Kanda [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Alexandra Gavilano
Kanda
technologies_1659 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Sediqi Ali Ahmad
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
Afeganistão
Especialista em GST:
Sthapit Keshar
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
Afeganistão
Especialista em GST:
Arbab Ziauddin
Sourakhak Watershed Committee, Kahmard
Afeganistão
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
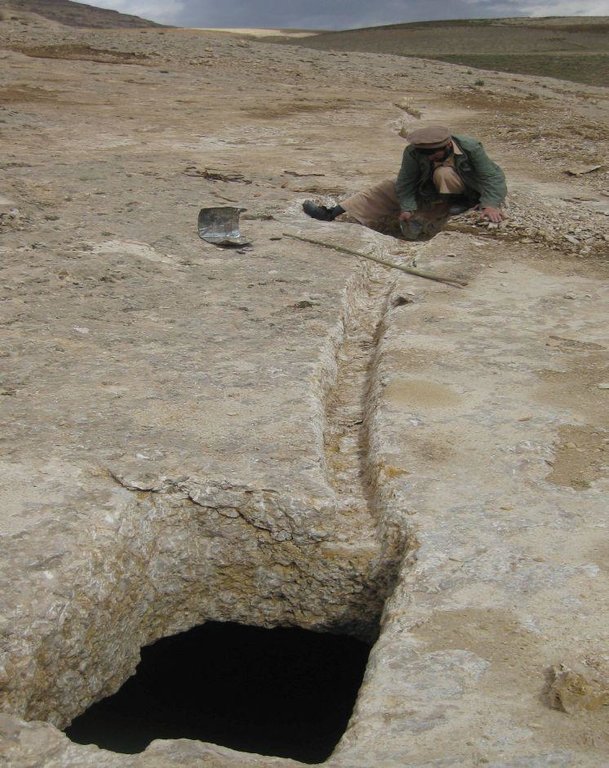
A traditional underground water tank carved out of rocks to collect rainfall and snow water and reduce evaporation losses.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
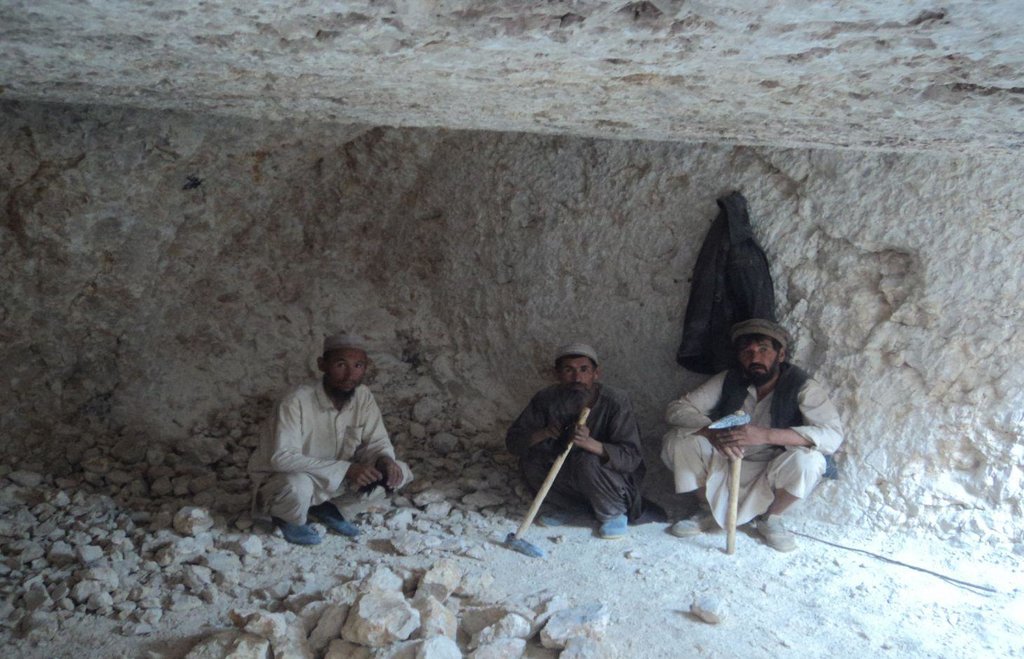
Kanda is an indigenous technology for collecting rain and snow melt. The technology comprises an underground tank carved out of rock (limestone), channels to convey the runoff into the underground tank or kanda and a rocky catchment from where runoff is collected. Kanda technology is applied in Afghanistan in many places, particularly in areas which experience scarcity of water for human beings, livestock and irrigation.
Purpose of the Technology: Due to high evaporation rates and low precipitation, harvesting runoff in open tanks is not an efficient way of water harvesting. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation is implementing community based watershed management projects in Kahmard district of Bamyan province (Afghanistan) since 2008 with financial support from the International Swiss Re Award for sustainable watershed management (2009) and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). One of the activities for sustainable watershed management is plantation of fruit and non-fruit trees in the selected watersheds (upland areas) which were used for grazing and extraction of vegetation for domestic use. Due to water scarcity in the upland areas, irrigation of the planted saplings becomes very difficult and water has to be transported on donkey from far locations. To overcome this constraint, Kanda was identified as the most potent technology for harvesting runoff and snow melt.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For constructing Kandas, Kanda makers from Dara-e Suf district in Samangan province had to employed as there are no experts in Kahmard. Based on feasibility studies, eight kandas have been constructed including 4 kandas in Sourakhak wa-tershed and 4 in Baqa Kushta watershed. The size of each kanda is 6 m length, 6 m in width and 3 m in height. To convey the runoff into the tank, 10-20 m long graded channels were carved out of the rocks. The establishment cost of one Kan-da was approximately US$ 7163. Kanda making requires special skills, especially when it is carved out of rocks. A kanda maker has sound understanding of the area’s geology, and this wisdom is gained through learning by doing and ances-tors.. In Kahmard, 2-3 experts worked for 4-5 months for one Kanda.
Natural / human environment: In 2012, due to sufficient rains, 2 Kandas which did not have leakage problems in Sourakhak watershed got full with runoff water, which was then used for irrigating 6500 saplings seven times during the year. Kahmard district has a semi-arid cli-mate. Some years are dry with rainfall of about 190 mm. Considering this context, it becomes very necessary to tap rainwater, especially in the rainfed uplands, and use it for irrigating saplings or for livestock.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Bamyan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kahmard
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.005 km2.
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Kanda technology is an age old water harvesting traditional technology.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
- ovelhas
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Scarcity of water in the upland makes plantation activities and livestock productivity difficult. Carrying water from far places for irrigating plants is an expensive activity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Degraded upland watershed resulting severe flash flood.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Other forest products and services: flash flood
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: March-July
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?

Pastagem
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Specification of other structural measures: Under ground cistern
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Bush collection for fire wood), overgrazing (By sheep and goets), droughts (Natural climate phenomenon), land tenure (Common land without good management), poverty / wealth, governance / institutional (Lack of organizationals for organization for supporting management of common resources.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Rainfed agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Change in climate patterns), population pressure (Fast increasing population which depands on natural resources for livelihoods), war and conflicts (Leading to uncontrolled cutting down of trees and shrubes)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
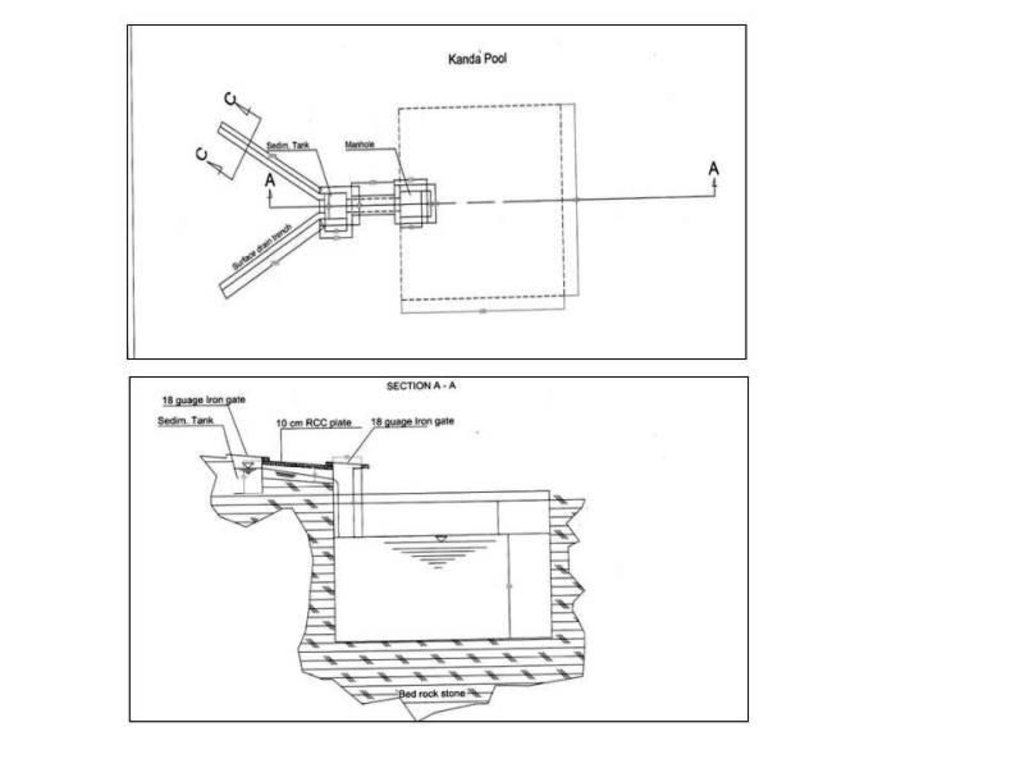
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical drawing of a Kanda constructed at Baqa Kushta watershed in Kahmard district (Bamyan province).
Size of one Kanda tank:
Length:6m
Width :6m
Height:3m
108 cu.m water can be stored in one Kanda.
Location: Baqa Koshta watershed. Kahmard
Date: 24/03/2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, Reduction in evaporation and seepage losses
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Structural measure: cistern(from rock)
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Construction material (other): Constructed from rock
Autor:
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperatio, Kabul Afghanistan
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | kanda | 1,0 | 5640,0 | 5640,0 | 15,0 |
| Equipamento | Equipement | kanda | 1,0 | 458,0 | 458,0 | |
| Material de construção | Materials | kanda | 1,0 | 1065,0 | 1065,0 | 8,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 7163,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 7163,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | once/year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | persons/day/kanda | 2,0 | 5,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 10,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 10,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The kanda is for water collection which runoff and snow melt. The usage of water for sapling irrigation because there is upland and no water resources.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Because there is fully of rocks.
Soil texture: Mostly rocky
Topsoil organic matter: Because there is erosion
Soil fertility is low (Loss by wind and water erosion)
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor because there is fully of rock
Soil water storage capacity because of rocky catchment
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Because there is to much workload
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
50% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Risco de falha de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Qualidade da água potável
Renda e custos
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
expense for construction
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Increased availability of water for small scale irrigation such as trees, sapling and livestock and increase successful afforestation in dry land areas which in the longer term will lead to increased income, fuel wood and timber for land user and greener watersheds
aesthetic value due to greener watershed
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
due to water harvesting
Outros impactos ecológicos
sediments due to excavation of rocks
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Contributes to flash flood risk reduction by supporting regreening effort
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
This technology is very positive and useful for land users and collected the water for irrigation and livestock.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is an indigenous technology applied in many other districts of Afghanistan in Dara-e Suf and Ruy-i Doab districts of Samangan province by several families either collectively or privately without external support. In Dare-e Suf are not constructed inside of rocks but in soil.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The technology supports plantation activities in sites which are far from perennial water sources How can they be sustained / enhanced? The collected water should be used efficiently during irrigation by combining with conservation measures like mulching, drip or pitcher irrigation |
|
As the kanda catchment is rocky, infiltration losses are minimized and most of the surface runoff is harvested How can they be sustained / enhanced? The channel must be constructed properly so that all runoff is trapped and conveyed to the Kanda. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
An indigenous multipurpose technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda size can be improved if the catchment area and precipitation amount are considered. This also depends on availability of long-term rainfall data. |
|
Requires minimum maintenance when constructed properly How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda, conveyance canals, sediment pits and catchment areas should be cleaned. If any leakages occur in the tank, they should be sealed. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Due to a lack of geological and hydro-meteorological information, it is not possible to prepare precise and cost-effective kanda proposals | Make best use of traditional wisdom, install hydro-met stations if possible and make adjustments based on regular monitoring. |
| If the kanda and sediment trap tanks are not cleaned regularly and the kanda opening is not covered, sedimentation can be problem leading to reduced Kanda capacity and also animals could fall | Cleaning and maintenance works must be carried out by the local people every year before spring rains. The openings must be covered. |
| Due to availability of water, there can be grazing pressure near the Kanda | Watershed committee members and guards should ensure that the site is protected from over grazing. Construct Kandas outside the selected watershed for livestock purposes. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Establishment cost is high if the catchment is rocky | Needs external support during the establishment phase |
| Lack of kanda makers in some districts like Kahmard | Get kanda makers from other districts and build capacities of interested local people. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
URL:
www.wocat.net(Online Technology Database)
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos