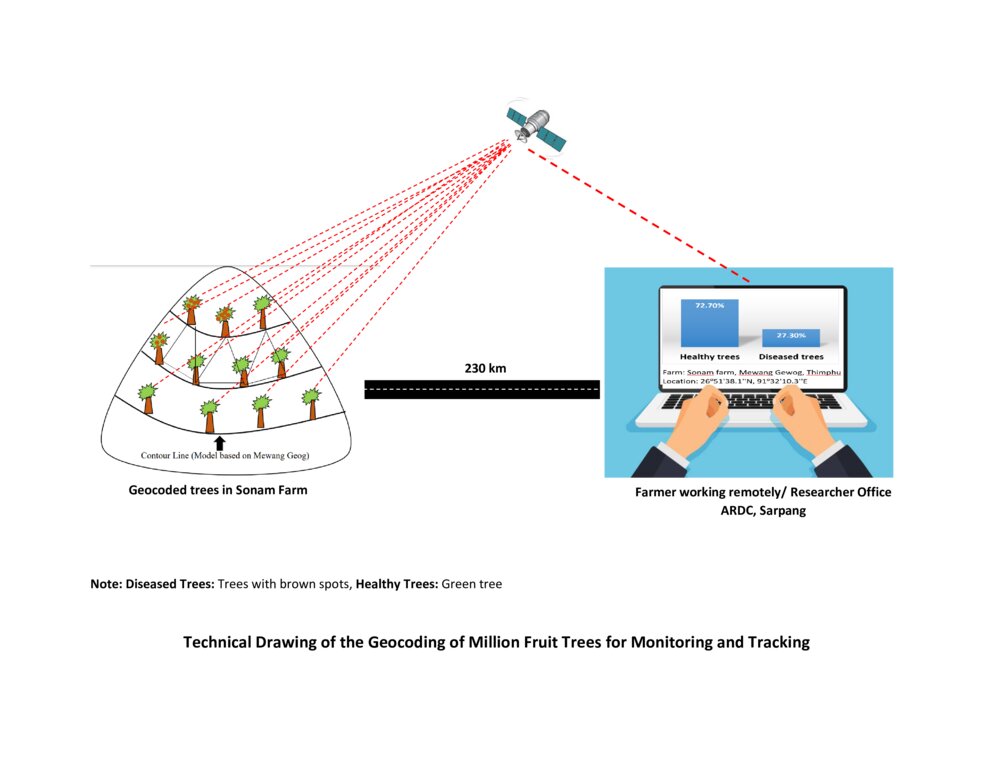
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The technical drawing represents the general method of million fruit tree plantation and geocoding done on each tree. It depicts how geocoding enables the researcher or farmer to remotely check the health of the trees using satellite data. ARDC stands for Agriculture Research and Development Center.
Autor:
Nima Dolma Tamang, Singye Dorji, Tshering Gyeltshen
Data:
07/07/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
No of Seedlings
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
8000 seedlings (Only in Mewang Geog)
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
82,62
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
800
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting between Gewog leaders and land users | NA |
| 2. | Identified a village for planation | NA |
| 3. | Identified households that wanted the seedings and number of seedlings | NA |
| 4. | Site identification | NA |
| 5. | Orchard layout | NA |
| 6. | Pit digging | NA |
| 7. | Plantation | March- April |
| 8. | Basin making | After planation |
| 9. | Geocoding | After one month of orchard establishment |
| 10. | Growth Tracking | After every six months |
Comentários:
The above information is limited to only Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6,0 | |||
| Mão-de-obra | Farmers | Person-days | 10,0 | 800,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Shovel | No. | 10,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipamento | crow-bar | No. | 5,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipamento | Spade | No. | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipamento | GPS remote | No | 6,0 | 12000,0 | 72000,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6,0 | 15000,0 | 90000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Apple | No. | 3500,0 | 70,0 | 245000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Walnut | No. | 1000,0 | 120,0 | 120000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Almond | No. | 500,0 | 120,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Peach | No. | 1000,0 | 70,0 | 70000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Pear | No. | 2000,0 | 70,0 | 140000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16,0 | 1600,0 | 25600,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 830600,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 10053,26 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Almost all the cost were covered by the Million Fruit Tree Project of Desuung National Service and Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock jointly.
Comentários:
The total cost calculated is for planting and geocoding. The actual costs borne by land users are very minimal. The only cost the land users have to bear is labour cost and fertilizer cost. The high cost of the project is contributed mainly by seedling cost, GPS remote, tablets and mobile phones which was used during the marking position of fruit trees.
Cost for shovel spade and crowbar is not included as they are available at the farm and are reused.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Twice a year |
| 2. | Fertillizer application | Twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | Once a week |
| 4. | Replacement of dead plants | After 6 months from plantation |
| 5. | Growth tracking | After every six month |
Comentários:
The information obtained are through verbal communication with the Agriculture Extension Officer of Mewang Gewog.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4,0 | 1600,0 | 6400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| Mão-de-obra | Geocoding | per plant | 8000,0 | |||
| Material vegetal | Replacement of plants | per plant | 10,0 | 70,0 | 700,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 7100,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 85,94 | |||||
Comentários:
The geocoding was done by the Desuung volunteers. so, the exact costs cannot be deduced.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Most important factors affecting the costs are seedling and labour cost.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
2076,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The rainfall data for Mewang Gewog is not available. The provided data is for Thimphu Dzongkhag as Mewang Gewog is under Thimphu Dzongkhag (Gewog is one of the geographic units below Dzongkhag). Thimphu falls under a temperate region and experiences minimal rainfall compared to the other parts of Bhutan. Thimphu had the wettest month in July with 497 mm and experienced the least rainfall in December with 5 mm.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
National Center for Hydrology and Metoerology, Thimphu.
Zona agroclimática
There are six Agro-ecological Zones (AEZ) in Bhutan and the current place of study falls under warm temperate zone which occurs between 1,800 – 2,500 m. Rainfall is low but the temperature is moderately warm in summer with frost in winter.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The area was characterized by a steep valley near the river with minimal slope as the valley widened.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The availability of water in Mewang Gewog was a concern since a decade ago. Irrigation water was not enough for every farmers which resulted in delayed paddy plantation.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The species of flora and fauna diversity cannot be quantified under "high" as per the field observation. The area was surrounded by coniferous forest which generally has low biodiversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The majority of the land users who were part of the Geocoding of million fruit plantation had already established apple orchards.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
An average land holding capacity for Bhutanese household as per the Land Act is 3 acres. The land holding that exceeds 3 acres are categorized in large scale in Bhutanese context.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Internet:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
It adds to farmers sources of income other than vegetable and dairy product sale.
Disparidades econômicas
Comentários/especificar:
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
Microclima
Comentários/especificar:
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | muito bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | muito bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | muito bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | muito bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de granizo local | muito bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | muito bem |
Comentários:
The technology copes very well with gradual climate change because it sends rapid messages to farmers on actions to take (e.g., concerning pests and diseases). In a way it’s a form of early warning systems (EWS).
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Although the initial establishment of the orchard is costly considering the labour charge, it is expected to have positive income and impact once the fruit trees start bearing.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Total 8000 fruit trees are planted in the five Chiwogs (third level administrative division under Gewog) under Mewang Gewog.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Almost all those who adopted the technology are funded by the government.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| 1. Precision Mapping: Geocoding allows for accurate mapping and identification of fruit trees. By assigning specific geographic coordinates to each tree, it becomes easier to locate and monitor individual trees or orchards. |
| 2. Efficient Resource Allocation: Geocoding helps optimize resource allocation by providing information on tree density and distribution. Land users can identify areas with high fruit tree concentrations and strategically allocate resources such as labour, water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. |
| 3. Data-driven Decision Making: Geocoded data on fruit trees can be analyzed to gain insights into their distribution patterns, growth rates, and health status. This information enables land users, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding fruit tree cultivation, pest control, and disease management. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| 1. Conservation and Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data aids in the conservation and analysis of biodiversity. By mapping the locations of different fruit tree species, experts can assess the distribution and abundance of specific varieties, identify endangered local or traditional landraces varieties, and develop strategies for their preservation. |
| 2. Targeted Marketing and Distribution: Geocoded fruit tree data facilitates targeted marketing and distribution strategies. By understanding the location of fruit trees and their yields, producers can identify potential markets and plan transportation logistics more effectively, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery to consumers. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Geocoding large numbers of fruit trees can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, particularly when manual processes are involved. It may require extensive fieldwork and manual data entry, making it impractical or costly for large-scale fruit tree inventories. | |
| Privacy Concerns: Geocoding fruit trees raises privacy concerns, particularly when tree locations are associated with specific individuals or properties. Care must be taken to ensure that privacy is respected and sensitive information is appropriately handled | An updated and secured security-protected website can be used. |
| Lack of knowledge of geocoding by the farmers. | Provide awareness trainings |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The higher expense of the geocoding in terms of labour cost for geo-coding | Train land users on geocoding, instead of using trained professionals. |
| Difficult to constantly update information on time. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
The information documented was from the field visit to orchards near the RNR center.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
The information collected are from first-hand interview with the Agriculture Extension Officer who was engaged fully during the implementation of the technology.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
07/07/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
De-suung National Service (DNS). (n.d.). Million Fruit Trees Plantation
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://desuung.org.bt/25978-2/#:~:text=In%20order%20to%20monitor%20the,from%20the%20date%20of%20plantation.
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched
URL:
http://www.bbs.bt/news/?p=166763
Título/ descrição:
Kuensel. (2022). Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched. Thimphu.
URL:
Website: https://kuenselonline.com/414000-fruit-trees-planted-in-45-days/
Título/ descrição:
Geocoding of trees from street addresses and street-level images
URL:
https://www.fs.usda.gov/psw/publications/vandoorn/psw_2020_vandoorn001_laumer.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos