Hydromulching for reducing runoff and soil erosion [Portugal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Sergio Prats Alegre Prats
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Valentin Zuercher, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Hydromulch
technologies_1299 - Portugal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Keizer Jan Jacob
Centre for Environmental and Marine Studies (CESAM) - Department of Environment and Planning-University of Aveiro
Portugal
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) - PortugalNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - Portugal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
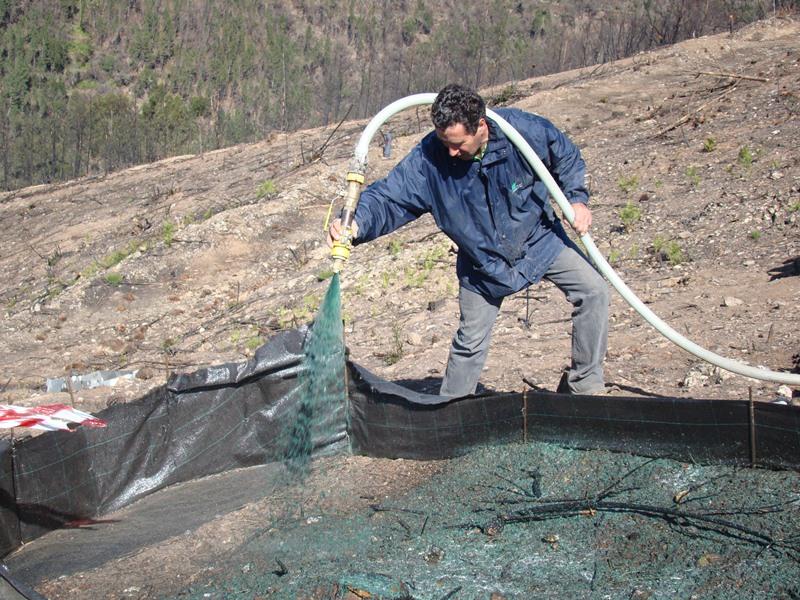
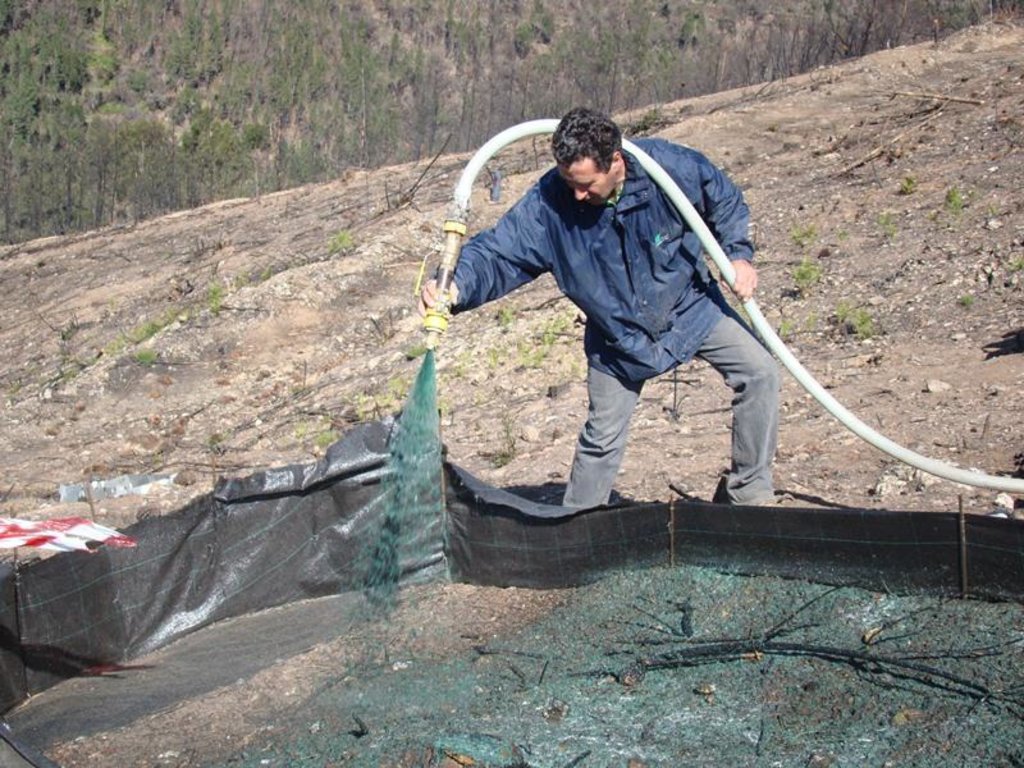
Hydromulch is spread immediately after a wildfire in order to reduce overland flow and prevent soil erosion.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The research team of the University of Aveiro in collaboration with the fire Brigade and a private company applied the hydromulch in a burnt pine area burnt at moderate fire severity. Hydromulch was spreaded manually from a jet hose over a group of erosion plots, and both runoff and erosion were compared to an untreated group of plots.
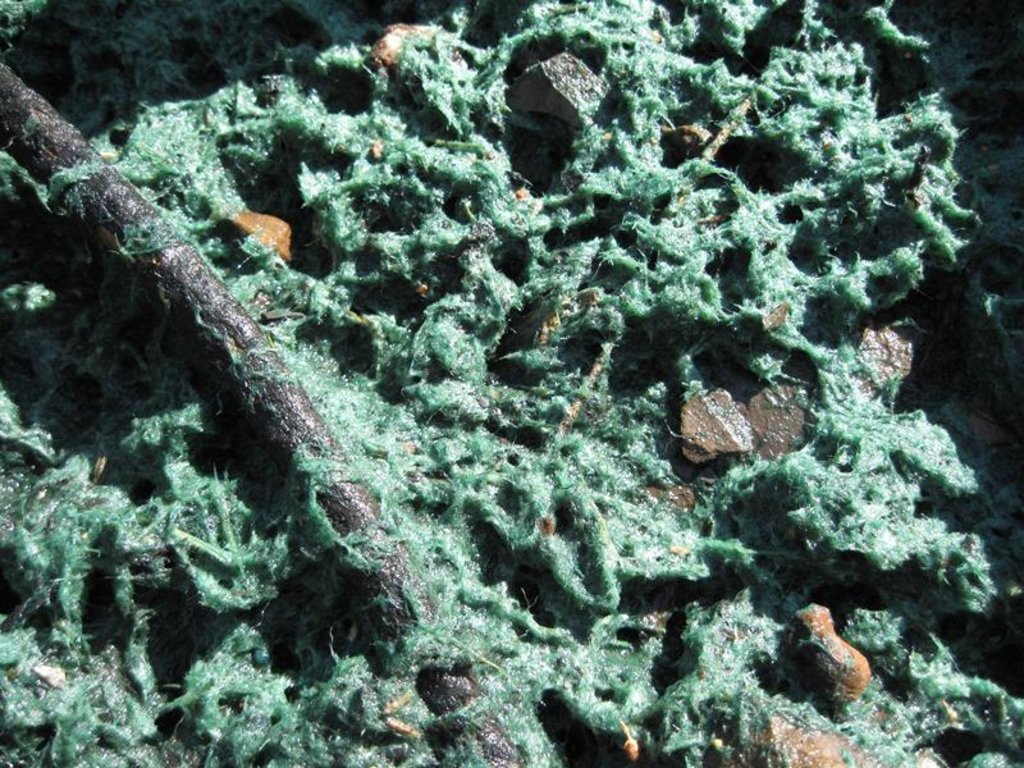
The hydromulch was applied at a ratio of 3.5 Mg ha-1 providing an initial ground cover of 80%, and was found to reduce post-fire runoff in 70% and soil erosion in 83%.
Purpose of the Technology: Hydromulch has been particularly useful on steep slopes and strongly modified areas such as quarries, construction sites, and cut and fill slopes along roads (Robichaud et al., 2010). The hydromulch is a complex mixture which contain basically water and wood or paper fibers. Additionally it can contain seeds, surfactants, seed-growing biostimulants, nutrients and a green colorant. It is intended that each component affected some of the pieces of the post-fire runoff erosion process.
The high effectiveness in runoff reduction could be related to the effect of the wood fibers, because it increases the surface water storage capacity, but also due to the effect of the surfactants, a wetting agent that reduces SWR and increases soil infiltration. Ideally, post-fire hydromulching must be carried out immediately after the fire, over bare, unprotected and steep burnt areas. It is intended for places in which burnt severity was moderate to high and where there are very important values at risk, such as water reservoirs, populations, industries, human and wild life.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The hydromulch is applied once, immediately after the wildfire, aerially, from a tractor or also manually by using a jet hose operated by a person on foot. It basically consisted of a mixture of water, wood fibers and seeds. The seed composition should include autoctonous plant species, in order to avoid alien species into the burnt area and increase the germination success. Besides the composition, the application technique can influence the hydromulch effectiveness. Rough (2007) and Robichaud et al. (2010) reported that the hydromulch sprayed from vehicles was intercepted by the standing trees, and they recommended special caution when applying the mixture in areas with a high density of dead trees and from long distances. Aerial hydromulch can be a better and less expensive option, but Hubbert et al. (2012) checked that the intended application rates of 50% and 100% hydromulch cover resulted in only 20–26% and 56%.
Natural / human environment: The natural forest in central Portugal has been substituted by pine and eucalypt trees that are typically planted as monocultures for wood and paper pulp production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. In recent years, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, and have been associated to soil fertility losses, and consequently to socio-economic losses.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Portugal
Região/Estado/Província:
Portugal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Gois-Colmeal
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Plot experiments
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Hydromulch has been particularly useful on steep slopes and strongly modified areas such as quarries, construction sites, and cut and fill slopes along roads (Emanual, 1976; Benik et al., 2003; Robichaud et al., 2010).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Floresta/bosques
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Increased runoff and soil erosion, resulting in a decrease of on-site fertility and derived off-site effects such as loss of water quality, reservoirs water volume storage, higher risk of flooding and human beings damage.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources and productivity.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): price
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: September to May
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Monoculture of forest plantations prone to forest fires)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
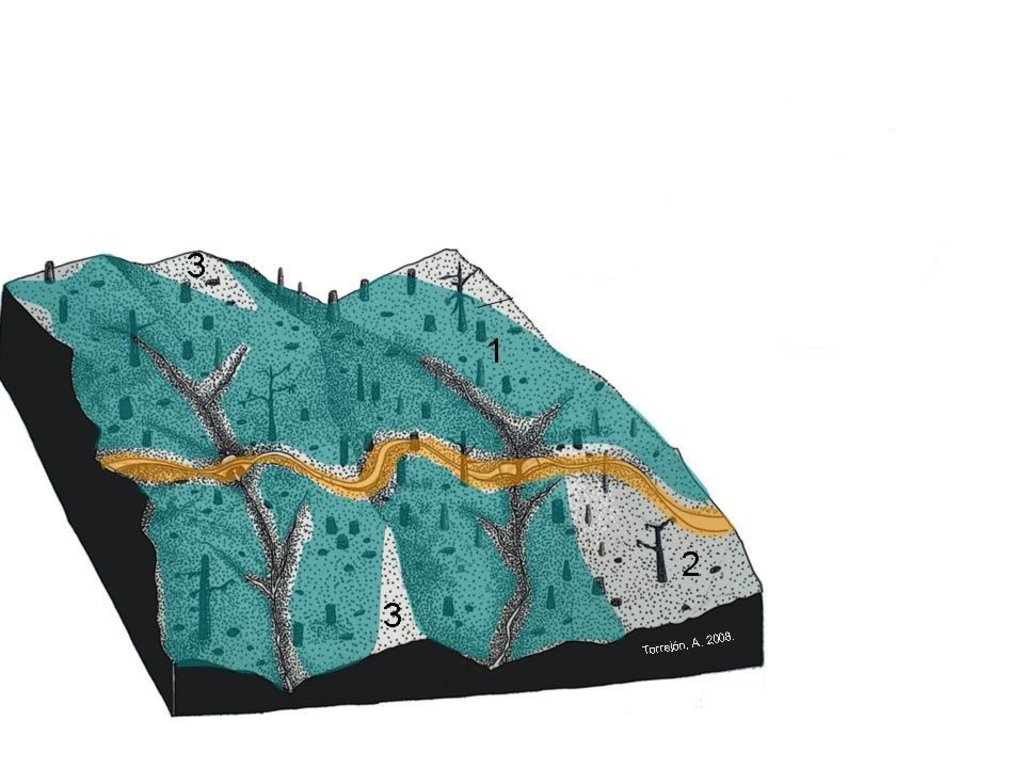
Hydromulch should be spread as homogeneous as possible over steep areas (higher than 15º) burnt at high fire severity (represented in green and 1). Other areas which are flat (2) and burnt at low severity or only partially burnt (3) must be avoided.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: water-based mixture of organic fibers and green colorant
Quantity/ density: 3.5Mg ha-1
Remarks: achieve a ground cover of 80%
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
euros
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
0,78
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
64.50
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Apply hydromulch | |
| 2. | Trasportation (Track with a jet-spreading system) | |
| 3. | Other |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 128,2 | 128,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 128,2 | 128,2 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Hydromulch | ha | 1,0 | 3205,0 | 3205,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Others | ha | 1,0 | 128,2 | 128,2 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 3589,6 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 4602,05 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
Lifespan of the hydromulch: 1 year
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
The prices were determined in winter 2009 for central Portugal. In other regions and for other formulations these prices can vary. When compared with straw mulch its price is extremely high, but despite this greater expense, hydromulching has been used especially in the USA after some fires when access was difficult, the slopes were too steep or subject to wind to use straw mulch and when there were particularly important ‘values at risk’, such as water reservoirs, cultural or natural heritage sites, national or regional wildlife protected areas or industrial plants
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Accessibility and steepness will raise the costs, but selecting hydromulchings is also a main factor. The more complex the hydromulch the more expensive the application cost. Hydromulch with seeds have also the possibility of introducing invasive plants into the ecosystems and increase the costs. For large and inaccessible areas the aerial hydromulch can reduce the costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture is medium (sandy-loam)
Soil fertilits is high
Topsoil organic matter is high (forest soil)
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor-medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water quality (untreated) is for agriculutral use only (surface water)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Forest plantation
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
60% of the land users are poor.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Livelihoods and human well-being (eg education, health) are not changed by the use of Hydromulching.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Comentários/especificar:
If hydromulching is with seeds, it can introduce invasive species
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Hydromulch is seen as a very expensive treatment without clear advantages at the short term, but good at the long term period.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology has not been applied by any land user. It is a newly research-developed technology.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The owners are not aware because of the costs, but they will change if the government start funding it.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
It will prevent sediment movement and accumulation over roads and down slope properties and values at risk. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By developing more economic application formulations and schemes. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It is a technology that has the advantages of the mulching technique and also can be used as a tool for increase the biodiversity, expand the distribution of some protected plant species at the same time that soil is keep in place. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The use of longer mulch fibers can still increase the hydromulch effectiveness, since some researchers found the longest fibers to be more effective in soil erosion control than the shorter ones. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Hydromulch is very expensive when compared to straw mulch, but not more effective in post-fire soil erosion reduction. | To develop hydromulch mixtures using the lowest amount of water as well as other chemical components to the minimum. |
| Some researchers found very low performance due to the interception of the hydromulch jet by the dead standing trees | Verify when applying it that the ground coverreach a minimum of 60% |
| Sometimes the mulch component (wood fibers, chopped paper) can be removed very easily by heavy rainfall, and thus treatment effectiveness can decrease greatly. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
EFFECTIVENESS OF HYDROMULCHING TO REDUCE RUNOFF AND EROSIONIN A RECENTLY BURNT PINE PLANTATION IN CENTRAL PORTUGAL. Prats et al. (in press). Land Degradation and Development DOI: 10.1002/ldr.22362-Effects of hydromulch on post-fire erosion and plant recovery in chaparral shrublands ofsouthern California. Hubbert et al. 2012 International Journal of Wildland Fire 21:155–167.Rough D. 2007. Effectiveness of rehabilitation treatments in reducing postfireerosion after the Hayman and Schoonover fires, Colorado FrontRange. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. MsC. Thesis; 186.Robichaud PR, Ashmun LE, Sims BD. 2010. Post-fire treatment effectivenessfor hillslope stabilization. General Technical Report, RMRS-GTR-240. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain ResearchStation, Fort Collins, CO.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos