Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Santosh Gupta
- Editores: Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Kim Arora
- Revisores: Udo Höggel, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_6721 - Índia
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level: 25 de Junho de 2023 (inactive)
- Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level: 14 de Setembro de 2023 (inactive)
- Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level: 11 de Abril de 2024 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - AlemanhaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - QuêniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Índia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
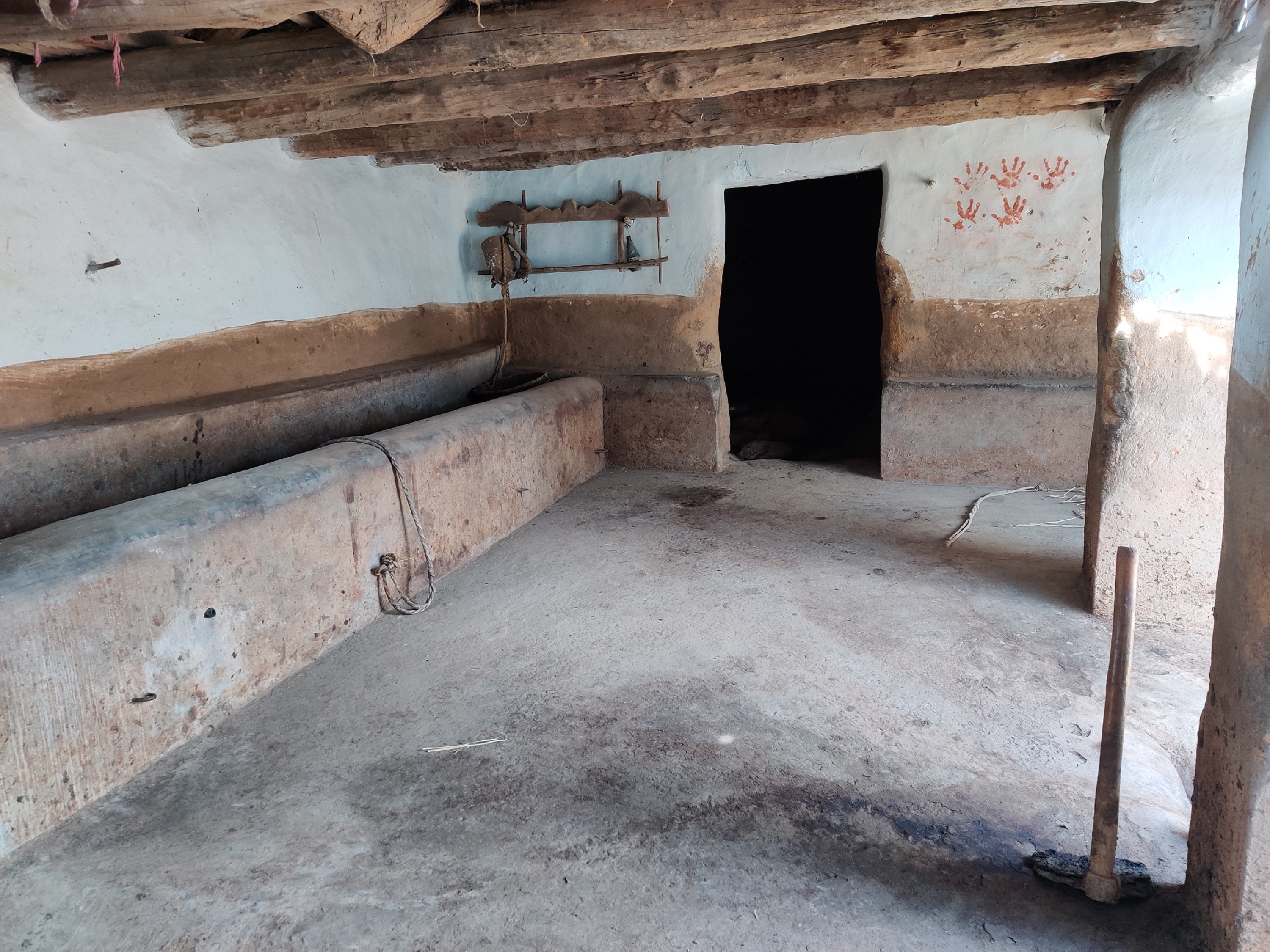
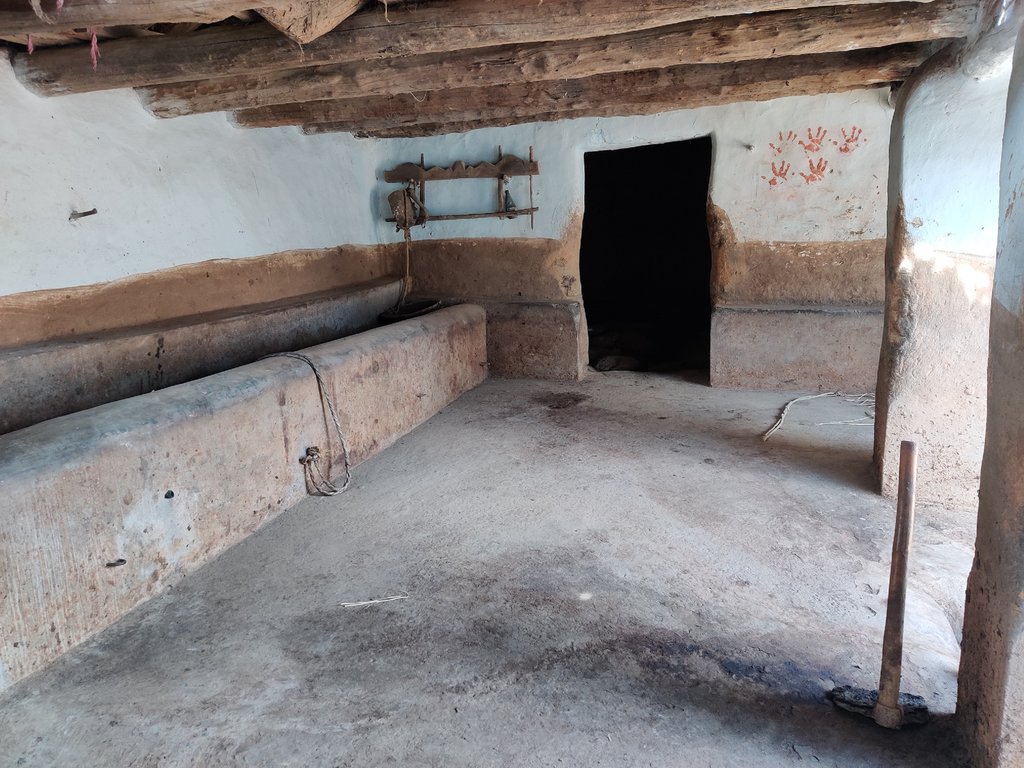
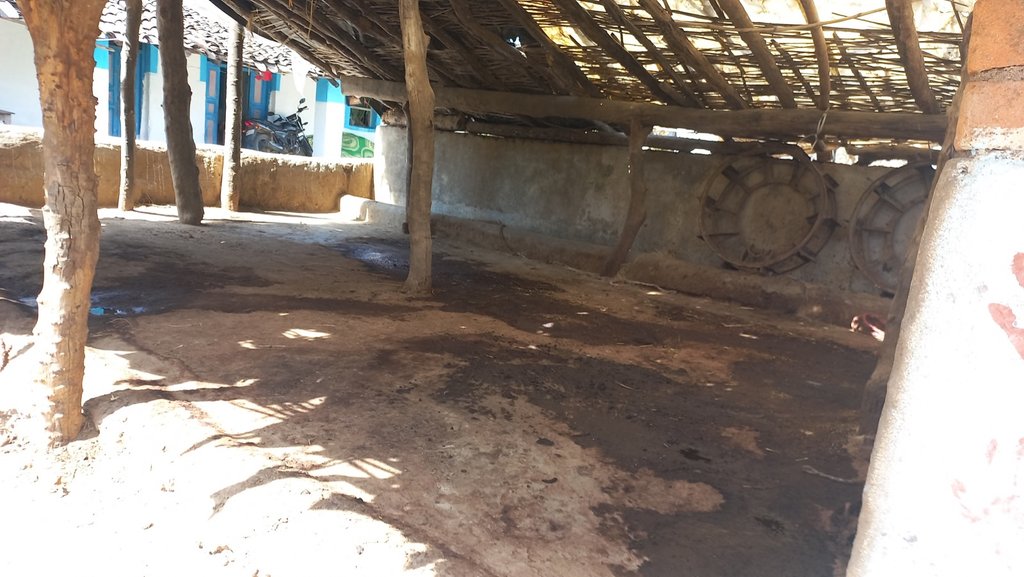
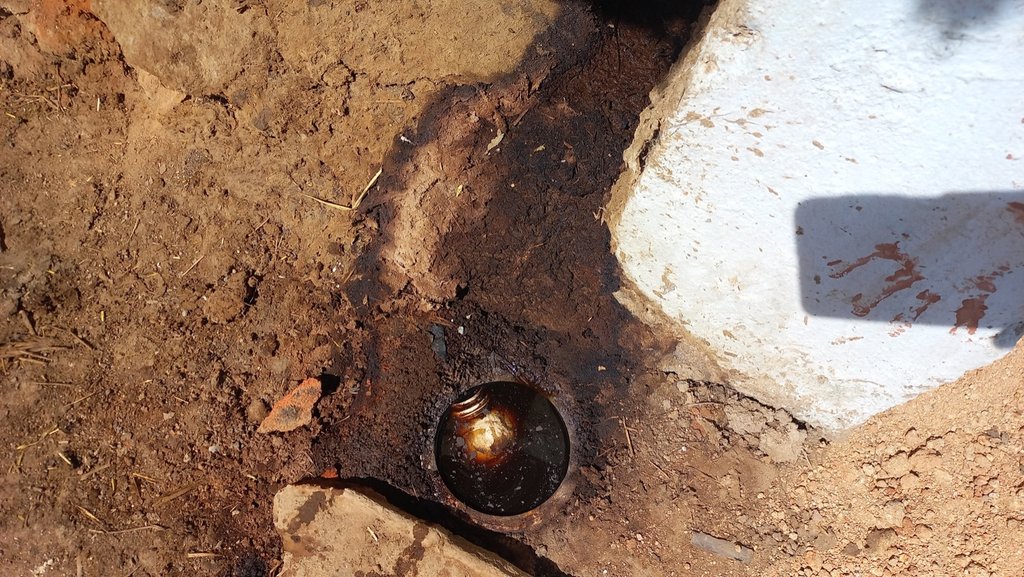
In the cattle shed management system, the cattle shed should be constructed with an elevated concrete floor that slopes slightly toward a cow urine collection point. The collection point should be equipped with a drainage system to easily remove cow dung and urine.
An elevated concrete floor for cow dung and urine collection can improve hygiene, and waste management, and reduce labour costs in cattle sheds. Collected cow urine and cow dung can be used to prepare biological inputs and compost for nutrient and pest management in agriculture.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
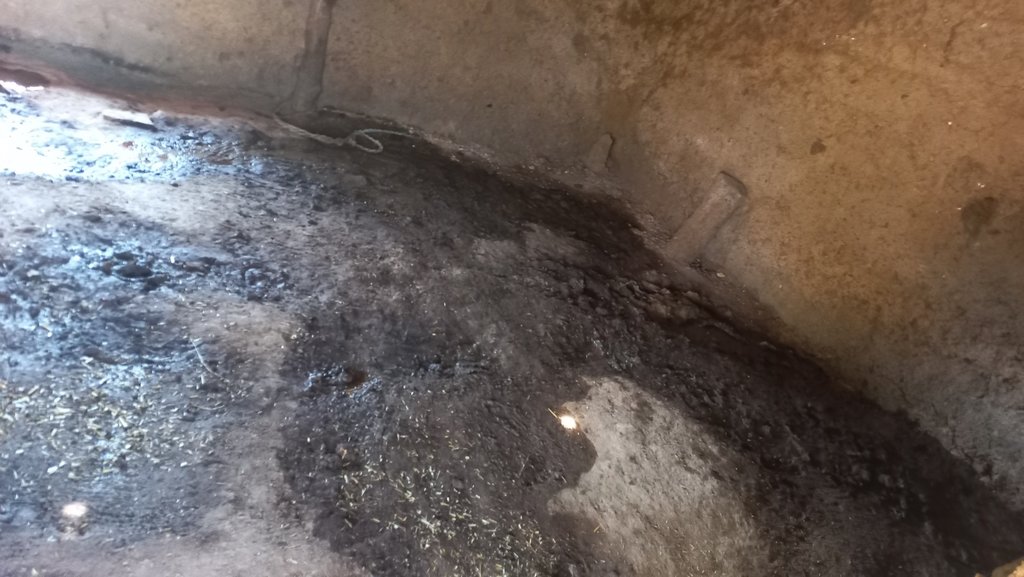
Cattle shed management technology, including the use of a concrete elevated floor for cow dung and urine collection, is a cost-effective and efficient technology to support the natural farming system. This technology can be applied in both natural and human environments. In natural environments, such as rural or agricultural areas, cattle sheds are typically used for dairy and farmyard manure production. The use of this technology can improve the hygiene of cattle and their environment, reduce waste and pollution, and promote the sustainable use of natural resources. The cow dung and urine so collected can be used as fertilizer to improve soil quality, and the improved hygiene of the cattle can reduce the risk of diseases spreading to other animals or humans. The use of this technology can help to reduce the negative impacts of cattle farming on the surrounding environment, such as odours and pollution. It can also improve the hygiene of the cattle and their environment, which is important for both animal welfare and public health.
Traditionally farmers were constructing the floors of cattle sheds using mud and soil. These floors absorb the cow urine and the movement of animals also makes holes in it because of that cow urine and cow dung are used to get filled in these halls. Which made the entire floor unhygienic for both animals and farmers. Because of such surfaces, it was very hard to clean these sheds. The use of an elevated floor made with cement-concrete and a waste management system can help to keep the cattle shed clean and dry, which can reduce the risk of disease and infection among the animals. The collection and disposal of cow dung and urine can help preventing environmental pollution, reducing the negative impacts of cattle farming on the surrounding area, and promoting sustainable use of natural resources. The use of a concrete elevated floor can make cleaning the cattle shed faster and easier, reducing labour costs and improving the efficiency of the farming operation.
Technical specifications for the construction of cattle sheds can vary depending on factors such as the size of the herd, local environmental regulations, and available resources. However, in general, the main characteristics and elements of cattle shed management technology are designed to promote animal welfare, hygiene, waste management, and sustainability. Proper cattle shed management technology can provide a comfortable and safe environment for the animals, which can reduce stress and promote animal welfare. Proper waste management and ventilation can help to minimize unpleasant odours from the cattle shed, which thus reduces negative impacts on the surrounding community.
Establishing and maintaining cattle shed management technology requires a combination of technical expertise, labour, and resources. By investing in these inputs, farmers can promote sustainable and efficient cattle farming practices and improve the health and welfare of their animals.
The collected cow urine and cow dung are the main resources for preparing the biological inputs and different types of compost for meeting the nutritional requirement of crops while also addressing the challenges of pest and disease management in a natural or organic farming system. The improved flooring of cow shed units has been a great intervention to replace and reduce the usage of synthetic fertilisers and pesticides in the project region.
The views of land users, such as farmers or livestock keepers, about cattle shed management technology, including the use of a concrete elevated floor for cow dung and urine collection, can vary depending on their experiences and perceptions. The interviewed land user liked or appreciated, cattle shed management for improving animal health and productivity, increasing farm profitability, cleaning the cattle shed easier and faster, reducing labour costs, improving efficiency, and for environmental benefits.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
All of these phots have been taken with the consent of participants.
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Gd6u8yZ9DqY&si=EnSIkaIECMiOmarE
Data:
01/02/2021
Localização:
Mandla, Madhya Pradesh, India
Nome do cinegrafista:
Soil Matters
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
Madhya Pradesh
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mandla District
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is being adopted by more than 100 farmers across the 10-15 villages of the Bichhiya block in Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Initially, the project supported the farmers in the construction of cemented cow shed floors in a limited area. However, there has also been investment from the users either by putting extra funds to extend the area or by contributing labour.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Control cattle diseases
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- leguminosas e pulses - lentilhas
- culturas oleaginosas - girassol, colza, outros
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
In kharif (summer) season farmers are sowing paddy in wetlands and in rabi (winter) season wheat, chickpea, mustard, maize and other vegetables
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Chickpea intercropping with beans, mixed cropping system of vegetables present
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Rice- Chickpea
Rice-Wheat
Rice- Maize
Comentários:
The intervention is mostly focused on improved cattle shed units. However, collected cow urine and cow dung are good for restoring the degraded agricultural land.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
For irrigation, most of the farmers were dependent upon rain in the Kharif and Rabi season. Some of the farmers were using additional irrigation during critical crop stages by using water canals.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A6: Gerenciamento de resíduos
A6: Especificar o gerenciamento de resíduos:
A 6.4: retido

Medidas estruturais
- S9: Abrigo para plantas e animais

Medidas de gestão
- M6: Gestão de resíduos (reciclagem, reuso ou redução)
Comentários:
The implemented technology led to the management and use of waste for productive purposes. While it has improved the productivity of animals by reducing the occurrence of diseases, it has also enabled the preparation of organic inputs to replace the synthetic fertilisers in farming.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores

Degradação da água
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
Proper collection of cow dung and cow urine minimised run-off these substance and mixing with surface water used for various purposes including drinking water.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Application of cow urine and cow dung in soil by mixing with other organic matters improves the soil health and also reduces the dependency on synthetic fertilisers and pesticides
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
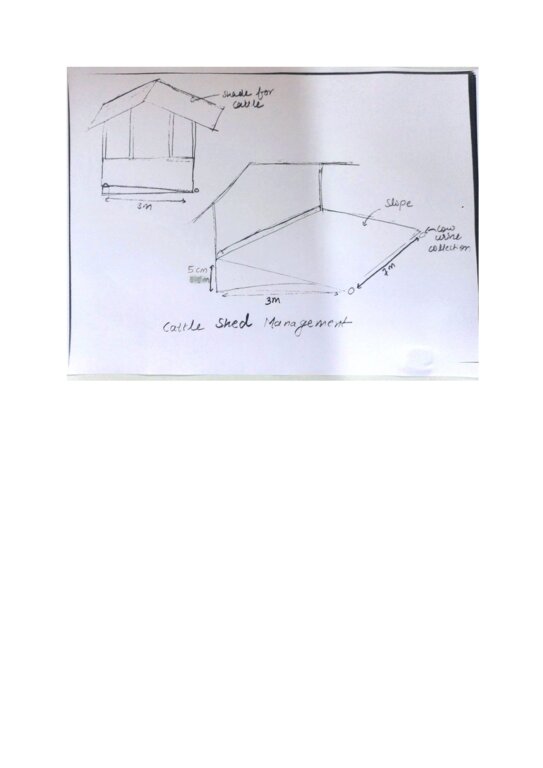
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Dimensions of the cowshed (depending on the number of cows kept):
Length: 7m
Width: 3m
Elevated: 5 cm (means in effect the slope: i.e. the front floor of the cowshed is 5 cm higher than the floor at the end, where dung and urine get collected)
Autor:
Payal Dewangan
Data:
22/02/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
one cattle shed
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
meter
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Indian Rupee
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
82,24
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
240
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Concrete floor construction for cattle shed | March |
| 2. | Cattle shed roof development | April |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
28000,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Gram Paryavaran Samiti and Prakritik Sansadhan Prabhandhan Samiti
Comentários:
Village groups were formed for the implementation of the technology
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of concrete floor | Once in a day |
| 2. | Collection of cow dung | Once in a day |
| 3. | collection of cow urine from the pit or drum | Twice in a week |
| 4. | Fodder and drinking water provision | Twice in a day |
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Design and technical specifications: The cost of the technology can vary depending on the design and technical specifications of the cattle shed, including the size and materials used.
Construction materials and labor costs: The cost of construction materials and labor can vary depending on local market conditions and availability.
Location: The cost of transporting materials and labor to the construction site can vary depending on the location of the farm.
Maintenance and repair costs: The cost of maintaining and repairing the cattle shed can also add to the overall cost of the technology.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity building to farmers and workers on proper cattle shed management techniques can add to the overall cost of the technology.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1427,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Highest rainfall occurs between June to September.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Mandla, Madhya Pradesh
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The climate of the District is tropical, with moderate winters, severe summers, and well-distributed rainfall received from the southwest monsoon. However, due to higher general elevation and abundance of forests, summer temperatures do not rise as much as in other areas.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The topography of the project area consists of a hilly area and a forest area. Mandla District is hilly and forested (Satpura hill range) and highly undulating with a narrow strip of cultivated plains in the valley portion of the river. The plateau is in the northern part formed by basalt, and east-west trending hills in the southern part. The highest elevation is 934 m amsl in the northern part, and the lowest is around 400 m amsl in the northwestern part of the area. The elevation of the studied block Bichhiya is 453 m amsl.
Source: District at a Glance; Ministry of Water Resources, Government of Madhya Pradesh
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil Testing Parameter status (Average) 2017-20 for the project areas is as follows. This data is based on the soil samples tested by the FES in its soil labs from the project villages.
Sail pH:-5.906548628; EC (electrical conductivity): 0.122993577: Soil Organic Carbon: 0:83%; Nitrogen:- 293.3696598; Phosphorus:- 25.77762582; Potassium (K):- 139.6696636: Sulphur
(S)-18.93457993; Zinc (Zn):-0.955246706; Boron (Bn):-0.490850376
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The groundwater status is within the safe limits as per the reports by the Government of Madhya Pradesh. People use water from rivers, streams, and traditional small wells for domestic purposes. In the absence of good vegetative cover, the rainwater washes off the fertile topsoil from the farmlands making the land barren and resulting in the siltation of ponds and other water bodies. Further, a heavy infestation of invasive species such as Lantana Camara compounds the degradation.
The studied block Bichhiya is in a better position in terms of stage of groundwater development with 17%, stage of groundwater development refers to the % of groundwater being used for various purposes from the available groundwater in that area e.g. net annual groundwater availability in Bichhiya block is 9087 ham (hectare meters) while the existing annual groundwater draft for all usage is 1523 ham, making it a 17% groundwater development stage, while the district average is 79%.
Source: http://cgwb.gov.in/District Profile/MP/Mandla.pdf
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The cattle shed management unit or center is present nearby the forest area of Kanha National Park. There is high biodiversity present in the technology implementation area. Ecological assessment report in Mandla (where this Technology is applied) showed improved biodiversity on common lands under village governance compared to open-access or commons under government ownership. On average, the Shannon Diversity Index of managed common lands was 1.45 compared to 0.42 for the open access of ungoverned commons. Most of the sites under open access lands are infested by Lantana Camara, which is the main reason for the lower biomass and diversity of the ungoverned lands.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
Some of the land parcels are ancestral land units while some have been transferred into private ownership by the State Government over the years
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
It was observed and noted from the field site that instead of using chemicals, the application of cow urine and cow dung in the form of farm yard manure has helped in improved production as it led to the reduction of pest infestation and better nutrient uptake from the soil.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction in the use of chemicals in the field and application of collected cow urine and other bioresource products made from cow dung helped in improving the quality of crop in terms of harder crops, good weight of grain, test etc.
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
The improved cattle shed played a crucial role in maintaining the hygiene of animal sheds, which led to the lesser occurrence of disease among animals. Also, the stress level of animals due to the presence of insects and flies reduced significantly. A combination of all these factors improved the milk yield.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Using sustainable methods for crop production by application of bio inputs not only helps in increasing soil fertility but also contributes to increasing crop resistance, pest control, and better crop development.
Diversidade de produtos
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced to some extent as now farmers can make their own bio-inputs using the cow urine and cow dung collected from the cattle shed
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
A combination of improved productivity, reduced cost towards agriculture inputs and better milk productivity has helped farmers in improving their income.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Some of the farmers have initiated their own bio resource centres to sell cow urine and cow dung-based bio-inputs, vermicompost etc.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
The workload of women members in the household was reduced very significantly due to covering the mud-based cow floor with cement-concrete-based cow floor, earlier cleaning of the cow dung and cow urine used to take a lot of the time. However with new floor, it can be cleaned in less than 5 minutes saving almost an hour in a day.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Improved hygiene is good for both animal and human health
Oportunidades culturais
Instituições comunitárias
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Application of cow dung, compost and other bio-inputs have improved the soil moisture
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Application of cow dung, compost and other bio-inputs will help in improving the nutrient cycling in the soil and will enhance the soil microbial activities
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Some of the farmers are using the collected cow dung as an input for their 'Bio-gas' plants. Thus, the use of biogas plants not only reduces the use of fire wood and LPG for cooking but its waste (slurry) is also used as inputs for agriculture fields. Thus reducing the overall footprint of GHG emission.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Some of the farmers have installed bio gas plants. Use of biogas plants not only reduces the use of fire wood and LPG for cooking but its waste (slurry) is also used as inputs for Some of the farmers are using the collected cow dung as an input for their 'Bio-gas' plants agriculture fields. Thus reducing the overall footprint of GHG emission.
Also the improved floor have helped in proper collection of cow dung and cow urine for the purpose of composting. Composting makes the compounds in manure more stable and therefore reduces the amount that is released into the atmosphere.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | muito bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Low maintenance cost compared with benefits of higher animal productivity and hygienic living
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Reduced labour of urine and dung collection |
| Better animal management |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Reduced GHG emission because of better handling of dung and urine |
| Increased productivity because of the use of animal manure |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High establishment cost | Subsidies and grants |
| Regular maintenance cost | Technological innovation |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Possibilities of disadoption because of maintenance cost | Increase returns of the units by extending new products from Urine and dung |
| No demand | Increase communication and extension on the benefits of different products from animals |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Repairing cattle shed floor
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Foundation for Ecological Security, Mandla, MP, India
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Cattle sheds: one intervention, several benefits for farmers
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gd6u8yZ9DqY
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos