Maize strip tillage [Suíça]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Streifenfrässaat
technologies_1010 - Suíça
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
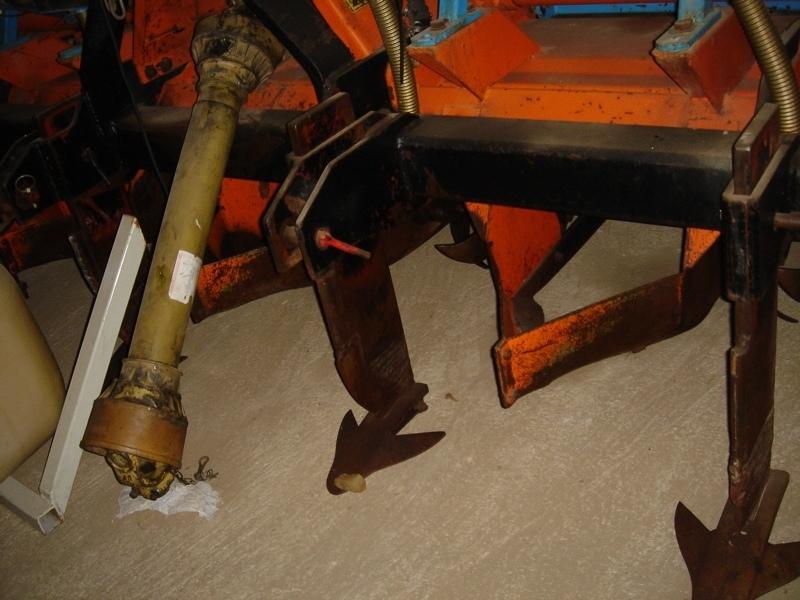
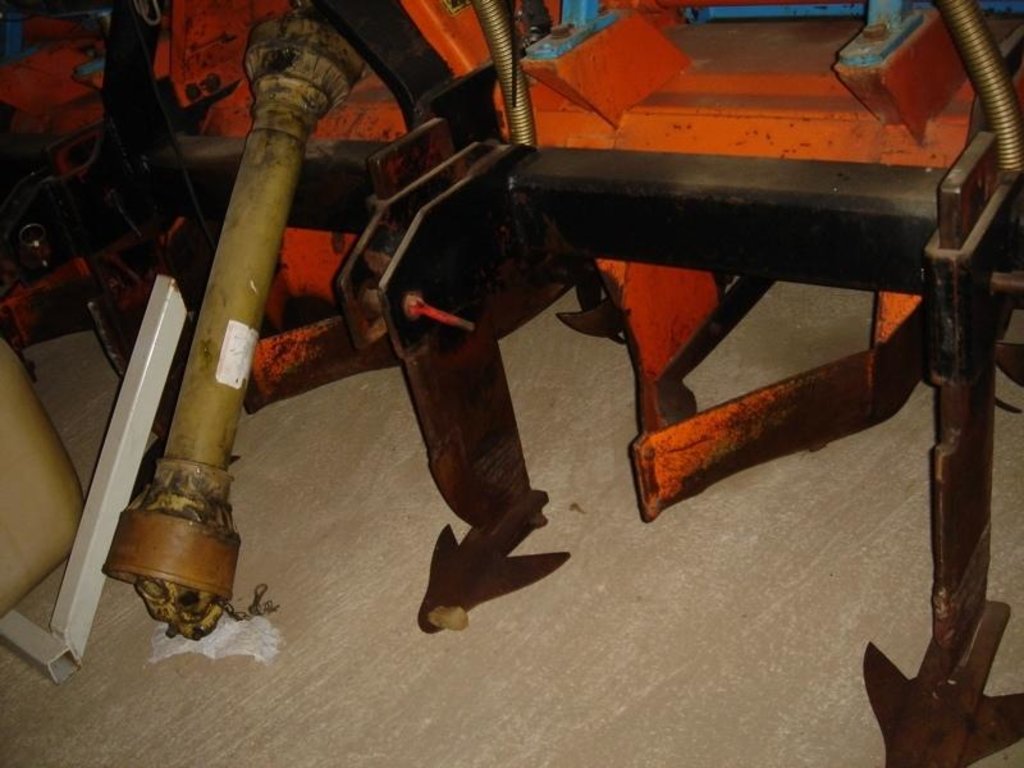
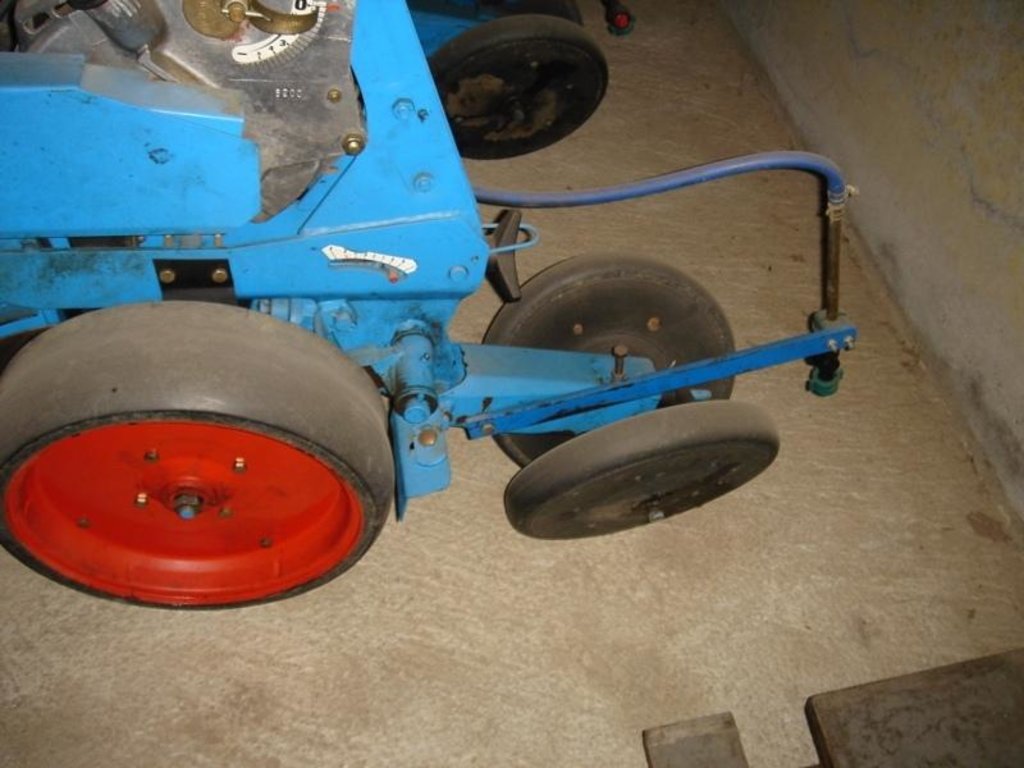
Maize strip tillage is a conservating method for corn production.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Maize strip tillage is a soil-conserving method used in crop production. First of all the grass in the area needs to be prepared by splattering round-up about 3-10 days prior to sowing.
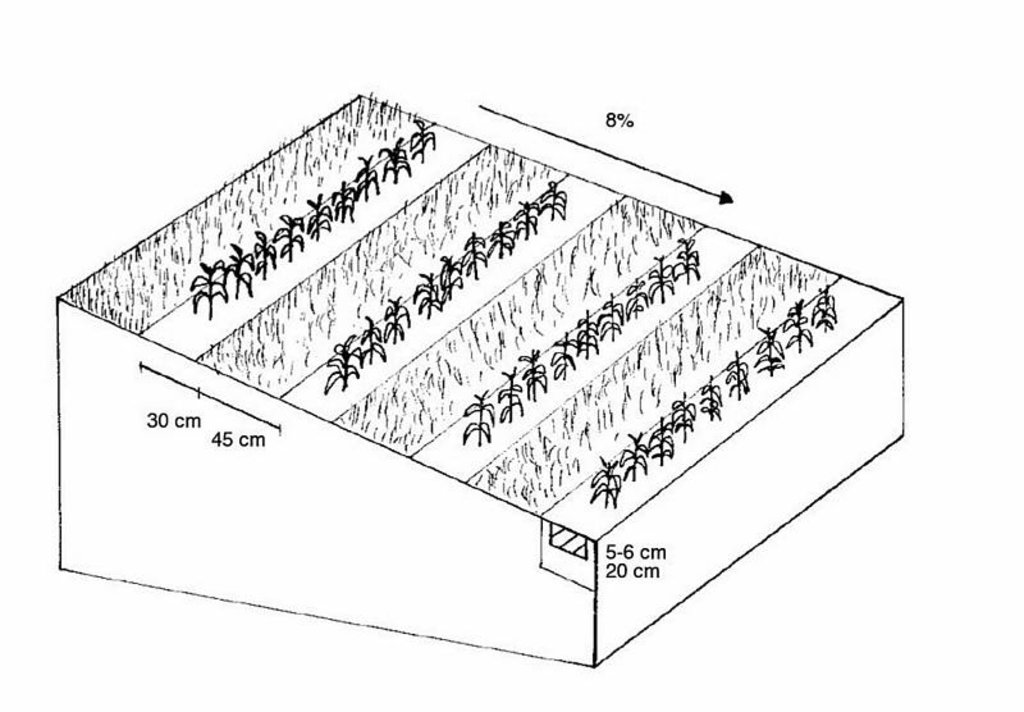
If the weather conditions are dry enough, a special grubber ('Flügelschargrupper') slacks the soil (20cm), the fertilizer is added in the stripes and afterwards the seed is added. Then the actual maize strip tillage machine carves a stripe and the seed are inserted within this strip of 30 cm. At the same time fertilizer is added on these cultivated stripes. Between those cultivated stripes the mulch-grass stripes (45cm) are unmechanised and protect the soil by increasing its stability. At the end a herbicide is applied on the cultivated strip. All working steps can be done at the same time compared to the traditional technique whereas the farmer needs to drive for each working step separately.
There are some clear economic advantages using this technology. It is less time consuming and the costs for diesel are also lower. On the other hand, by applying maize strip tillage the timing of the cultivation is very important and if the conditions are too wet, it is very likely that a farmer needs more herbicide in order to guarantee an optimal growth period.
However, like in a minimum tillage system there are some ecological advantages like enhancing soil stability. Another advantage is the better soil structure due to the mulch stripes. Due to these mulch-stripes the matrix of the soil is more complex and therefore the stability is better especially during the harvest in September. Soil compaction would occur less and the possibility of soil erosion is decreasing. Especially in hilly areas, as there are many in Switzerland, the technology is suitable since soil erosion is a problem in hilly areas when using a plough.
The interviewed farmer said that the farmers need a sound knowledge about the natural environment. Compared to the traditional technology, the farmers need to observe the corn plants carefully in order to ensure their growth period. Frthermore he said that the farmers need to get used to the sensitivity of this technology. If they are not applying the right amount of herbicide, the probability of getting a smaller harvest is increasing. If springtime is humid, the farmers should be able to use the traditional technology cause this SLM technology is only useful if the conditions are not too humid.
The interviewed farmer said that the economic advantages would be very beneficial to most of the farmers. Although the establishment costs for the machines needed for this technology seem to be high. The farmer can also hire a contractor like him and then he only needs to pay the labour but not the equipment itself. If a farmer wants to apply this technology, the canton of Bern provides them with subsidies during the initial 5 years.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Suíça
Região/Estado/Província:
Bern
Especificação adicional de localização:
Thunstetten
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
The farmer owns 35 km2 but is applying the technology on 100 km2 in the surrounding area
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
A decade ago a farmer invented the machine for maize strip tillage and the departmenet for soil conservation promoted this technology afterwards.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): If a plough is used when having a hillside situation the soil may easily erode.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The danger of erosion and soil compaction is accelareted when using a plough in a hillside area.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
A3: Diferenciar os sistemas de lavoura:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, minimum tillage
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (using the plough on hillside areas can increase soil erosion)
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Minimum tillage
Remarks: only where the crop seeds are inserted
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Swiss Franc
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
1,08
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
194.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying machine for stripe mill cropping |
Comentários:
Life span of the product: 15 years
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Applying Round-up herbicide on the area | 1 once before corn cultivation |
| 2. | Using of the machine for maize strip tillage, seeding and fertilizing within one workstep | 1 |
| 3. | Appliance for herbicide (Glyphosat) | 1-2 |
| 4. | Harvest of the corn | 1 |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Establishment costs are estimated for the contractor. Labour costs indicated above are the costs which the contractor is demanding for if he is hired. Additionally, those farmers who adapt this technology can get subsidies from the Canton if the farmer commits to apply soil conservation measures during 5 years, in Bern it is 450 CHF per ha.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour costs might seem high for a farmer if he delegates the establishment to a contractor. In comparison to the traditional cultivation system the contractor would ask about $240 for ploughing , $185 for harrowing , $92 for seeding, $70 for biocide and $46 for fertilizer per ha. Therefore using maize strip tillage is almost a third less expensive than the traditional cultivation. Most of the farmers that hire the contractor are applying the biocides themselves when using maize strip tillage, which makes the costs even lower.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average:
850-900 mm for the last 3 years
1200 mm some 10 years ago
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture is coarse/light (sandy) or medium (loamy, silty) (medium till light soils, depending on the area. On heavy soils technology is not applied).
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: 5-50 m (depending on the area)
Water quality (untreted): Good drinking water (depending on the region)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Usually the women are responsible for the administration and household and the men for the actual work on the fields, assuming that the decision to implement a new technology is made by both.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(His contract company is relatively large.).
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The area around the farmer house is individually owned but the surrounding agricutlural land is leased.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
With the grass stripes between the corn, the water can infiltrate faster and the soil is more stable and protected. The technology can be more tolerant towards intensive rainfalls but only to a certain moment. The technology is more sensitive towards humid conditions in spring and problems can accure when trying to apply the stripe mill cropping.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: If farmers have good experiences more than 80% are maintaining this technology even without external subsidies of the Canton.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The subsidies from the Canton are very supportive for farmers to implement the new technology
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos