A low-cost polyhouse for tomato production in the rainy season [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Shreedip Sigdel
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Sasto Plastic ghar ma barsha golbheda kheti (Main Contributor: Bishnu Bishwakarma, Helvetas Nepal)
technologies_1688 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
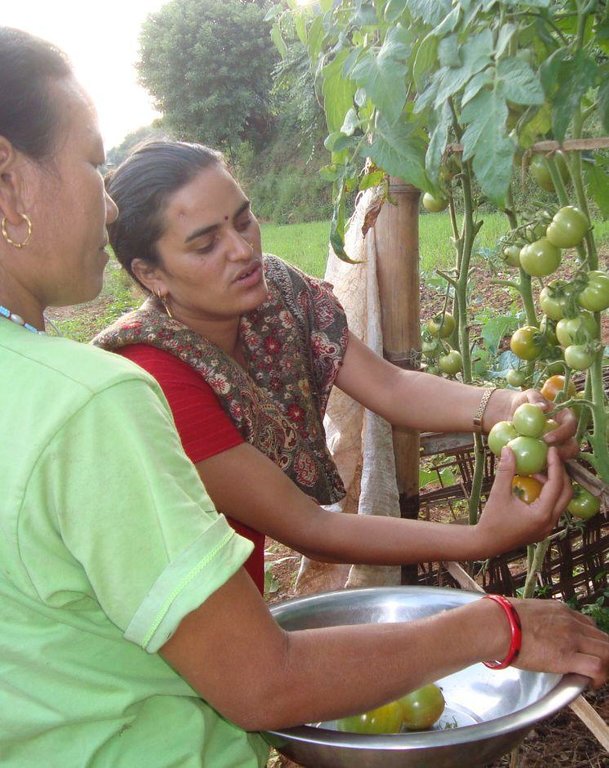
Smallholder farmers can use polyhouses to produce high demand vegetables, such as tomatoes, and can earn a substantial income from even a relatively small plot of land in a short time.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
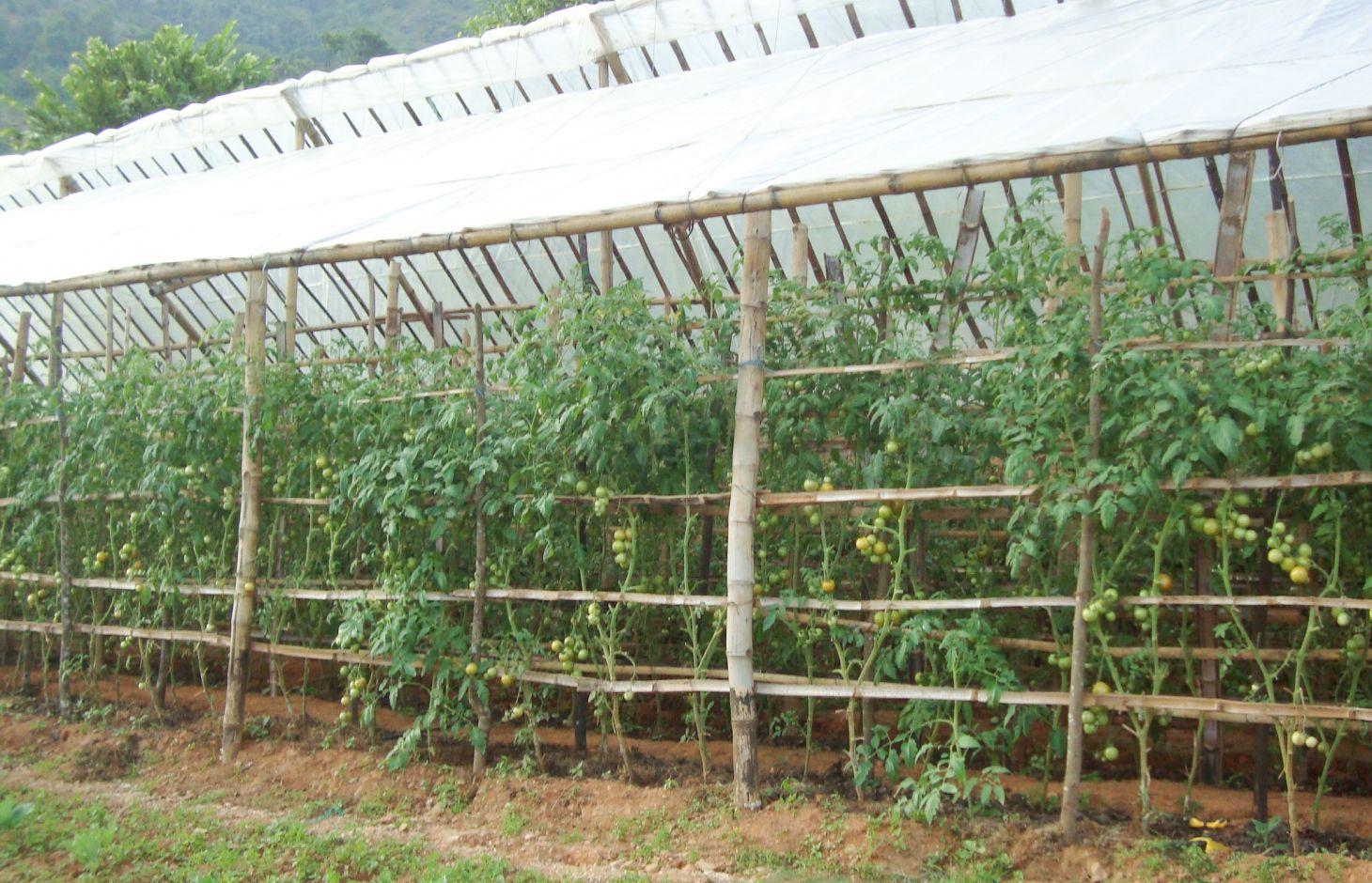
During the wet season (June–October), the monsoon rains severely limit the type of crops that can be grown in open fields and they also restrict the production of seedlings. Low-cost polyhouses can be used to protect crops from excessive rainfall and can provide a sheltered environment for the production of better quality crops over the rainy season cropping period. For example, smallholder farmers who produce high demand vegetables such as tomatoes can earn as much as USD 350–500 from a plot of land which measures only 100 m2 in area over the short time period from June to November. This is much more than they can earn by growing any traditional crop by conventional methods. The Sustainable Soil Management Programme (SSMP) is promoting this technology in several mid-hill districts of Nepal.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Polyhouses should be situated in well-drained areas where sunshine is abundant and there is no shade throughout the cropping period. The bamboo frame can be constructed earlier in the year but the plastic roofing is not added until after one or two rainfall events. The height of the polyhouse frame varies depending on the altitude. At higher elevations, the polyhouses are lower to help trap more heat and moisture, whereas at lower elevations the polyhouses are higher to allow more air to circulate and moisture to evaporate. The preparations, which take place mid-May to early June, consist of fertilizing the soil and planting the tomato seedlings. Throughout the growing season the tomato plants are staked, trained, and pruned and a top dressing of fertilizer is added to produce a higher quality product.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mid Hills of Nepal
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- tomatoes
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 214; Longest growing period from month to month: May to November
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): In the mid-hills of Nepal, the arable land of most farm households has been divided into very small plots. If this land is used to produce traditional crops such as maize, wheat, and millet using conventional farming methods, it cannot provide full employment for all of the householders and cannot yield sufficient cash income for the household. The risk of intense rainfall during the monsoon season, which can damage crops, has prevented these farmers from switching to more lucrative high value crops.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Greenhouses
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A7: Outros
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (During the summer monsoon (June-October), continuous or heavy rainfall can damage seedlings and erode the land; it is difficult to establish crops during this time.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
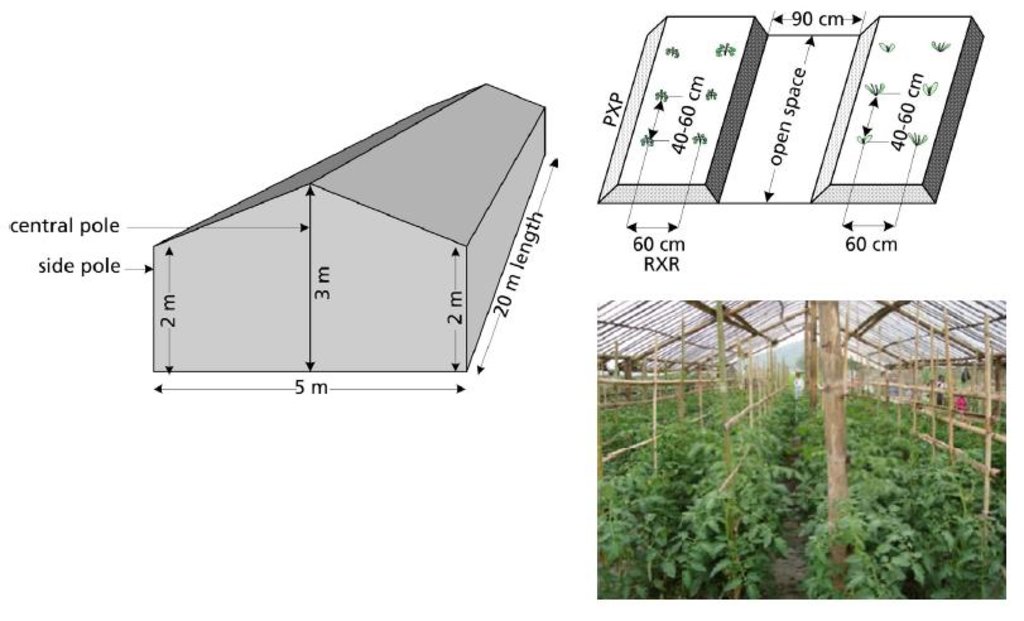
Left: Sketch of a polyhouse. The optimum length is 20 m and the width 5 m. The height of the central and side poles varies depending on the elevation. Note that there should be a space of at least 1 m between polyhouses.
Right top: Cross sectional view of a planting bed showing row-to-row (RXR) and plant-to-plant (PXP) distances. Note that there should be a space of at least 90 cm between beds.
Right bottom: Inside the polyhouse, the tomatoes can be staked using bamboo poles; the plants are trained along these trellises.
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Increase Productivity, Introduce high value crop
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Autor:
AK Thaku
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Polyhouse
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
4
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labour for construction of the Polyhouse | |
| 2. | Labour for planting, training,pruning,stalking | |
| 3. | Materials: Bamboo pole, plastics sheet, rope, nails, seed, poles | |
| 4. | Agricultural: seed, fertilizer, crop protection |
Comentários:
Details for the establishment of Poly house. Establishment activities 1. Construction of the polyhouse using bamboo poles, wooden posts, clear plastic sheet, nails, and rope. 2. How long it takes to construct the polyhouse and plant the crops depends on how much labour is available. Depending on their level of expertise, four to five people can construct the structure in one day; and two people can complete the soil preparation and planting in one day. Technical guidelines for erecting a polyhouse The optimum length of a polyhouse is 20 m, and the width is 5 m; 400–500 gauge plastic sheeting is used. The height of the polyhouse depends on the elevation: at 1200–1600 masl, the optimum height of the central pole is 3 m and the side poles are 2 m high; at 1600–2000 masl, the central pole is 2.5 m high and the side poles are 1.6 m high. There should be an open space of at least 1 m between polyhouses. Technical guidelines for preparing the soil and planting tomatoes Per plant, at least 3–4 kg of well-decomposed farmyard manure and compost are worked into the soil. Before transplanting the seedlings, the soil around each is dressed with 10 g of DAP (diammonium phosphate) and 6 g of MoP (muriate of potash). The seedlings are transplanted when they are 20–25 days old. In an open row system, the suggested row to row (RxR) spacing is 90 cm and the suggested plant to plant (PxP) spacing is 60 cm; in a closed row system the row to row and plant to plant spacing can both be 60 cm. At least two top dressings of DAP and MoP (10:10 g) are necessary 20–25 and 40–45 days after transplanting; 1 kg per 0.05 ha of borax is also added at the time of the first top dressing. Alternatively, these two top dressings can be substituted by a mixture of cattle urine (50 ml) and water (200 ml water) per plant. The dressing with this mixture can begin 20–25 days after transplanting, and is repeated every 10–12 days.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of the polyhouse | persons/unit | 5,0 | 4,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Training, pruning, stalking | persons/unit | 5,0 | 4,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seed, fertilizer, crop protection | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Bamboo pole, plastics sheet, rope, nails, seed, poles | unit | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 35,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 140,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 140,0 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | There are no major maintenance costs during the cropping season; but occasionally some minor maintenance is required (e.g., replacing damaged stakes and plastic sheet, or securing with additional rope and nails). |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance | persons/unit | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Equipment | unit | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Agricultural | unit | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Material | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 25,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 25,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors. Exchange rate USD 1 = NPR 71 in April 2011
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Annual rainfall: Also 1000-1500 mm and 1500-2000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium - high
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Initial cost
Technical knowhow
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Improved food security and reduced need for either seasonal migration or outside help
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Can be susceptible to some fungal diseases
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Impactos de ciclones, temporais
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Areas downstream benefit from soil retention
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| High relative humidity | não bem |
Comentários:
optimize the plant density; train and prune plants often to avoid overcrowding; modify the structure to provide more ventilation (ventilated polyhouse) in especially hot areas
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Although the technology is only moderately expensive to implement and provides a higher rate of return than traditional crops, smallholder farmers often need technical support and encouragement to get started. This support can be in the form of improved seed varieties and plastic sheeting for the polyhouse.
Driver for adoption:
• relatively simple technology
• higher economic return
• provides on-farm employment
Constraints
• smallholder farmers and poorer households need initial support to establish the polyhouse
• farmers need technical support
• farmers need practical information and technical backstopping
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Cost effective in terms of output as compared to traditional crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? Identify other cash crops that can also provide improved income opportunities |
|
This technology can be integrated to make maximum use of farm niches; it is especially beneficial for smallholder farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provide training on the construction of polyhouses to experienced lead farmers so that they can provide technical support to others. |
|
It mostly uses local materials How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ensure bamboo poles are available on the farm; encourage the use of silpaulin which is more durable than polyethylene |
|
Uses local expertise, farmer knowledge, and practices How can they be sustained / enhanced? Farmers can make the most of their investment by linking with markets and by providing support for value chain development. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Need to provide training and technical know-how and need on-farm research to identify alternative cash crops | Farmer-to-famer extension can help to identify other crops |
| Vulnerable to diseases and pests | Adjust planting time to local conditions; build the polyhouses in appropriate locations; plant resistant varieties; modify the structure to improve air circulation; prune and train plants throughout the cropping season; improve staking techniques; rotate crops or move polyhouse every three years |
| Some initial set-up cost | Silpaulin can be purchased at lower cost when farmers' groups buy in bulk. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Construction of polyhouse and rainy season tomato cultivation inside polyhouse (in Nepali). Kathmandu, Nepal: Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Helvetas Nepal, SSMP (2010)
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos