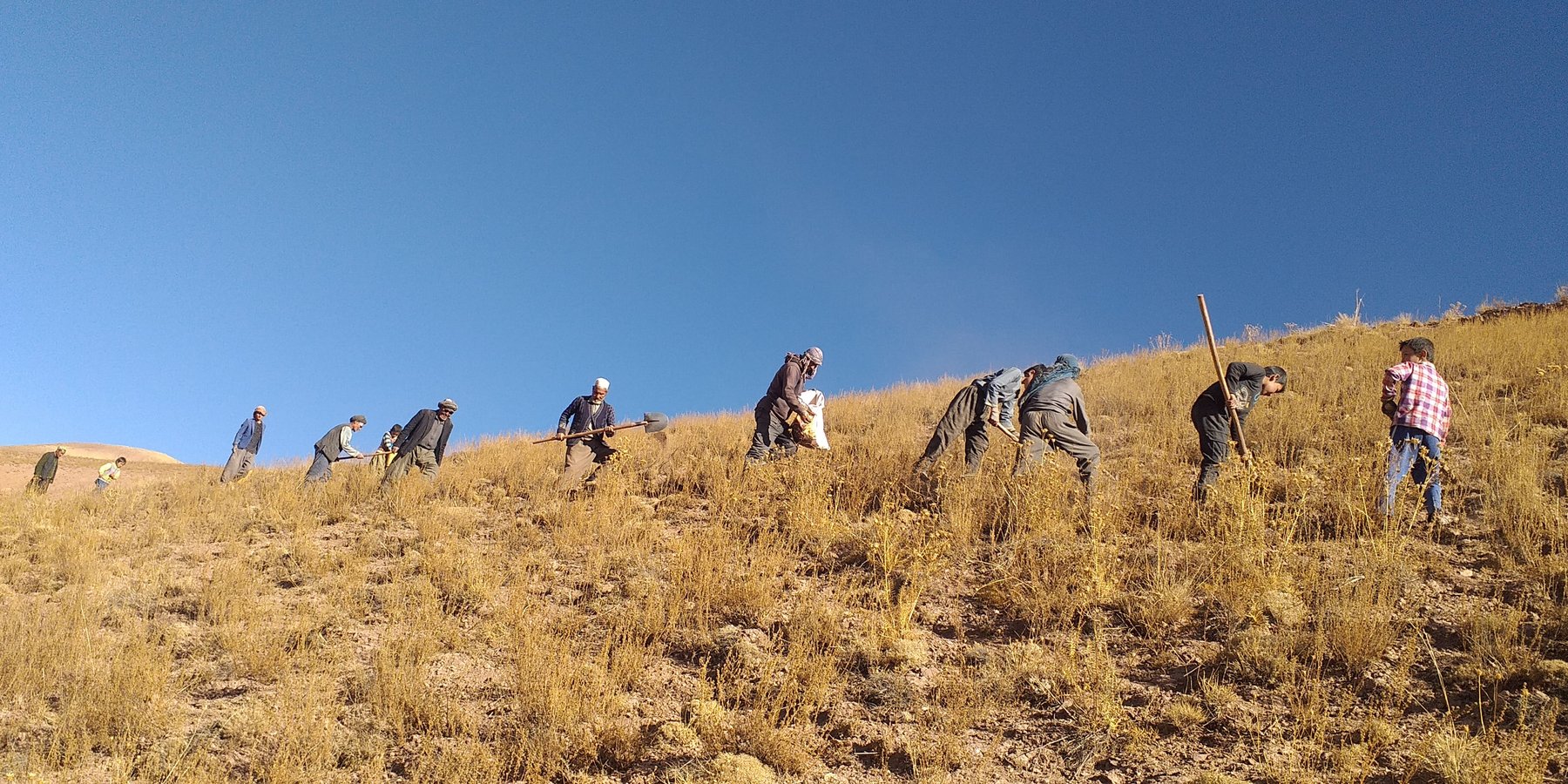
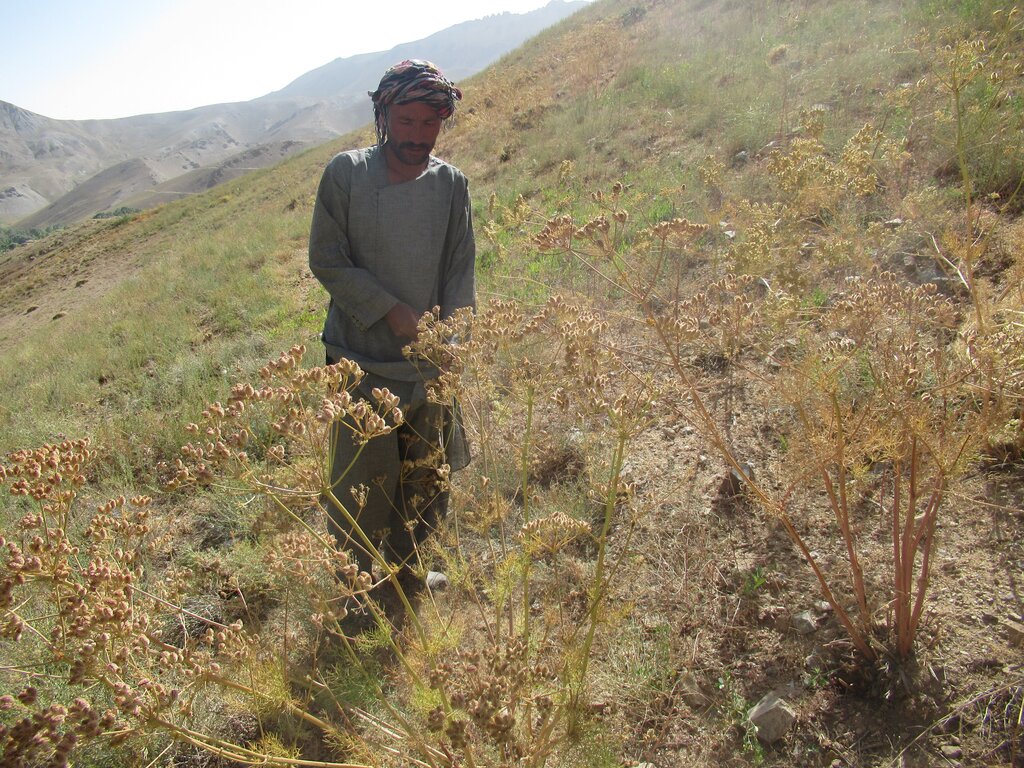
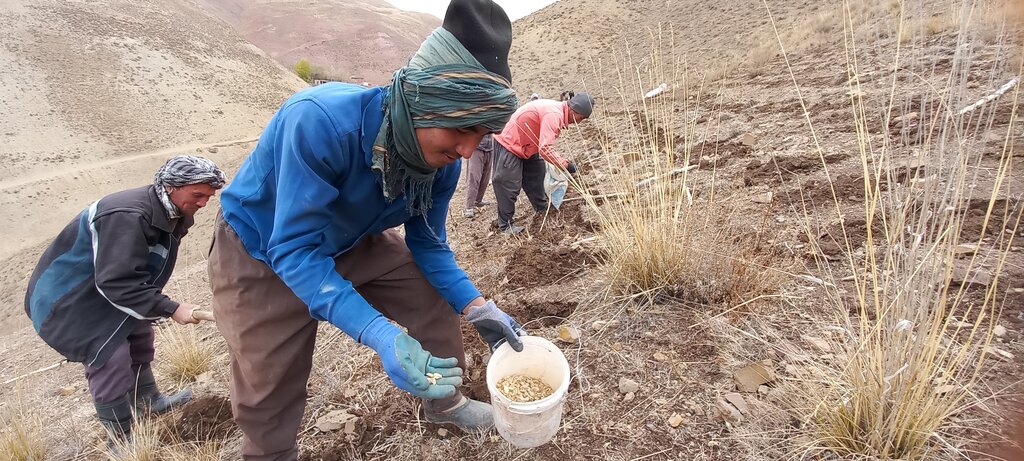
Reseeding local fodder species in Bamyan rangelands using indigenous and scientific methods [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Gul Nabi Khan Noorani
- Editores: Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal, Mohammad Mustafa Sahebzada
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
کاشت انواع علوفه جات محلی در علفچرهای بامیان با استفاده از رویشهای های بومی و علمی
technologies_7402 - Afeganistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Reseeding local fodder species in Bamyan rangelands using indigenous and scientific methods: 27 de Janeiro de 2025 (inactive)
- Reseeding local fodder species in Bamyan rangelands using indigenous and scientific methods: 24 de Março de 2025 (inactive)
- Reseeding local fodder species in Bamyan rangelands using indigenous and scientific methods: 6 de Maio de 2025 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Technician:
Alamy Sayed Basir
FAO Afghanistan
Afeganistão
Volunteers:
Masror Sayed Taqi
Volunteer Community Facilitator
Afeganistão
Volunteer:
Mohseenpor Sayed Azim
Volunteer Community Facilitator
Afeganistão
usuário de terra:
Arvin Ali
Volunteer Community Facilitator
Afeganistão
Volunteer:
Wafa Sayed Ihsan
Volunteer Community Facilitator
Afeganistão
usuário de terra:
The RMA Members
Members of Rangeland Management Associations in two target districts.
Afeganistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in AfghanistanNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afeganistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is sustainable and easily replicable by local communities.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Artificial reseeding is a key method for restoring degraded rangelands. It involves reintroducing native, palatable fodder species to improve vegetation cover, soil health, and biodiversity. This process boosts forage for grazing animals, stabilizes soil, and helps combat desertification, enhancing ecosystem health and productivity.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The project “Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistan”, implemented by FAO with the financial support of GEF, aims to conserve vegetation cover and ecosystems through introducing community-based sustainable land and forest management (SLM/SFM) practices in rangeland and forest areas within five targeted provinces, including Bamyan. The project introduced an integrated, community-based approach of SLM/SFM in Afghanistan for promoting biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, and rangeland productivity.
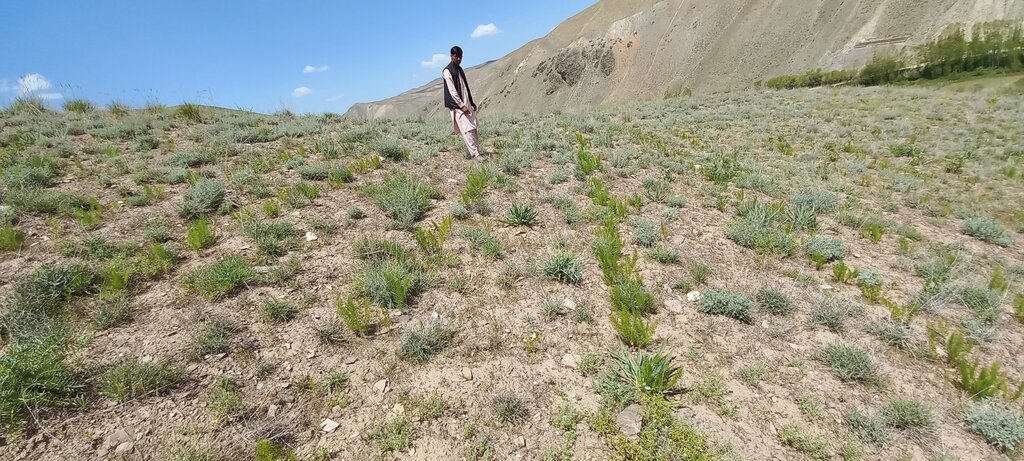
To enhance rangeland productivity in Bamyan province, artificial reseeding of native, locally adapted, and drought-resistant fodder species plays a vital role in restoring health and productivity of the degraded rangeland ecosystem, improving soil quality, and increasing fodder availability for livestock, which contributed to local livelihoods and environmental resilience.
Communities carefully identify highly vulnerable and degraded rangelands for reseeding initiatives. These include previously rain-fed wheat fields cultivated for human consumption, overgrazed sites, and areas with restricted grazing to support vegetation recovery before reseeding. Attention is also given to areas prone to snow avalanches and flash floods causing landslides and soil erosion, which impact downstream residential areas, irrigation systems, trails, roads, and farmlands. These zones are prioritized and mutually agreed upon for reseeding and restoration efforts.
This reseeding local fodder species technology involves several key activities.
1. Identification of locally adapted drought-resistant and palatable fodder species by livestock owners and land users.
2. Identification of highly producing areas of selected fodder species to collect quality seeds.
3. Defer grazing and delay fodder harvest for the purpose of seed maturity in the targeted area.
4. Awareness raising about the maturity stages of different fodder species seeds: Through project intervention and awareness campaigns, rural residents have gained a better understanding of the seed ripening, collecting, and cultivation stages.
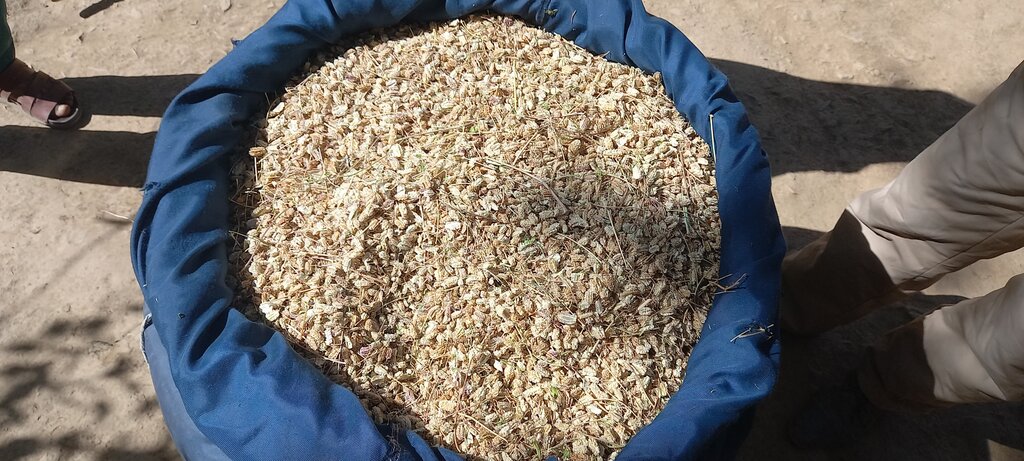
5. Collecting, drying, and storing seed: The fodder species’ seeds are collected manually by hand. These fodder species produce longer main stems with inflorescence and spikelets on the top at an average person's breast height. Collected seed is brought to the storing facility and laid out under sunlight for drying. Once seed reaches a certain moisture content, it's stored in a cool and dry place until the day of reseeding under the direct supervision of the rangeland management association (RMA).
6. Season of reseeding local fodder seed: Reseeding activities typically begin in the autumn season, just before the first snowfall. Seeds remain in the soil throughout the winter, allowing them to overcome dormancy and germinate in the spring of the following year. Local fodder species used for reseeding include various Fennel species and other plants traditionally relied upon for winter fodder. These include: Umbelliferae ferulus (Gheghu), Winklera silaifolia (Pali), Prangos sp. (Kami), Ferula sp. (Badran), Rheum spp. (Chukri), and Koeleria cristata (Khola), a shrub locally known as Qarghna.
7.Method of Reseeding: The spacing between seeding pits (with 2–3 seeds per pit) depends on terrain slope, fodder canopy size, and existing vegetation cover. On steeper slopes or with smaller canopies, rows and plants are spaced more closely, and vice versa. Typically, rows are spaced 1–1.5 meters apart, and two plants are placed 40–60 centimeters apart.
Pits about five centimeters deep using a hoe and shovel is dug, then seeds are placed, and the seed is covered with soil and pressed with boots.
Pit spacing is estimated by a person’s step length. One person can reseed approximately 3.5 kg of seed per day, and about 15 kg of fodder seed is required per hectare, though, this may vary depending on spacing and seed size.
The seeds are collected using the cash-for-work model. This served (i) to provide income support to poor, vulnerable men and women through short-term employment and (ii) to rehabilitate public assets (rangelands) that are vital for sustaining the livelihoods of livestock rearing. Both men and women-headed vulnerable households benefited from the cash-for-work program of seed collection. More importantly, these fodder species’ seeds are fresh, locally adapted, nutritious for livestock (help fatten livestock), available locally, and inexpensive compared to other types of fodder seed. The germination percentage of the seed and growth of the fodder is significantly high in the reseeded area.
Traditionally, rural communities knew that fodder crops grew from seeds; however, the main stems with inflorescences and spikelets were harvested before maturity and used as fuelwood for heating and cooking. Through awareness-raising campaigns and training workshops within the project, farmers were encouraged to leave the main stems intact for seed maturation, allowing for natural seed dispersal and seed collection for reseeding. The success of natural reseeding is limited compared to artificial reseeding due to several factors. In natural reseeding, seeds are often exposed and not covered by soil, making them vulnerable to environmental conditions. Moisture availability may also be insufficient for germination, and existing vegetation can compete with new growth. In contrast, artificial reseeding ensures that seeds are properly covered, protected, and placed in areas with optimal moisture, which increases the likelihood of successful germination and establishment. Recently, the demand for the local fodder seed has dramatically increased because many non-profit organizations and private businesses are purchasing these seeds. It created a new source of income for the rural communities.
The technology combines both traditional knowledge and scientific understanding, contributing to more effective restoration of the degraded rangeland ecosystem, improving soil health, and increasing fodder availability, which benefited rural communities that rely on the ecosystems for their livelihoods and enhanced their resilience.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
The video shows the result of reseeding local fodder species in degraded rangelands, contributing to land restoration and improved fodder availability.
Data:
28/10/2024
Localização:
Balderghoto village, Punjab district Bamyan province
Nome do cinegrafista:
Gul Nabi Khan
Comentários, breve descrição:
The video shows the result of reseeding local fodder species, such as Umbelliferae Ferula and Prangos sip., showed improved vegetation cover, enhanced soil stabilization, increased forage availability for livestock, and greater ecosystem resilience.
Data:
03/06/2023
Localização:
Village Kandogak, RMA Sayed Bacha, Punjab district Bamyan
Nome do cinegrafista:
Gul Nabi Khan
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Bamyan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Punjab and Yakawalang districts
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
These sites are subject to a five-year quarantine following the reseeding activity, meaning that they are designated off-limits for grazing, shrub gathering, and fodder harvesting during this period.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2021
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The project “Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistan,” is implemented by FAO with the financial support of GEF, which is focused on reducing land degradation, enhance biodiversity and climate change mitigation.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
- Direct grazing and remaining fodder is cut for animal feeding
Tipo de animal:
- gado - lácteo
- caprinos
- ovelhas
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Não
Produtos e serviços:
- carne
- leite
- wool
Espécie:
ovelhas
Contagem:
647703
Espécie:
caprinos
Contagem:
250869
Espécie:
gado - lácteo
Contagem:
165274
Comentários:
It has been agreed among community members that, following the reseeding program, the area will be quarantined for at least 4-5 years. During this period, no grazing, shrub collection, or fodder harvesting will be allowed in order to enhance vegetation coverage.
The exact number of livestock in the reseeding area of the rangeland is currently unknown, as no formal count has been conducted. The numbers provided reflect an estimated count of livestock in the target districts of Yakawlang 1 and Punjab. The data was sourced from the Department of Livestock and Animal Health of the Provincial Directorate of Agriculture, Livestock, and Irrigation of Bamyan.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
The rangeland is rainfed and experiences heavy snowfall during the winter season.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Reserva ( suspensão do uso, apoio à recuperação)
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- rangeland restoration
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
The land is closed/rested for both natural and artificial vegetation to recover.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Comentários:
Reseeding various fodder crops helps control soil degradation by restoring plant cover, which stabilizes the soil and reduces erosion. Improved soil cover minimizes the loss of fertile topsoil and can enhance soil organic matter, leading to improved soil fertility over time.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Reseeding technology helps restore degraded land by introducing vegetation that stabilizes soil, improves water retention, and prevents erosion. Once the land is restored, reseeding continues to prevent further degradation by maintaining protective vegetation that sustains soil health and reduces environmental pressures.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
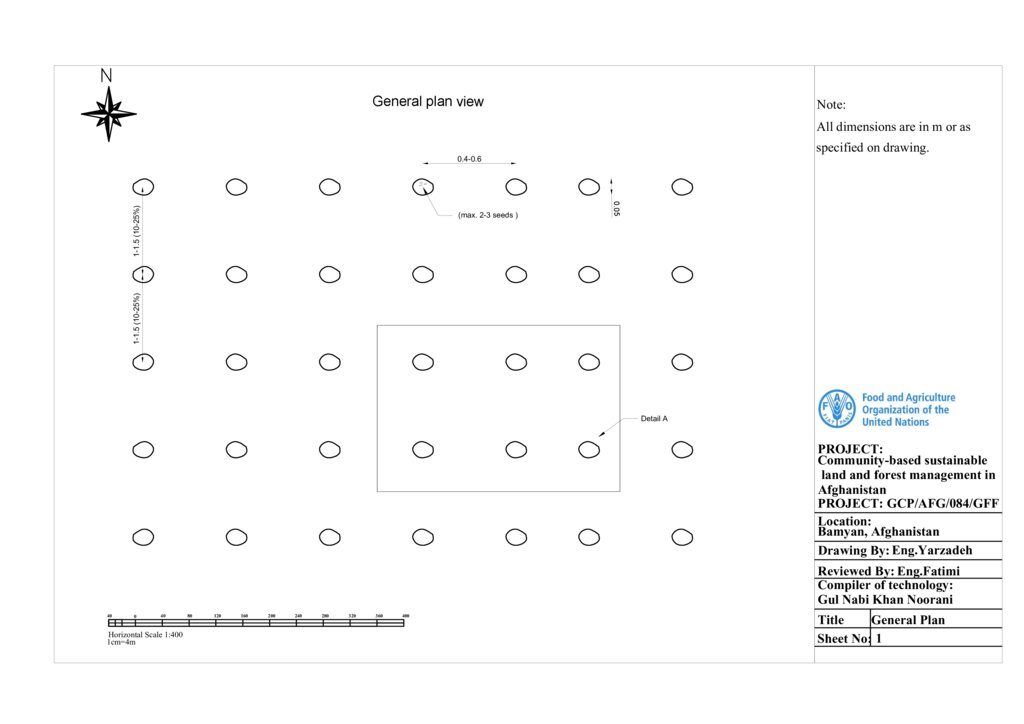
General specifications of the technology:
1. Local fodder crops, such as species from the Ferula and Prangos genera, are well-suited to semi-arid conditions due to their drought and cold resistance.
2. A moderate slope of 10-25% is ideal for reseeding.
3. On such slopes, the recommended distance between two rows is 1-1.5 meters, while the spacing between two seeding pits should be 0.40-0.60 meters. The spacing between pits can be estimated using a person’s step. The depth of each pit should be approximately 0.05 meters.
4.The width of the pit is determined by a single strike with a hoe or mattock.
5. The distance between rows and plants can vary depending on the slope, soil type, vegetation cover, and canopy size of the fodder crop. For steeper slopes or species with small canopies, the spacing between rows and plants should be reduced, and vice versa.
6.Small pits for planting are dug using tools such as hoes or mattocks.
7. 2-3 seeds are placed in each pit.
8. The seeds are covered with soil using a person's foot, boot, or a similar implement.
9. Approximately 15 kilograms of seed are required per hectare for reseeding using this technology.
10. It is important to note that the quantity of seed required per hectare depends on the spacing between rows and plants, as well as the size of the seed.
Autor:
Ms. Samira Yarzadeh and Mr. Sayed Habibullah Fatimi
Data:
16/12/2024
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
539 hectares
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
AFN
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
69,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
350 AFN
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identification of locally adapted drought-resistant and palatable fodder species by livestock owners and land users. | April and May |
| 2. | Identification of highly producing areas of selected fodder species for seed collection. | June and July |
| 3. | Deferring grazing and delaying fodder harvest for the purpose of seed maturity in the targeted area. | June, July, August and September |
| 4. | Awareness raising about the maturity stages of different fodder species seeds: | August and September |
| 5. | Collecting, drying, and storing seed | September |
| 6. | Identifying sites for reseeding | September |
| 7. | Mobilization of community members for reseeding campaign | September and October |
| 8. | Reseeding: Transporting seed and agricultural tools to the area, preparation of field, digging planting pits, reseeding and covering the seed. | October and November |
| 9. | Controlling grazing in the next growing season | April, May, June, July (following year) |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Collecting of local fodder seed (Kami, Ghegho, Chukri, Khola, Badra, Qarghana) | person-days | 5,0 | 350,0 | 1750,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Drying and storing of local fodder seed | person-days | 3,0 | 350,0 | 1050,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Reseeding of local fodder seed in rangeland | person-days | 8,0 | 350,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Pit digging equipment i.e., shovel, hoe, pick mattock | no. | 5,0 | 250,0 | 1250,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Plastic bags for collecting seed (reusable) | pieces | 3,0 | 20,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 6910,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 100,14 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The cost of collecting the plant material is paid by the project under the cash-for-work intervention (110 AFN/kg))
Comentários:
In reference to the agreement with the Rangeland Management Association, reseeding is voluntarily carried out by its members. Additionally, the necessary farming equipment for digging pits is provided by the members themselves.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control grazing and fodder harvesting | 12 months/ annually |
| 2. | Restrict cutting perennial shrubs for forage, firewood and their uprooting | 12 months/ annually |
| 3. | Reseeding is done in the pits where there was no germination. | Growing season/ once a year |
| 4. | Conduct workshops and awareness raising for herders on SLM. | Growing season/ twice a year |
Comentários:
After reseeding, the area is closed off for 4-5 years to prevent grazing, fodder collection, and shrub harvesting or uprooting as firewood. Once the area has recovered, it will be sustainably used by harvesting one-third as fodder after it matures and the seeds have naturally dispersed.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Community members, acting as rangers, patrol the area to control grazing, fodder collection, and shrub harvesting | person-day | 240,0 | 200,0 | 48000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Reseeding of pits where there was no germination. | person-day | 2,0 | 350,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Conduct awareness raising for herders on SLM. | no. | 3,0 | 3000,0 | 9000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 57700,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 836,23 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Even when there is no cash for work from the project, the community collects seeds and does reseeding in some areas. The rest are sold in the open market depending on the demand for seeds.
Comentários:
Patrolling reseeded rangeland to prevent grazing, fodder harvesting, and shrub collection is a critical step in sustainable rangeland management, particularly in regions like Bamyan, Afghanistan, where rangelands are vital for pastoralist livelihoods. The community selects one or two herders to monitor and manage land use for eight months each year, until livestock return to indoor barns for the winter season. Rangers are paid annually for patrolling the entire rangeland area, rather than by hectare, which makes it challenging to calculate the cost per hectare. The land is divided into different zones, including grazing areas during specific periods, rotational grazing zones, and restricted grazing areas such as reseeded land. Rangers are trained to enforce the agreed regulations and ensure compliance effectively.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most important factors affecting the costs are the seed of local fodder types and their availability during the growing season, as well as the cost of rangers patrolling the technology area.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
150,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The average annual rainfall in Bamyan, Afghanistan, is relatively low, as the region is characterized by a semi-arid to arid climate. On average it is around 100–150 mm annually.
Most of the precipitation occurs during the spring season (March to May) and occasionally in the early summer. Snowfall is common in the winter months due to Bamyan's high elevation (about 2,500-3,000 meters above sea level), contributing to water availability through snowmelt in spring and summer seasons.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
World weather online
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The mean annual temperature in Bamyan varies around 6–8°C (43–46°F). The region experiences a wide temperature range throughout the year due to its high-altitude and semi-arid climate. Bamyan winters are very cold and snowy, while summers are hot and dry.
Winter (December–February): Extremely cold, with average temperatures ranging from -10°C to -15°C (14°F to 5°F). Nights can be even colder, with temperatures dropping below -30°C (-4°F).
Summer (June–August): Relatively mild, with average daytime temperatures around 20–25°C (68–77°F). Nights remain cool due to the high altitude.
Spring and Autumn: Transition seasons with moderate temperatures, ranging from 5–15°C (41–59°F).
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Bamyan, located in Afghanistan's central highlands, is characterized by a mix of high mountain ranges, valleys, and plateaus. The Hindu Kush Mountain range 4,000 meters (13,100 feet) contributes to the region's cold climate and water source. The Bamyan Valley, known for its ancient Buddha statues, supports agricultural activities. High-altitude plateaus create grazing lands for pastoralist communities. The Kunduz River and seasonal streams sustain the region's water systems.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
The soil characteristics of Bamyan, as detailed by FAO's Afghanistan Soil Information System (AfSIS) and the FAO Soil Atlas of Afghanistan, indicate that the soils are predominantly loamy to sandy with varying organic content. They are slightly alkaline, with pH levels ranging from 7 to 8 in many areas. The topsoil is characterized by low organic matter content, typical of arid and semi-arid regions, and moderate cation exchange capacity. Nitrogen levels are low, necessitating careful management to ensure sustainable agricultural productivity. Salinity levels are generally low to moderate across most parts of the region.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water salinity does not appear to be a major problem in Bamyan. Most water sources, including those originating from snow and glacier melt, show good quality for drinking, with low to moderate salinity levels. However, localized issues such as high total dissolved solids (TDS) or electrical conductivity (EC) have been identified in certain areas, indicating potential salinity concerns, particularly for irrigation or drinking in specific contexts.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The state of biodiversity in Bamyan varies across its ecosystems and is influenced by factors such as altitude, land use, and conservation measures. The protected areas, such as Band-e-Amir National Park and Shah Foladi, are rich in endemic plant species, wildlife species like snow leopards, ibex, wolves, and a variety of bird species. Outside protected zones, biodiversity is under pressure due to overgrazing, hunting, unsustainable land use, and land degradation, which reduce the habitat quality for native plants and animals. Medicinal plant species, important for local use, are declining due to unsustainable harvesting practices. Overall, biodiversity in Bamyan's protected areas is better compared to unprotected regions.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
- Semi-nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The main characteristics of land users in Bamyan are predominantly rural, with around 90% of the population engaged in agriculture, agroforestry, and livestock farming. These communities rely heavily on the rangelands for grazing, fuelwood, and other natural resources. The province is home to agro-pastoralists, where both crop farming and animal husbandry are integral to their livelihoods.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
In the context of Bamyan’s agricultural and rangeland management, more than 100 hectares of artificial reseeding activity is typically considered medium-scale.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
Customary systems (Jirgas and Shuras)
Comentários:
Land use rights in Bamyan are governed by a combination of national laws, customary practices, and local governance structures. Customary practices such as Jirgas and Shuras, often mediated by local elders, dominate in rural areas but frequently conflict with state laws over issues like grazing rights and communal resources. These overlapping systems lead to disputes, particularly between nomadic and settled communities, with ongoing efforts to create a unified legal framework.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
Access to services and infrastructure in Bamyan is limited due to its remote location and mountainous terrain. Basic services such as healthcare, education, and clean water are available but often insufficient, particularly in rural areas. Infrastructure like roads and electricity is underdeveloped.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Quantidade anterior à GST:
560 Kg/hectare
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1050 kg/hectare
Comentários/especificar:
The fodder production per hectare in Bamyan’s rangelands varies significantly based on land conditions and management practices. In rehabilitated rangelands, such as those supported by FAO-GEF projects, forage production enhanced through reseeding and rotational grazing strategies.
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
6 litters milk/cow/day
Quantidade posterior à GST:
12 litters milk/cow/day
Comentários/especificar:
The integration of indigenous and scientific fodder production techniques (reseeding of local fodder) and availability of nutritious fodder has boosted both health and livestock productivity sustainably.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
539 hectares
Comentários/especificar:
The fodder producing area has been increased from zero to hunderd hectares of rangeland.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5 liters/minute (discharge of spring)
Quantidade posterior à GST:
11 liters/minute (discharge of spring)
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding and improving vegetation cover on rangelands significantly enhanced the infiltration of rainfall and snowmelt, ultimately benefiting underground water reserves and increasing the availability of animal drinking points, irrigation water and drinking water sources such as spring.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Potato cultivation and Livestock
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Potato cultivation, livestock and seed collection
Comentários/especificar:
RMA members now harvest fodder seeds once they reach maturity and sell them in the market, contributing to both local livelihoods (income) and the sustainability of rangeland management.
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Zero community institution
Quantidade posterior à GST:
7 rangeland management associations (RMAs)
Comentários/especificar:
The community institutions in the area are primarily organized as Rangeland Management Associations (RMAs).
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Zero capacity building workshop
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Capacity of 10,000 RMA's member build.
Comentários/especificar:
The capacity of RMA members is enhanced through training, community-based workshops, and awareness-raising initiatives focused on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Sustainable Forest Management (SFM).
Atenuação de conflitos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4 conflicts / village/year
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0 conflicts/village/year
Comentários/especificar:
Increasing the quantity and availability of water and fodder helps reduce conflicts by addressing resource scarcity, which is often a source of tension. When communities have enough access to these essential resources, competition decreases, and cooperation can grow.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
30-40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
70-80%
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding improves soil cover, protecting it from erosion, stabilizing the soil, enhancing water retention, and restoring nutrients. This supports ecosystem recovery and promotes healthier soils and sustainable land use.
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40-50%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0
Comentários/especificar:
Soil loss varies depending on topography, land use, and management practices. Soil loss rates typically range between 2.2 to 38 tons per hectare per year (t/ha/year), depending on slope steepness and vegetation cover. Higher rates are observed in areas with steep terrain and minimal vegetation, while conservation practices can reduce these rates significantly.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
30-40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
70-80%
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding improved vegetation coverage by introducing new plant seeds to degraded areas, promoting their regrowth and restoring ecosystems.
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0.2-2 Ton/hectare
Quantidade posterior à GST:
4-5 ton/hectare
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding local fodder seeds in rangelands enhances aboveground biomass carbon by increasing vegetation growth, which sequesters more carbon.
Diversidade vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5-15 species/species/square meter
Quantidade posterior à GST:
15-25 species/species/square meter
Comentários/especificar:
Plant diversity is relatively high, featuring a variety of native grasses, shrubs, and medicinal plants adapted to the region's arid and semi-arid conditions. The plant diversity can vary widely depending on factors like altitude, grazing pressure, and management practices.
Espécies benéficas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2-5 species/ technology area
Comentários/especificar:
Bees and birds
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2-3 floods / year
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0 floods/year
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding reduces flooding by establishing vegetation cover that stabilizes the soil, enhances water infiltration, and slows surface runoff, thus decreasing the volume and velocity of water that can lead to floods.
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50,000 m3/winter season
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5000 m3/winter season
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding helps reduce landslides by promoting the growth of vegetation. The roots bind soil particles together, increasing slope stability and reducing soil erosion caused by water runoff and snow fall.
Impactos da seca
Quantidade anterior à GST:
560 Kg/hectare (fodder yield)
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1050 kg/hectare (fodder yield)
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding of different fodder species enhances soil moisture retention, reduces surface evaporation, and improves water infiltration.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5 liters/minute (discharge of spring)
Quantidade posterior à GST:
11 liters/minute (discharge of spring)
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding and improving vegetation cover enhanced the infiltration of rainfall and snowmelt, ultimately benefiting ground water recharge and increasing water availability: animal drinking points, irrigation water and drinking water sources such as springs.
Cheias de jusante
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2-3 floods/year
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0 floods/year
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation cover stabilizes the soil, enhances water infiltration, and slows surface runoff, thus decreasing the volume and velocity of water that can lead downstream floodsing and damage.
Sedimentação a jusante
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2-3 floods/year
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0 floods/year
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding helps reduce downstream siltation and river water pollution by stabilizing the soil, preventing erosion, and promoting the growth of vegetation that intercepts and filters runoff.
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding helped increase buffering and filtering capacity by reintroducing vegetation that acts as a natural barrier against pollutants and runoff. The plant roots stabilize the soil, reducing erosion, while the vegetation cover slows water movement, allowing it to infiltrate the ground.
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2-3 floods/year
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0 floods/year
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding and better soil cover helped reduce flash flood damage to neighboring agricultural fields downstream.
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0.5-2 tons of sequestered CO₂/ hectare annually
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3-4 tons of sequestered CO₂/ hectare annually
Comentários/especificar:
Reseeding reduces greenhouse gases by enhancing carbon sequestration in plants and soil, while also minimizing emissions of nitrous oxide and methane from degraded areas.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
The off-site impacts of reseeding local fodder seeds in degraded rangelands are measured through improvements in water infiltration, reduced soil erosion, expanded vegetation cover, enhanced biodiversity, and increased carbon sequestration. Social and economic benefits, such as higher incomes from fodder sales and reduced grazing pressure on communal resources, are assessed through community surveys.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | redução/diminuição | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | moderadamente |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação súbita | muito bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | muito bem |
| avalanche | muito bem |
Comentários:
Reseeding mitigates gradual climate change by sequestering CO₂, stabilizing soil, and improving water retention, while reducing the impacts of climate-related extremes like floods, droughts, and erosion by restoring ecosystems and enhancing local climate resilience.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Reseeding Bamyan rangelands requires investment in seeds, labor, and maintenance, but provides long-term benefits like better vegetation, soil stability, and carbon sequestration. It improves grazing, reduces flood and erosion risks, and helps mitigate climate impacts. The ecological and economic gains outweigh the initial costs.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Enhances the availability of high-quality forage, leading to better livestock health and productivity. |
| Restores degraded land which increasing grazing rangeland area. |
| Alternative source of income through temporary employment. |
| It's easy to adopt and many pastoral communities have already replicated. |
| It requires locally available seeds, labor, and traditional knowledge, making it cost-effective and practical for communities to implement. |
| Community members choose palatable, nutritious and drought resistant fodder species which enhance their livestock production. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Reseeded areas help control soil erosion and improve soil fertility through vegetation cover. |
| Improved biodiversity through the reintroduction of native species. |
| Reseeding supports carbon sequestration and contributes to climate resilience and adaptation. |
| The technology involved local communities which ensures better understanding, ownership, replication and sustainability of the process. |
| Local or indigenous species used in reseeding are well-adapted to local conditions, increasing the likelihood of successful germination and growth. |
| Through training and awareness raising, now community members are allowing fodder to grow until seeds are fully mature. This ensures effective seed production (collection) and natural dispersal, aiding in rangeland regeneration and biodiversity improvement. |
| Alternative income through employment in local fodder seed collection and sales. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Reseeding requires an initial investment in establishing a rangeland management association, seeds and labor. | By establishing RMA and mobilizing community members to contribute and seek funding from governments, NGOs, or international organizations. |
| Control grazing: Livestock grazing in reseeded areas can damage young plants, reducing effectiveness. | Require an agreement with community to control grazing in the area. Also, implement rotational grazing systems and fencing to protect reseeded areas until vegetation is established. |
| Benefits from reseeding take time to return, potentially discouraging land users seeking quick results. | Identify alternative grazing area. Provide short-term solution of supplemental feed to address immediate needs. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Implementing reseeding may limit access to grazing lands temporarily, potentially causing disputes among land users, especially in areas with shared resources. | Through agreement of all land users. |
| Reseeding success is highly dependent on favorable weather conditions. Drought or erratic rainfall can lead to poor germination and growth. | Explore the potential to integrate rainwater harvesting structures in future reseeding activities |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Seven field visits and surveys
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
A total of 32 land users were interviewed.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
10/11/2024
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
The Status of Forage Production in Afghanistan: Forage Options for Smallholder Livestock in Water-Scarce Environments of Afghanistan. Ates, S., Hassan, S., Soofizada, Q., Biradar, C., Esmati, H., & Louhaichi, M. (2018).
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://research.aciar.gov.au/aik-saath/sites/_co-lab.aciar.gov.au.aik-saath/files/2020-08/ICARDA%20forage%20Afghanistan_0.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
FAO brings life to degraded rangeland thanks to GEF funding. FAO, 2022
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.fao.org/afghanistan/news/detail-events/en/c/1505486/
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Community-based Sustainable Land and Forest Management in Afghanistan,
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.thegef.org/projects-operations/projects/9285
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
An introductory guide to sources of traditional fodder and forage and usage, Anthony Fitzherbert, 2014
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.acbar.org/upload/1493193872857.pdf
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Rangeland rehabilitation measures reduces pressure on land, boosts household income and induces peace of mind
URL:
https://www.fao.org/afghanistan/news/detail-events/fr/c/1606232/
Título/ descrição:
Managing rangelands: promoting sustainable practices: Reseeding: a practical and costeffective technique that enhances ecological sustainability while strengthening system resilience
URL:
https://dspacetest.mel.cgiar.org/items/a8eee495-817c-4dfb-a737-90db7eb19378
Título/ descrição:
Reseeding improved soil and plant characteristics of degraded alfalfa (Medicago sativa) grassland in loess hilly plateau region, China
URL:
https://pdf.sciencedirectassets.com/271742/1-s2.0-S0925857423X00032/1-s2.0-S0925857423000423/main.pdf?X-Amz-Security-Token=IQoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEH4aCXVzLWVhc3QtMSJIMEYCIQD3T2VNZYEr3aSuPiqIB%2BrFarS8RQXlWNUJd9eV1MHa2wIhAOTmszFUNpOgWgs2rvkxfFWu%2FtyDr0deq4kp4Ytkz%2F%2BCKrMFCCYQBRoMMDU5MDAzNTQ2ODY1IgwoXO8sdzB5A1xzYE0qkAW%2FZw%2F9bgO%2BKFg9iCfslLE01ANYhMnSDoaX8g7Pvy7dpTxLjw4rBvTCJsIOus%2FHHzuUWQb%2ByL4ne4mRVs4OHcZkmbbo7FxbyIzVnmCvn2QEFcneRX2VjxKsgmVjYC6QjVbAVR6EUAa0JHv6NB5n8LgI9kQCNti1OHeAjuH9hTcUnus2QMLZhDFEWxkuUmhaZE7p81ZypqZuENHYywVw5LXF1ctJOV8vKDtuxdq7zCG4OkusqlAWVW0dN%2F49OxCc4mT1ihIlFIiFZOemqYH2X2K7%2BVgPsCDQq9Ru7pXlQrG%2FrvnU71QY6vZF%2F0ZsT6jImwz36Vjy8Q%2B%2Fgba3kVcua5e8W%2FxQ5GZ0wYu3f2NT2gZf%2BEe1hUbHtDLUz6GkSVbjqmKEcqb7t3x8oC0ugPE%2BhBCwLtUHUOVohxDTiqLC%2BSvNCtB7PcYTbJ2gqAIG7J%2BnRklhh8WfQ%2Fj68Hem6lzXOhkmrvs78tQ2hpbbvkdalAaGUvmw4Y9wJgvNZZQrzchIKTXBTM2zAbbMF%2FQOWgagPhYAO7P7HMccBJ5syuYXL9HhDYhDeOuK2MwduI7IKFhDA%2BXA7NyLcu4YSiBExUVxSaCDWaSNg5FiCE3Xi7l80Y8iUuCij8sc%2Fi2Fc6OV36ZmIhkSF%2B5AtR5kHP0PMJ2NCTvI%2FNj16hGvUhtclYx3KaqmtU7yNLiSFEba7CncTs38LydQYg4ToBUxyeHFZzdvkq3RXG7BJgv4%2FkkPEpVKs2dsQ%2FJEwdDW%2F3JFxxJkDfwIPEGmdD607FBpDyw9C%2BvfMF4T6r1uVyxqjHwkeMxrH%2BDh0QMt2q2gIwbfYWeKDtA571zpg752C8851tpCCMPSeL%2BW3JdgsdjL4ng0VWLdUXd3zjC1tJW6BjqwARofYsHni1Xzn9OgNnont1g19Z0VSFHYkyaTzXs2nKfM%2FdNVkoXtu%2BX6u0gNmy0a7ed%2FqrC7p8fKqYxAT3FwOjrQBWDK%2Bm8xHfvyk%2B%2BESKBVsXMmC8KhodGoX318C7esUlWpsv953SgG%2FxWob5bsnNe0t470flsh%2F5MhbT%2BCpLRFnBtjwq5JcmDT9QqWAc%2FdxQNd8zPWUPIFh2n3Wtuhg8x9Pmuw5MXc8hiTAmjjlsV4&X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20241126T060240Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Credential=ASIAQ3PHCVTYRWMK75KH%2F20241126%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Signature=7a5092467ceabe0252cbb05beaac0328e6ecfabcc339848f188b3a2bec804b5e&hash=7568b619a05163bde587f16f742fee7be12c85d1b227b62b701e53c7e9720c71&host=68042c943591013ac2b2430a89b270f6af2c76d8dfd086a07176afe7c76c2c61&pii=S0925857423000423&tid=spdf-fb3cf116-0053-4002-ac10-7417b6a882b9&sid=93e7b4418d
Título/ descrição:
Highland Rangelands of Afghanistan
URL:
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwis2PTzqfmJAxXMlP0HHeLQKG8QFnoECBsQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Flib.icimod.org%2Fapi%2Ffiles%2Fb329e25d-b7b2-439c-b29f-471fde5d2ead%2F2.HAR.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1PptmgEEuGRY1LyVLMO4ZR&opi=89978449
Título/ descrição:
Dryland agriculture and rangeland restoration priorities in Afghanistan
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272524566_Dryland_agriculture_and_rangeland_restoration_priorities_in_Afghanistan
Título/ descrição:
Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan
URL:
https://www.thegef.org/sites/default/files/web-documents/10169_MFA_Afghanistan_PIF.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Community-Based Ecosystem Restoration and Climate Change Adaptation in Afghanistan
URL:
https://kosmospublishers.com/community-based-ecosystem-restoration-and-climate-change-adaptation-in-afghanistan-2/
Título/ descrição:
Flora and Vegetation of Afghanistan
URL:
https://www.doc-developpement-durable.org/file/Culture/Fertilisation-des-Terres-et-des-Sols/cultureIntercalaire/Flora&VegetationOfAfghanistan_Siegmar&Breckle.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Constraints to Forage Production and Rangeland Management in Afghanistan
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306344635_Constraints_to_Forage_Production_and_Rangeland_Management_in_Afghanistan
Título/ descrição:
Effect of Planting Atriplex seedlings in micro-catchments on attributes of natural vegetation in arid rangelands
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140196320301038
7.4 Comentários gerais
WOCAT is a highly regarded platform for sharing and documenting knowledge on sustainable land management (SLM). Its extensive database of practices and technologies serves as a valuable resource for practitioners worldwide. Users appreciate the detailed and well-organized questionnaires, which make it easier to document and analyze SLM practices comprehensively. However, some feedback suggests that simplifying the questionnaires could improve accessibility and save time during data entry. Additionally, enhancing the platform's search functionality and incorporating more visual tools, such as maps and graphs, could further improve the user experience and accessibility of the database. Thank you
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos