Water Source Protection [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ONGPO LEPCHA
- Editor: Haka Drukpa
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Chhu Ka Soongchop (ཆུ་བརྐ་སྲུང་སྐྱོབ།)
technologies_6842 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Dorji Sangay
Yakpugang Community
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
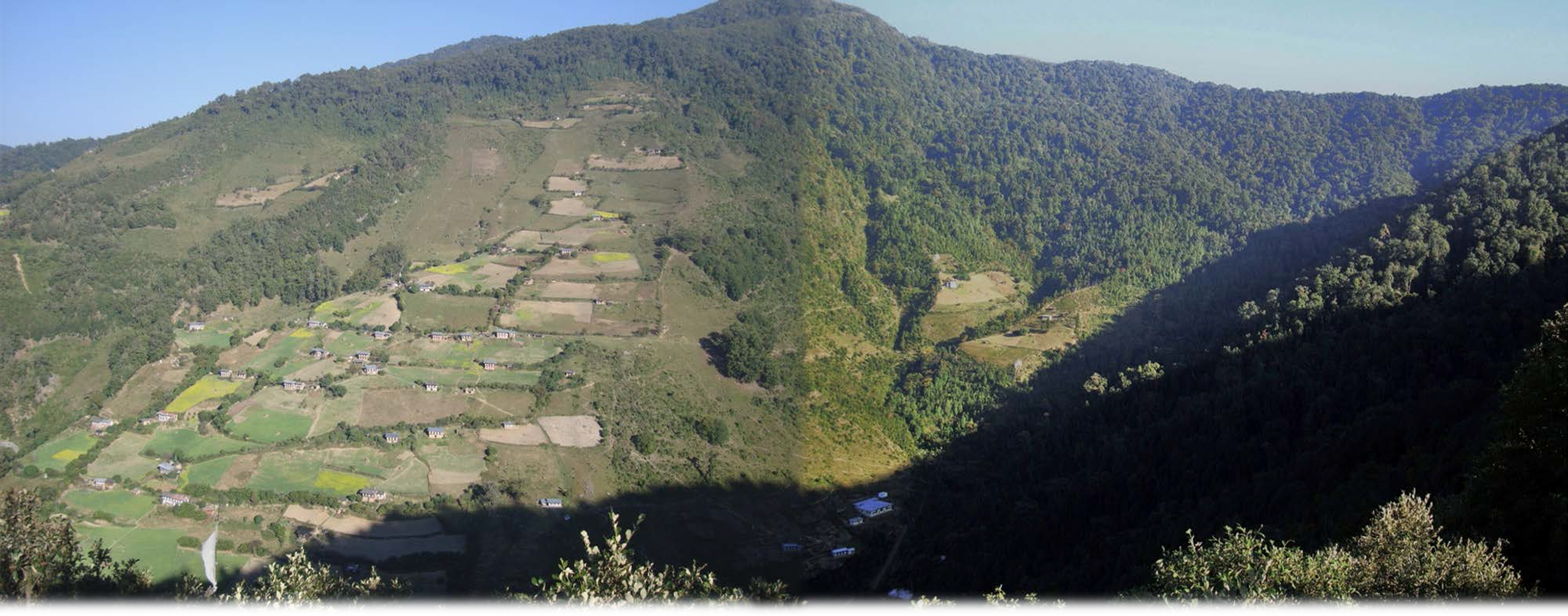
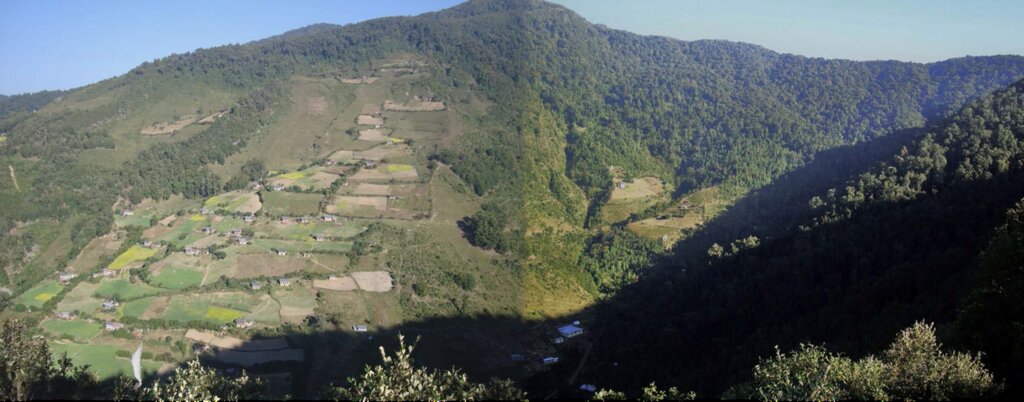
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs, or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past, the emphasis was on fencing and improving vegetation cover at the discharge point itself, but a recent focus is on groundwater recharge areas.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
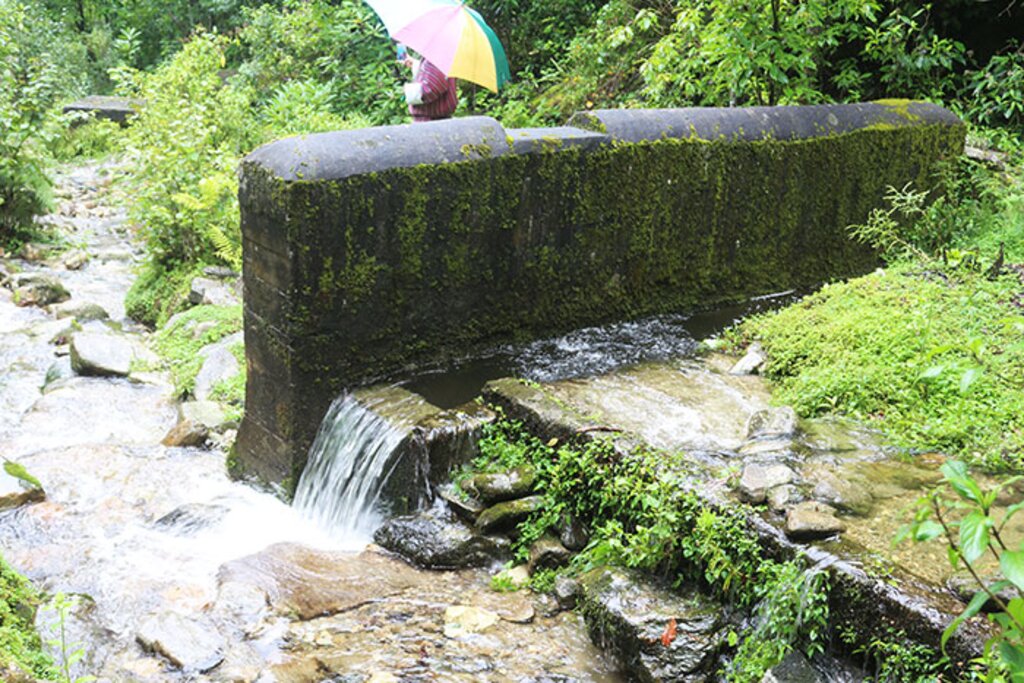
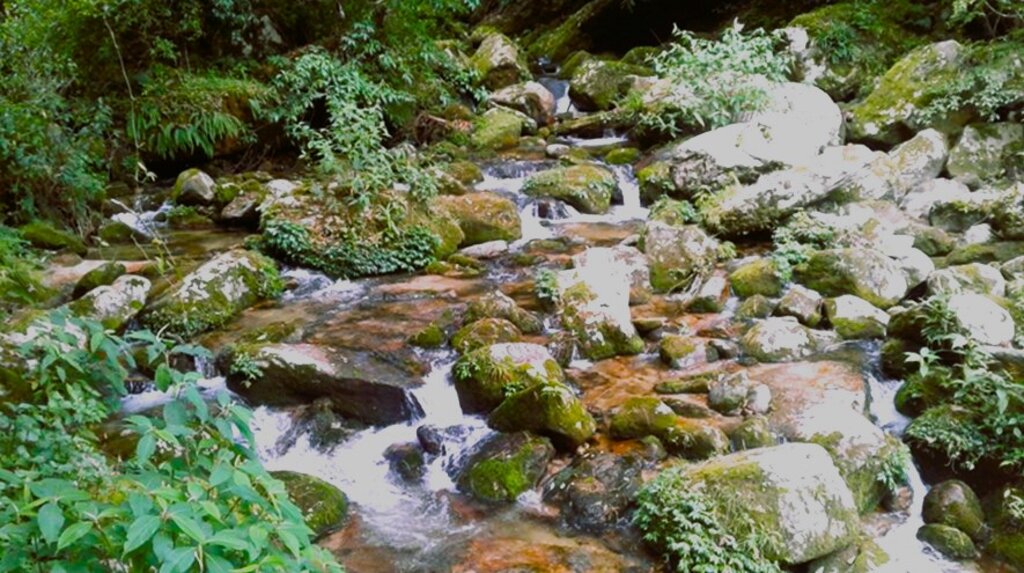
Water source protection involves protecting lakes, rivers, springs or man-made reservoirs to avoid water pollution and damage by livestock and wild animals. In the past this included fencing and enhancing vegetation cover at the discharge point – that is, where the water starts flowing. However, today, water source protection also focuses on improving groundwater recharge areas. The water source protection technology has many benefits. In addition to providing a clean and regular supply of drinking and irrigation water, it also enhances the vegetation cover of the catchment area.
Strategies target maintaining adequate water levels in underground water reservoirs to ensure a continuous flow of streams and springs. In Yakpugang Community Forest, the technology has been applied specifically in the southern mountainous part of the village. An area of 638 acres (255 hectares) has been established as the recharge zone, and three springs have been identified for source protection. Native tree species have been planted annually in the degraded watershed to improve forest conditions. The main purpose is to protect the quality and quantity of the water for both drinking and irrigation purposes. The technology is supported by an approach that involves collective efforts of the community who realize that if their drinking and irrigation water supply is to be sustainable, they must work together.
The main purpose is to ensure a continuous supply of water for drinking and irrigation to the community. This is achieved through managing the catchment areas where rainwater soaks through the ground to reach a groundwater reservoir, and one of the key interventions is protecting the water sources from wild animals and livestock.
The water source protection technology involves 1) meeting different stakeholders, 2) signing agreements between the stakeholders, 3) site selection and survey, 4) planting of native tree species, and 5) conducting annual monitoring and evaluation. Inputs like fencing materials, planting materials, and human resources are required for the implementation and maintenance of the technology.
The technology is liked because it helps provide a continuous supply of both clean drinking and irrigation water. Furthermore, protecting water sources by the community is rewarded in monetary form by the nearby town as part of the Payment for Environmental Services (PES). This incentive helps the community to generate income which is ploughed back into the improvement and maintenance of water sources. What is disliked is the reduction in grazing land since the land users are not allowed to graze their cattle inside the water source areas.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Mongar Dzongkhag (District)
Especificação adicional de localização:
Yakpugang village
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2007
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The project was conducted with technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and and funded through Blue Moon Funding with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services. Later Mongar Regional Referral Hospital was also involved as one of the major water users.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Preserva ecossistema
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
- legumes - raízes (cenouras, cebolas, beterraba, outros)
- Chillies
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Vegetables are cultivated in one growing season, however, fruit trees are perennial.
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
The cole crops are rotated with root vegetables and legumes.

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Linhas de drenagem, vias navegáveis
Principais produtos/serviços:
Irrigation channels for farming and drinking water pipes
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
The community was benefited greatly from the technology, and thus farming is mostly irrigated and rainfed is done, when rain falls in the area.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
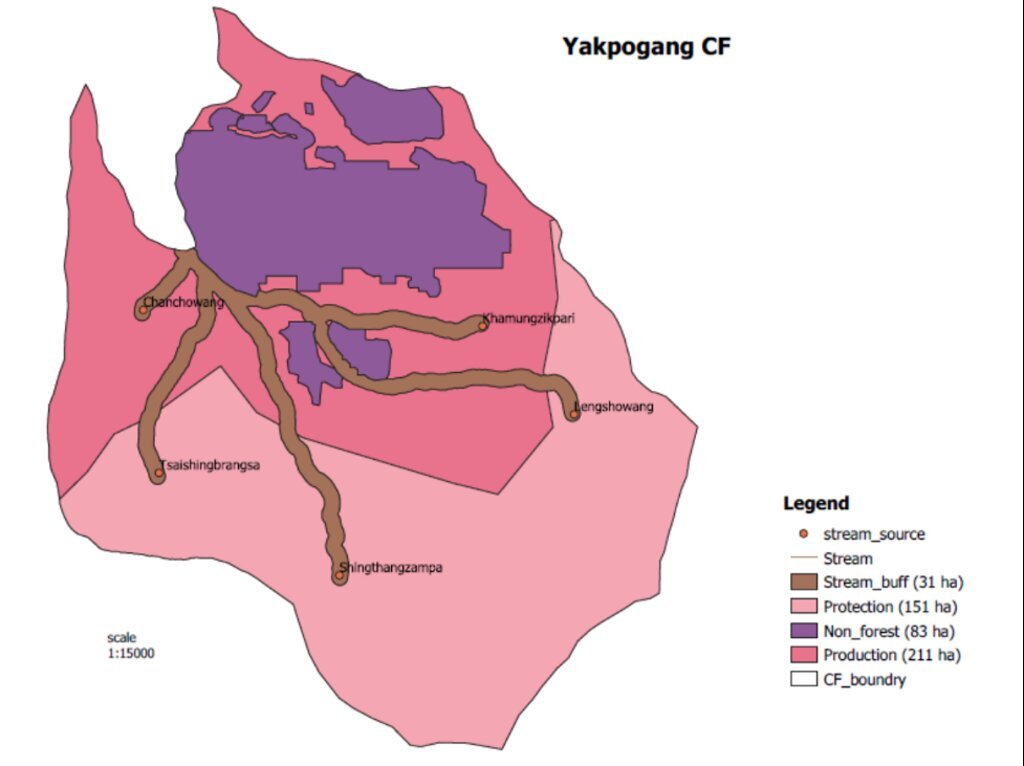
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
GIS map of the recharge zone of the Yakpugang spings
Yakpugang village, Mongar Gewog (Block), Mongar Dzongkhag (District), Bhutan
Autor:
Ugyen Norten
Data:
07/10/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Recharge zone of 638 acres (255 hectares)
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
638 acres (255 hectares)
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
82,08
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1000
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community meeting | Conducted several times |
| 2. | Survey of the recharge zone and site selection | The survey took around 2 to 3 weeks |
| 3. | Agreement between the stakeholders | Agreement done thrice |
| 4. | Native tree species plantation around the watershed | Based on a specified date and each individuals from household came |
Comentários:
The establishment activities were done with the technical assistance from SNV Bhutan and the Department of Forests and Park Services since the water source falls under the community forest.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
258500,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The project was funded through Blue Moon in collaboration with Watershed Management Division of the Department of Forests and Park Services and Global Environment Facility (GEF) was also involved.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of the water source | Thrice annually |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Community Forest members | person/day. | 102,0 |
Comentários:
Since the water source is a community asset, an individual from each household goes to the water source area for annual maintenance. This happens three times a year, and no cost goes into it except labour contribution from each household during which they bring their own tools and food.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
None.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The data was used from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Warm temperate zone
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water quantity and quality have been greatly improved with the intervention of water source protection. These three water sources provide drinking water to Mongar town and Mongar hospital.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Alto
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Total land is 1.5 acres and total cultivated and is 1 acre
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the Land Act and Land Rules and Regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
15 baskets of maize
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20 to 25 baskets maize
Comentários/especificar:
There has been an increase in the amount of maize, which has been credited to the increase in the amount of water than in the past.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
According to the land user, crop quality has been relatively better after the implementation of the technology than in the past.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the presence of water in the community, production has decreased.
Diversidade de produtos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
maize and some other cereals and vegetables were grown
Quantidade posterior à GST:
maize together with cole crops, tubers and fruits are grown
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1 acres
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1.5 acres
Comentários/especificar:
In the past, the lack of water would lead the land users to keeping some of the land fallow.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Water would be scarce periodically
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water is now available throughout the community
Comentários/especificar:
Drinking water availability has increased compared to the past. This is mainly due to the protection of water sources. In addition, now community members also go for regular clearing of irrigation channels, drinking water pipelines, and sources to keep the supply steady.
Qualidade da água potável
Comentários/especificar:
Quality in terms of cleanliness of drinking water was reported to have enhanced because in the past nearby streams from where they get their drinking water used to get polluted by rainwater, animals, etc.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Water would be taken to the nearby streams
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water is now provided near there house
Comentários/especificar:
Since supply is continuous the water availability for livestock also increased.
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Water for livestock are also improved than in the past.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Focused more on growing crops requiring less water
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Now grows variety of diverse crops
Comentários/especificar:
Since the water flow is continuous, there is enough water to carry out multiple cropping.
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Water quality for irrigation is better than the past
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
focuses mostly on commercialising maize
Quantidade posterior à GST:
now commercialises diverse vegetable crops as well
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
The availability of water in the community, allowed for the land users to grow a diverse vegetable crops in large amount.
Estado de saúde
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Community members prone to water related disease
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water is relatively cleaner
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Comentários/especificar:
Agreement for water source protection is conducted after every end of the agreement year, where water use rights are also discussed.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
water from the source would dry up most of the times
Quantidade posterior à GST:
water in the water source is almost always filled.
Qualidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Would be dirty due to wild animals and grazing cattle
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Since water source is protected, water is relatively cleaner
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Quantidade anterior à GST:
in the past, drought would occur periodically
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Even during the absence of rain, water is still available
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Would normally be polluted due to wild animals and grazing cattles
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water is now clean and also drinkable
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | moderadamente |
| Trovoada local | muito bem |
| Tempestade de granizo local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
| Incêndio florestal | não bem |
| Queimada | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
| Inundação súbita | não bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | não bem em absoluto |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The income earned from the project goes into community development and the community forest, and the expense for the project is already funded.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
102 households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Continuous supply of both drinking water and irrigation water |
| Water is supplied to Mongar town, and income is earned from it under Payment for Environmental Services (PES) arrangement b |
| Has helped in community development and improvement of community forest |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Water quality is preserved, and pollution and contamination of the water sources are prevented. |
| The plantation of native tree species helps conserve the ecosystem. |
| Long-term sustainability and enhanced climate resilience of the water source |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Decreased grazing land | Shift the grazing area outside the community forest or establish improved pasture land in their registered land |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
One household
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
One individual
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
11/07/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Norten, U. (2021). Impact of Water Management strategies- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) in Bhutan. International Journal of Science and Innovative Research, 2(8), 109-144.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://ijesir.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/0100072IJESIRnew.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
WWF. (2017). Valuing Ecosystem Services in Chamkharchhu Sub Basin: Mapping Sediment Using InVEST. WWF.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://wwfasia.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/final_invest_report_final_draft_may_17_spread_compressed_2.pdf
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/programs-initiatives/source-water-protection
Título/ descrição:
Water Source Protection
URL:
https://sswm.info/arctic-wash/module-4-technology/further-resources-water-sources/water-source-protection
Título/ descrição:
Basic Information about Source Water Protection
URL:
https://www.epa.gov/sourcewaterprotection/basic-information-about-source-water-protection
Título/ descrição:
Conserving water resources with PES, an example from Yakpugang
URL:
https://kuenselonline.com/conserving-water-resources-with-pes-an-example-from-yakpugang/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos