Double Basin Masonry Check Dam [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
NA
technologies_6716 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Abdi Amir
Dry valley Rehabilitation and Productive Use (DVRPU) project of the GIZ
Etiópia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The Check Dam helps to arrest the runoff of flood and rehabilitate the gully development.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [Etiópia]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A double basin masonry check dam is a physical structure that helps to stop gully formation or further development of gullies in dry valleys. It rehabilitates small to a medium-sized deep gullies that are eating into the heart of adjacent land.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
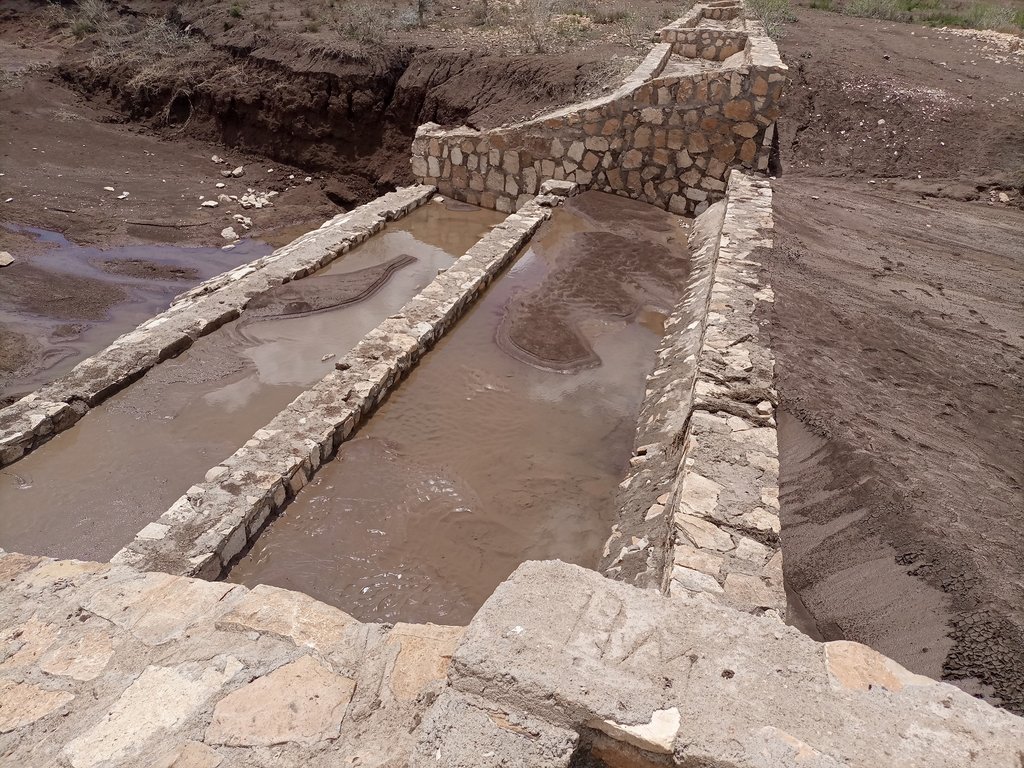
A “double basin masonry check dam” is a structure built in a narrow gully or depression to stop further gully formation. It is made of stone, concrete, gabions and wooden bars and serves as a permanent barrier. In this particular site stone is used as the structure is masonry. The technology is applied in areas where there are concentrated flows of water or runoff. The double basin masonry check dam is sited across a slope or a deep gully to slow water flow and capture sediment from upstream in the basins and behind the structure, thereby preventing expansion of the gully. The width of a check dam is variable. This particular structure is 14 meter wide, three meters deep and about 52 meters long. By helping to fill up the gully with sediment, it leads to rehabilitation and makes productive use of the area for growing trees, forage, and other plants. Apart from reducing the speed of surface runoff, the structure also promotes water infiltration, and recharges the groundwater reserves in the aquifer.
The main inputs necessary to build the check dams are financial resources, technical skills, skilled and unskilled labour, and construction materials including sand, stone, cement, water and other materials. Furthermore, construction tools such as a theodolite, line level, string, hammers, spades, hoes, and other tools are essential for design & construction. Technical skills for designing and profiling, and further capacity-building training are essential also. Application of the technology is also supported by satellite image and ground truthing to ensure the precision of siting.
The agropastoralists in the dry basin areas are pleased to see a huge movement of the soil arrested by the structure. The reduced expansion of the gully into the heart of the farm and grazing lands raises hopes of their land become productive and remaining so for generations to come. This hope and expectation have motivated them to welcome the intervention and develop an understanding of the actual benefits accrued from it. This leads to their support for the construction efforts. The disadvantages are that the technology is labour and resource-intensive which can be unaffordable for resource-poor agropastoralist communities living in food-insecure areas where rainfall is unreliable. This may make the adoption of the technology difficult to establish and nurture on their own without outside support.
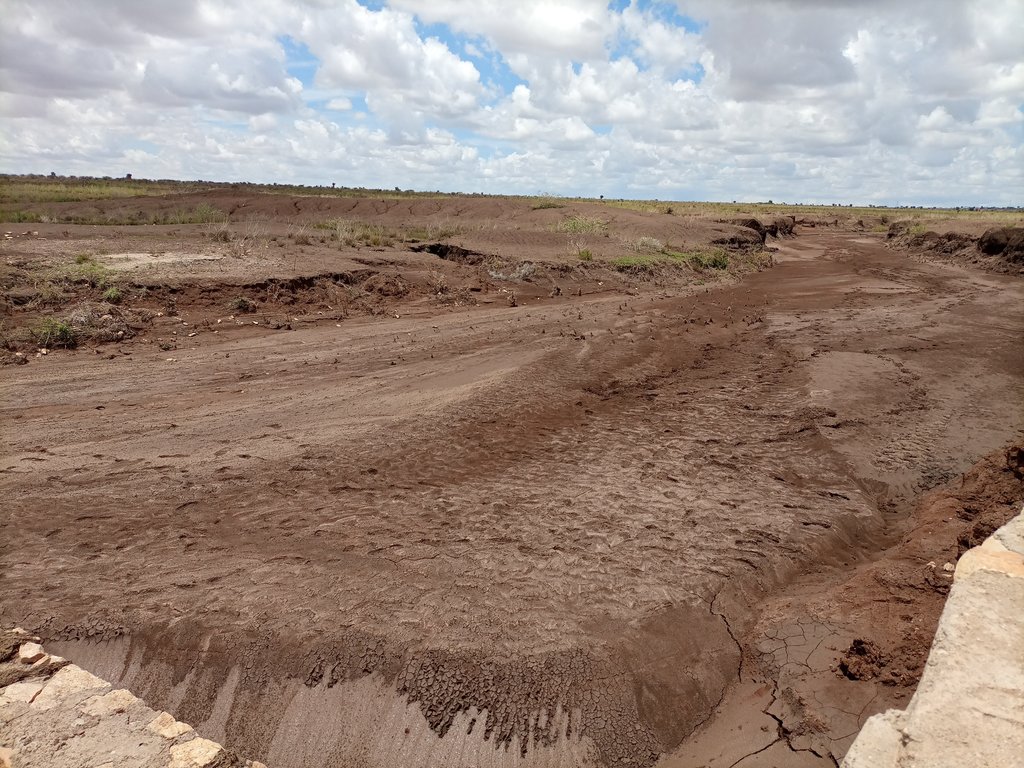
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The photos display a large amount of sediment captured by a few days' shower post recurrent droughts experienced in the area over the last two to three years.
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
Video of the technology was not taken by this particular documentation exercise.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Somali
Especificação adicional de localização:
Hadow kebele of south Jigjiga district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
Locating the check dam closer to each other may help to stop the damage of heavy and concentrated flood moving in the drainage basin.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2021
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) project of the GIZ in Somali Region.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Rainfed is the type of water supply that often experiences erratic distribution characterized by the reception of lower amounts. Mostly characterized by erratic and erosive feature.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Coleta de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The technology stops the mass movement of soil and water. As a result, it reduces land degradation, rehabilitates the degraded dry valley, and makes the land available for productive uses.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
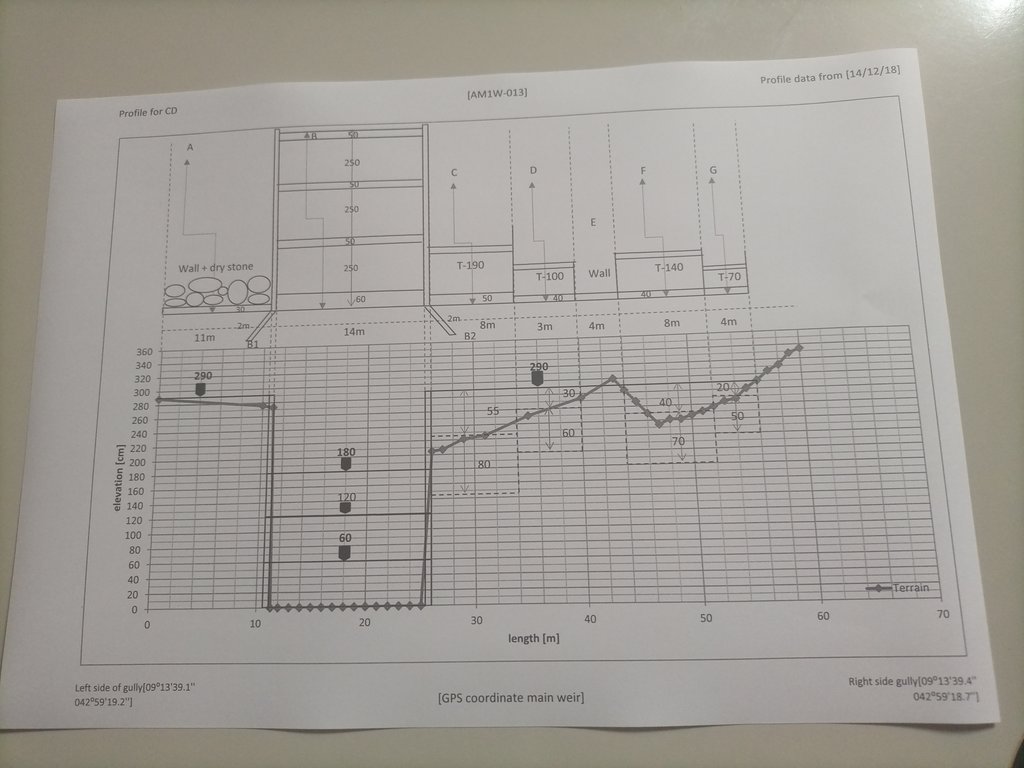
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The design (layout - top view) and profile (lower view) of the technology is presented with universal units to clearly read and understand by the SLM experts or engineers. In addition, there are section drawings of the main weir and Bill of Quantity (BOQ).
Autor:
Amir Abdi
Data:
14/12/2018
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
check dam
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
14m*3m*52m =2184m3
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
8.5 - 16 USD based on their skills
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduct rapid assessment and Surveillance of intervention site | During the off-season |
| 2. | Finalize site selection | ditto |
| 3. | Layout, Design and profiling works | |
| 4. | Identify and train masonry workers | During off-season |
| 5. | Material supply | |
| 6. | Start actual layout and excavation work | |
| 7. | Supervision... |
Comentários:
Once intended to put the technology or the structure in place, a series of activities are conducted involving experts and contract workers until the activities are effectively finalized.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
9200,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The project is responsible to cover the cost.
Comentários:
The cost for an unskilled casual laborer a day is 8.5 USD whereas the daily cost of a skilled Masonry worker is 16 USD per day.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Oversee and identify damage | During and after rainy season |
| 2. | Measure the degrees of damage | ditto |
| 3. | Quantify cost and materials needed | |
| 4. | Schedule the maintenance work | Right before the off-season |
| 5. | Employ the workers and reconstruct the damaged parts or upgrade it. | During off-season |
Comentários:
As some of the technology implementation sites are inaccessible during the rainy season, implementing the activities during the off-season is commendable.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia:
3244,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The project is expected to cover the entire maintenance cost. However, maintenance cost is attributed to various factors including the degree of damage, material costs at the time, etc. The figure merely represents an estimation of the cost, on average.
Comentários:
As the dry land receive erratic and erosive rain, damage to the structure is not uncommon. Combining fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial fodder grass stabilizes the sediment and reduces the speed of run-off on top of the structure. Therefore, associating the structure with biological barriers right after the first season of rain is a mandatory action that assists to reduce the damage and maintenance cost that is not affordable by resource-poor communities.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Inflation and increasingly changing material prices, labor and transportation costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Rainfall distribution is erratic and erosive.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Jijiga Meteorology station
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
There are bimodal rainfall patterns but the distribution in each respective season is not uniform. Particularly, the past consecutive seasons have been characterized by drought.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The technology is implemented in the gully or depression to reduce the speed of runoff and hold back the sediment and running water itself.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Especifique:
Land users communicated the presence of a medium level of water salinity.
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The water quality is a relative description as it is not supported by facts. Both livestock and human beings are using ponds and still water for drinking after rainfall.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
A few tree and shrub species are common in the area. Acacia, opentia (Euphorbia species), and some invasive weed species are common.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
Outros (especificar):
Agro-pastoralist
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The agro-pastoralist settlement pattern is stable except their mobility with their livestock looking for water and feed. Land users of various age groups are benefiting from the technology.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
Land use is largely communal and individual inherit it from their lineage.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
Not much service is available in the pastoralist area except that the road paths through the area also create access to the market and other service centers.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
With the development of the sediments trapped by the structure by fodder crops of multipurpose tree species, it is possible to boost production and ensure the sustainability of the structure.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
As the sediment brings in fertile topsoil from the upstream catchments, the likelihood of producing quality fodder in the rehabilitated area is so high.
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
The multipurpose tree species assumed to be planted in the rehabilitated area are expected to increase wood production.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
As the rehabilitated valley reduces runoff and increases the groundwater reserves, it caters to the opportunity to access drinking water.
Qualidade da água potável
Comentários/especificar:
Succeeding vegetation covers enables to filter of the water and improves the quality of surface and subsurface water.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Slightly increases as the structure and rehabilitated areas improves water infiltration and formation of still water or micro ponds behind the structure.
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Simultaneously increases with the availability of surface and subsurface water.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction of gully formations that consume the rangeland allows accessing relatively more rangeland areas for the livestock to graze over. This inevitably improves the food security of the pastoralist community.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
The technology and its function along the mainstreaming work with local development actors certainly improve the understanding and evidence-based knowledge of the land users.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
The technology is believed to increase both surface and groundwater quantity in the intervention valley.
Qualidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Surface runoff speed and volume are gradually decreased with the rehabilitation of the gully and the development of the area behind the structure.
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Soil moisture in the rehabilitated area positively increased.
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
As the structure on the upstream side reduces the speed of runoff, soil, and water loss decrease, and soil accumulation is increasing over time.
Acumulação de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
It increases with the deposition of sediments. Seeds of different trees and vegetation can emerge as succession species.
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Increases!
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
The structure and rehabilitated areas reduces the speed and impacts of the flood.
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Impactos da seca
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Overtime, tree cover reduces emission of carbon and green gases.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
Assessment of on-site impacts desires long-term follow-up, data collection, and analysis.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
As the technology put in place in recent times, off-site impacts need assessment based on facts.
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
The structure and rehabilitated areas inevitably reduces downstream flooding and siltation in the future.
Sedimentação a jusante
Comentários/especificar:
There is visible siltation held back by the structure. However, quantifying demands empirical analysis.
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
The facts regarding the off-site impacts will certainly be assessed as a long-term impact.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
| Inundação súbita | muito bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | bem |
Comentários:
Similar to on-site impacts, the off-site impact assessment needs, facts, and long-term follow-up.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Adoption rate is yet to be evaluated. The technology put in communal land.
Comentários:
No community so far adopted and implemented the technology on its own.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Rehabilitate the gully, and stop and reverse the gully formation. |
| It creates the opportunity for productive use of the degraded environment. |
| Recharge the groundwater aquifer and supply still water for temporary use by local people and livestock. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Promote regeneration of the lost species through resilience building. |
| Improve the landscape feature. |
| Improve the ecosystem and its overall services. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High investment cost to implement the technology. | Promote government awareness and emphasis on the benefit and investment in developing the technology. |
| Lack of implementation skills. | Develop the skills and motivation of the community and other stakeholders. |
| Conflict of interest on the use of the rehabilitated land in the intersection of neighboring kebeles. | Awareness creation and promote behavioral change on the joint benefit of the technology. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Inability to put micro check dams along the drainage line before it cuts deep into the soil. | Improve surveillance and promote early intervention. |
| Lower level of participation from the land users. | Develop the capacity, awareness and motivation of the land users. |
| Stakeholders and land users lower level of environmental education, improper land management and the consequent climate change and other associated adversities. | Promote environmental education, emerging climate change and climate variability in adult and vocational education. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Four individuals
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Two individuals.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
23/03/2023
Comentários:
The flash flood post three years of drought is so damaging. The fragile soil that has been exposed to the sun is easily detached and moved away by the flood. Substantial tons of soil stopped by the check dam signals the positive effects of the structure in changing the trends.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Criteria for optimizing check dam location and maintenance requirements. Hassanli, A. M. & Beecham. 2013; ISBN: 971-1-60876-146-3
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287636490_Criteria_for_optimizing_check_dam_location_and_maintenance_requirements
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Different Types of Check Dams & Design Procedures
URL:
https://forestrybloq.com/different-types-of-check-dams/
7.4 Comentários gerais
The questionnaire is comprehensive. However, to answer every question, there must be a tradition of long-term data collection and documentation exercises by either the project or the partners government organizations. In that way, it is possible to fully address the multifaceted demands included in the questionnaires such as " the before and after SLM intervention" which is dire to address them for those projects at their early stages of implementation.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [Etiópia]
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
Módulos
Não há módulos