Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Julie Zähringer
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1453 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 21 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 23 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 14 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Tree nurseries to test tree species adapted to local climate: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Kyrgyzstan Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Aga Khan Development Network (MSDSP KG) - QuirguizistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Tree nurseries are established to test and identify varieties of tree species that are tolerant to climate change in the region.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
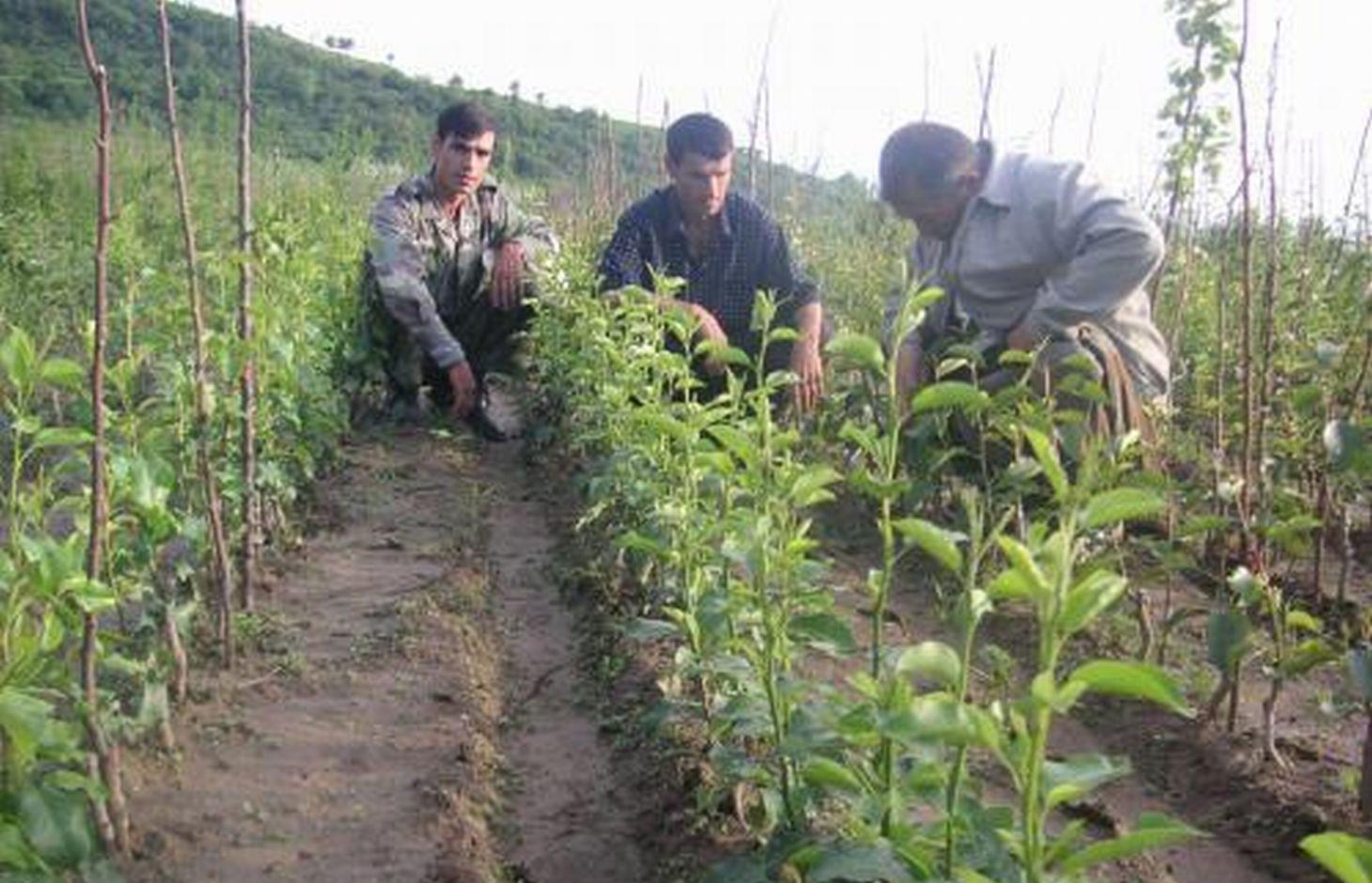
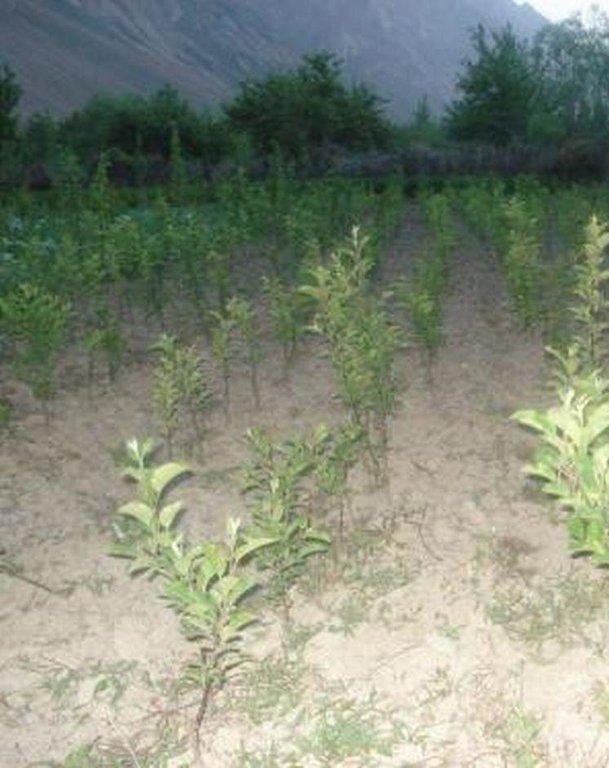
In 1995-96 the first tree nursery was established in the Vanj valley with support from the Mountain Societies Development Support Programme (MSDSP) of the Aga Khan Foundation. During Soviet times there were no tree nurseries in this region and seedlings had to be brought in from outside. Only the Pamir Biological Institute (PBI) was able to obtain seedlings for research purposes. A nursery of about 0.1 ha was established by one farmer on his own land. Tree species grown in the nursery include apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherry and pear.
Purpose of the Technology: The main goal of the project was to make varieties of tree species adapted to different climatic conditions in GBAO locally available. The seedlings are used for other MSDSP projects, such as orchards for soil stabilisation, and are also purchased by private land users for their own land. In addition, the land user was taught how to establish a business by selling seedlings to other land users. There is a strong need for quality tree seedlings in the whole region and even people from as far away as Ishkhashim (7 hour journey by car) travel to Vanj valley to purchase seedlings from this nursery. The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The steps necessary for the establishment of a tree nursery are the following: (1) a suitable plot of flat land is chosen by the farmer, (2) the plot is fenced with dead branches to protect it from roaming animals, (3) in March, the farmer prepares several wooden boxes filled with humid soil in which he distributes 10 kg of seeds of different tree species and varieties. Those boxes have to be irrigated for a month while the seeds are germinating, (4) in April, the nursery plot is ploughed along the contour using animal traction and 1 ton of organic manure, 20 kg of phosphor and 2.5 kg of nitrogen is mixed with the soil, (5) seedlings are planted linearly along the contour with small irrigation ditches running parallel to the planting lines. These ditches were automatically established through the ploughing process, (6) two more times during the first season another 3 kg of nitrogen are applied. In the second year the grafting process is started and in the third year the farmer starts selling the seedlings. The farmer therefore splits up the nursery plot in three parts so that he can always have newly planted seedlings at the same time with second-year seedlings for grafting and third-year seedlings for selling
Natural / human environment: The technology was adopted by two other farmers from the village who had successfully applied to MSDSP for financial support for seeds and fertilisers. Many other farmers from neighbouring villages are interested. The bridge that is currently being built to allow for more trade between Afghanistan and Tajikistan might open further market opportunities for the land user. Furthermore this type of experience is being widely replicated in other districts and supported by MSDSP.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Vanj
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
1995, through MSDP project
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
- frutos secos (castanhas do Brasil, pistache, nozes, amêndoas, etc.)
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: March-May
Comentários:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): reduction of vegetation cover, erosion of slope areas, decline of soil fertility,
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Comentários:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (avalanches, mud flows), population pressure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 3000 / 0.1 ha
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Trees/ shrubs species: apple, peach, apricot, walnut, cherries, pear
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from cropland to tree nursery
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
4.50
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a place with enough water and good soil fertility on flat land for establishment of nursery | |
| 2. | Fencing with dead branches | |
| 3. | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | March-April |
| 4. | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | March |
| 5. | After one month transfer seedlings to planting lines | March-April |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Fencing with dead branches | Persons/day | 80,0 | 20,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Ploughing and distribution of fertilisers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Plant seeds in box with humid soil and irrigate | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Transfer seedlings to planting lines | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | kg | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2370,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 526,67 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | during first year |
| 2. | Apply nitrogen fertiliser twice more during the growing season | during the growing season |
| 3. | Grafting | second year |
| 4. | None | None |
| 5. | None |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Apply nitrogen fertiliser | Persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Weeding | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Grafting | Persons/day | 28,0 | 20,0 | 560,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 6,0 | 3,0 | 18,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 1158,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 257,33 | |||||
Comentários:
The costs were calculated for a nursery of 0.1 ha.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most determinate factors affecting the costs are for labour, although in the documented example, labour was provided voluntarily by the family of the land user. Costs for labour are estimates for a situation in which labour had to be paid in Tajikistan.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
500,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1800 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: teacher
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The land belongs to the state but the land user has a certificate.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Nursery established on cropland
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The economic benefit for the land user is very high as during one year he can make more than 18,000 TJS (4000 USD) of profit from selling seedlings while the investments in fertilisers are comparably small.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Availability of fruits
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
More fruits provide a more balanced diet with more vitamins
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
Aesthetic value of trees
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Higher income from selling the tree seedlings, about 3,000 USD per year, allowing people to provide better education for their children and better access to healthcare
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
Outros impactos ecológicos
Hazard towards adverse events
Comentários/especificar:
Indirect benefit, occuring where the trees grown in tree nursery will be planted later
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Increased income and benefit start after three years when seedlings can be sold.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
3 households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: people from other villages in the valley contacted MSDSP because they would like to adopt the technology (however, they would need financial or material support).
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
The technology is very important to the whole of the GBAO region as nurseries were not available during Soviet times and all tree seedlings were brought from outside How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improved access for farmers of interesting tree varieties that they can reproduce in their nurseries |
|
Creation of business opportunities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing between farmers from outside GBAO |
|
Through the spreading of this technology there will be more seedlings available to all interested households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Establishment of farmer field schools to disseminate the positive experiences of this technology and to increase the number of nurseries |
|
Varieties of trees that are adapted to local climate can be more easily obtained How can they be sustained / enhanced? Access to other new varieties should be improved |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It is quite a complicated process that requires some expertise; the farmer needs to know about planting technologies, grafting and market opportunities etc. | Farmer to farmer dissemination of knowledge could be facilitated through the establishment of farmer field schools. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos