Establishment of a paddock system and improvement of degraded pastureland. [Geórgia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Kety Tsereteli
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_4276 - Geórgia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
co-compiler:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Geórgia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Rehabilitation of Pasture Land through fencing [Tajiquistão]
The approach demonstrates the effect and importance of rotational grazing by fencing certain areas of land in pasture areas as well as it demonstrates the rehabilitation process in comparison to the open space which is overgrazed. The approach involves mobilizing communities to observe the rehabilitation process by not grasing in …
- Compilador/a: Askarsho Zevarshoev
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
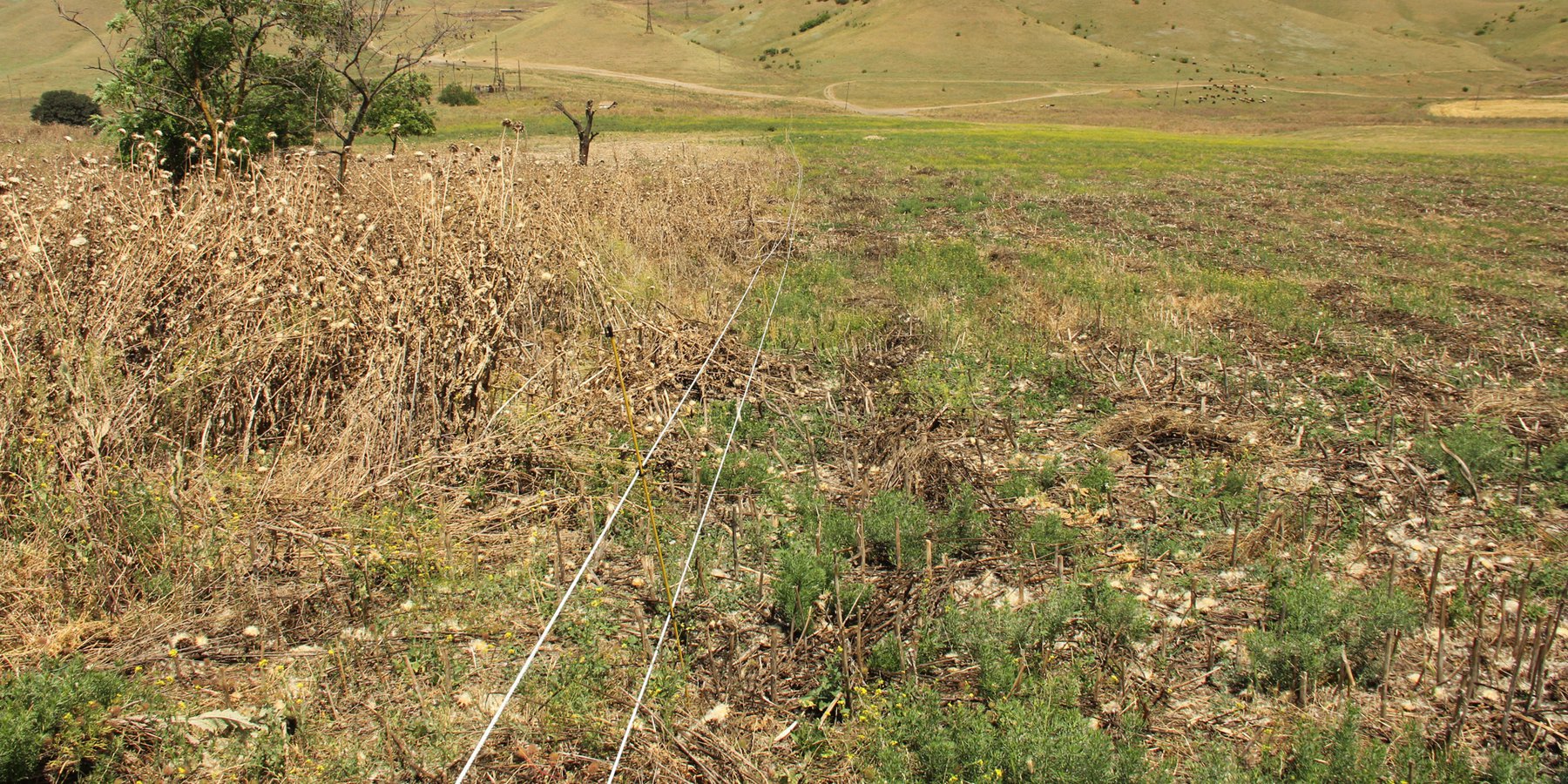
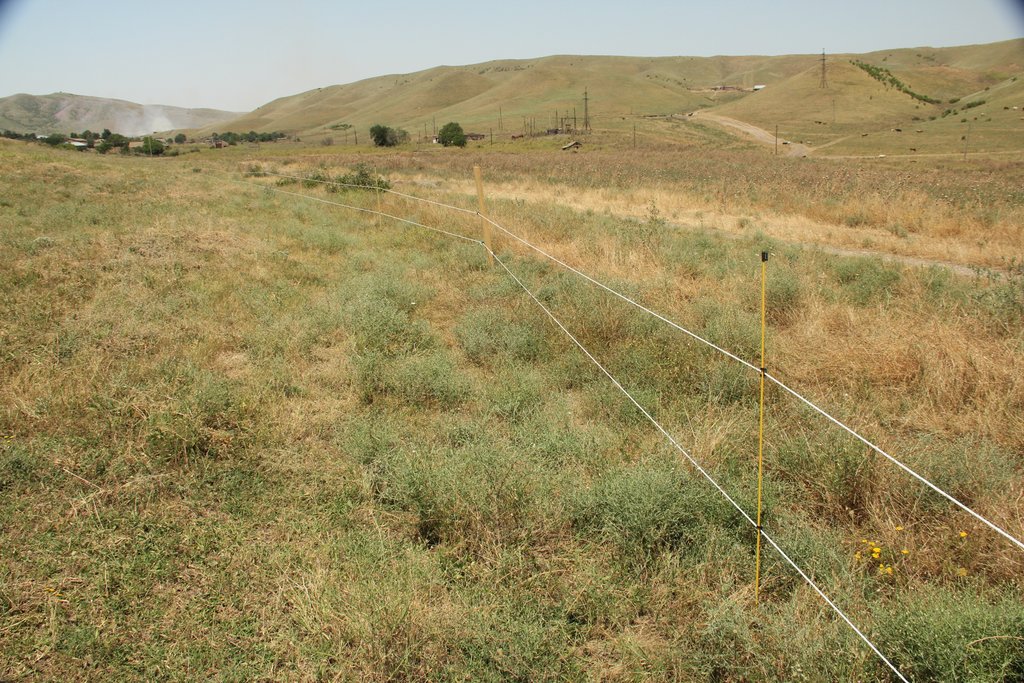
In a pilot project, degraded pastureland near the settlement of Kasristskali was regenerated by introducing a fencing, mowing and grazing regime that favours the growth of forage plants instead of weeds and, where necessary, reseeding forage plants.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
This showcase is part of the project "Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas", implemented by the Regional Environmental Center for the Caucasus (REC C).
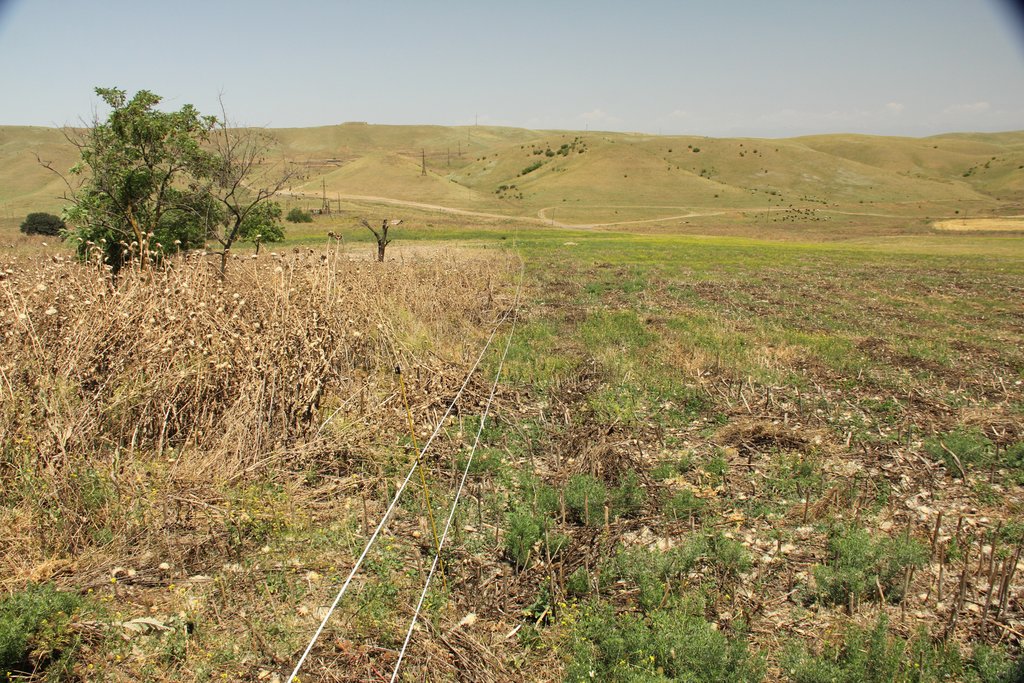
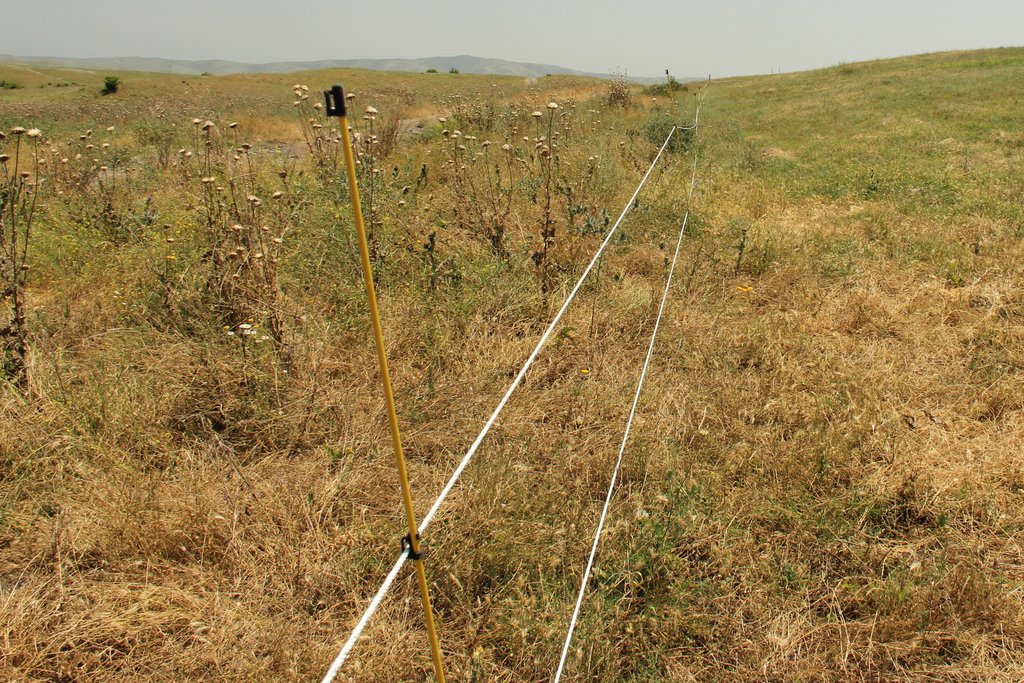
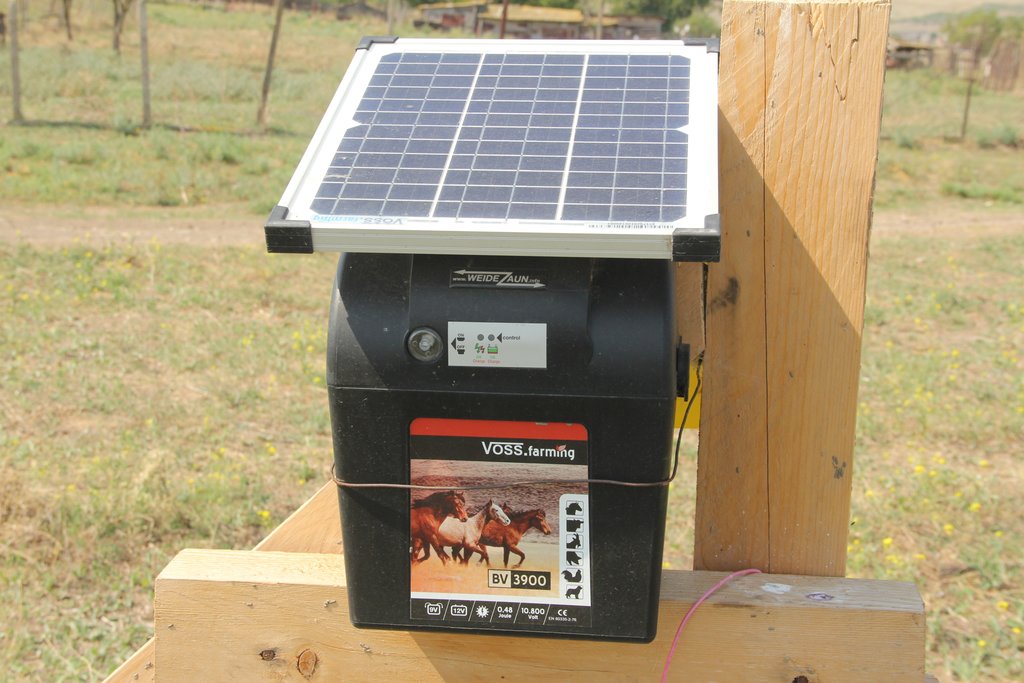
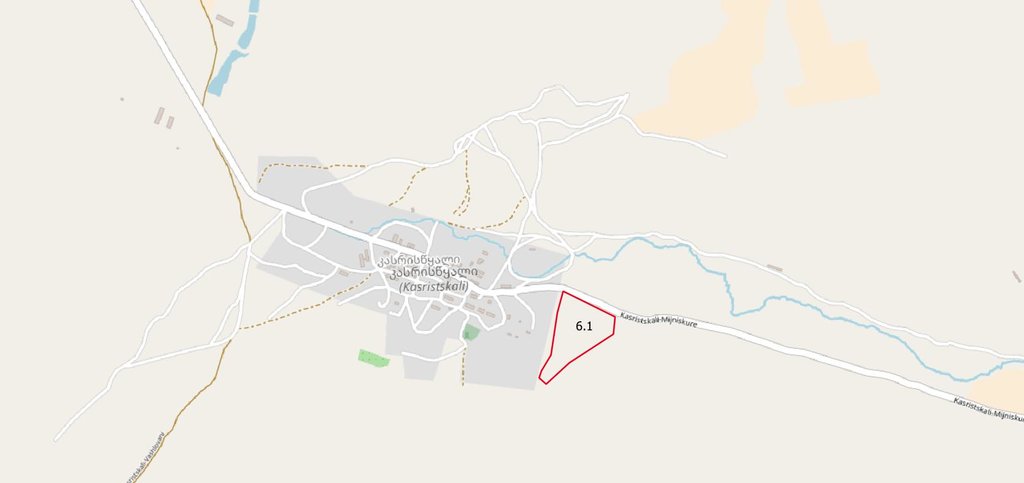
The implementation site was selected by national experts together with stakeholders from the village. This site is located close to the settlement Kasristskali. It is community pastureland, which was abandoned and not maintained for many years. The site had been dominated by thistles and weeds before the intervention took place and was not suitable for grazing. 30% of the area was previously used to store manure and is rich in nutrients. To reclaim the pastureland for cattle, an area of 6.1 ha was mowed twice and equipped with an electric fence (two lines of electric wire and a solar-powered energizer brand Voss). This was done to regenerate the area so that a grazing regime could be introduced later. An electric fence was chosen because wood is not available in the area and a wire mesh fence would be more expensive. Furthermore, an electric fence is flexibly adjustable, which is essential for a rotational grazing system. It is important to remove the residues after the mowing to reduce the amount of weed seed. The time of mowing should be before the flowering of the most common weed species. An ongoing mowing and grazing regime was set up to favour fodder plants instead of weeds: Since the cows only eat the fodder plants and leave the weeds standing, the weeds have a clear advantage. To counteract this, the weeds are mowed, and fodder plants are sown. Mowing is needed for the first 2 years and after that, it is enough to control the quality of pastureland by a grazing system. For maintenance purposes, the area was cut once in early spring and a second time in summer. The evaluation in September, after the pastureland was recultivated, showed that the northern and eastern parts now have a grass and herb cover suitable for grazing, while the central, western and southern parts are still overgrown by weeds. This is due to the fact that these parts were very rich in nutrients from the very beginning and consisted exclusively of thistles. In order to improve the productivity of the site, it is recommended to cut the vegetation again in autumn, remove the residues, open the soil with a harrow and sow a pasture seed mixture adapted to the climatic conditions in February.
The local community farmers were involved in all activities. They were participated in development of local pasture management plan. The plan was approved by the community members and they are ready to follow the applied methodology and maintain the pastureland after the project completion. The farmers acknowledged the benefit from the proposed methodology and they invested to rehabilitate the additional area (6 ha) of pastureland with their own financial sources.
The 6.1 ha plot which was restored as pastureland with this technology is planned to be used as a paddock for alternating grazing between free-range and the paddock.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Geórgia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kakheti
Especificação adicional de localização:
Municpalty of Akhmeta, Kasristskali village
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The national park Vashlovani is nearby.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas; GEF funded, implementation by the Regional Environmental Center for the Caucasus (REC).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
The area east of the village is rich in nutrients but was not maintained. A dense weed layer of milk thistle (Silybum marianum) was established.
Comentários:
The main income of the village comes from agriculture in the plains of Shiraki Valley and livestock breeding in the hilly land east of the plains.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- gado - lácteo
- gado - carne bovina não-láctea
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Não
Produtos e serviços:
- carne
- leite
Espécie:
gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
Comentários:
The 6.1 ha plot which was restored as pastureland with this technology is planned to be used as a paddock for alternating grazing between free range and the paddock.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Reserva ( suspensão do uso, apoio à recuperação)
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A7: Outros

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
- V4: Substituição ou retirada de espécies exóticas/invasivas

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M5: Controle/mudança de composição de espécies
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
The technology enables efficient weed control on common pasture land. The improvement of degraded pastures is achieved through weed control and sowing of fodder crops and the use of a rotational grazing system.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
The degradation is driven by excessive spread of milk-thistles on nutrient rich pasture land because of missing maintenance. Those thistle stand are of low plant diversity and have no fodder value.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The technology supports the restoration of the weed dominated pasture land. This will increase biodiversity and productivity.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The area on which the technology is applied is 6.1 ha. The paddock is on community rangeland and managed by the village people. It is located on a slightly north-oriented slope near the village. The area was used to store manure. The high nutrition values led to the enormous growth of weeds, especially thistles.
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Data:
22/03/2019
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
13 USD/day
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | First mowing of the site, clearing from thistles and removal of hay/residuals | Early spring (March) |
| 2. | Establishment of electric fence | June |
| 3. | Opening the soil with a harrow | February of following year |
| 4. | Seeding of fodder plants | February of following year |
Comentários:
It is important to remove the residues after mowing to reduce the amount of weed seed. The time of mowing should be before the flowering of the most common weed species.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Setup of fence | person-days | 2,0 | 13,0 | 26,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Open the soil with a harrow | person-days | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Seeding of fodder plants | person-days | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Mowing (1st time) an manual removal of thistles | person-days | 18,0 | 13,0 | 234,0 | |
| Equipamento | Equipment for 1200m electric fence including energizer | set | 1,0 | 2547,0 | 2547,0 | |
| Equipamento | Machinery for mowing (rental) | days | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| Equipamento | Machinery for harrowing (rental) | days | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seeds (Onobrychis) | kg | 300,0 | 1,5 | 450,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 4083,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 4083,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The equipment, renting cost of machines and labor was financed by the GEF SLM project.
Comentários:
The local village is very poor and lacks of infrastructure and financial capabilities.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Second mowing and removal of hay | July |
| 2. | Third mowing and removal of hay | September |
Comentários:
The weed population is still very high. These are poisonous or spicy plant species which cannot be controlled by intensive grazing. To reduce the dominance of this weed, it is recommended to mow the entire area of 6.1 ha three times a year. The best time to mow is before the weed blossoms.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Mowing (2nd and 3rd time) | person-days | 2,0 | 13,0 | 26,0 | |
| Equipamento | Machinery for mowing (rental) | days | 2,0 | 400,0 | 800,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 826,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 826,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The community is very poor so the costs for maintenance was covered by the project. After the difficult removal of the thistles, the second and third mowing was done only by machinery and has not needed that much man power than the first time.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most important factor was the equipment for the electric fence. Electric fencing material is not common in Georgia and there are no relevant national suppliers.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
697,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The pasture is located on top of a small hill and its north-eastern slopes.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
30% of area was used of manure storage before and is rich on nutrients.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Only a few weed species where dominating the area before the intervention.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The village is very remote. Driving distance to the municipality is about 1h on bad roads.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
Community pasture land.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1-2 t/ha
Comentários/especificar:
The fodder production will increase in the next few years as mowing and grazing affect weed control.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
The fodder production will increase within the next years when mowing and grazing shows effect in the decrease of weeds.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0 ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
6 ha
Comentários/especificar:
6 ha of degraded and unused pastureland have been recultivated.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Community is equipped with electric fencing infrastructure (including training)
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
Most of the area could not be used for cattle grazing due to the dominance of weeds. Based on biomass harvesting experiments in Tusheti, it is expected that at least 1-2 tons of fodder per hectare will be available on the pasture.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
No significant effects are expected off-site
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Comentários:
When temperatures rise and precipitation decreases, productivity falls. If productivity is below 1t/ha, the investment in an electric fence will not pay off.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
In the first two years, the forage harvest will be low, while the costs for erecting the fence and maintenance by mowing will be high. In the long run, unproductive land will be productive again. On the 6 ha, 6 to 12 tons of biomass per year can be expected (depending on rainfall in spring and summer). This is equivalent to 500-1000 USD/year.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
There is strong interest to establish a second plot for rotational pasture systems of 20ha near by. The financial capacity of the village is to low to cover the investment of the fencing material.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| improved pasture quality and new fencing technology introduced |
| raised production of fodder plants |
| pasture management plan is developed and local farmers are able to manage the pasture rotational system themselves. Also the farmers were trained in installation and maintenance of el-fence. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| A fertile land near the village, which was unusable, was turned back into productive land. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The pasture land has already been severely degraded (mainly by weeds) and it will take time and more resources to restore it. | Small grants to support the rental of machines for mower maintenance (topping cuts). |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The investments for the fencing cannot be made by the villagers. | Long-term microloans with low interest rates. |
| Seed of local, climate-adapted forage plants is not available. | Establishment of local seed suppliers in cooperation with the agricultural extension service. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
2 field visits in 2018
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
two interviews with local land users and one training on rotational pasture management, hands on training on installing and maintaining electric fence.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Discussion with national field experts
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
12/09/2018
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas: Final report. 2017. Kirchmeir, H., Joseph, A., Huber, M
Disponível de onde? Custos?
RECC Caucasus
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Rehabilitation of Pasture Land through fencing [Tajiquistão]
The approach demonstrates the effect and importance of rotational grazing by fencing certain areas of land in pasture areas as well as it demonstrates the rehabilitation process in comparison to the open space which is overgrazed. The approach involves mobilizing communities to observe the rehabilitation process by not grasing in …
- Compilador/a: Askarsho Zevarshoev
Módulos
Não há módulos