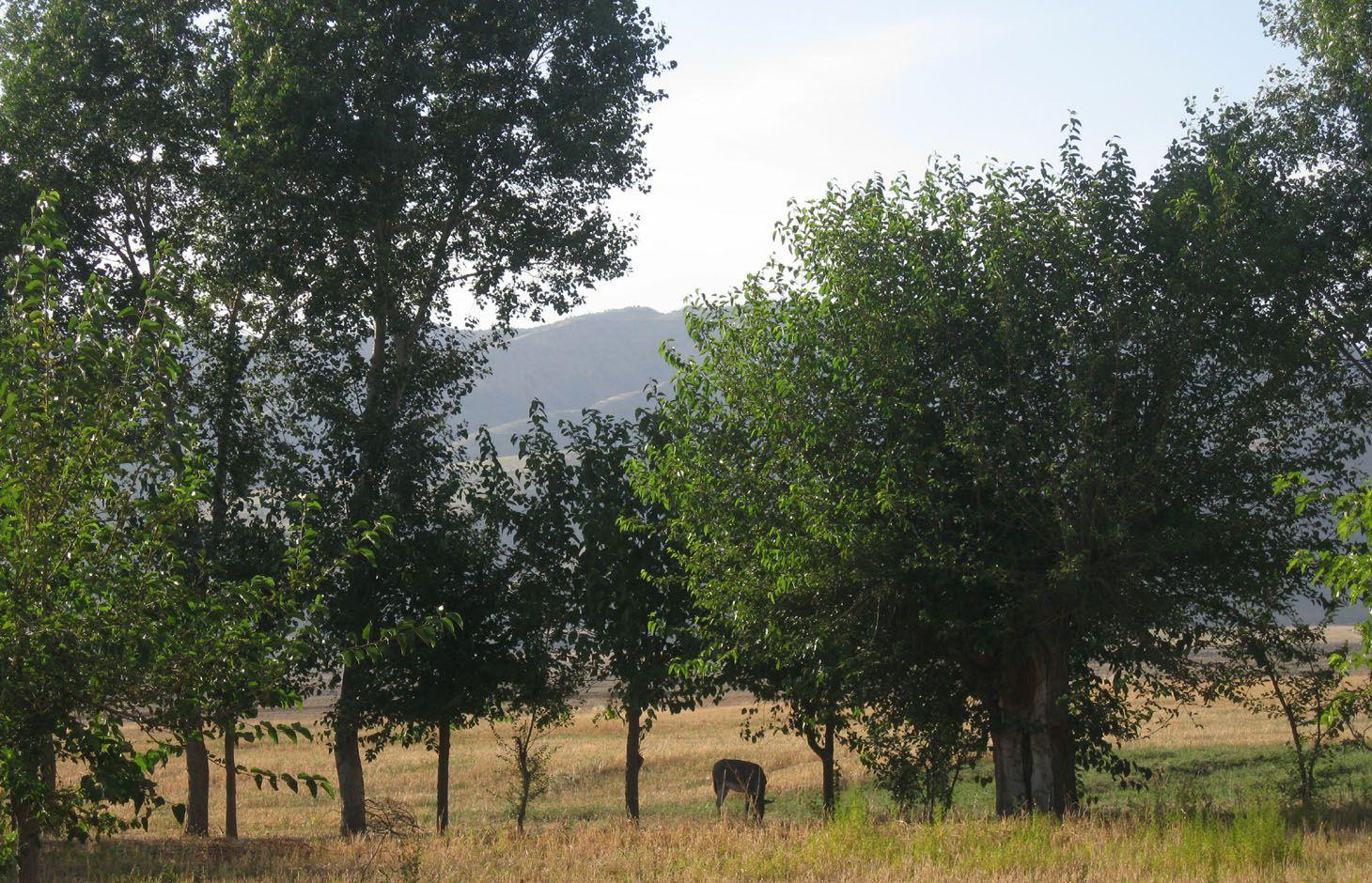
Current agroforestry: orchard with wheat intercropping [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1134 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Current agroforestry of a degraded mulberry and apple orchard with wheat intercropping
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Since 1992 an area of around one ha has been owned by the farmer. He planted mulberry trees the same year. At that time, orchards were established in the whole surrounding area because the government decreed that a territory should have plenty of mulberry trees. Despite the government plan, all the land users of that area began to switch their orchards into wheat crops. Five years later the farmer planted apple trees within the mulberry orchard. The orchard had 200 mulberry and 100 apple trees. The motivation was to feed the working farmers of the fields around. Five years later the apple trees gave fruits. But only the first two years gave a good yield and income from selling them. Later on the fruits were just eaten by the farmer’s family. After another seven or eight years the farmer grew a wheat crop in between the tree lines. Nowadays it's the only remaining orchard in that area. Due to the lack of proper maintenance and water availability the orchard is degraded and the output is very low.
Purpose of the Technology: The government established a large territory of mulberry orchards, for three reasons: First to reduce the impact of natural hazards, second to increase silk production and last to improve fire wood availability. The planting of apple trees should be beneficial for farmers working in the surrounding crops and well as for the family, who sell the fruits and the mulberry leaves. As the yield started to decrease the wheat crop was established to have a bigger output for that crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Due to the government’s order to establish orchards, the local authorities provided the mulberry trees. Hence, it was in the responsibility of the farmer to plant the trees and to look after them by soil loosening and pruning. The latter activity must be done once in the first five years after planting. The farmer bought the apple trees himself as they were cheap at that time. To establish the wheat crop, ploughing, seeding, fertilizing and finally harvesting must be done. One person is supposed to guard the orchard and wheat crop every day. Yearly maintenance consists of soil loosening around the fruit trees and the above mentioned task for cropping. The maintenance of the orchard seems to be abandoned more and more, probably because the output decreases year by year.
Natural / human environment: The orchard is situated below Momandion village, on the very last foot slope before the valley plain begins and, hence, it has a slight slope,. In the past, orchards were numerous, but nowadays wheat crops have mostly replaced the orchard. As there is no fence and no one to control it regularly, livestock invades the property. During its first two years there was a water source, which had dried up by the time. The orchard is a relic being the only and last one in that area. Broken branches, unpruned trees and a trampled crop, show signs of insufficient control and maintenance and therefore of a gradual abandonment of the orchard.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Muminabad
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
According to farmer it's 1 ha, according to GoogleEarth around 1.6 ha
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
- government
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Since 1992 it's property of the farmer
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- frutas silvestres
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas, outros
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
wheat crop

Pastagem

Floresta/bosques
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Trampled and degraded soil as a consequence of no fences or control. Soil crusting and compaction because of lack in organic matter resulting in a low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water scarcity and low soil moisture, small yield of the fruit trees
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: In the past the wheat and apple yield was much higher thereby they were cash crops. As the yield decreased by then and he gets low yield the use them as food crops.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (monocropping, lack of maintenance)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Because if no fence), education, access to knowledge and support services (More agronomic/ technical advice needed)
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Location: Muminobod, South of Momandion, Obishur Watershed. Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (How to regenerate the poor soil and water conditions, which species are useful to plant etc)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat intercropping within orchard
Agronomic measure: vertical plowing
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, apple
Change of land use type: Mulberry and apple orchard combined additionally with wheat crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More pressure on natural resources because of additional wheat crop in the orchard
Autor:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,83
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
12.40
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying, transport and planting of mulberry trees, 10 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1992 |
| 2. | Buying, transport and planting of apple trees, 5 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | once, 1997 |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 497,4 | 497,4 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 311,0 | 311,0 | 33,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 808,4 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 167,37 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing vertically, 4 hours of labour, tractor and petrol | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 2. | Buying (200 kg) and sowing wheat, 2 hours, 3 persons | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer, 2 hours, 1 person, 2 bucks à 50 kg | once a year, september |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 4-5 days (6 hours/ day), 4 people | September, once a year |
| 5. | Guardening | every day |
| 6. | loosening around trees (ca. on 1/3 of the trees), 4-5 trees a day | every year, spring |
| 7. | pruning (ca. 1/2 of mulberry trees), 7-8 days (2-3 hours/ day), 3 persons | every year, autumn |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 572,2 | 572,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 24,8 | 24,8 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Petrol | l | 25,0 | 28,5 | 712,5 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 82,8 | 82,8 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 76,6 | 76,6 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 1468,9 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 304,12 | |||||
Comentários:
The cost were calculated for 1 ha, but one have to consider that an orchard and wheat crop is on the same plot. This means that there's not fully a wheat crop of 1 ha.
Mulberry seedling were paid by the government, apple trees by the farmer.
Machine use and petrol, are all included in the labour input in the establishment phase, as it was not separately mentioned by the farmer.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour is the most important input, but as it is done mostly by the farmer or the family itself it's mainly agricultural material as seedlings, seeds and fertilizer. Latter particularly as recurrent costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked1, mostly) and rolling (ranked 2)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, no rainfall from July to August) and medium (ranked 2, winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm))
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and mechanised (ranked 2, only for plowing)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, mainly subsistent, depending on yield more or less commercial) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Based on land user's Certificates
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
less apple and wheat production
Risco de falha de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
More fertilizer and pesticides needed than in the past
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced crop production and fruit yield
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
less maintenance work
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Mulberries were shared with other people working next to the field (no fence)
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
negligible thanks to a little slope
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
Higher vegetation cover, which would make the land use more resistant to drought, more stable in case of floods and heavy rainfalls.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The orchard gave by-product as leaves for silk production and branches. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It is the only orchard in the neighbourhood, which is why it would be worthy to maintain it. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Put more effort and labour into the orchard, currently only the wheat crops seems to be of interest for the farmer. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Currently the orchard is too old to get a good yield and maintenance activities are comparatively high. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Lack of maintenance and guarding or fencing. | More focus on the orchard as it has also ecological benefits. Enhance the farmer to put more labour into the orchard. |
| Show good examples of orchards and their resulting benefits. Round tables by and for farmers to share experiences. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos