Mechanical Bench Terracing [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ONGPO LEPCHA
- Editor: Tashi Wangdi
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Thruel Chhey Lag Len Thap Tey Aring Chey Ni (འཕྲུལ་ཆས་ཐོག་ཨ་རིང་བཅད་ནི།)
technologies_6836 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Penjor Tenzin
Bemji village
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation. Indeed, the terraces helps in avoiding and reversing land degradation by reducing surface erosion, retaining soil moisture and improve soil fertility.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
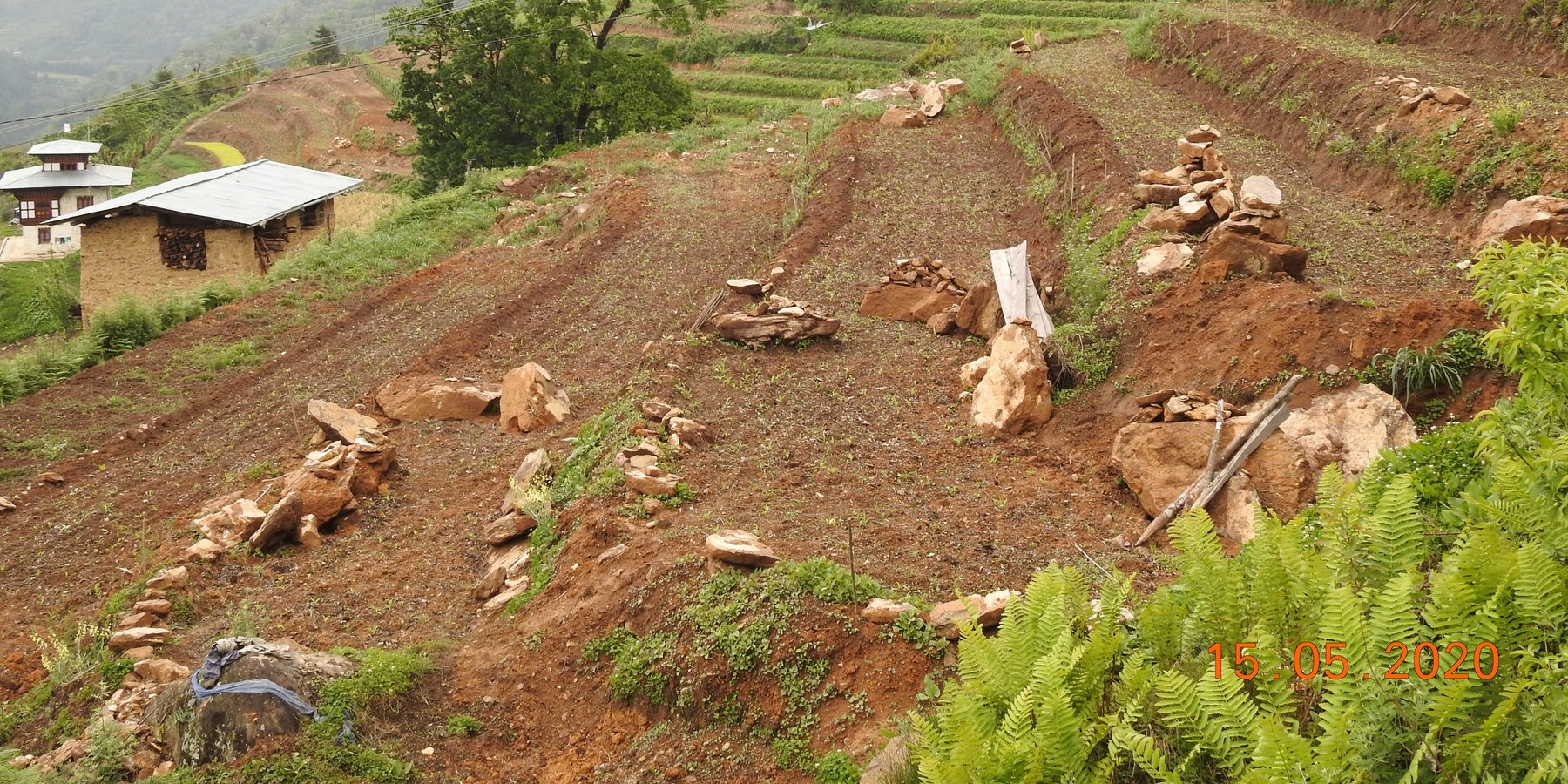
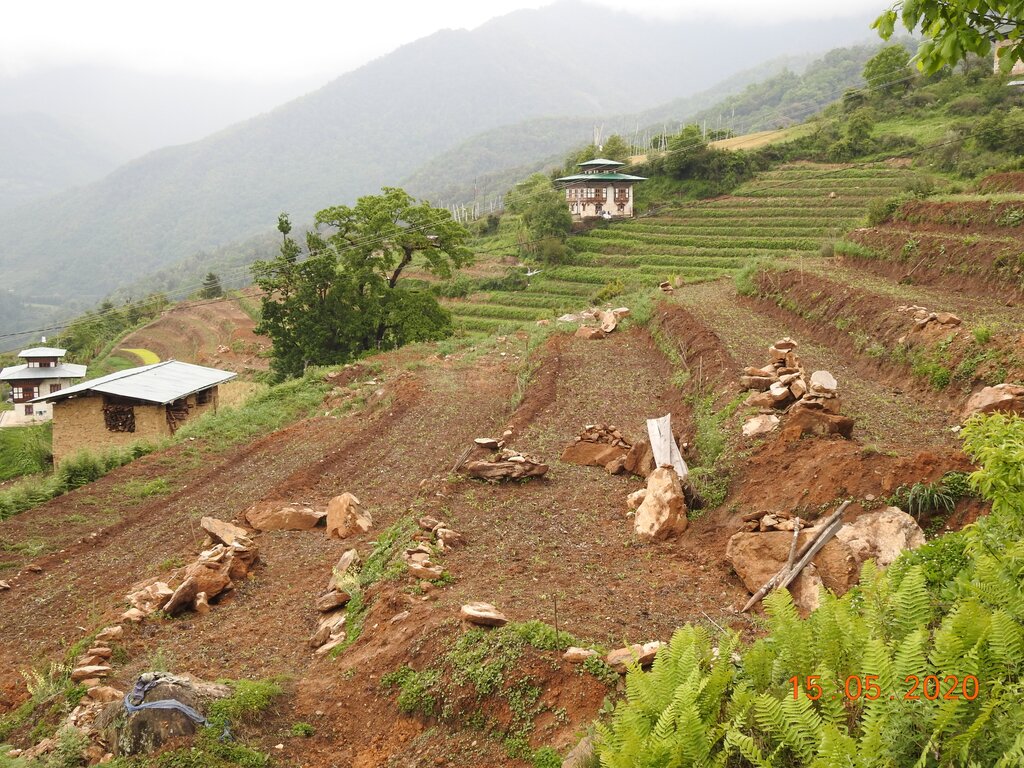
Soil erosion by water is one of the major problems in hilly or mountainous countries like Bhutan. In such areas, effective erosion control measures are required to reduce the slope gradient and minimize surface runoff. Among many SLM interventions, mechanical bench terracing is one of the most widely promoted and popular technologies in Bhutan.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
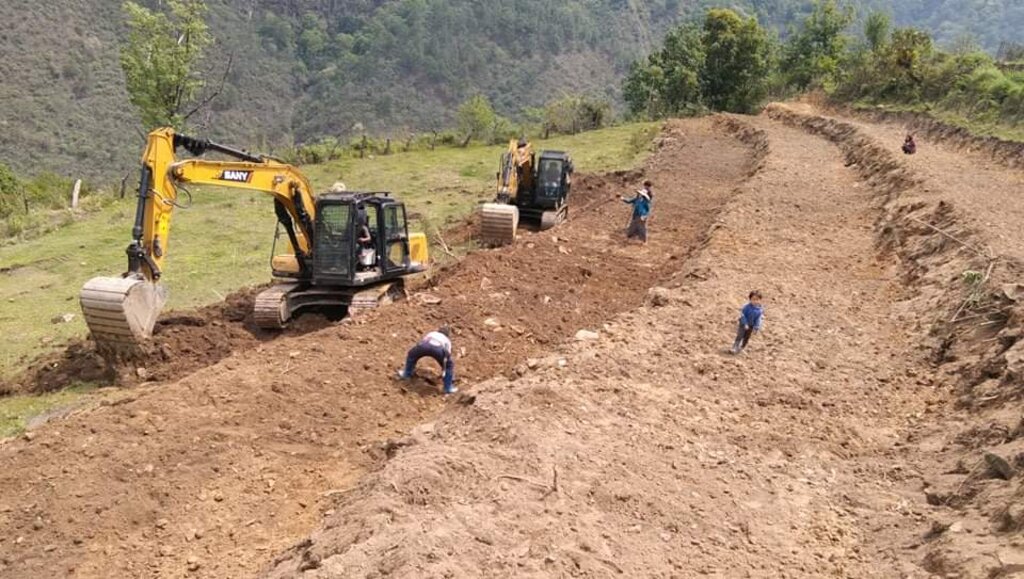
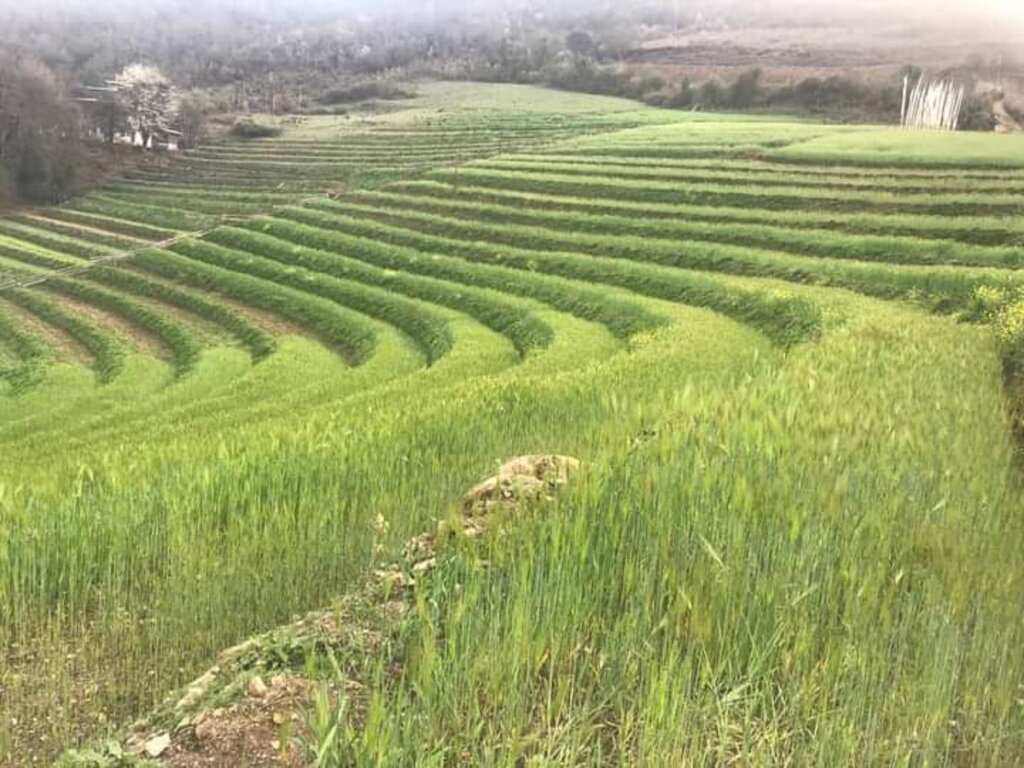
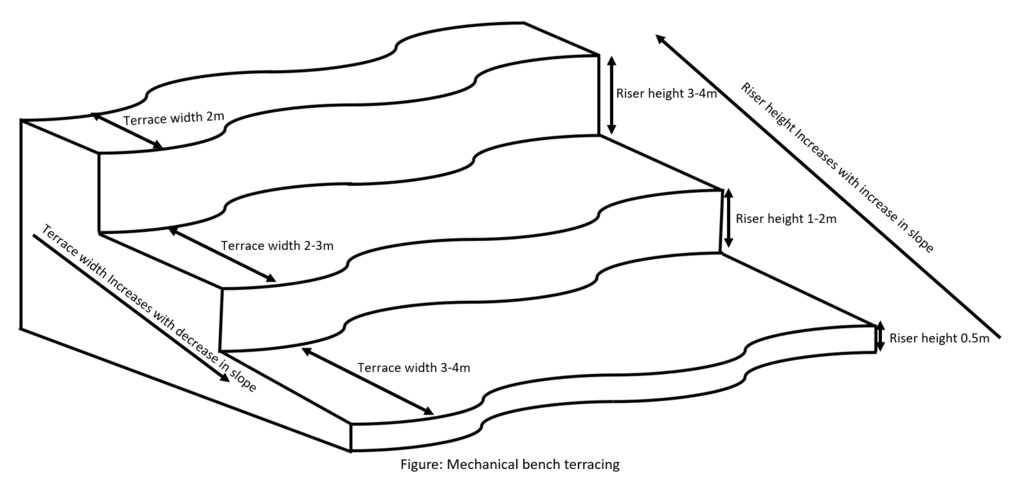
Bhutan is one of the most mountainous countries in the world and agricultural activities are carried out on slopes up to 35 degrees (70 percent). Erosion by water is one of the major causes of land degradation. In such areas, effective erosion control measures include reducing slope gradients to minimize runoff by creating a series of level platforms or “bench terraces” along the contour. Current bench terracing is made using small to medium-sized earthmoving machines called excavators, and thus the technology is called Mechanical Bench Terracing. This is one of the main SLM measures promoted widely and most preferred by landowners who claim that it reduces soil erosion, improves soil fertility, conserves soil moisture, and eases field operations. Bench terraces create impact by 1) helping minimize the risk of soil erosion caused by surface runoff, 2) effectively regulating water flow, and 3) preventing soil saturation by allowing better drainage. Additionally, bench terracing transforms previously unusable or less productive land into cultivable areas, maximizing the utilization of limited land resources. A typical bench terrace on a 20-25 degree slope has a terrace bed of 2-5 m meters and a riser of 0.75 to 1 metre high. The risers are made of earth and the terrace is made flat most of the time to prevent runoff of rainwater.
Establishing and maintaining bench terracing involves a feasibility study of the sites, participatory planning, hands-on training of the landowners, and surveying of contour lines using A-frames. There is also procurement of construction materials, arranging labour and machines and training machine operators. Once constructed, proper water management, soil fertility, and nutrient management practices are crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability and productivity of the terraced land. Furthermore, knowledge and training on crop cultivation techniques, field management, and maintenance are vital to optimize the benefits.
In summary, bench terracing offers numerous benefits. These include:
1) Overall reduction in land degradation
2) Soil conservation by prevention of erosion by runoff
3) Conservation of soil fertility
3) Increase arable land available for cultivation
4) Ease of mechanized field operations with level terrace beds
5) Water conservation and drainage6) Improved crop production
Land users like the fact that bench terracing provides land that is easier to work. The land is better utilized for cultivation, resulting in improved productivity. Land users generally appreciate its numerous benefits in terms of land productivity, soil conservation, and water management. What they dislike are the expense and labour input if expenditure has to be borne by the land owners and neither machine operators nor small to medium-sized machines are readily available in the market for hire.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Trongsa Dzongkhag (district)
Especificação adicional de localização:
Bemji Village, Nubi Gewog (block), Trongsa Dzongkhag (district)
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
1,0097
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2019
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Mechanical bench terracing in Bemji Village was implemented by Dzongkhag Agriculture Sector with technical support from the National Soil Services Center and funded by GEF-LDCF, UNDP
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Improve farm mechanization
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Paddy followed by Wheat or barley
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Paddy followed by wheat or barley/vegetables
Comentários:
The crops are grown mostly for self consumption, however, the surplus productions are sold at the weekly local market in Trongsa Dzongkhag (District).
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Paddy followed by Wheat/Barley/vegetables
Comentários:
In the past when terracing was not done only flat land was used to grow cereals but sloppy ones were left as grazing land or kept uncultivated. After terracing land user were able to use most of their land for cropping.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
According to the land user, the water supply is mostly rainfed; however, water for irrigation is also readily available.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Bench terracing is generally constructed to prevent and reduce land degradation due to surface runoff caused by water/rainfall.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical Drawing of bench which are made mechanically
Autor:
Ongpo Lepcha
Data:
21/11/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
2.4 acres
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,62
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Feasibility study | Based on land user and extension agents convenience |
| 2. | Participatory SLM Action planning | Based on land user and extension agent convenience |
| 3. | Hands on training for land owners and machine operator | Prior to actual implementation of the activity |
| 4. | Bench terracing by machine | When the land is fallow (Nov-Feb) |
| 5. | Leveling and removal of stones | Based on land user convenience |
Comentários:
It take about three weeks to implement all the activities in 2.40 acres of land
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | person-days | 98,0 | 500,0 | 49000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Excavator | nos | 1,0 | 40916,0 | 40916,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 89916,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1115,31 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The land owner bore about 32% of the total cost while the remaining cost was covered by the GEF-LDCF Project
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of terrace bunds | When ever necessary |
Comentários:
According to the land users, maintenance of the technology involved very little expense because once the terrace was formed the land became more stable.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Once the terraces are well established the maintenance costs are minimal.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The data used was from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Warm temperate zone
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
However, excess rain can cause flooding in the terrace but instances like this has never happened.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
As most of the terraced fields are properly fenced with electric fencing, the incidences of wild animal crop damage are minimal.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- idosos
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
In total, land users have around 23 acres of land, however the technology was applied on 2.40 acres of land.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the Land Act and the Land Rules and Regulations of the Kingdom of Bhutan, which dictate the overall land use in the country.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Before 1,814 kgs/acre
Quantidade posterior à GST:
After bench terracing 1,971 kgs/acre
Comentários/especificar:
According to the land user, there has been increased crop production.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
According to the land user, the quality has relatively improved but is unable to describe the changes, however, he observed changes in the size of the grain and enhanced grain filling ability.
Diversidade de produtos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
In the past, the land owner has been growing only wheat or barley
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Now the owner is growing paddy followed by wheat or barley in a year
Comentários/especificar:
The land user shared that the number of crops grown in the area has increased, and people also started commercial farming.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
23 acres of land
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2.4 acres of land are currently being cultivated after bench terracing
Comentários/especificar:
This is probably due to the lack of labour and some of the farm lands located very far from the home/settlement.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
The land users shared that after bench terracing, the management of land has greatly improved. This is evident from the quality of crops that they grow on the terrace. Working on the land is also easy unlike working on slopes.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Before bench terracing the owner used oxen for ploughing
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Now they use power tillers and cost have reduced for agriculture farming
Comentários/especificar:
Other objective of promoting bench terracing is also to enable farm mechanization.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Before bench terracing the land owners use the field for growing only wheat or barley. After bench terracing they grow two crops in a year, paddy followed by wheat or barley
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Since the land is on a sloping area there is surface and rill erosion in the past, but after the bench terracing, the incidences of surface and rill erosions are minimal
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
As the terraces field are used for paddy cultivation there is no excess water. Even if there is excess the land owner can easily drainage to water ways
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
Erosion was easily observable in the past due to the agricultural land being on mountain slopes. However, now, due to the series of levelled land, water erosion and landslides are no longer observed.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Before terracing rainwater is lost due to surface runoff however with terracing surface runoff is prevented as a result the amount of irrigation water required has reduced. Thus increasing water availability.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | muito bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Trovoada local | muito bem |
| Tempestade de granizo local | não bem |
| Tempestade de neve local | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Deslizamento de terra | bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | não bem |
| Infestação de insetos/vermes | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Comentários:
The land users were not able to explain very clearly the benefits of the technology. This is because land users were supported by the government for the establishment of the terrace. They didn't have any idea how much would it cost if they had to do everything by themselves.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
16 hhs covering 19.50 acres of vulnerable land were brought under bench terracing in Bemje village
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Agronomic management and working have become relatively easier: with bench terracing working with animals or machinery for tillage activities becomes very easy unlike in slopes. |
| Land can be better utilized, despite decreased total cultivated land: Terrace provides land users the option to fully utilize the available land. If it was a slope, even if they have more land they cannot use them for farming. |
| Prevents the degradation of the land by rain: The main purpose of terracing is to reduce and prevent land degradation caused by surface runoff. |
| Irrigation water is better utilized and conserved: When the surface is properly leveled irrigation water is well distributed. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Prevents landslide: Since the surveyed area was located on the mountain slopes, there are chances of slides if measures were not taken and bench terraces were not made. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It is a very expensive affair: If machinery and laborers have to be managed by individual land users it would be very expensive. | However, in Bhutan, the technology is mostly funded by the project and Government of Bhutan |
| Land users could not convert all available land into the terrace. | More support from the government so that they can convert all slopy areas into terraces. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Since bench terracing required huge expenditure it is difficult for the owners to bear the full cost | To implement the intervention through donars fund on cost sharing basis |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
One household
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
One individual
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
09/07/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Bizoza, A. R. (2011). Institutional Economic Analysis of Bench Terraces in The Highlands of Rwanda. Farmers, Institution and Land Conservation. Wageningen University
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/29235864.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Mesfin, A. (2016). A Field Guideline on Bench Terrace Design and Construction. Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://nrmdblog.files.wordpress.com/2016/04/bench-terrace-manual.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Dorji, S. (2017). Soil Conservation in Serthi Gewog: A Case Study. Samdrup Jongkhar Initiative.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.sji.bt/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Soil-Conservation-Pilot-Impact-Area.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
BTFEC. (2019). Evaluation of Sustainable Land and Management and Innovative Financing to Enhance Climate Resilience and Food Security in Bhutan. BTFEC.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.bhutantrustfund.bt/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/CIF-Report1.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management: Guidelines and Best Practices 2021
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.nssc.gov.bt
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Turning slopes, dry land into viable agricultural land in Trongsa
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/stories/turning-slopes-dry-land-viable-agricultural-land-trongsa
Título/ descrição:
Bench Terraces: Classification and Maintenance | Soil Management
URL:
https://www.soilmanagementindia.com/soil-erosion/terracing/bench-terraces-classification-and-maintenance-soil-management/15307
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos