Black plastic covered farmyard manure ( FYM) [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kalo plastic le chhopeko mal - Nepali
technologies_1495 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
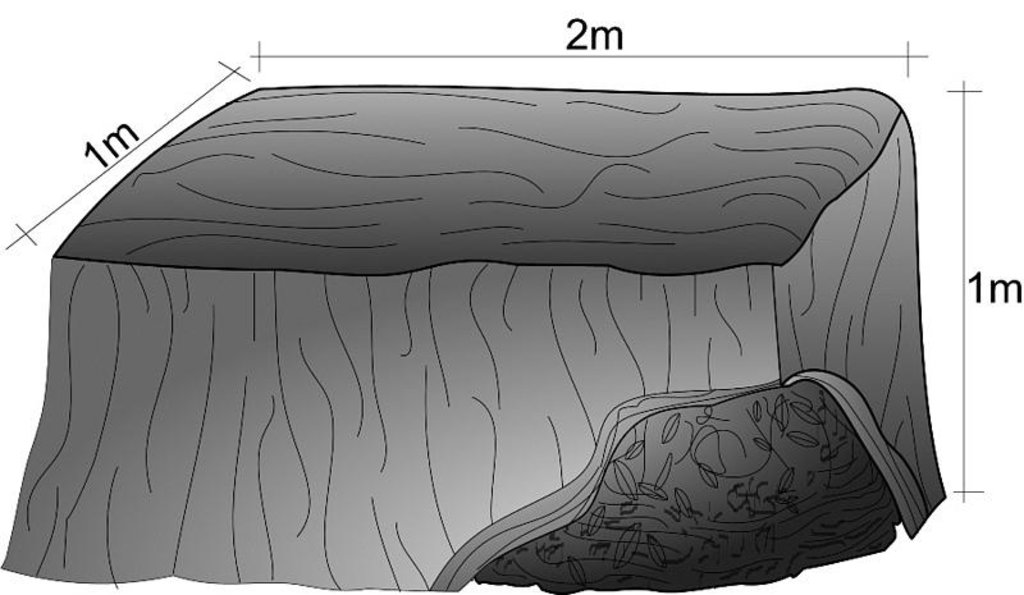
Improving farmyard manure (FYM) by covering it with black plastic sheeting to provide a favourable environment for microbial activities, and to conserve available nutrients and moisture
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Applying compost or farmyard manure (FYM) is an excellent way of maintaining and building soil fertility. Considerable nutrient losses often occur through the inappropriate handling or storage of compost and FYM. Drying out causes losses through volatilisation and rainfall whilst runoff causes leaching and the washing out of nutrients. To reduce nutrient losses, farmyard manure needs to be protected from direct sunlight, rainfall, run-on, and runoff.
A number of improved composting methods have been tested and demonstrated with farmers in the Jhikhu Khola watershed. The Sustainable Soil Management Project (SSMP) has recommended black plastic-covered farmyard manure as one of the most promising methods. Farmyard manure is covered with a piece of black plastic to prevent nutrients from leaching out, to decrease evaporation losses, and to provide a more favourable environment for the growth of microbes due to the increased temperature and moisture content. This method is especially suitable for areas with low temperatures.
In this method, raw organic materials that are used for animal bedding - crop residues, leaves, grass, weeds and other organic materials - are piled up or put into a pit in layers together with animal urine and dung. The pile is then completely covered with black plastic sheeting. This method is based on the passive aeration approach, the plastic sheet is removed from the heap each day to add more bedding materials. It is then covered again immediately. Maintenance is easy although care is needed to avoid damaging the sheet. The black plastic should be handled carefully while taking it off and returning it to the pile as the composting material may contain sharp-edged plant stems.
The method was found to be easy to apply and took little time and labour. In the Jhikhu Khola area, women are mainly responsible for preparing manure and carrying it to the fields. This technology reduces their burden as a smaller amount of black plastic FYM is needed to meet soil nutrient requirements compared to traditional FYM, which is normally applied in a poorly decomposed form and in large quantities.
The method was tested in the middle mountains of Nepal in the Jhikhu Khola watershed, located at 800-2200 masl and with 1200-1600 mm annual rainfall, about 70-80% in the monsoon months (June to September). The temperature ranges from 3-40 degree Cel. in the lower parts of the watershed and about 3 degree Cel. less at the higher elevations.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Região/Estado/Província:
Kavrepalanchowk/Jhikhu Khola watershed
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
The black plastic covered FYM was tested at about 50 households of above mentioned villages Development Committees ( VDCs) and Dhulikhel municipality.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It was first tried at Lumle agriculture research centre in Nepal.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Improve farmyard manure
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- legumes - outros
- rice, wheat, tomatoes
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Comentários:
major cash crop: Tomato, potato
major food crop: Rice, maize , wheat
other: Vegetables
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop production is limited as a result of soil fertility deterioration, high cropping intensity, and a scarcity of irrigation
water. Application of increasing amounts of agrochemicals is further deteriorating soil health.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Increased amount of chemical fertilizer input, less production, and irrigation water shortage.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: rice- wheat- vegetables; rice- vegetables-vegetables; maize - vegetables
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Water supply: Also rainfed
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Black plastic covered farmyard manure
Location: Jhikhu Khola watershed. Kabhre palanchowk district
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: nutrient conservation, accelerated decomposition
Change of land use practices / intensity level: traditional FYM used to be uncovered
Autor:
Madhav Dhakal, A.K. Thaku
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
black plastic sheet
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
5 kg
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.10
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bedding material (e.g. crop residues, leaves, grass, weeds) along | Daily |
| 2. | Each day farmers add bedding material to the piled heap or into the | Daily |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Black plastic sheet | pieces | 1,0 | 17,6 | 17,6 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 17,6 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 17,6 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moisture and temperature is checked regularly | / weekly |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Check mosture and temeprature | Persons/day | 4,0 | 2,1 | 8,4 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 8,4 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 8,4 | |||||
Comentários:
The only establishment cost is the cost of the sheet. In this case study, a 5 kg black plastic sheet costing about $17.6 was used. This sheet was thick (800 microns thick) and is expected to last for 4-5 years. Less durable and smaller sheets cost less. Each day a farmer needs about 30 minutes to add bedding materials, equivalent to 4 person days per month for 2 months. The labour is mainly done by women and girls. All costs were based as in 2006.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Black plastic sheet, per kg cost of which is about $3.5. It is thick (thickness: 800 micron) and durable for 4-5 years.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1200,00
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: Also gentle and moderate
Landforms: Also mountain slopes and valley floors
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: variable
Soil fertility is very low and medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor and good
Soil water storage capacity is low - very low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
15% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for planting, irrigation and harveting; Land preparation mostly with animal traction but at valley bottom also with machines.
Market orientation of production system: Commercial is only grrowing vegetables
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers indicated that after the application of improved compost ( black plastic covered) crop yield increased compared to traditionally prepared compost application.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
from higher crop yield
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
on nutrient status of improved and traditional compost.
Village cleanliness
Impactos ecológicos
Outros impactos ecológicos
soil fertility
Comentários/especificar:
compared to traditional FYM; improved FYM is rich in nutrient content ( N,P,K,organic matter,C/N ratio )
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The investment costs are paid back within the first year leading to positive results due to higher production due to more nutrient-rich compost.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
50 households in an area of 1 - 10 sq km (200-500 persons per sq km)
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Spontaneous adoption of the technology was not seen as the sheeting was not locally available and also due to the lack of dissemination and awareness raising activities.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
More production observed (especially for vegetables) with black plastic FYM compared to traditional FYM How can they be sustained / enhanced? Carry out comparative production studies on more crops |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Less workload for women during FYM preparation and transportation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote and implement the technology more |
|
The technology will promote organic production of desired crops as avoids the need for chemical fertilisers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
|
FYM decomposes within 45-50 days compared to about 180 days with the traditional method; the improved FYM is very fine and with equal decomposition from top to bottom of the heap. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Share experiences with a wider audience and test the technology in different ecological zones. |
|
The quality of FYM is better than traditionally made FYM; nutrient content (N, P, K, organic matter, C-N ratio) is higher. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
|
Black plastic is easy to handle, light, and durable. This method is very much appropriate for high mountains and middle mountains. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Poorer rural people are put off by the cost and unavailability of the sheets; they have to bear the extra cost of bringing sheet from a far. | Make the sheets available in the local market and arrange for the cost to be subsidised by agriculture departments and non-government organisations. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Unavailability of large enough sheets to cover huge heaps. | Make two or more smaller heaps; or cover big heaps with two or more sheets. |
| Plastic sheet gets damaged if not handled carefully and is easily damaged by rats. |
Handle sheets carefully and protect from rats using locally available rat repellent plants like Artemisia indica (titepati). |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ICIMOD
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos