Citrus Canopy Management and Rehabilitation Program [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Nima Dolma Tamang
- Editor: Kuenzang Nima
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Tshel Shing Zin Chong Dang Nyam Sung Ley Rim (ཚལ་ཤིང་འཛིན་སྐྱོང་དང་ཉམས་སྲུང་ལས་རིམ།)
technologies_6847 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Lethro
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Citrus canopy management refers to the set of practices and techniques employed to optimize the growth, health, and productivity of citrus trees by manipulating the structure and density of their canopy. Effective canopy management is crucial for achieving desirable outcomes in citrus cultivation, such as improved fruit quality, increased yields, efficient use of resources, and enhanced tree health.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
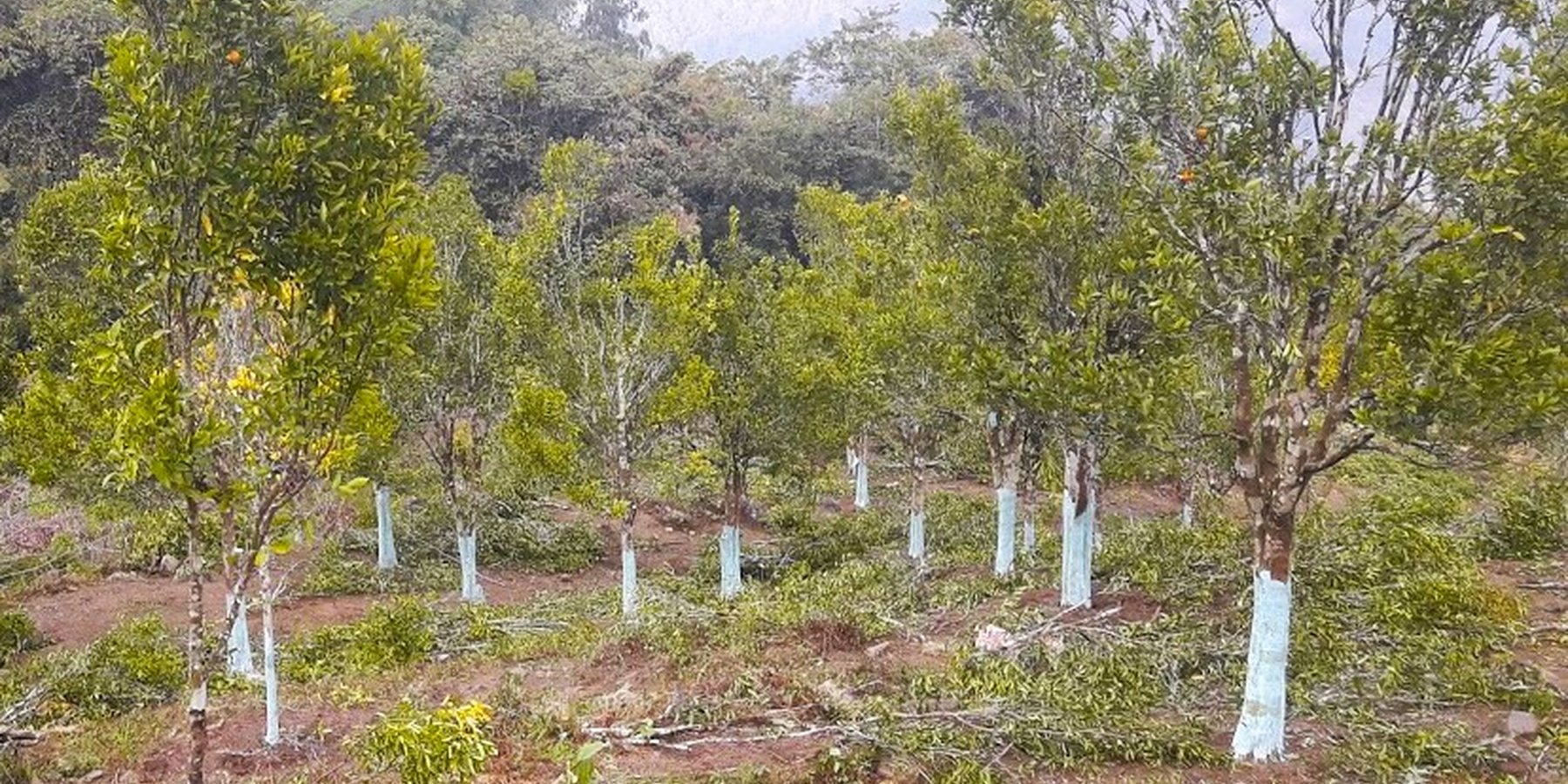
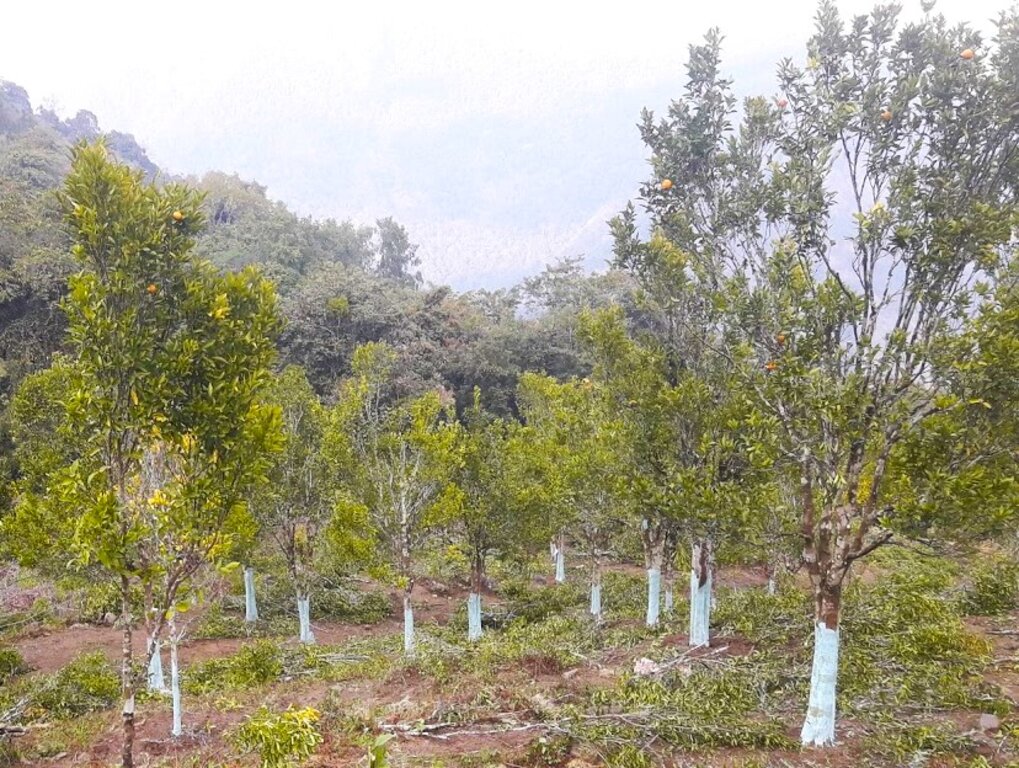
Citrus canopy management practices remain basic in Bhutan. Thus, the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR) project was initiated and demonstrated citrus canopy management practices in selected orchards in 2010. In the same year, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) project trained land users and extension officers in eastern Bhutan on citrus management practices such as planting methods, nutrient management, pruning and training including top working, fruit thinning and post-harvest management practices. Since then, citrus growers have been slowly adopting the practices in their orchards. However, the adoption rate is low - affecting the yield and quality.
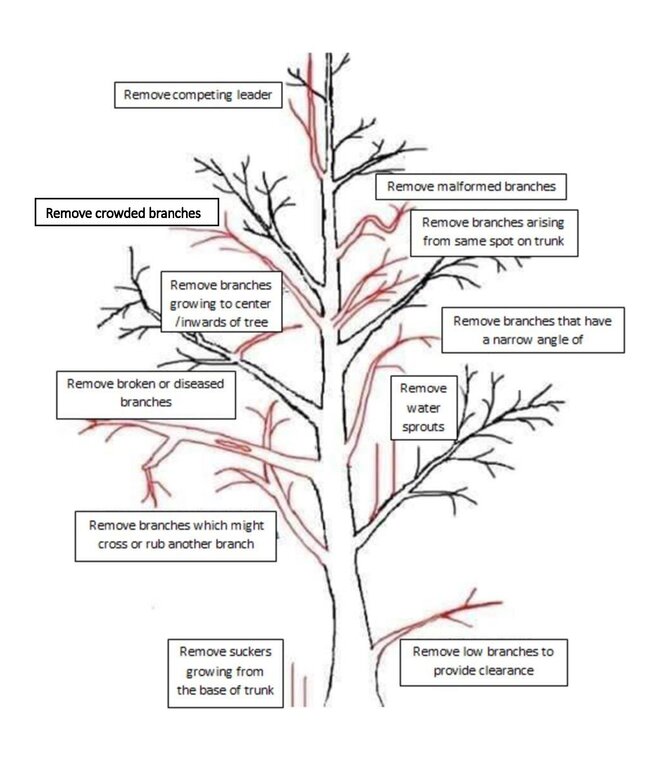
Bhutan has suitable climatic conditions for citrus production, particularly in the southern parts of the country due to the subtropical climate. Citrus such as oranges, mandarins and lemons are grown in orchards and home gardens. In Bhutan, citrus canopy management practices focus on optimizing tree growth, fruit production, and overall tree health. The main elements include pruning, training systems, canopy density management, tree height and size control, and disease and pest management integrated with irrigation and nutrient management practices. Pruning involves selectively removing branches, shoots, or foliage to shape the tree and improve its health. The stump should always be cut as close to the collar region as possible. Training structures the tree in a specific manner to optimize growth and management. Canopy density management regulates foliage density for light penetration and airflow. Techniques such as hedging or topping control the height and size of trees. Disease and pest management practices include adequate air circulation and sunlight exposure. Integration with irrigation and soil nutrient management enhances tree health and productivity. The desirable shape and size of citrus are variable depending on the grower's choice, location, and - most importantly - operational health and safety concerns. In general, the desirable shape and size of the tree should be 2 to 5 m tall, 2 to 5 m width of canopy, and 4 to 6 primary (scaffold) branches that are at least 1 m above the ground level.
The purposes/functions of citrus canopy management technology are to optimize fruit production, improve tree health, and facilitate harvest and maintenance operations. It helps maximize fruit yield and quality. Pruning and maintenance practices enhance tree vigour, reduce the risk of diseases and pests, and improve overall plant health. Controlling tree size and shape makes harvesting easier and more efficient, and simplifies other maintenance activities such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
To establish and maintain citrus canopy management technology, activities such as regular pruning and training, knowledge and skill development, use of proper tools and equipment, monitoring and assessment, irrigation, and nutrition management are required. Regular pruning and training of citrus trees according to the selected system and management objectives is essential. Monitoring tree growth, health, and productivity is important, along with proper irrigation scheduling, water management, and nutrient application.
The benefits/impacts of the technology are improved sunlight exposure, enhanced air circulation, reduced disease incidence, increased fruit size and quality, ease of harvest, consistent yield, optimized water use, better pest management, and others. A well-managed canopy makes it easier to access the fruit during harvest, and achieve higher yields and better-quality fruits, reduced need for pesticides, as well as directing nutrients toward fruit production rather than excessive vegetative growth. However, there are some drawbacks of the technology such as the requirement for time-consuming manual labour, lower initial yields, high initial investments for equipment, and concerns about over-pruning.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Dagana Dzongkhag
Especificação adicional de localização:
Nindukha Village, Kana Gewog
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2019
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- cítrico
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Tree canopy management
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V5: Outros

Outras medidas
Especifique:
Improve/optimize fruit production and quality by manipulating the growth and structure of trees.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Citrus canopy management increases productivity and reduces its susceptibility to diseases which ensures vegetation cover as the trees are not removed.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The spacing between trees is 6 m. There are a total of 100 trees per acre. Diseased or damaged trees are removed.
Autor:
Thinley Penjor Dorji
Data:
22/08/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
2.47 acre
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
1
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum (Nu.)
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
500
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning | Right after harvest |
| 2. | Applying Bordeaux mixture | Anytime |
| 3. | Making basin | Winter |
| 4. | Applying manure | Anytime |
| 5. | Removal of dead woods or shoots | Anytime |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Pruning | Person/day | 17,0 | 500,0 | 8500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Pruning saw | Number | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Secateurs | Number | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Sapling | Number | 247,0 | 150,0 | 37050,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Bordeaux mixture | Litres | 12,0 | 125,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 51550,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 644,38 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The cost for sapling and biocide is borne by the Royal Government of Bhutan.
Comentários:
The total establishment cost of the technology for one hectare is USD 644.38. The Land users paid 100% of the equipment's cost. They follow a labour-sharing system whereby the labour employed in the farm is compensated by working in their fields and there is no cost involved.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning of dead woods and water shoots | Anytime |
| 2. | Fertilizer application | Anytime |
| 3. | Shoot selection in the following years | Every year when new shoots sprout |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Pruning | Person/day | 7,0 | 500,0 | 3500,0 | 98,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 3500,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 43,75 | |||||
Comentários:
Only labour input is needed for maintenance/recurrent activities but the cost is zero as land users follow labour-sharing system.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The land users mentioned that the equipment is the main factor affecting cost.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
The area falls under the humid Subtropical zone from the six Agro-ecological zones of Bhutan.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Moisture content 2.88%, organic matter 6.17%, Organic carbon 3.59%, pH 6.23, electrical conductivity 178.27 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.18%, phosphorus 0.57 ppm, Potassium 134.73 mg/100ml, texture sand clay loam.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The species and habitat diversity provided above are for the citrus orchard.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The orchard was of 1.3 acres or 0.52 hectares. The average land holding of Bhutan is 3.4 acres. Land users owning less than 3.4 acres are categorized as small-scale.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The land use rights in Bhutan is traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Land users mentioned that there was a significant increase in crop yield after canopy management.
Qualidade da safra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50-60%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
80%
Comentários/especificar:
The land users stated that the size of the fruit was bigger and of better quality after canopy management.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The land users stated that the risk of producing lower quality fruits that are not acceptable in the market has greatly reduced.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
The cost of equipment is moderately expensive. However, the land users feel the cost is compensated by the increase in income. The land users also take special care of the equipment.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Improved quality and quantity of citrus are directly related to increased farm income as there is a higher price provided for good quality produce.
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50%
Comentários/especificar:
The management practices such as training, pruning, and application of Bordeaux mixture are laborious. Therefore, the workload of land users has increased by about 10 per cent.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
The land users are self-sufficient in terms of citrus. Further, the portion of their yield is shared with their relatives making the community self-sufficient. The income generated from selling the produce is used to procure nutritious foods from the market making them food secure.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Improved income if used efficiently increases the health situation of the family members.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
The traditional practice did not include nutrient management of the orchard. The citrus canopy management technology includes proper manuring or nutrient management of the orchard leading to increased knowledge of SLM for the land users.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
The technology improved tree health reducing the risk of orchards converting to fallow land and increasing vegetation cover.
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
The improved soil and canopy management increased earthworm and bee populations on the farm.
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
After canopy management, the land users stated that they have experienced fewer pest and disease incidences. This could be due to better sunlight penetration and air movement in the tree canopy.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
The orchard harbouring pests and diseases can damage neighbouring fields as the diseases are transmitted from one field to another through vectors and other sources. Therefore, the technology improves the health of the orchard and prevents the risk of damaging neighbouring orchards.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de granizo local | não bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | não bem |
| Infestação de insetos/vermes | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
7 households adopted the technology from the total of 50 households.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
All the farmers received material incentives from the government.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Increased production. The canopy management technology increases production in the long run although there is a sudden reduction in the yield in the first year of implementation. |
| Improved quality. The technology is a wholesome approach to improving the canopy, nutrient management and irrigation management leading to quality fruit production. |
| Reduced pests and disease incidence. The technology reduces the favourable environment for the multiplication of diseases and pest. For example, by pruning the canopy which increases aeration ultimately reducing fungal growth. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Increased income and improved livelihood. Canopy management increases yield in the long run leading to increased farm income and improved living standards of the land users. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive. The technology includes pruning, thinning, irrigation and nutrient management activities which require a lot of labour. | Implementing a labour-sharing mechanism as it is cost-effective and strengthens community collaboration. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Low initial crop yield. Due to excessive pruning in the first year of technology implementation, there is a marked reduction in the yield of the citrus. | With better care and management, yields increase after 2 to 3 years. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
One
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
One
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
15/07/2023
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Canopy Management Guide for Citrus Mandarin in Bhutan
URL:
http://rcbajo.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Canopy-management-guide-for-citrus-mandarin.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Pruning and Training - Evergreen Trees
URL:
http://rcbajo.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Pruning-Training-evergreen.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos