SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT AND FOR MITIGATION OF SALINITY [Tailândia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Laksamee Mettpranee
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_7274 - Tailândia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Siangsunthia Mana
Tailândia
Compiler:
co-compilador/a:
Raksasarp Pithcanun
Land Development Department
Tailândia
co-compilador/a:
reviewer:
reviewer:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - TailândiaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Centre of Excellence for Soil Research in Asia (CESRA)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

EXTENSION OF SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT … [Tailândia]
An outreach programme aims to educate farmers about the benefits of ploughing rice stubble into the soil and incorporating green manure crops such as sunn hemp - as well as other sustainable practices. Groups of farmers are formed, and they are assisted by various organisations including the Land Development Department …
- Compilador/a: Laksamee Mettpranee
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
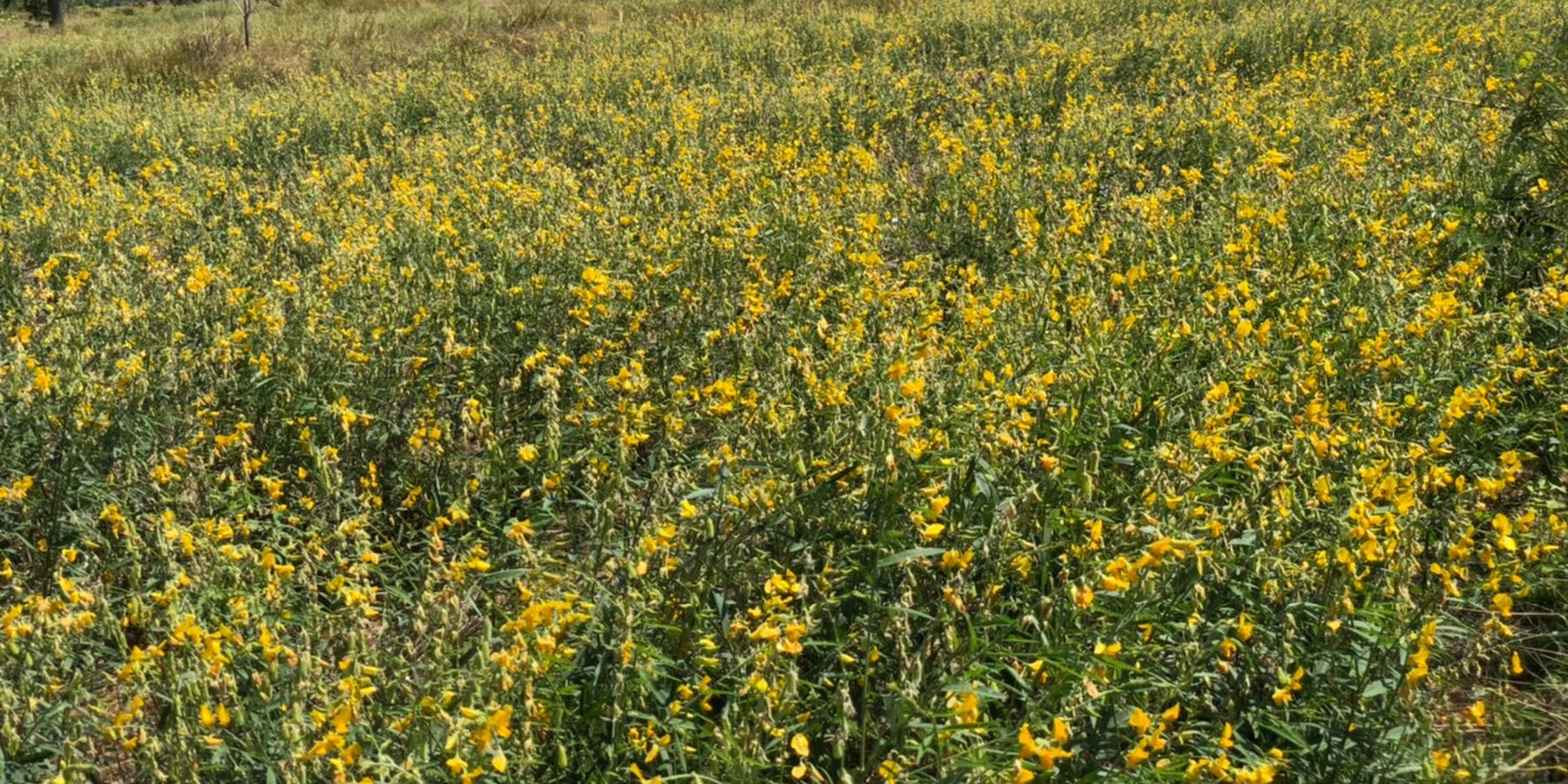
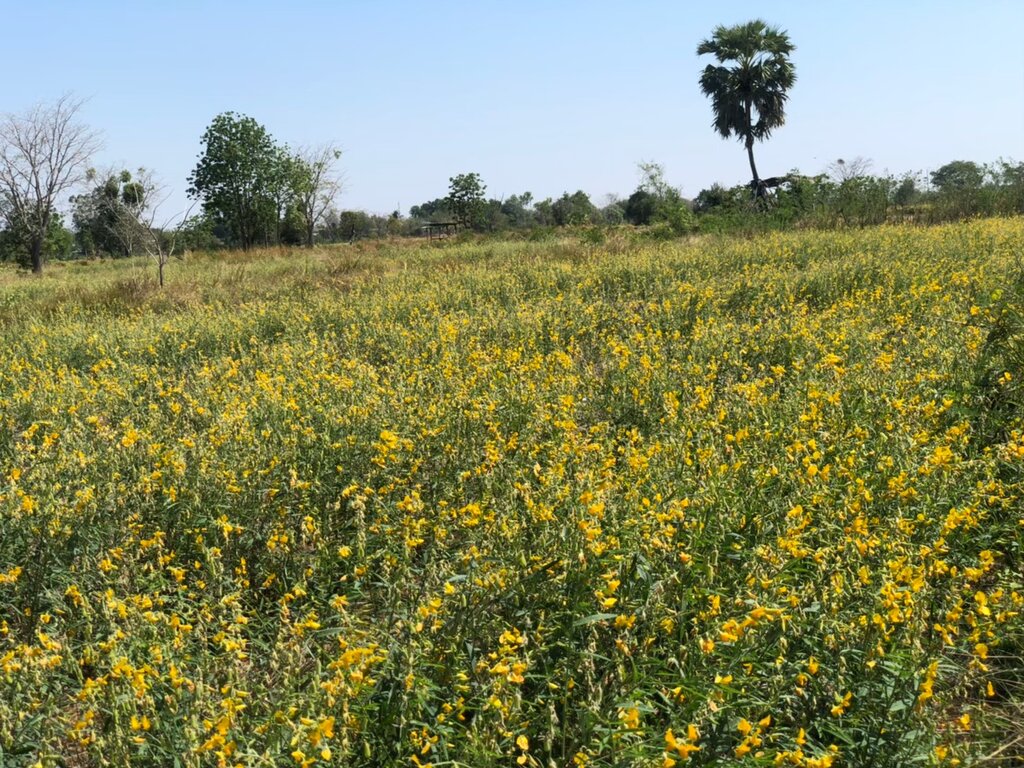
Sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) has been promoted by the Land Development Department as a green manure plant with the objectives of increasing soil organic matter, improving soil fertility and reducing salinity levels.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Northeast of Thailand has the largest area dedicated to rice production in the country. However, the average yield per hectare remains low. Here, rice production heavily depends on rainfall, but distribution is inconsistent. Additionally, soil fertility is low, with a rapid decline in soil organic matter (SOM). Another significant threat to productivity in this area is salinity, with 17% of the rice production area affected.
The Land Development Department (LDD) of the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives has promoted the use of soil amendments, such as green manure plants - including sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) - to enhance organic matter and restore soil fertility under saline conditions. Green manures are ploughed under, and incorporated into the soil to achieve their effect.
In the Non Thai district of Nakhon Ratchasima province, farmers face water shortages during the dry season, as the area lies outside the irrigation zone. Farmers, along with officers from the Land Development Department, have worked to increase SOM in degraded soils through knowledge transfer. Volunteer soil doctors and local farmers have adopted technologies that combine SOM improvement with soil and water conservation measures.
One notable example is Mr. Mana Siangsuthia: since 1997, he has collaborated with LDD officers, receiving beneficial microorganisms (PD microorganisms), green manure plants, vetiver grass, and water resources for his paddy fields. He has implemented LDD guidelines to develop his 1.12 hectare rice plot. Previously, this land was unproductive due to soil degradation caused by long-term monoculture of industrial crops and excessive use of synthetic fertilizers.
Fermented bio-extracts from banana shoots and chemical fertilizers were applied according to recommended guidelines. In 2004, rice yields averaged 1,125–1,550 kg/ha. Continuous implementation of these practices raised yields to 2,500 kg/ha by 2011. Over 16 years, using sunn hemp as a soil amendment significantly improved soil aggregate stability and reduced salinity. This success led to a shift towards natural agriculture practices in 2013, where chemical fertilizers were no longer used.
Farmers in the area now employ weather observation techniques and efficient water management strategies during dry spells. Green manure plants are sown every two years, complemented by the cultivation of salt-tolerant rice varieties, which also exhibit drought and pest resistance. These practices have resulted in rice yields of 3,125–3,750 kg/ha.
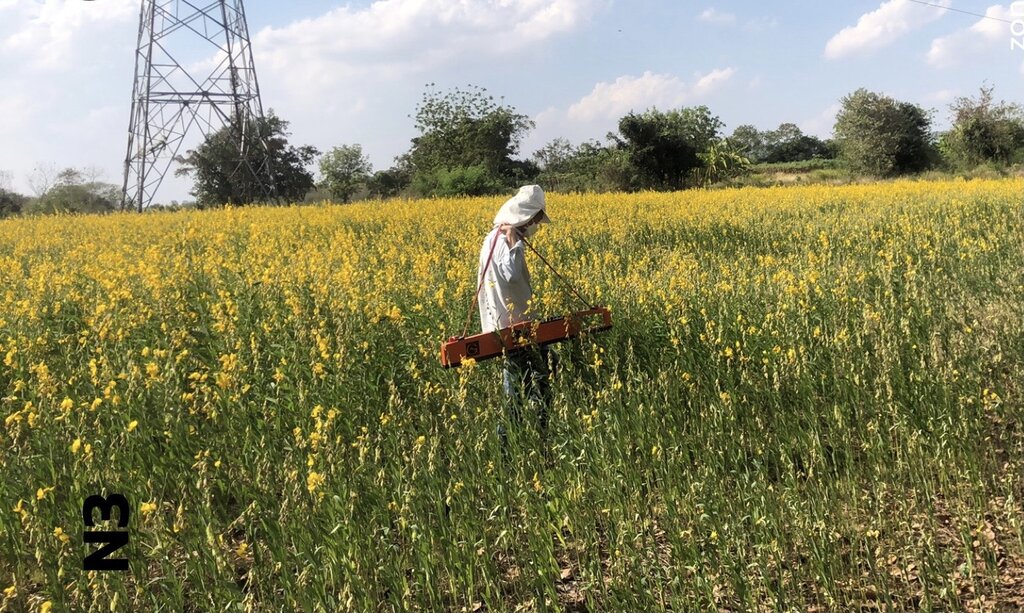
After rice harvesting, rice straw and stubble are ploughed in together with banana shoot PD 2 bio-extract. After approximately 2 weeks of decomposition, sunn hemp is sown at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha. When sunn hemp reaches 120 days, its seeds are collected. Then sunn hemp stems of around 1.2 meters height are ploughed in order to obtain more biomass.
Water conservation remains a focus in the cultivation area. During the rainy season, excess rainwater is stored for use during dry periods. Additionally, farmers employ techniques to wash salt from the soil surface into drainage channels. Water quality is enhanced using fermented bio-extracts, ensuring adequate water for dry-season cultivation.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tailândia
Região/Estado/Província:
Nakhonratchasima
Especificação adicional de localização:
Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
11200,0
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
1999
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology arises from land users’ innovation and is supported by external interventions and government agencies that acknowledge the value of technology to the community by providing resources, funding and supporting research and development.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- sunhemp - rice
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Rice and sunn hemp
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- sunhemp-rice
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Rainfed lowland rice can be supported by small ponds for irrigation.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
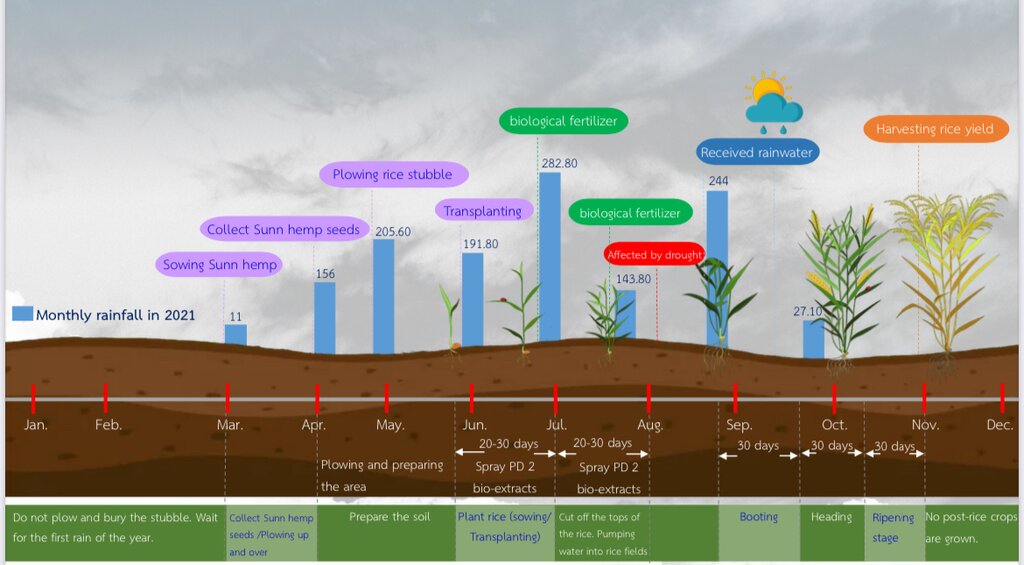
Above shows irrigation ponds associated with rice production. Below is the annual planting calendar where sunn hemp is used.
Autor:
Wanaporn polsang
Data:
02/08/2020
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Methods of planting Crotalaria juncea (sunn hemp) to be used as a green manure plant in areas with saline soil are as follows:
1. The period of planting is during February to April whereby planting is conducted in between after harvesting rice yields so that Crotalaria juncea ( Sunn hemp) can thrive and give out high biomass.
2. Plough and ferment rice stubble together with using PD 2 bio-extracts to create bacterial process in the soil accelerating decomposition taking about 2 weeks. Then, sunn hemp is sown at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha in the soil with appropriate moisture throughout the plot in order to bring about regular germination.
3. Plowing up and over to cover sunn hemp stubble at the age of 120 days after collecting seeds of sunn hemp whereby the stem of sunn hemp is at the average of more than 1.2 meters resulting in obtaining more biomass. After that, during the period of preparing the area for planting rice, rice can be sowed in May or when there is enough amount of water.
4. When the seeds are kept to be used in the following season, the seed coat of sunn hemp is used as material incorporated with soil to make compost for soil amendment in growing vegetables.
Autor:
Wanaporn polsang
Data:
02/08/2020
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1.12 ha
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha=6.25 rai
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
34,0
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting is conducted in between after harvesting rice yields so that Crotalaria juncea ( Sunn hemp) can thrive and give out high biomass. | February-April |
| 2. | Plough and ferment rice stubble together with using PD 2 bio-extracts to create bacterial process in the soil accelerating decomposition taking about 2 weeks. Then, sunn hemp is sowed at the rate of 31.25 kg/ha in the soil with appropriate moisture throughout the plot in order to bring about regular germination. | February-April |
| 3. | Ploughing up and over to cover sunn hemp stubble at the age of 120 days after collecting seeds of sunn hemp whereby the stem of sunn hemp is at the average of more than 1.2 meters resulting in obtaining more biomass. After that, during the period of preparing the area for planting rice, rice can be sowed in May or when there is enough amount of water. | May-August |
| 4. | When the seeds are kept to be used in the following season, the seed coat of sunn hemp is used as material incorporated with soil to make compost for soil amendment in growing vegetables. | May-August |
Comentários:
Ban Kok Phrom Village, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district, Nakhon Ratchasima province
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Plow to prepare plots | Time | 1,0 | 14,71 | 14,71 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Sow rice | Time | 1,0 | 17,65 | 17,65 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Pump water | Time | 2,0 | 58,82 | 117,64 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Harvest yield | Time | 1,0 | 183,82 | 183,82 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Rice seeds | Kilogram | 8,0 | 0,53 | 4,24 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Weight | Liter | 40,0 | 0,29 | 11,6 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Green Manure | Kilogram | 5,0 | 0,68 | 3,4 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Oil costs for farm truck | Time | 1,0 | 58,82 | 58,82 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 411,88 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 12,11 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The Land Development Department does not provide financial support but instead supports agricultural production inputs, such as green manure seeds and raw materials for compost production.
Comentários:
Calculation of costs and expenses
Expenses are calculated per areas using technology (Unit of size and area: 1.12 ha)
The currency used to calculate expenses with the unit as Baht
Exchange rate (to US. dollars) 1 US. Dollars = 34.0 Baht
Average wage in hiring labor per day is 8.82 USD
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
1. Labour costs
2. Fuel costs
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- idosos
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Being areas with saline soils with salt stain on the soil surface, yields per hectare
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Soil properties become better, the quantity of products increases
Qualidade da safra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Yields per hectare are low.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
The plants receive nutrients and the soil quality improves resulting in better product quality.
Gestão de terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Factors and soil amendment materials are used continuously every year.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Good soil properties make soil management for cultivation become easier.
Comentários/especificar:
Using a questionnaire
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Rainwater is used for conducting agricultural farming.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water resources in the paddy field
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Affected by salt water
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water qualities are improved by using fermented bio-extracts.
Comentários/especificar:
Salt meter
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
A large quantity of factors and soil amendment materials were used
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Materials easily found in the area such as fermented extracts, green manure are used.
Comentários/especificar:
Using a quetionnaire
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Low productivity
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Received higher quantity of rice products
Comentários/especificar:
Using a quetionnaire
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Yields not enough for consumption in the household
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Having the quantity of rice products for household consumption enough throughout the year accounting for 700 kg./year
Comentários/especificar:
Using a quetionnaire
Estado de saúde
Quantidade anterior à GST:
--
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
Comentários/especificar:
Using a questionnaire
Instituições comunitárias
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Study how to solve proStudy how to solve problems by themselvesblems by themselves
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
There is no knowledge propagation.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Farmers in the adjacent plot accept the technology and implement methods of soil management in their own areas.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
The soil is arid with flaky salt on the soil surface.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
There has been accumulation of organic matter and mulch keeps moistures and reduces water evaporation in the soil.
Comentários/especificar:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Quantidade anterior à GST:
--
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Nutrients increase due to planting different crops such as sunn hemp and plowing up and over rice stubble.
Comentários/especificar:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
Salinidade
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Moisture in the soil was low. The soil was characterized by having flaky salt appearing on the soil surface.
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Salinity measured from the soil surface decreased. Organic matter and the number of microbes accumulating in the soil increased.
Comentários/especificar:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
--
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Organic matter from plowing up and over to cover rice stubble, green manure plants
Comentários/especificar:
Collect samples for laboratory testing.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
--
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Plant varieties which can be planted and grow in the area more such as rice, sunn hemp
Comentários/especificar:
Observation
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Small-scale water resources
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Expansion of digging ponds resulting in more areas of water storage
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | moderadamente |
| Seca | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
The land users are responsible for covering the costs themselves. The Land Development Department provides support by supplying green manure seeds to demonstrate and test whether growing green manure crops can effectively improve saline soil.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Farmers manage soil and water use integrated farming methods, leading to additional income opportunities |
| Farmers in the area are committed to overcoming challenges and limitation related to soil, water, and environmental conditions |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Support for forming farmer groups in the area to exchange knowledge on soil management for increasing crop yields and addressing local farming issues, as well as developin professions for community farmers. This includes promotiong the production of safe |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Quality problems of Sunn hemp seeds result in low germination rates. | Land Development Department officials inspect the quality of seeds before they are distributed to farmers. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
8
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
1
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
5
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
URL:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

EXTENSION OF SUNN HEMP AS A SOIL AMENDMENT … [Tailândia]
An outreach programme aims to educate farmers about the benefits of ploughing rice stubble into the soil and incorporating green manure crops such as sunn hemp - as well as other sustainable practices. Groups of farmers are formed, and they are assisted by various organisations including the Land Development Department …
- Compilador/a: Laksamee Mettpranee
Módulos
Não há módulos