Introduction of Crop Rotation [Geórgia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Kety Tsereteli
- Revisor: Ursula Gaemperli
technologies_4275 - Geórgia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
co-compilador/a:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Geórgia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
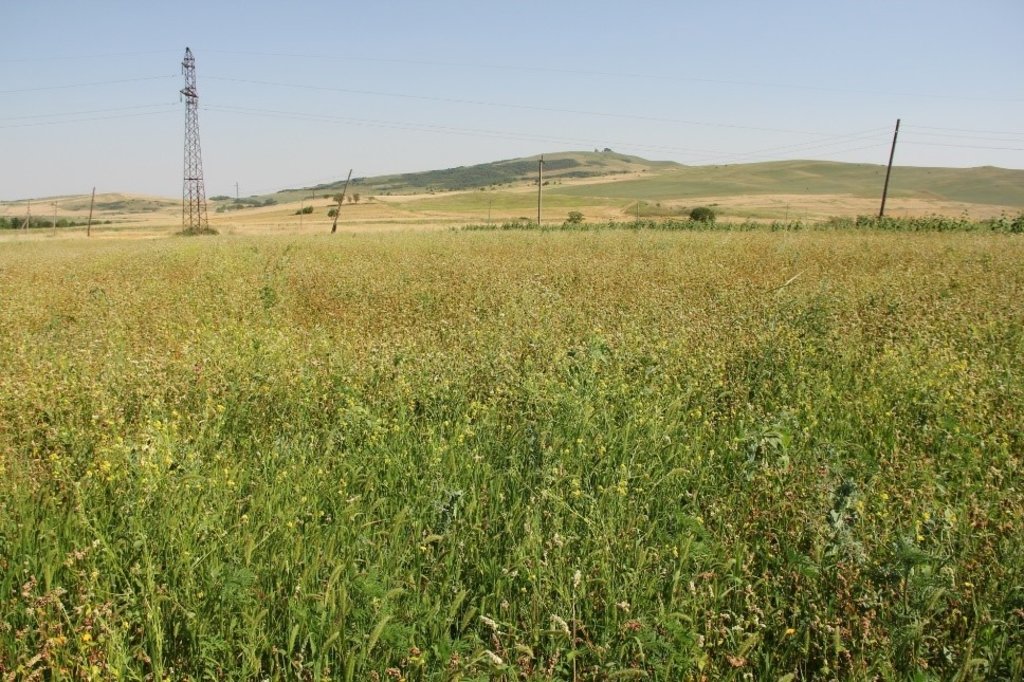
In the municipality of Dedoplistskaro, Georgia, 100 ha of land have been cultivated with peas on approx. 25 fields (each 1-10 ha in size). The introduction of peas as an alternative crop that is now used in rotation with wheat, helps to increase soil fertility sustainable and ecologically.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Dedoplistskaro is located in the Shiraki Plain, in eastern Georgia, and consists of steppes, where grain crops are cultivated and livestock is grazed in the winter. The steppic soils are dominated by Chernozems and Kastanozems, the climate is warm and temperate and the small-scale land (2-5 ha) is in individual ownership. The labour including plowing, seeding and harvesting is fully mechanised, the machines are mainly borrowed from agricultural machinery cooperatives and less often from private machinery suppliers. For the inhabitants of Dedoplistskaro municipality, agricultural production is an important source of income. 74% of the Georgian wheat production is located in the Kakheti region. Shiraki valley has a great share of this. The area of wheat production in Dedoplistskaro is 13,693 ha (Census 2014). Securing the productivity of arable land and stopping degradation due to the loss of soil fertility is of local and national importance. The introduction of pea as an alternative crop, which can be used in rotation with wheat or other crops, should help to increase soil fertility in a sustainable and ecologically viable way. Pea is a plant from the legume plant family. The root system of Pea can thus fix nitrogen from air by symbiotic bacteria. This helps to increase the C/N ratio in the soil leading to higher decay rates of organic carbon (e.g. from straw residuals) and higher fertility of soils. Most farmers sowed on 23 and 24 March 2018 - some until 29 March 2018. Later sowing led to lower yields.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Geórgia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kakheti
Especificação adicional de localização:
Dedoplistskaro
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
1,0
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- legumes e leguminosas - ervilhas
- buckwheat
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Crop rotations with wheat, pea and buckwheat. Different systems, one example: Year 1: Wheat, Year 2: Pea, Year 3: Wheat, Year 4: Wheat, Year 5: Buckwheat, Year 6: Wheat, Year 7: Wheat, Year 8: Pea, Year 9: Wheat
Comentários:
Before the implementation of the technology wheat was cultivated without intercropping or crop rotation.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
Comentários:
It is envisaged to continue with crop rotation in the following years.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
Comentários:
The nitrogen fixing capabilities of the pea-roots will increase fertility of the soil additionally to the crop-rotation effect.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
The permanent cultivation of wheat on the same field leads to degradation of fertility.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
The crop rotation will reduce and/or prevent from land degradation by permanent wheat cultivation.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Proposed rotation schema for wheat, pea and buckwheat
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Data:
07/02/2018
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
100 ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
20
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of farmers and fields according to the selection schema and signed subsidy contracts to all farmers | Until January 2018 |
| 2. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2017-Novembver 2018 |
| 3. | Seeding, maintaining and harvesting | March-October 2018 |
| 4. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2018 |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | plowing | ha | 100,0 | 35,71 | 3571,0 | 40,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | harrowing | ha | 100,0 | 14,29 | 1429,0 | 40,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | seeding | ha | 100,0 | 8,93 | 893,0 | 40,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | harvesting | ha | 100,0 | 35,71 | 3571,0 | 40,0 |
| Material vegetal | pea-seeds (250kg) | ha | 100,0 | 133,93 | 13393,0 | 40,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | herbicide (1l) | ha | 100,0 | 5,36 | 536,0 | 40,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 23393,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 23393,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
60% of the cost have been added as a subsidy payed from GEF project funds.
Comentários:
The funding was organised in a public call. Farmers from the Dedoplitskaro region have been invited to apply for a 60% co funding of the pea/buckwheat planting.
The costs stated in the section "Labour" for plowing, harrowing, seeding and harvesting include costs for labour and for equipment. The work was done partly by the farmers themselves and partly by an agricultural contractor such as for driving the harvester. The machines are mainly borrowed from a local machinery cooperative, but also from private machinery suppliers.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
Comentários:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
It was a challenge to organised the high amount of pea-seeds, as they are not commonly available in the region.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
697,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
In the region steppic soils are dominating (Chernozems and Kastanozems)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The landscape is intensively used by agricultural purpose. The former network of windbreaks was massively reduced in the last decades. Re-establishing could support the habitat diversity significantly.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The local farmers-association was an important partner in promoting the imitative.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
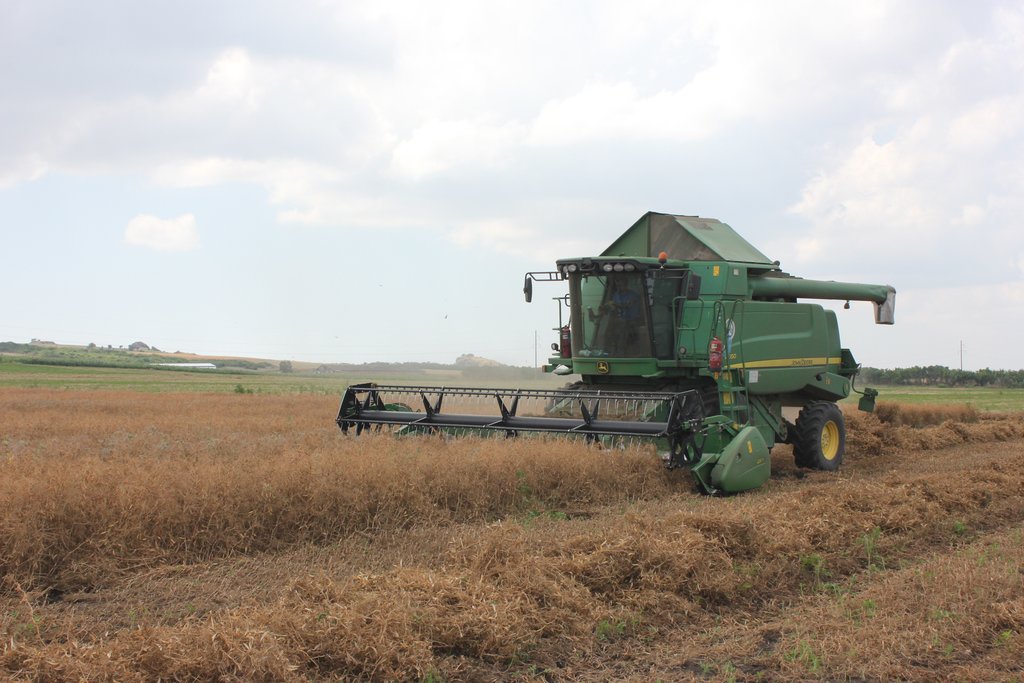
The average yield of peas 3 t/ha, 98 t pea yield was taken from the pilot plots. Some of the farmers will sow the peas in other plots to improve soil fertility on another land under their ownership. Buckwheat was sown only on 2 plots, 450 kg at all. The farmers who had opted for the concept of starting the crop rotation with buckwheat cultivated the green mass in the soil to improve their fertility. The harvest of peas/buckwheat was very variable between the different farmers depending on their timing of measures: 1. The farmers who could not use the possibility to seed the crops in March - 1 farmer, because of rainy weathers afterwards, seeded pea later , in the middle of April. This farmer could not get yield from the plot. The others (2-3 farmers) who could not harrow the soil after seeding (as we recommended to harrow), they got the small yield.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
When peas are used as a intercrop between winter wheat cultivation, this would have a positive effect on wind erosion. Since the implementation of the crop rotation just started in 2018, evidence-based further impacts are only expected in the following years, e.g. impacts on soil quality.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
No off-site effects are expected.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Comentários:
Maintenance costs were not applied.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
It is a very new technology. But success of the first year will help to spread it across the region.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The project gave farmers the opportunity to try the new crops (peas and buckwheat) for the community of Dedoplistsakro, as they only sow wheat and barley over the years. They had the opportunity to get advice on how to sow peas and buckwheat and how to improve the soil fertility of their land. They invested through ploughing, harrowing and maintenance, as well as by taking over the yields. They were also interested in maintaining the yield from the proposed crops, using this seed for further plots next year and passing on the knowledge to other farmers. Some farmers sold harvested peas as forage, some gifted others for the same purposes to improve soil fertility. |
| The farmers, who sow the peas in time and cultivate them with appropriate agrotechnical measures, harvested 3.5-4t/ha. The profit was 12 250 - 14 000 GEL/ha. The yield rate was as follows: 3.5.5 t/ha yield - 4.8 yield rate; 4 t/ha --- 5.5 yield rate. |
|
The expected yield of barley per hectare in the years following pea sowing will be 7-9 tonnes. Income ratios - 9.6 for 7 t/ha yield; 12.4 for 9 t/ha yield. The expert calculated the expected yield on the basis of yield data from the davit Nateladze area in Dedoplistskaro, where peas were sown in 2017 and then 5.5 t barley/ha instead of 1.5 t barley/ha (in previous years before peas were sown) was harvested. As part of the pilot project, 23,750 kg of peas were sown on 92 ha in Dedoplistskaro in 2018. 98 t of peas were harvested in mid-July in the municipality of Dedoplistskaro. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The machinery for preparing the soil and seeding are available. |
| Especially pea has a very positive effect on soil fertility. |
| Most of the farmers used the technology for next year(2019). They seeded the harvested pea in spring 2019 at another plots in Dedoplistsakro municipality (about 100 ha). This confirms the positive impact of the approach on soil fertility and guarantees the sustainability of the project. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Some farmers (2-3) sow the pea later than others. They did not get a good yield because of the sowing in April. The reason for the delay was 1. rainy weather; 2. lack of machinery. Timely harvesting was also the problem because of the lack of machinery, since Dedoplistskaro is called the barn of wheat and there are not enough machines in the community. The problem of the realization of peas and buckwheat was also the problem because of the lack of companies for peas and buckwheat not only in the municipality but throughout the country. | The farmers asked for a support for the municipality in the development of such enterprises to process the mentioned crops for realization. |
| Of the 3 schemes proposed, 19 farmers choose the first scheme to sow the peas in the first year. The second scheme was not chosen at all. The 3rd scheme to start crop rotation in the 1st year with buckwheat was chosen by 2 farmers. A farmer ploughs the yield of buckwheat as a green mass in the soil and improves the fertility of the soil. Another harvested and prepared 120 hay presses. The farmers improved the soil, but the expenses were at 1 ha / 2 645 GEL, 1 press / 7 GEL, the income ratio 0,31. The sowing of buckwheat to prepare the press is ineffective to benefit from the harvest. The farmers who opted for the third scheme (start of croprotation with buckwheat) were geared towards improving soil fertility, but most farmers prefer to do the rotation in order to benefit from the yield. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| There is no local marked or seller for peas and it is difficult to sell the product for the local farmers. | It needs national support to develop a pea-processing industry. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Two field visits.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Interviews with the implementing national field expert.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Documentation from the field expert
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
12/09/2018
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos