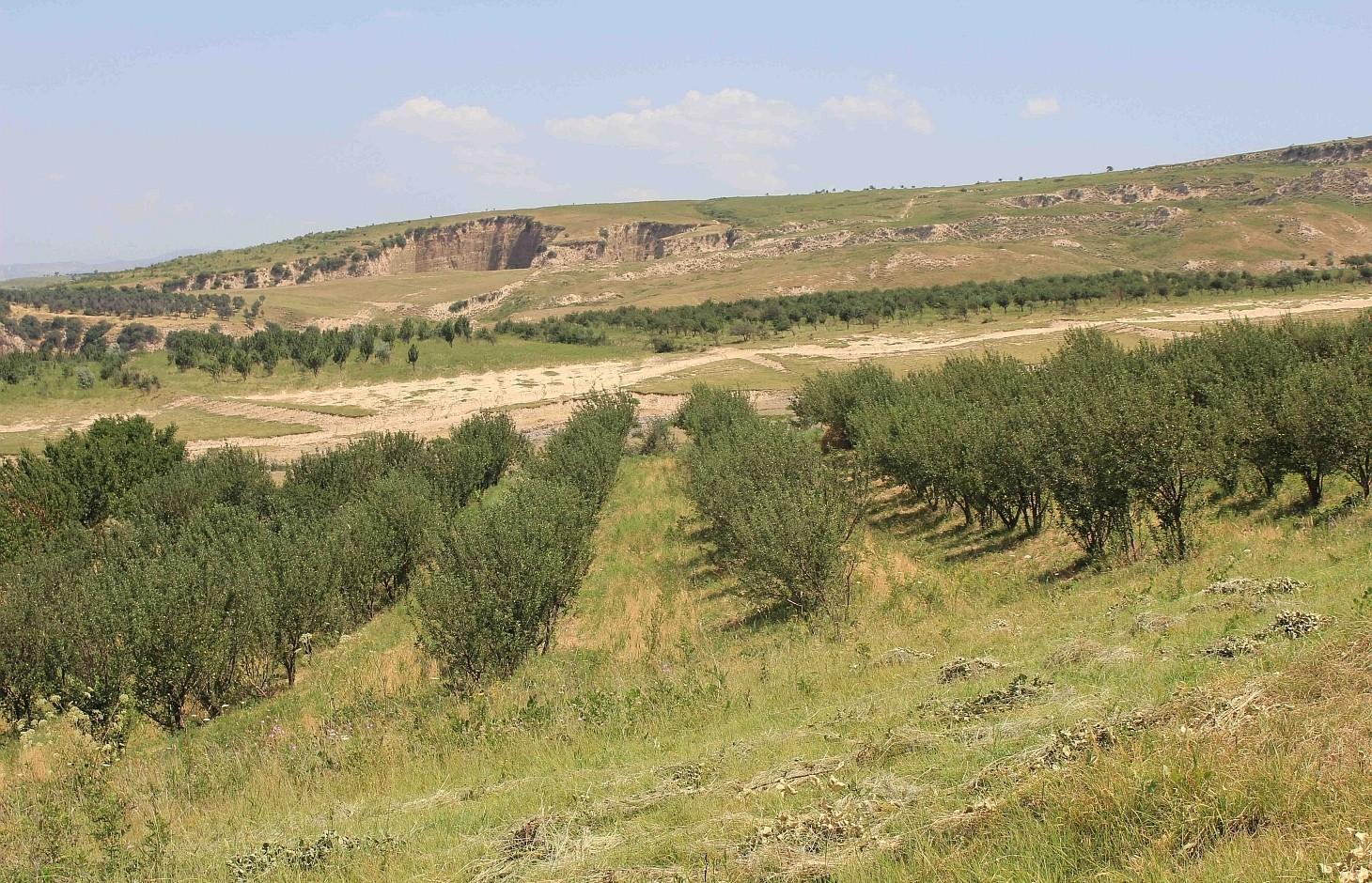
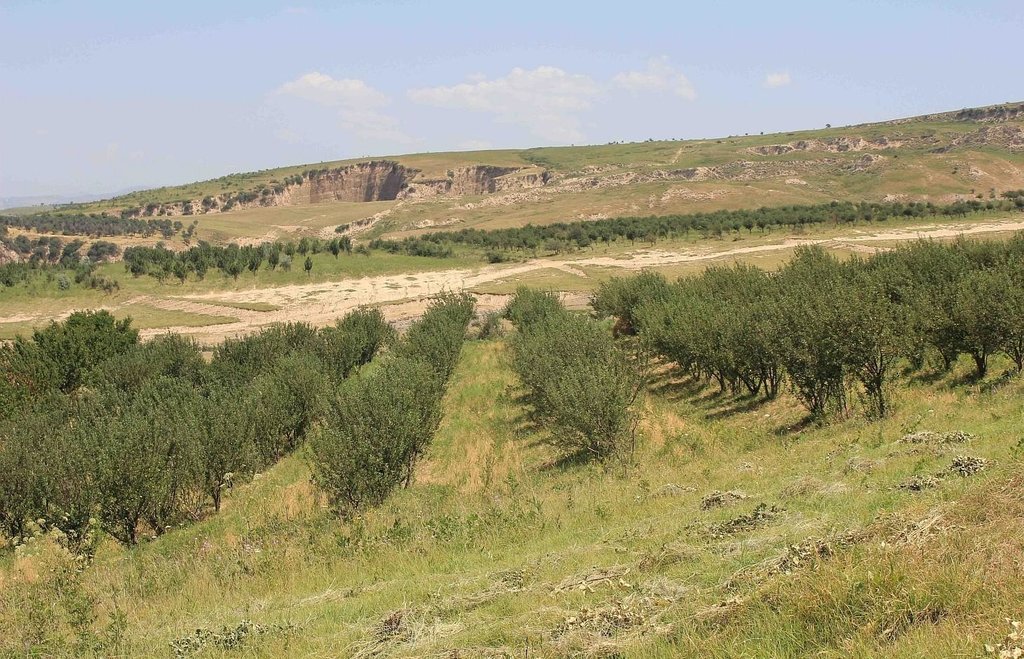
Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Laura Ebneter, Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
Bog
technologies_1128 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 28 de Dezembro de 2016 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 31 de Maio de 2017 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 2 de Junho de 2017 (inactive)
- Mixed fruit tree orchard with intercropping of Esparcet and annual crops in Muminabad District: 4 de Agosto de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - QuirguizistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Orchard based agroforestry established on the hill slopes of Muminabad
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Between 1993 and 94 an individual farmer initiated an orchard by planting a mix of fruit trees, such as apricots, walnuts, cherries, almonds and mostly apple trees in the rainfed hill zones of Muminabad District.
In the first couple of years 416 newly planted seedlings were watered manually: water was brought by trucks near to the plot and distributed to the seedlings with buckets. The orchard was established on the existing grazing land and therefore the seedlings had to be secured with a fence from livestock grazing nearby. First hard wire was used for fencing. Simultaneously, hawthorns (Dulona in Tajik) were planted along the fence in order to provide even stronger protection and establish a live fence for the future. Now, the fruit trees are fully-grown and fruits can be harvested every year. The farmer prunes trees annually, which is the key for fruit production. The farmer pointed out that in rainfed areas soils contain less nutrients and usually big trees do not produce high yield. Furthermore, pruned tree branches are used as firewood. The farmer also applies the pesticides B52 and B58, three times a year in the months of April, May and June. The total area of the plot is 1.03 hectares, whereof 0.60 hectares are orchard; Esparcet is covering roughly 0.30 hectares, 0.07 hectare is for haymaking and the rest of the 0.06 hectares is used for growing chickpea and wheat. There is also a road for machinery to pass and to turn around when plowing the land.
Purpose of the Technology: Shortly after the fall of the Soviet Union, the government officials distributed land to the villagers. The farmer always had a big interest to establish a small orchard and he obtained little more than a hectare of land. It is his project for retirement. He and his family worked hard throughout the establishment phase. They experimented by planting a variety of vegetables including melons and watermelons. The wild animals ate many of the vegetables and melons, what resulted in the farmer's idea of intercropping Esparcet.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: According to the farmer, the first two years were very labor intensive and crucial to establish the orchard. He also had to face a challenge posed by the community, as overnight people from the nearby villages stole roughly 100 of his newly planted seedlings. This is one of the reasons why the farmer had to plant hawthorn in order to establish a live fence. In summary: The establishment phase included planting of young seedlings; manually watering for the first two years; plowing in between the tree rows by machinery; building a fence around the plot and planting/sowing hawthorns. Maintenance activities consist of the following activities: planting new seedlings; pruning of existing trees; grafting new sorts of trees, plowing by tractor in between the tree rows annually; chickpea and wheat cultivation; application of chemical pesticides three times a year. For cutting wheat, the farmer gets support from his son and friends. Every day, he goes to his orchard, which is located at a distance of more than 1.5km from his house. When this technology was documented he was about to build a small clay hut in his orchard.
It should be noted that the terrace structure was not implemented at once, but over the years tilling in between the tree rows along the contour lines formed terrace shaped rows.
The structure of terraces has been built over the years by tilling in between tree rows along the contour lines.
Natural / human environment: Muminabad is situated in the southwest of Tajikistan (Khatlon Province) and its hills are covered by loessial soil. Winter temperatures are low and the amount of precipitation is high. Summers are very hot and dry. The growing season lasts from March/ April to September/ October.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Muminabad
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
1.03 ha in total, whereof 0.6 ha is orchard
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/oct
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
wheat, chickpeas

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade

Floresta/bosques
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion by water, heavy rainfalls, absence of vegetative cover on the hill slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water, extensive grazing, gully erosion.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Extensive grazing led to a reduction of soil cover, which is the major source of erosion), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Removal of trees left the soil unprotected against precipitation and extreme weather events), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees were cut as firewood for fuel consumption), overgrazing, land tenure (Land abandonment after Soviet collapse), governance / institutional (Lacking istitutional support)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More extreme rainfall events), floods (As a result of extreme events there are more floods in the region)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The fenced plot is mainly used for the orchard intercropped with chickpea, flax and wheat. Esparcet and grass for haymaking covers only a small part of the plot. The part on the left handside is also used to turn the tractor when ploughing, which is why this part is affected by soil erosion and rills. The whole property is fenced by hawthorns (dulona). The orchard has a terrace-like structure due to annual plowing by tractor.
Location: Sarmaydon 2. Muminabad
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 416
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, apricot, pear, cherry
Other species: intercropped with chickpea and wheat
Autor:
Q. Shokirov
Data:
12-07-2012
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,83
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
12.40
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging a deep barrier for protection around the plot with a bulldozer, 1 day | once (1993) |
| 2. | Plowing in between the rows by tractor, labor, petrol and rent for one day | once (1993) |
| 3. | Planting fruit trees, 3 days by 3 persons (3-5 Somoni per seedling, 3 Som/ seedling planting) | once (1993) |
| 4. | Watering young seedlings for the first couple of years by truck (60 TJS per truck) | one day a week/ 50 times a year |
| 5. | Construction of fence with hard wire and haw thorn (approx. 320m) | once |
| 6. | Buying and replanting of 100 stolen fruit seedlings | once |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4629,333 | 4629,33 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 227,833 | 227,83 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Petrol | l | 20,0 | 1,14 | 22,8 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | Pieces | 516,0 | 0,621 | 320,44 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Hard wire and pillars | m | 320,0 | 1,4556 | 465,79 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 5666,19 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1173,12 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor ploughing, labor, petrol and rent, 1-2 hours, 2 persons | spring, once a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around trees, 5-6 days, 3-4 persons | spring, once a year |
| 3. | Pruning of the approx. 400 fruit trees (3 TJS per tree) | every year |
| 4. | Bringing water from village and watering (40 liters a day,20l on each donkey, 3 h for walking and watering) | every day |
| 5. | Applying pesticides, 1 person, 7 days (5 hours per day) | Three times a year: April, May, June |
| 6. | Sowing wheat and chickpea (1 person, 2 hours) | spring, once a year |
| 7. | Cutting wheat and chickpea (2 persons, 4 hours) | autumn, once |
| 8. | Harvesting fruit trees (3.6 TJS per fruit tree) | autumn, once a year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4493,5 | 4493,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 10,3 | 10,3 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Petrol | l | 20,0 | 1,14 | 22,8 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Pesticides | kg | 0,25 | 186,0 | 46,5 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | pc | 1,0 | 3,7 | 3,7 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 4576,8 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 947,58 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The technology was established during the Soviet Union and most of the expenses were calculated on the price basis of that time. If technology is priced by current prices, the total sum would be very high and no farmer would be able to afford. Thus, current prices were not identified. Nowadays, machinery cost, buying hard wire for fencing and buying seedlings would be the most costly factors.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Inutilizável
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Comentários:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção de madeira
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Oportunidades de lazer
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
After 6 years income is very comparable to the establishment cost
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
98% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Cost of the technology is very expensive, which discourages farmers to implement orchards based agroforestry.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Grafting trees especially apple and pear trees on native hawthorns is an affordable and sustainable way of creating orchards in semi-arid areas with rainfed agriculture. Hawthorn is a plant adjusted to dry areas with strong and deep roots, which endures the hot summer months. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tree nursery workshops and educational programmes about local species through seed associations |
|
Intercropping wheat, chickpea, flax and Esparcet in between the tree rows gives an extra economic incentive and also improves land productivity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge raising, inspection of those good practices by other farmers |
| Haymaking with natural grass and Esparcet provide the farmer with an opportunity to produce hay for the winter months for his livestock, so that he does not need to purchase it from the market at high costs. |
| The farmer practices pruning on a regular basis to keep the trees in good shape for better fruit production, but also to have sufficient fire wood for the winter months. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Compared to other plots with orchards there is almost no soil erosion which is mainly due to good land management practices, e.g. the slow building up of terraces. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustain the practice of contour ploughing |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It is expensive to establish such orchards nowadays, because of the high cost for purchasing seedlings and hiring other machinery. | See comment below |
| Growing new seedlings and grafting trees is a cheaper way of establishing a new orchard, but it is not commonly practiced among the farmers in the region. | There should be a tree nursery workshop in order to raise awareness among the young generation of farmers. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Since the orchard is located in a rainfed area, hot summer months make the technology vulnerable to drought. To some extent the technology is tolerant to dryer summers, but maybe not for prolonged droughts (e.g. two successive drought). |
The farmer has suggested that grafting fruit trees on native hawthorn (dulona) trees has potential for farmers when establishing orchards in rainfed areas. In extreme events (extremely dry years), the farmer brings water for supplementary irrigation from his house by donkey. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos