Vermicomposting [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Likissa Kurmana Dufera, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Komposti Ramo
technologies_6643 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Dinqa Degu
Farmer
Etiópia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology restores degraded soil and reduces investment costs on chemical fertilizers.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [Etiópia]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
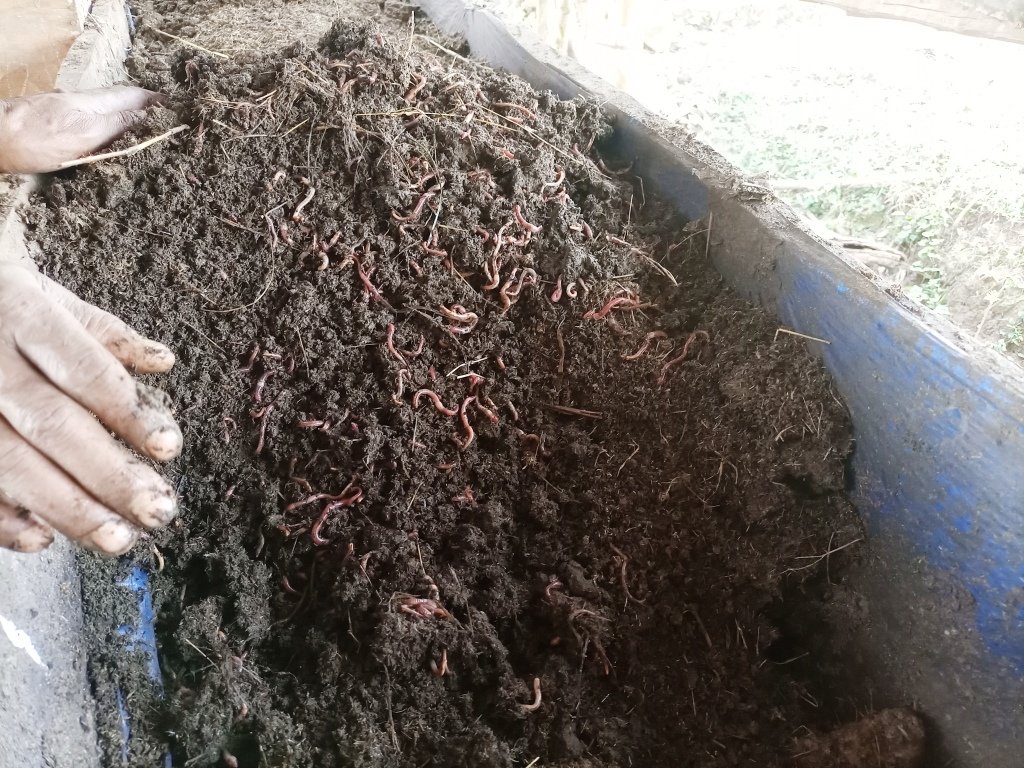
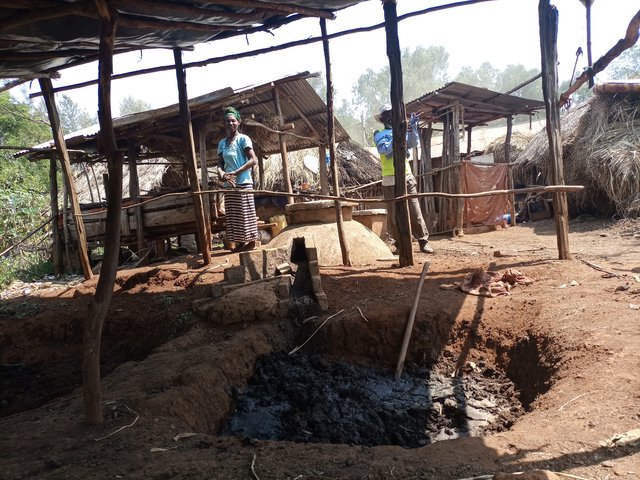
Vermicompost is the product of the decomposition process using various species of earthworms. It is a form of humus and is produced through worms digesting and excreting organic in their casts. Vermicompost has been shown to be an effective organic soil amendment, reducing the need for inorganic fertilizers.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
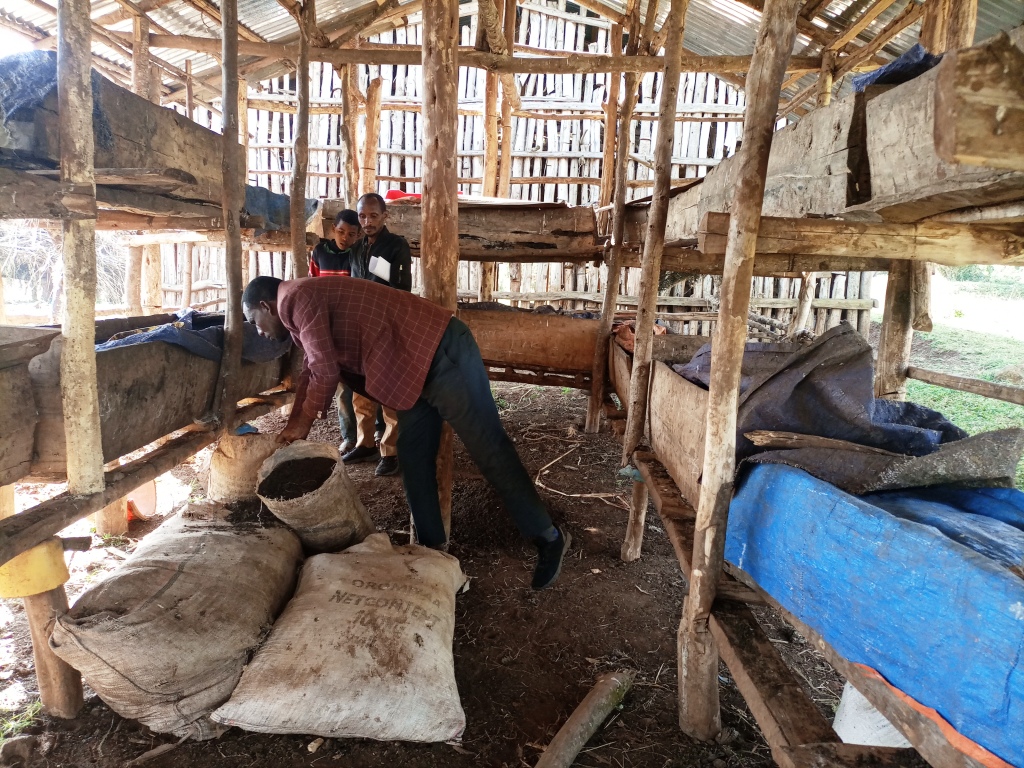
Vermicomposting is the process by which worms convert organic materials (usually wastes) into a humus-like material known as vermicompost. The process is an aerobic, bio-oxidation, non-thermophilic process of organic decomposition that depends upon earthworms to fragment, mix and promote microbial activity. In making vermicompost, earthworms are very good at transforming dead plant material, and livestock droppings into excellent manure. The excrement of the worms has high nutrient levels and a growth‐promoting effect on plants. Earthworms are very sensitive to changes in moisture and temperature. They need a continuous food supply and protection from ants, birds, and chickens. Compared to ordinary compost making, it needs maximum care. For optimum management practices, vermicompost production must be located close to the homestead where livestock barns are usually located. Livestock droppings (especially those of horses and donkeys) are the best sources of feed in addition to plant biomass and other household refuses. Vermicompost production needs a bin in which the worms live. This holds the bedding and food scraps, regulates the amount of moisture and temperature in the bedding, and blocks light which is harmful to the nocturnal worms. Worm bins can be made from plastic or wooden materials. In Ethiopia, wooden boxes are preferred because they are more absorbent and provide better insulation.
Vermicompost reduces farmers’ investment costs on chemical fertilizers. It also has a sustainable role in restoring soil fertility, ameliorating soil acidity and rehabilitating degraded farmland – all of which are problems in the southwestern part of Ethiopia. In the farm where vermicompost is applied, newly transplanted seedlings, in the case of vegetables, remain green and resilient as the compost improves not only the nutrients but also the moisture content of the soil. According to the land users, annual and perennial crops such as horse beans (Vicia faba), wheat, cabbages and avocados grown under vermicompost do very well. Under ideal conditions, 1,000 earthworms can convert 45kg of wet biomass per week into about 25kg of vermicompost. Therefore, the size of production depends on the number of worms, supply of foods, availability of boxes, and associated management practices. In rows and spot application of vermicompost during planting the crop allows efficient and effective uses of the products.
Currently (2023) the government in the southwestern zones of Oromia Region is promoting vermicompost as a vital organic fertilizer. This signals a change in the public sector's and end-users’ mindset in the use of organic fertilizer as a reliable soil amendment, particularly in acid-prone areas. In general, compost restores soil fertility, increases crop production and improves the livelihood of the end users. While the initial cost of constructing the house and installing bins and worms is high, there is potential for the use of local materials. However, it demands considerable household labour for upkeep.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
Video of the technology was not taken.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Oromia, Buno-Bedele Zone
Especificação adicional de localização:
Gechi district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is located close to the home.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2020
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
ISFM+ project (Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project of the GIZ).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- legumes - raízes (cenouras, cebolas, beterraba, outros)
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Cereals with legumes (wheat with faba beans/horse beans).
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Vermicompost was applied to produce Faba beans under rainfed and vegetable production under irrigated conditions.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
- A4: Tratamento do subsolo

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
- Ca: acidificação

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Ps: Subsidência de solos orgânico, sedimentação do solo
- Pu: perda da função bioprodutiva devido a outras atividades

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Chemical fertilizers trigger the soil to dry compared to vermicompost, which keeps the soil moist and the structure firm and coherent. This indicates relieving the degraded soil by changing its color and properties. Also, it allows an increase in the biodiversity of flora and fauna.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
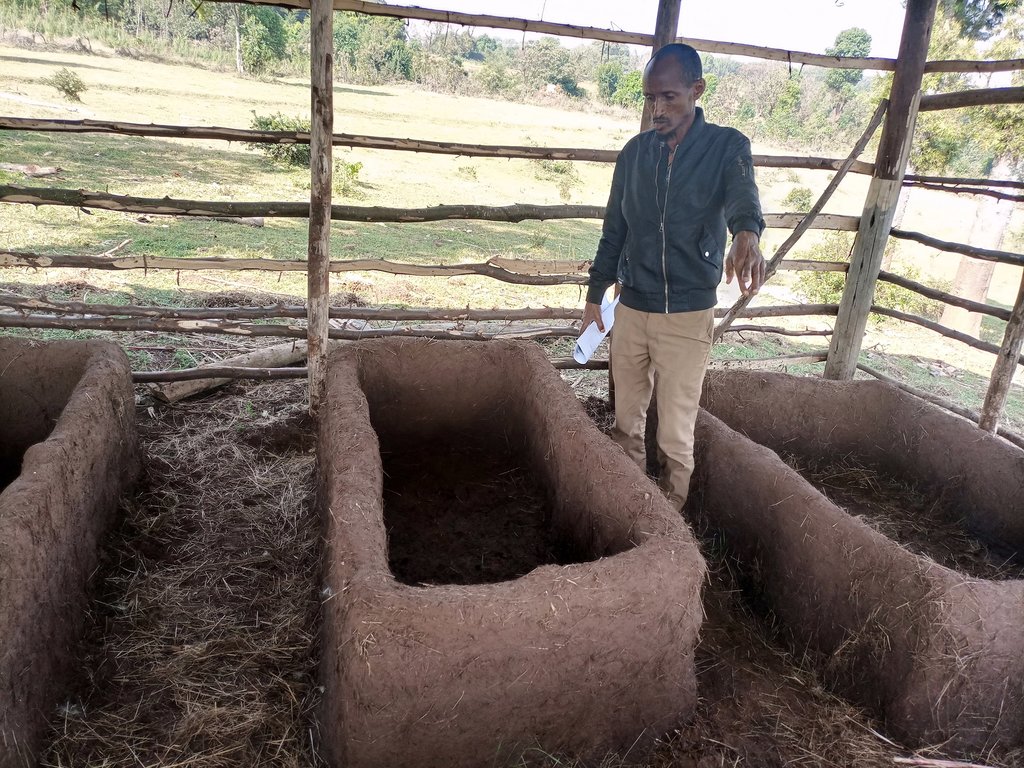
The box is also made with wooden pegs supported with thin horizontal bars and plastered by mud made of soil and water mixed with straw of teff (Eragrostis tef). The box is usually 3 meters long, 60 cm wide, and 50 cm deep, with a total capacity of carrying 0.9 m3 of worms and feedstock at a time. This is a manageable size with 50 cm wide between the structure to allow mobility of the caregivers for effective management of vermicompost.
Autor:
Gerba Leta
Data:
04/02/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
House, boxes, worms, labor...
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
The preferred box size is 3m (L) x 50cm (W) x 30cm (H) with holes (0.5cm diameter).
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
ETB
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
53,12
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
200
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Constructing house or huts. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 2. | Build or purchase the worm bin/ boxes/structure with same function. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 3. | Purchase and/or introduce the worms. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 4. | Add the food and water to the box/structure. | Regularly, through monitoring the status of the worms in the bin/box. |
| 5. | Monitor the surround from the predators and aerate the structure. | Regular monitoring is commendable. |
| 6. | Harvest and dry the vermicompost for use. | When the worms feed on the feedstock and cast the compost (brown humus). |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labor | PDs | 183,0 | 200,0 | 36600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Boxes | number | 14,0 | 250,0 | 3500,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | House with corrugated iron sheet | Lump sum | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Worms | kg | 12,0 | 500,0 | 6000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 71100,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1338,48 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
ISFM+ project of the GIZ covered some minor costs of a farmer.
Comentários:
Labour cost is estimated for a year, each with half a day for follow-up and care. The establishment price is just an estimation. A farmer can start with a few boxes: a couple or more boxes made of local materials that are less costly. Therefore, the estimation is based on the model farmer's approach since he used corrugated iron sheet roofed house and wooden boxes to establish the vermiculture/ vermicompost production center. Otherwise, locally available materials can be used to build hats and wooden structure with plastic lining to serve as boxes. Once established, the recurrent cost is limited to labor and some pesticides.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labour to supply feedstock and provision of other related management practices. | It needs follow-up and supplying the feedstock throughout the year. |
Comentários:
It demands supplying feedstock and water, protecting the worms from predators, and providing other management practices.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labor for follow-up and related practices | PDs | 183,0 | 200,0 | 36600,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 36600,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 689,01 | |||||
Comentários:
Family must sources free labour at least for half a day throughout the year.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The cost is consistently changing. It might be attributed to the economic crisis and the growing inflation.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Bedele
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The altitude is also descending as one travel from highland to lowland agroecology.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Species diversity has been improved with the application of compost to the farm.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Especifique:
Land use right is half inherited, and the other half is self-appropriated but got approval from the local administration.
Comentários:
The land user appropriated some parts of his possession and has changed the marshy land to a farm where irrigation water is accessible.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Abandoned for faba beans
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1.2 tons/ha
Comentários/especificar:
The yield of Faba bean increased from negligible yield where a farmer abandoned it to over 1 ton per hectare.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
It was not scientifically measured but the farmer communicated the harvest of good seed size with better tastes as compared to the harvest without using vermicompost.
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
There is an assumption and evidence that validate that compost favors the growth of diverse wild species. Also, it increases biomass production that associates with fodder or feed production.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
The use of vermicompost enables to regain of the lost crop species because of soil degradation.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
As it added organic matter to the soil, it improves soil structure and other attributes of the soil that improve the land.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
It reduces investment on synthetic fertilizers and allows to harvest organic products.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
As most of the distinctions between the treatments with SLM technology vs without technology are not properly documented by the land users, it is difficult to quantify them. However, the evidence from the demonstration plots shows the yield increments by more than quadruple per unit of land. Since then the technology is applied recently, and promoting documentation of the yield difference by the land users themselves is commendable to ensure access to reliable data.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Generally, it added value to the efforts of ensuring food as well as nutrition security.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Health situation is converging with ensured food and nutrition security.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Increased through exchange visit and participatory learning of the effect of the technology on the farm.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Slightly improved with access and use of the technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
This is with the assumption that vermicompost improve soil structure via the addition of organic matter and improves water infiltration than favoring runoff.
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Acumulação de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Acidez
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
Vermicompost improves soil properties and related attributes to crop and the environment. Most of the assumptions made here are based on the knowledge and skills of SLM experts and land users than the empirical analysis because there is no such detailed data documented and available either by the land users or the project itself.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
As the application of the technology is on a plot basis, assessing its off-site effects necessitates widespread adoption and application of the technology. This may need long terms and intensive follow-up.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
As the technology is recently introduced, the level of awareness is low and it is in the pilot phase.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
Produced the boxes from local materials such as mud and posts.
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
The land users and the district ISFM+ project focal person modified the boxes by building with a bunch of sticks plastered with mud to replace the priceless boxes made up of timbers.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Reduce investment costs on chemical fertilizers. |
| Partly replace the role of chemical fertilizers. |
| Improve soil fertility and reduces soil acidity. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Rehabilitate the degraded land and improve the biodiversity of flora and fauna. |
| Reduce risks of crop failure. |
| Creat employment opportunity |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Labor demanding. | Engage family labor. |
| Shortage of biomass to supply feedstock. | Improve access to biomass supply and improve practical uses of crop residue and animal excreta. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Lack of proper documentation by the land users inline with such comprehensive questions. | Promote the capacity of land users to document the various facets of the technology on land management, production, and other multiple pros and cons. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Two
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
One
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
One
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
05/02/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Organic Exchange. 2009. Soil Fertility Management: An introductory Fact-Sheet for Farmers and Projects.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Free online
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
MoA. 2016. Technical Manual: Integrated Soil Fertility Management. SLMP Training Series 14. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Free online
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Vermicomposting
URL:
https://composting.ces.ncsu.edu/vermicomposting-2/
7.4 Comentários gerais
Similar to the other integrated soil fertility management practices /technologies, in this questionnaire, there are clearly irrelevant questions to this particular technology or too comprehensive to be addressed by the land users.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [Etiópia]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
Módulos
Não há módulos