Rehabilitation of degraded lands [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Yetegoda Meret Magegem (Amharic)
technologies_1070 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Incentive Based Local Level Participatory Planning Approach [Etiópia]
The approach involves, the use of incentives to motivate particpation of communities in the planning and implementation of SWC activities which improve land productivity and income.
- Compilador/a: Philippe Zahner
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Activities that help maintain the productive potentials of soils through prevention and reduction of erosion, enhancing of rehabilitation rate by practicing measures such as microbasins, trench, eyebrow terrace, terraces, pitting and plantation of trees.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The SWC technology comprises a combination of measures, which include agronomic, vegetative, structural and management measures. This means that in implementing the SWC technology combination of measures such as contour cultivation, grass strips, soil and stone bunds, area closure and improved grazing are applied in integration to rehabilitate degraded lands and restore their productivity. The purpose is to improve food security by reducing erosion and enhance the productivity of land by planting useful trees and fodder species. Unproductive land is changed to productive land by the practicing of the technology. The SWC technology is continously maintained and improved to meet the standards and qulity such that erosion is minimized. The technology is suitable to degraded and unproductive lands which were abondoned as result of low productivity and were previously under cultivation or grazing land. Closure of the area is followed by vegetative and structural measures to speed up the recovery / regeneration rate.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
SNNPR
Especificação adicional de localização:
Alaba special woreda
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 60 km2.
Some of the SWC technology areas are well rehabilitated and the remaining sites are partially treated, because these are being newly started sites.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is introduced technology.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrossilvipecuária

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- cereais - centeio
- cereais - sorgo
- Legumes e leguminosas - outras
- pepper, teff, chat, haricot beans, wheat
- vetiver, elephant grass
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- abacate
- cítrico
- café, cultivado ao ar livre
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
- Eucalyptus, sesbania, grevillea, acacia
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem

Floresta/bosques
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
- Conservação/proteção da natureza
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Improper landuse, defforestation, overgrazing, lack of action to control erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of awarness, traditional way of ploughing, lack of technolog on SWC
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: open grazing is practiced
Grazingland comments: Nowadays closing a small individual plots and practicing cut and carrying system is being popular among land users.
Plantation forestry: replacing natural forests
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Forest/woodlands are mainly communal, so, replanting forests is undertaken by the community. Individual forests/woodlands are very few and small in size since there is a shortage of land for forests and tree plantation.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Haricot bean is planted after maize is planted and has allowed some height.
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of Stone excavation (quarrying has caused a lott of damage on land.)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Coleta de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
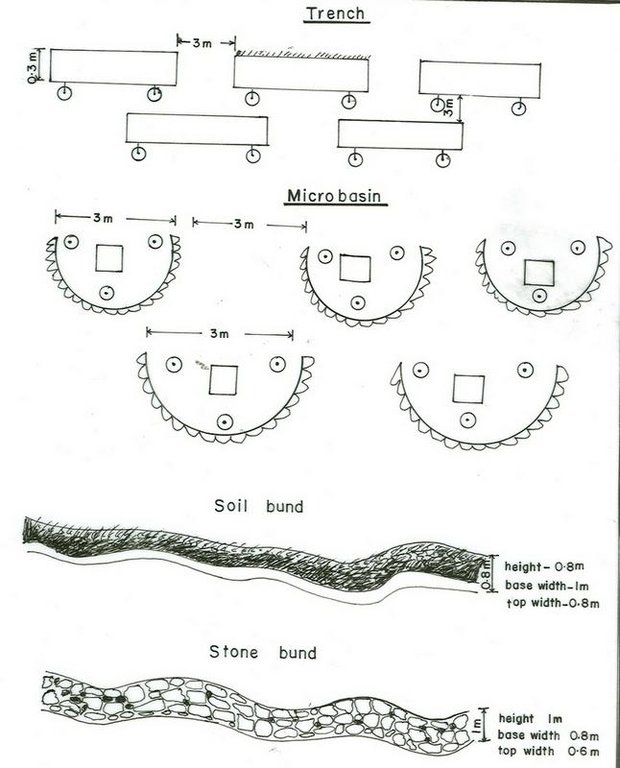
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Better crop cover
Material/ species: teff, wheat
Quantity/ density: 10,000,000
Remarks: broad casting
Early planting
Material/ species: maize, sorghum
Quantity/ density: 60,000
Remarks: row planting and broad casting
Relay cropping
Material/ species: maize-haricot bean
Quantity/ density: maize-hari
Remarks: row planting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize and haricot bean
Quantity/ density: 120,000
Remarks: row planting
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize, sorghum
Quantity/ density: 50,000
Remarks: strip cropping
Green manure
Material/ species: legumes
Quantity/ density: 100,000
Remarks: broad casting
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: leaves, cow dung
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: DAP, UreaTillag
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 10,000,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 111
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40000
Trees/ shrubs species: sesbania, grevillea, acacia
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango, avocado, orange
Perennial crops species: coffee, chat
Grass species: vetiver, elephant grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 80
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 40
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Bund/ bank: graded
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: degraded land to forest land
Major change in timing of activities: structure in dry season, plantation in rainy season.
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - protection of the closed area by site guards.
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Birr
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
8,6
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
0.70
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seed collection (grass, trees) | dry season |
| 2. | Seed bed preparation | on set of rain |
| 3. | Sawing & Planting | rainy season |
| 4. | Site selection | dry season |
| 5. | participatory planning | dry season |
| 6. | Area closing | dry season |
| 7. | Trench, microbasin bund construction | dry season |
| 8. | Plantation | rain season |
| 9. | Site selection for closure area | dry period |
| 10. | Closing the degraded land | dry season |
| 11. | Construction of structural measures | onset of rains and dry seasons |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 387,0 | 387,0 | 26,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 85,0 | 85,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| Material de construção | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 512,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 59,53 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage/plough | dry season / annual |
| 2. | Compost making and application | before dry season / annual |
| 3. | Sawing and planting | / each cropping season |
| 4. | Plant protection | wet season / annual |
| 5. | Harvesting | dry season / each cropping season |
| 6. | Replanting | rainy season /once a year |
| 7. | Weeding | after rains /once a year |
| 8. | Cutting the matured trees | dry season /once a year |
| 9. | Replanting | rainy season/once a year |
| 10. | Reconstruction of structures | dry season/once a year |
| 11. | Planting trees | rainy season / once a year |
| 12. | plant and harvest grass | / before and after rains |
| 13. | Replanting | / once a year |
| 14. | Terench and structural measures stablization with plantation | / once in a year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 46,7 | 46,7 | 5,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 60,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 6,6 | 6,6 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 10,0 |
| Material de construção | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 41,4 | 41,4 | 2,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 101,3 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 11,78 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, wheel barrow, hammer
The cost is calculated for PD/person days on a hectar basis
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Tools and transport facilities (motorcycles), fuel and food grain.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
850-950 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (ranked 1) and 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (1700-2200m a.s.l., ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (ranked 1) and moderate (ranked 2, about 70% of the land is on a slope of 2-8%)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked1) and medium (ranked 2, sandy loam)
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (well drained)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (because it is sandy loam soil)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are very rich.
25% of the land users are rich.
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
5% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who practice SWC measures get better production. Their incomes has increased compared to those who have not applied SWC.
Market orientation of cropland production system: subsistence (self-supply, part of the production is sold at local market), mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: subsistence (self-supply, fodder plant for milk cow), mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Market orientation of forest production system: subsistence (self-supply, tree plantation on individual plots ), mixed (subsistence/ commercial), commercial/market (plantation of a community forests)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Cropland: average cultivated land is about 1.5 ha/household
Grazing land: not more than 0.125 ha on average
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção de madeira
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
decrease of grazing land
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
75
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Comentários/especificar:
structural measures
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
52000
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
46800 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays land users have better understanding on SWC technologies, so they protect their farm land from erosion with vegetation.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
SWC knoweldge is gained How can they be sustained / enhanced? through training and practical works |
|
additional income is created How can they be sustained / enhanced? diversification of SWC measures with in the same plot |
|
group work is encouraged/introduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? strengthening group formation |
|
food value has increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? from vegetables and fruits |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
degraded lands are rehabilitated and covered with plantation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? through increased participatory planning approach |
|
crop production has increased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? apply more combined technologies to enhance production |
|
wood production has increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting multipurpose plant species increased |
|
extensive grazing is changed to intensive grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? to some extent number of animals are reduced |
|
the community is aware of the technilogy How can they be sustained / enhanced? land users construct SWC technologies on their farm land by their own |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| shortage of grazing land | use cut and carry system |
| destruction of crop by wild animals | making farmers group to protect them |
| shortage of incentives | practicing more community participation works. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Incentive Based Local Level Participatory Planning Approach [Etiópia]
The approach involves, the use of incentives to motivate particpation of communities in the planning and implementation of SWC activities which improve land productivity and income.
- Compilador/a: Philippe Zahner
Módulos
Não há módulos