Shrubbery buffer strip with bund [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Mei Zhao
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Grass Buffer Strip
technologies_1544 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
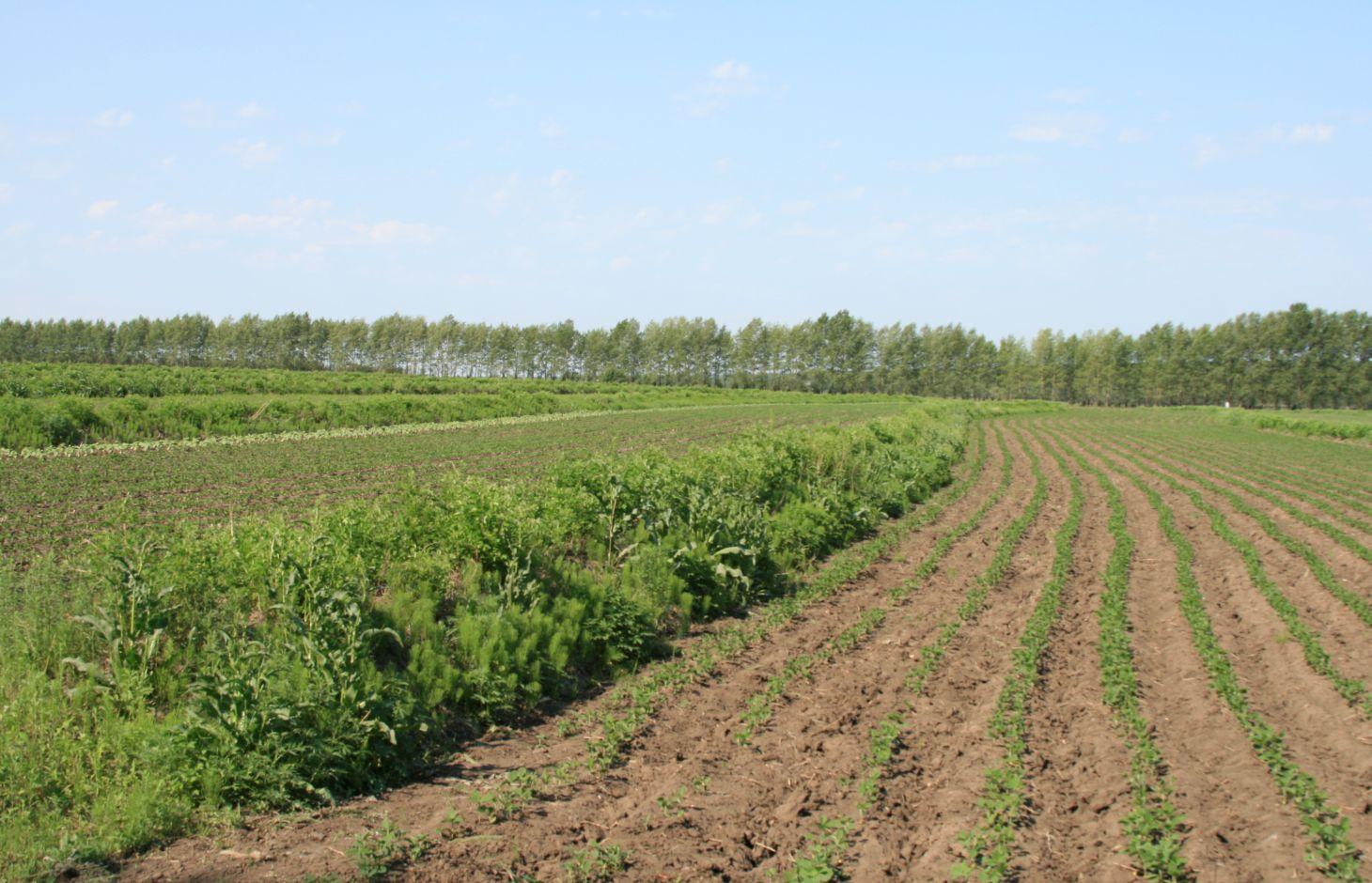
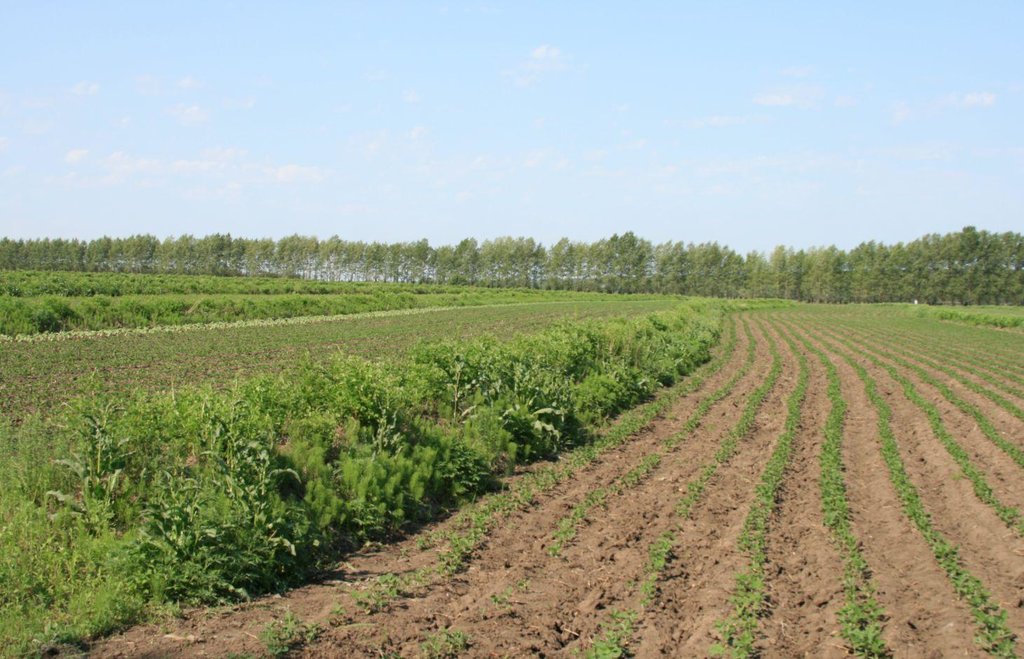
Belts of shrub or grass, planted on the level bund which constructed along contour line in gentle slope farmland in the black soil region of Northeast China.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Shrubbery buffer strip with bund(SBSWB) is a traditional technology, it is introduced by the field staff about 60 years ago who worked in the farm in Heilongjiang province.This technology with low-cost, high effectives and easy to construct, which has been widely applied in all black soil region of Northeast China (Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region).
Purpose of the Technology: The final purpose of these buffer strips is increasing crop production by decreasing soil loss. More specific objectives include: 1)protect the land from surface erosion by cutting slope length, increase infiltration and soil moisture; 2)to prevent soil loss of gentle slope farmland by allowing excess runoff to filter through but trapping sediment; 3) through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips, level bund lead to the formation of forward slope terraces over time, then developing into terrace final;4) creation of opportunities for additional income by harvesting fodder(grass) production and fruits(shrub).
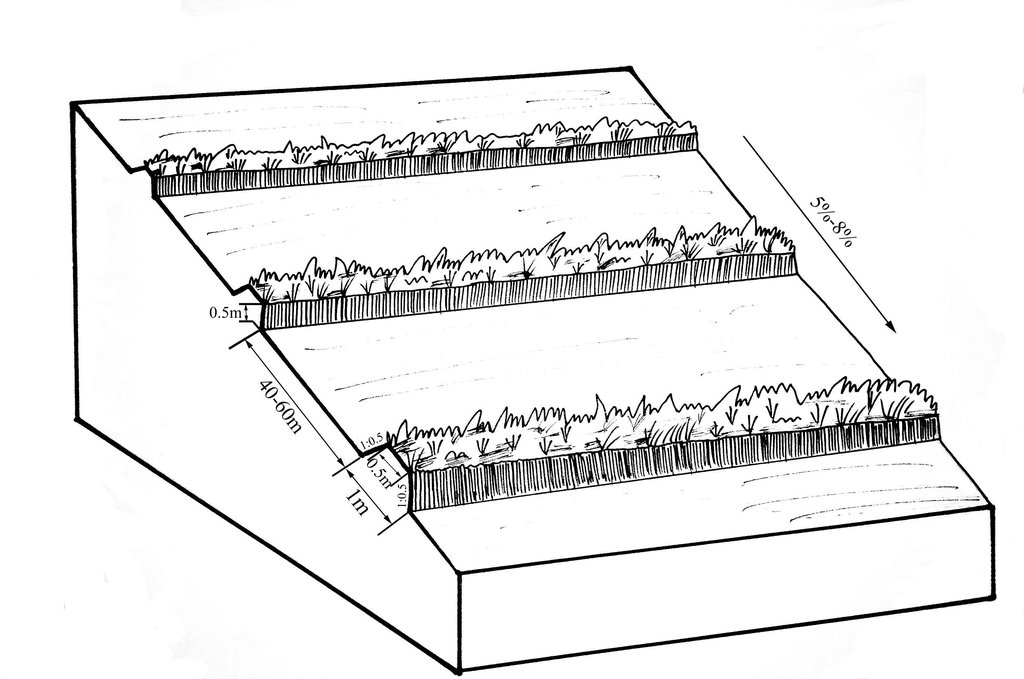
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A construction is generally carried out in autumn of the year; plantation is made in spring of the next year. The construction in a man-machine integration mode is generally carried out step by step and from top to bottom along the contour line(s). The ladder-shaped cross section of a ridge is 0.3-0.5m in width (suitable width on the top), 0.5-0.6m in height, 1:1 or 1:0.5 in inner-side gradient and 1:0.5 in outer-side gradient.
In a construction, peel the surface soil with machine, with the peeling depth generally being 0.3m, which should be subject to soil layer depth; then haul the ridge construction plough (a kind of machine or device) with a tractor to build the ridges, consolidate the ridges through artificial slapping; Finally restore the surface soil to accomplish ridge construction. The tops of the constructed ridges should be maintained to be in a horizontal surface. The distance between two ridges in this region is generally stipulated to be 50 meters. The soil for ridge construction should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Natural / human environment: Shrubbery buffer strip is found mainly in Northeast China, at altitudes between 700 and 1600 m. Climate there is cold in winters and cool in summers, with a monsoon moisture regime. In the area, the annual mean temperatures is from 2 to 8 °C, and the annual mean precipitation is from 500 to 1000 mm. Most of the farmland slopes are less than 7°but slope lengths mainly range from 200 to 1000m in this area.
Northeast China, the grain production base of China, or the bread basket of China, includes three provinces (Hei-long-jiang, Ji-lin, and Liao-ning) and the eastern part of the Inner Mongolian autonomous region. In 2009, 17.1% the China’s total grain production came from this region, which included 33.5%, 55.7% and 9.6% of corn, soybean, and rice, respectively. Approximately 118 million people live in this region. Grain produced per capita is over 1000 kg annually.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
The black soil region of Northeast China
Especificação adicional de localização:
Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
This technique has been common applied in gentle slope farmland of the black soil region of Northeast China. It is very useful for reduce soil loss and intercept runoff.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
SBSWB appear in the vicinity of Heilongjiang province in the last century 60's
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- legumes e leguminosas - soja
- culturas de raízes/tubérculos- beterraba sacarina
- rice
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: April to August
Comentários:
Main cash crop: soybean, sugarbeet
Main food crop: paddy rice, maize
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Beacuse of long slope, high rainfall intensity, freezing and thawing processes, and intensive cultivation has lead to substantial water runoff, soil erosion, and gully formation. Soil erosion has been the serious problem threatening agriculture sustainability in the region for decades.The flora of the area are very diverse.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil fertility and crop yeild are decreasing year by year.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: soil management (The extensive cultivation and management modes reduce the thickness of black soil layer by 0.5 cm per year.), population pressure (Great population pressure makes the land carrying capacity decline year by year.), education, access to knowledge and support services (The channels for the local peasants with low levels of education to learn knowledge are few, and they will not take initiative to learn knowledge.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (This area is the most important grain production area in China, there is serious excessive exploitation in this area.), change of seasonal rainfall (The rainy seasons mainly focus on July and August.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (The downpours in summer bring about soil loss.), land tenure (As the lands are owned by country or by peasant communities, the peasants are not strongly aware of the importance of land protection.), poverty / wealth (The serious gap between rich and poor)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
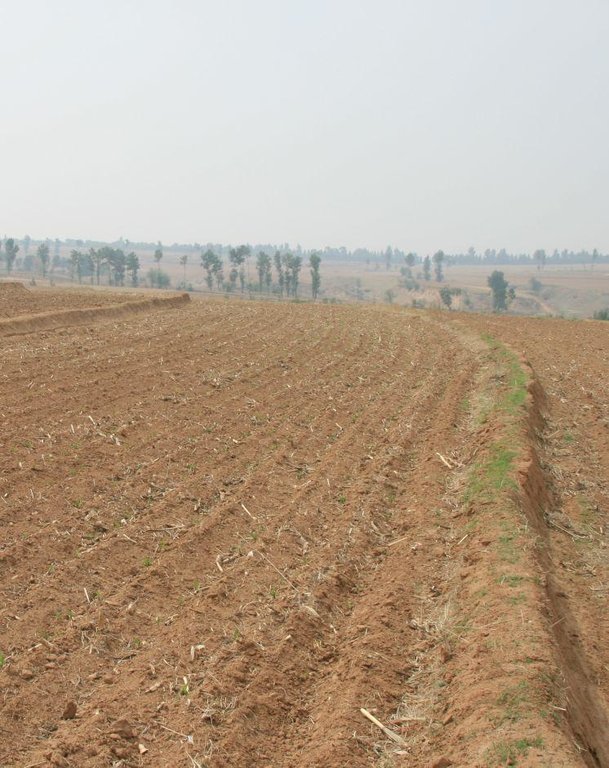
The upper-base width, lower base width, height, slope ratio and spacing of a ridge are 0.5m, 1m, 0.5m, 1:0.5 and 40-60m respectively. A row spacing of the shrubs planted on the ridges should be 0.5m. Generally one row on each ridge is enough. About 80 shrubs are needed for every hectare; if herbaceous plants are planted, no special plantations are required.
Location: Chao Yang City. Liao Ning Province
Date: Nov 12,2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Field staff/agricultural advisor should have intermediate know-how level, because land user should be instructed by them)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The knowledge level of lander user is not required to be high, who just need(s) to follow the instructions from field staff/agricultural advisor)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200-600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.644-8.466
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 40-60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: caragana, lespedeza, amorpha, daylily, Melilotus
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.09-5.55
Spacing between structures (m): 40-60
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): >100
Construction material (earth): The soil should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Autor:
Zhao Mei, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
RMB
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
6,25
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
9.25
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant shrubbery | autumn |
| 2. | Layout of contour and the line of SBSWB with the leveling | autumn |
| 3. | Build the ridge | autumn |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Layout of contour | Person/day | 3,0 | 16,0 | 48,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Build ridge | Person/day | 36,0 | 9,6 | 345,6 | |
| Equipamento | Machine use | hours/day | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| Equipamento | tools | day | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedling Plant shrubbery | ha | 600,0 | 0,016 | 9,6 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 491,2 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 78,59 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
| 2. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, Spade
3 people are required to layout contour, daily labor cost for per person is 100 Yuan, so the total labor cost is 300Yuan ($48), tools fee is 50Yuan ($8).
One tractor can built 2.6 ha of ridges per day at a cost of 500 Yuan ($80). The ridges constructed should be artificially tamped, 120 people are needed to tamp the ridges in an area of 2.6ha, about 46 people for each hectare. As the daily labor cost for per person is 60 Yuan, the total expense on each hectare is 2760 Yuan($441.6), and the labor intensity is intermediate.
If shrubs are planted on the ridges, 400 shrubs are required for each 1 hectare management area. In addition, as the price of caragana microphylla in 2012 is 0.1 Yuan per one, the total cost of the caragana microphyllas per hectare should be 40Yuan($6.4).
Therefore, the total construction cost per hectare is 3650Yuan($584).
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most determinate fators affecting the cost is labour
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: high
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich.
45% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
5% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Geração de energia
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Disparidades econômicas
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Atenuação de conflitos
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Salinidade
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Although Certain quantity of land will be occupied and grain output will be affected in SBSWS during the early period of a construction, in the long run, SBSWS can prevent the loss of the most fertile surface soil, in addition, with the ever increased quantity of the sediment intercepted by SBSWS and as the heights of the vegetational belts increase year by year, the slope croplands will become bench terraces, and the grain output will be increased.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
NA
Comentários:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Large-area popularization of SBSWB has been achieved in the locality.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The implementation of this measure was accomplished under the encouragement and support of the government. There are relatively few peasant households who initially take this measure. The main reason for the peasant reluctance to adopt this measure is that the ridges will occupy land and reduce arable area. They are unconscious of and do not care about soil loss, and unable to realize in the long run the harm brought about by soil loss.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The trend depands on government support
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Convenient for construction How can they be sustained / enhanced? Popularization carried on |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Gradual formation of the slope-type terraces, which can be developed into bench terraces many years later How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase of ridge height year by year |
|
Intercepting the sediments carried by runoffs, preventing water and soil loss of the arable lands on the gentle slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? In combination with other water and soil conservation measures during operation, such as no-tillage and drainage ditches; |
|
increase of infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Chopping down branches at regular intervals to guarantee that the plants on the ridges will not enter into rivary with the crops over water and sunlight; |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The ridges occupy land and reduce arable area | government support |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of arable lands brings about low enthusiasm of the peasants | Conflict between the arable lands and the immediate interests of the peasants. Popularization of water and soil preservation knowledge should be strangthened to make the presants realize that although the immediate interests will be hurt, the long-term interests will increase. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Title:Techniques standard for comprehensive control of soil erosion in the black soil region Author:Shen bo; Meng lingqinYears:2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
internal materials
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos