Drought-resistant crops [Suíça]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Seraina Lerf
- Editores: Tatenda Lemann, Maria Eliza Turek, Joana Eichenberger
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6272 - Suíça
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Brunner Stefan
Brunner Eichhof
Suíça
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The technology described covers one such response in Switzerland.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The key is the improved adaptation of the crops to heat and drought. These adaptations are based on plant physiological and morphological characteristics that confer increased drought tolerance, as well as phenology, which can also affect the plants' water requirements. The goal is to reduce production losses and promote a regional, plant-based food system in Switzerland. To introduce and maintain drought-resistant crops requires specific activities and inputs, such as selecting suitable seeds and ensuring long-term profitable cultivation. This technology is applied to cropland in Switzerland, especially in the Swiss Plateau, where climate change is causing increasingly warmer and drier summers, as well as more intense precipitation in the winter months. These climatic changes favour the cultivation of crops that can better cope with drought periods, allowing for the replacement of crops that require irrigation in the same growing areas.
The main purpose is to adapt agricultural production to the effects of climate change while simultaneously reducing the emissions caused by farming. By cultivating drought-resistant crops, the risk of production losses during drought periods can be minimized, and a transformation towards more diverse, plant-based, and regional food production systems can be promoted. A major advantage of this technology lies in the adaptability of the selected crops to climate change. Since they are better adapted to tolerating drought periods, no additional irrigation is needed: this saves labour and other resources. Moreover, growing drought tolerant crops enables the production of regional, plant-based, and protein-rich foods (especially legumes) that are appreciated by certain consumer groups and can be better marketed.
However, there are also challenges and disadvantages that are not yet appreciated by land users. The lack of knowledge about non-traditional crops in Switzerland is a significant problem. Both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in cultivation are lacking, leading to high risk for farmers who must experiment with cultivation. Additionally, despite climate scenarios predicting drier summers, there is still the risk of cool and wet summers with increased precipitation. Besides the biophysical challenges, there are also socio-economic obstacles, as the demand from wholesalers is often focused on traditional crops, and niche crops like millet are commonly not popular.
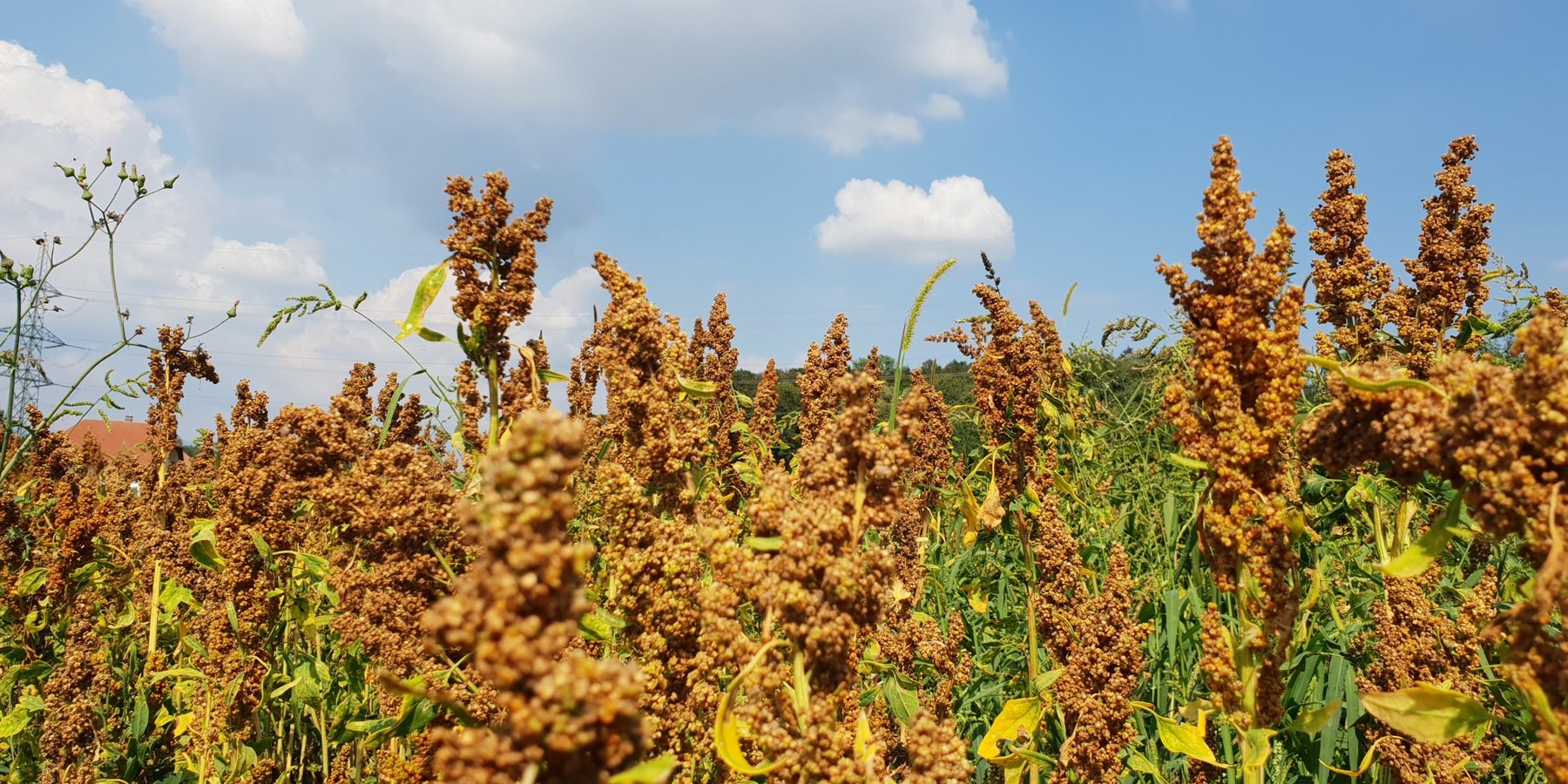
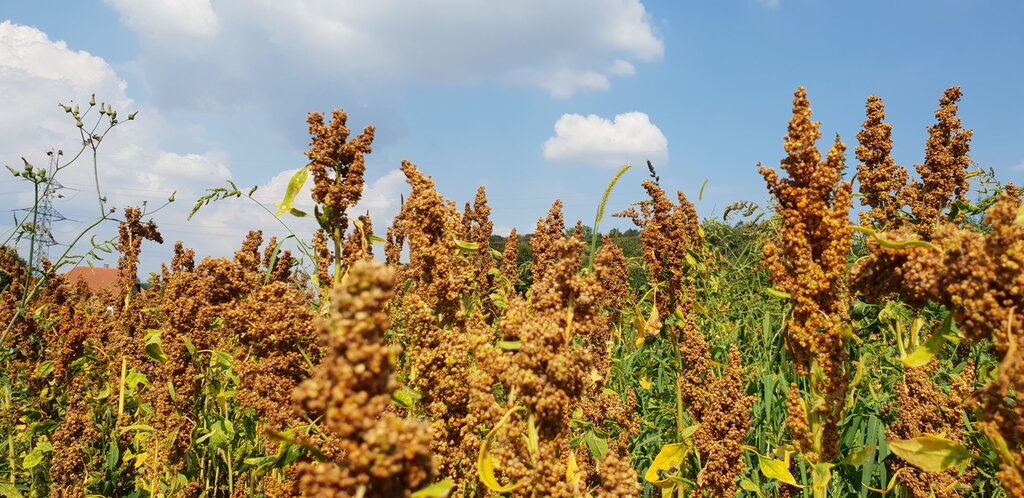
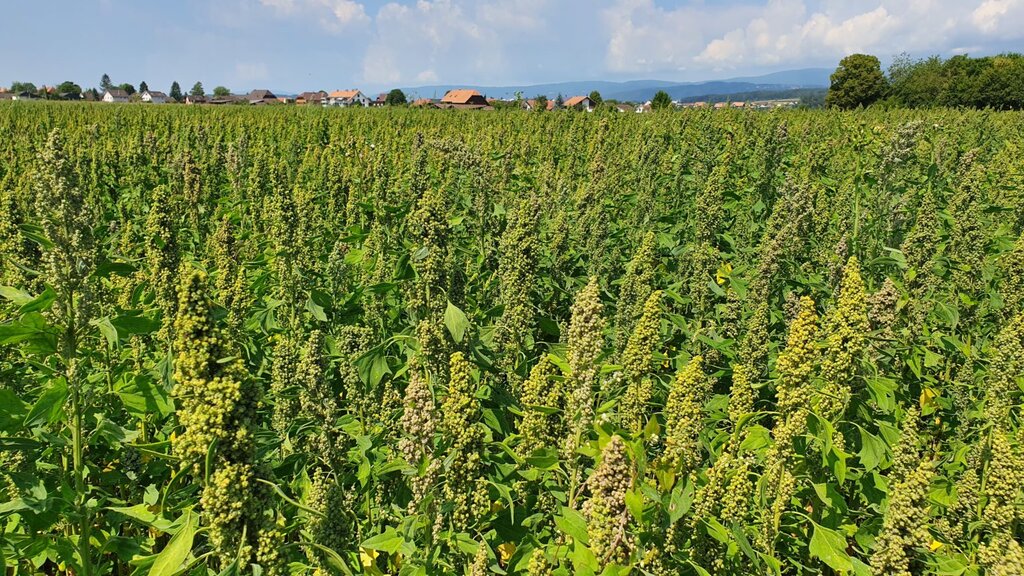
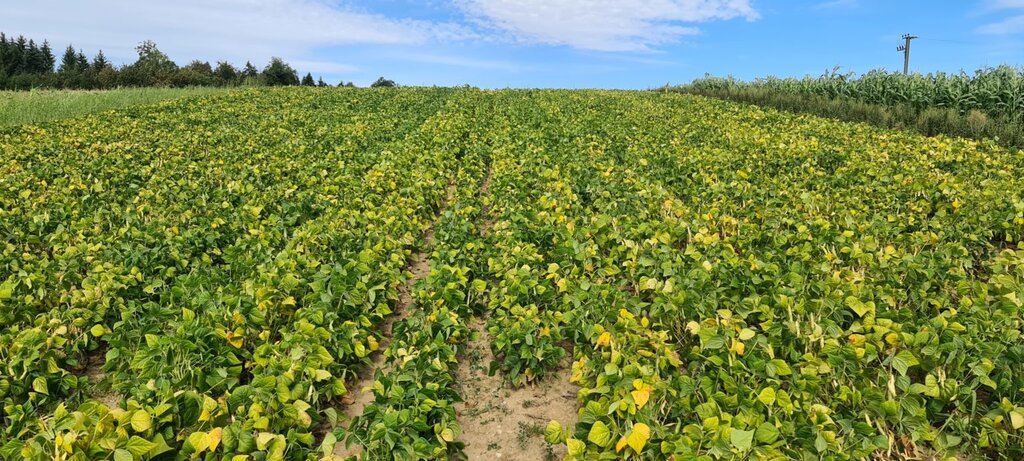
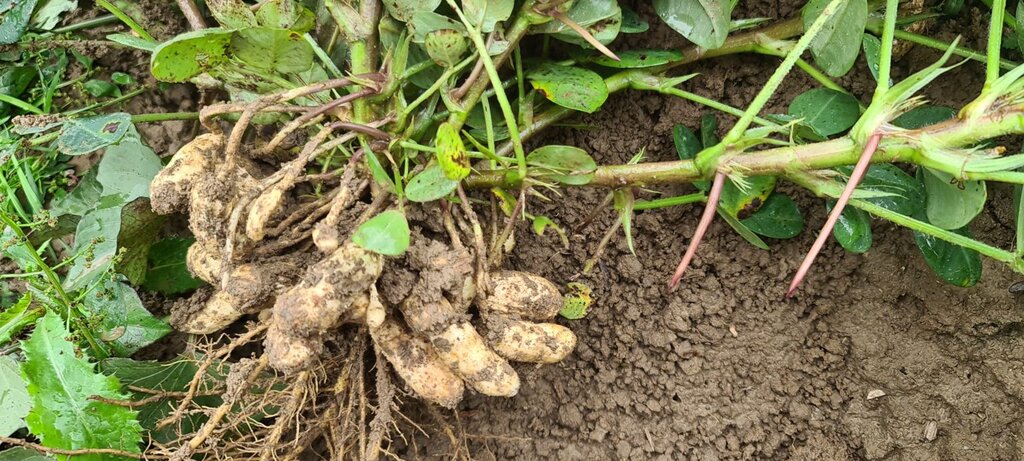
This documentation focuses on an example of an innovative farmer in Spins, Switzerland. Stefan Brunner has been testing a wide variety of drought-resistant legumes such as lentils, lupins and black runner beans on his Eichhof farm since 2017. In addition to the large-scale cultivation of these drought-resistant crops, he also cultivates quinoa, peanuts, chia, sorghum, millet and rice in a demonstration plot. Stefan Brunner simultaneously attaches great importance to sustainable cultivation methods which include surface tillage and mulching.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
All pictures were taken on the agricultural land of Stefan Brunner in Spins near Aarberg. The pictures of the quinoa field, the bean cultivation and the peanut harvest were taken from the website of the Brunner family's Eichhof farm:
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Suíça
Região/Estado/Província:
western midlands of switzerland
Especificação adicional de localização:
western midlands of switzerland (Broye catchment area), example farm in the canton of berne in Spins (near Aarberg)
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The regions in which the technology is used are located in the agricultural zone of Switzerland
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2017
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- cereais - quinoa ou amaranto
- cereais - sorgo
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- culturas forrageiras - gramíneas
- leguminosas e pulses - lentilhas
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
The number of growing seasons depends on the crops grown. With a crop rotation of 6 years, winter cereals, winter lentils/winter legumes and lupins are grown overlapping after three years of permanent grassland (grass production). Brunner also uses green manure between the different crops and therefore has around 2 growing seasons per year
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
6 years crop rotation:
3 years grass
Winter cereals
Winter lentil (winter legumes)
Lupin

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Comentários:
Stefan Brunner is able to irrigate all his fields in Spins near Aarberg. He owes this to the nearby location of the "Alte Aare" river, which gives him the privilege of having sufficient water available even during the summer.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A5: Gestão de sementes, variedades melhoradas
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Brunner sees soil degradation as an unavoidable consequence of all agricultural tillage. However, this can vary greatly depending on the type of tillage. Brunner does not see a direct improvement in soil degradation through the cultivation of drought-resistant plants. However, in combination with soil-conserving forms of cultivation. Brunner attaches particular importance to shallow tillage (maximum depth of 5 cm). Accordingly, crops that can be sown at this depth are suitable. Brunner strives for permanent rooting of the soil and prefers crops that can be sown in the fall so that the soil is rooted over the winter or can handle green manure. These measures (shallow cultivation and root penetration) keep the soil looser. The roots form flow paths, which increases the water storage capacity of the soil. The shallow tillage with small machines, which Brunner uses for his drought resistent crops, also reduces the physical pressure on the soil compaction.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
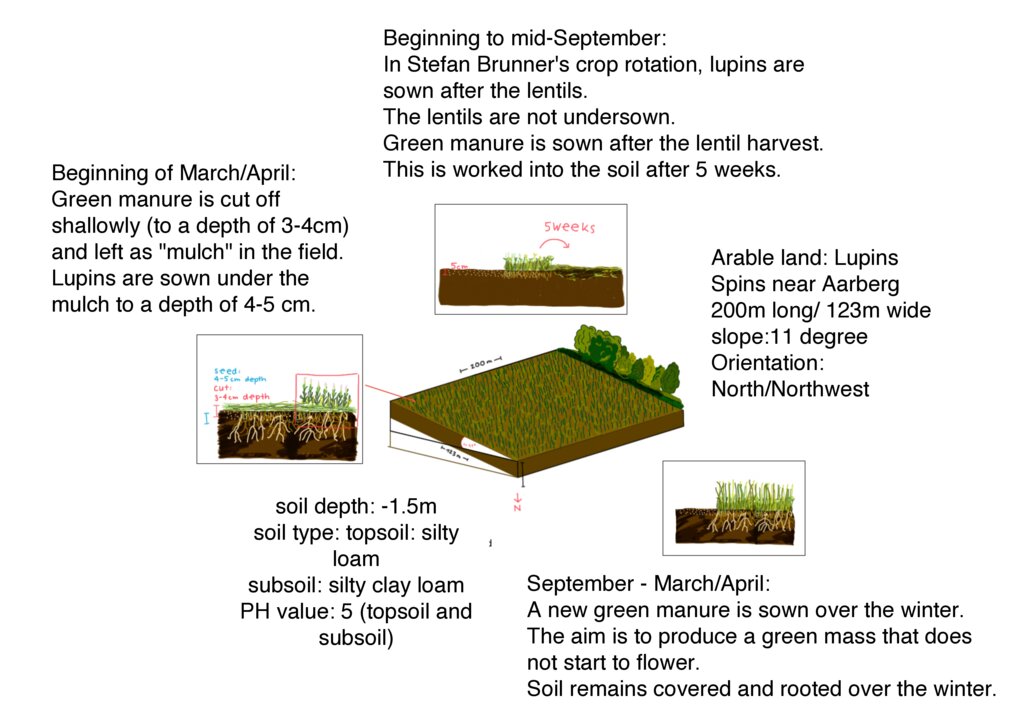
The depicted technical drawing shows the farmland of Stefan Brunner, where lupins were sown in the spring of 2024. This field is representative of all the arable land, totaling 14 hectares of crop rotation areas managed by Brunner. The cultivation areas are situated at an altitude of 487 meters above sea level on flat or slightly sloping terrain on a hill range in the Bernese Mittelland. The depicted field is 200 meters long and 100 meters wide, with a slope of approximately 11° and an orientation towards the north/northwest. The soil is classified as silty loam based on the finger roll test, with the subsoil containing more clay compared to the topsoil. The pH value is 5, which is in the slightly acidic range.
The fields in Spins are located near the river "Alte Aare." Due to the proximity to the water, the farmer has the privilege of having irrigation available for all his fields. Since the implementation of large-scale cultivation of drought-resistant crops in 2017, Brunner has been growing a variety of crops on his land. According to Brunner, the following crops that he cultivates can cope well with drought: lentils, lupins, sorghum, corn, peanuts, millet, and cabbage. In combination with the method of surface rotting and mulching, the soil is protected against drying out and erosion and can retain moisture for longer. The cultivation of various crops can be combined with this farming method, leading to better drought resistance.The graphic illustrates the cultivation of lupins using a green manure cultivation method.
Autor:
Seraina Lerf
Data:
21/06/2024
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
18 ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage: and sowing | (once per cultivation period) |
| 2. | maintenance: weeding (recurring work step, but less labor-intensive than tillage) | (Recurring work throughout the year) |
| 3. | harvesting: threshing | (once a year for grain legumes) |
| 4. | Threshing the previous crop. Before the lupins, lentils were grown in Stefan Brunner's crop rotation. | summer (july-september) |
| 5. | If there is no undersowing (as with the lentils), the soil must be tilled. This is very shallow, i.e. no more than 5 cm deep. | summer (july-september) |
| 6. | A varied green manure is sown in the cultivated soil. The aim of this is to keep the soil rooted and to incorporate nutrients into the soil | summer (july-september) |
| 7. | After 6-7 weeks, the green manure is worked back into the soil. When the plants are still young, they have the highest nutrient input before they extract the nutrients from the soil again if they continue to grow. As a result, the nutrients are mineral-bound in the soil, i.e. stored so that they are available to the plants. | autumn (early/mid-September) |
| 8. | Another green manure is sown, which produces a lot of mass but freezes off in winter before it starts to flower. The aim is to keep the soil covered and rooted throughout the winter. | autumn |
| 9. | In spring, the soil is again worked shallowly. This means a maximum depth of 3-4 cm. The winter green manure is "planed". This means cutting it to a depth of 3-4 cm and leaving the plant material on the ground. | spring |
| 10. | The lupins are sown under the plant material to a depth of 4-5 cm, so that the soil remains moist and the plant material protects the soil from drying out. | spring (beginning of March/April) |
Comentários:
The first three information does not refer to a specific crop, but describes general maintenance activities that Brunner takes into account when cultivating his crops.
Stefan Brunner's crop rotation also includes 3 years of grassland. This cultivation reduces the workload, as no maintenance work has to be taken into account in addition to the harvest.
The activities 4-10 described relate to the cultivation of lupins. This crop was cultivated at the time of documentation in spring 2024.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia:
22575,0
Comentários:
The costs of cultivating drought-resistant plants cannot be precisely quantified. Based on the interview results, it is therefore not possible to make any general statements about the costs of cultivation.
Nevertheless, in order to be able to make a rough estimate of the input costs required to implement the technology (Example based on the cultivation of lupins), information from REFLEX 2024 (AGRIDEA's business database) and FiBL (Research Institute of Organic Agriculture) was used. According to REFLEX 2024, the target price for lupins in 2023 and 2024 is 144Fr./dt. A FiBL leaflet also states a requirement of 130-170kg seed/ha (blue lupins).
According to the results collected, the documented farm uses a disk coulter seed drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm, sows approx. 3-4 cm deep and requires 200 kg/ha of seed.
With a field size of the documented farm of approx. 2 ha, the costs for the required lupin seed amount to CHF 576 according to the data from REFLEX 2024.
Then there are the labor costs and the machines. Depending on which machines are required and whether the required machines are already available or whether a new investment or rental would be necessary.
The estimate only refers to the seed required. Additional recurring costs include maintenance/ rental costs for machinery and labour. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more precise information on this. It depends on the machines and labor costs used.
However, according to the interview results with a farmer who grows drought-resistant crops, there are no significant additional costs if the drought-resistant crops can be grown with the same machinery as for conventional crops.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The greatest difficulty in terms of costs lies in the lack of knowledge in the cultivation of these crops. The fact that very little scientific and practical knowledge and experience is available means that farmers take a greater risk in cultivating these crops. If cultivation is not carried out correctly and the farmer suffers production losses as a result, he bears the consequences. This is why they have to look for inventive solutions.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
865,00
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Payerne
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Production losses during periods of drought can be minimised
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Product diversity can be increased by growing alternative drought-resistant crops
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
By improving the soil's ability to cope with weather extremes (drought/heavy rainfall), land management in cultivation is simplified through greater flexibility.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
Gentle tillage without the use of pesticides in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops (good groundwater quality)
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Drought-resistant crops require less irrigation. In addition, the tillage method (surface rotting) also prevents the soil from drying out.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Gentle soil cultivation with minimal use of machinery (and application of surface rotting) requires more labour, even if the cultivation of drought-resistant crops does not mean additional work compared to conventional crops
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Less water required for irrigation
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Avoiding the use of pesticides leads to improved water and soil quality
Harvesting/collection of water
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods) can lead to improved groundwater recharge
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Surface runoff can be minimised by improving the water absorption capacity of the soil (permanent root penetration).
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods), less excess water is formed
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil can lead to improved groundwater recharge
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Permanent ground cover can reduce soil drying out
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The permanent ground cover reduces drying out and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This can improve the soil water balance.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The ground should be permanently covered. The permanent ground cover reduces drying out.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
The permanent covering and rooting of the soil prevents surface run-off. This can prevent soil loss.
Acumulação de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Green manuring can ensure an improved hummus structure.
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The permanent ground cover reduces dehydration and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This prevents soil sealing.
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The soil should remain permanently rooted and covered and be worked with as few and light machines as possible. This minimises soil compaction.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
By applying green manure, the soil can be enriched with nutrients (nutrient cycle of the soil).
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
greater plant diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the improved ability of plants to cope with drought. to deal with drought. In combination with good water storage capacity of the soil, the effects of drought on the harvest can be minimised.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
Information in this chapter on practical experience in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops is based on interview results from Stefan Brunner. He cultivates drought-resistant crops in combination with surface cultivation and mulching. As a result the effects of the two technologies cannot be considered entirely separately.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Comentários/especificar:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
The use of herbicides and fungicides was avoided in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, thus preventing contamination
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
improved water absorption capacity (through soil cultivation methods) of the soil
Stability of production
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the improved adaptability to climatic conditions, production remains more stable
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. Annelie Holzkämper
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | moderadamente |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | moderadamente |
| Onde de frio | não conhecido |
| Condições de inverno extremo | não conhecido |
| Seca | bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | não conhecido |
Comentários:
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. rer. nat. Annelie Holzkämper
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The more equipment has to be used in cultivation, the more expensive the maintenance costs become. As Brunner is able to cultivate drought-resistant crops such as lupins and lentils with the existing equipment, he did not incur any additional costs. Even if a new machine for gentle soil cultivation in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, such as a “planer”, had to be purchased, a plow could be sold in return. As long as the same mechanization can be used as Brunner was already using for conventional crops, the costs remain the same. As a result, Brunner's cost-benefit ratio was assessed as positive, even in the short term.
In the long term (over a period of 10 years), Brunner also sees an increased positive cost/benefit ratio. Consistently good soil cultivation regenerates the soil so well that it is able to absorb much more water. The amount of work required to implement this form of cultivation increases in the short term. However, the improved soil conditions in connection with the cultivation of drought-resistant crops have a positive effect on the workload and yield in the long term, as the crops on healthy soil are more flexible in the face of extreme weather conditions such as increasingly frequent droughts. Brunner also emphasizes that, from his perspective, it is worth incurring higher start-up costs for careful cultivation in order to generate long-term benefits.
The start-up costs are often relatively high, but the long-term benefits are all the more valuable. Start-up capital is therefore essential to be able to generate long-term benefits.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Information based on the experience of Stefan Brunner (Spins)
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
breeding
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Continuous adaptation in the context of breeding
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| No Irrigation Needed: These crops do not require irrigation, thus saving water and reducing labor. |
| Promotion of Soil Health: The cultivation of these crops is beneficial for the soil, as as the tillage is shallow and legumes do not require additional nutrient inputs through fertilization. |
| Benefits in Direct Marketing: These crops are niche products produced in limited quantities in Switzerland. Conscious consumers who value regional food products appreciate these items and understand the higher costs due to the high labor requirements. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Reduced Irrigation Needs: If the crops can tolerate more drought, less irrigation is needed. |
| Minimized Economic Risk: Drought tolerance reduces the risk of crop failure during dry periods. |
| Crop Rotation Benefits: Better adaptation through diverse crop cultivation. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High Labour Requirements: initial labour requirements are significantly higher due to limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation, but with time this reduces - as less and less work is required on healthy and nutrient rich soils. | More practical knowledge should be gathered by encouraging more farmers to cultivate these crops and facilitating knowledge exchange. |
| Lack of Mechanization: Available market machines are not suited for the desired cultivation methods. | Alternative machines are needed, which are smaller and lighter and only minimally till the soil. New approaches and inventions in machinery are required. |
| The wholesale market is not particularly interested in domestically produced alternative foods. Wholesalers are profit-oriented and primarily offer what is consumed in Switzerland. | A reorientation of dietary habits is necessary. Millet, for example, is ideally suited to the climatic conditions in the Seeland region. Increased consumption could lead to more extensive cultivation. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge: limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation | More research should be carried out in this area and practical experience in cultivation should be gained through practical implementation. Inovative farmers are in demand. |
| Weather Variability: There is no guarantee that heavy rains won't occur, potentially ruining the harvest. | The extent to which crops are affected by severe weather events depends on when they occur. Severe weather events have an impact on every crop, but of course you don't know when they will occur. A useful strategy is therefore to build a highly diverse production system at farm and landscape level. |
| Practical and Socioeconomic Challenges: Market preferences and practical issues, such as livestock not favoring sorghum feed, can be obstacles. | No answer given. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
On June 10, 2024, an interview was conducted with farmer Stefan Brunner on his farm in Spins near Aarberg. Additionally, the cultivated area was inspected
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
On June 20, 2024, an interview was conducted with PD Dr. Annelie Holzkämper.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
10/06/2024
Comentários:
Inspection of the cultivation aera
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve et al. (2023): How to find alternative crops for climate-resilient regional food production, in: Agricultural Systems, Bd. 213, S. 103793, doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103793.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Wuyts, Nathalie et al. (2023): Klimaresilienter Ackerbau 2035, Agrarforschung Schweiz, doi:10.34776/afs13-135.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve. (2021): Prospects of cultivating alternative crops in a changing climate in Switzerland, Master’s Thesis, University of Bern.
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Internet platform of the Eichhof of the Brunner family from Spins near Aarberg
URL:
https://www.brunnereichhof.ch
7.4 Comentários gerais
The information used to complete this documentation is mainly based on the experience reports of Stefan Brunner from an interview on June 10, 2024
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos