Learning Site to promote Sustainable Land and Forest Management Practices in Khost [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Mohammad Arif
- Editores: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Aslam Hasand, Afghanistan Safi
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
په خوست ولایت کی د ځنګل او ځمکی بنسټیزه مدیریت عملی کارونو د پاره دزده کړی ساحی رامینځ ته کول
technologies_7460 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Akbar Muhajir
Sparkai Forest and Rangeland Management Association
Afeganistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in AfghanistanNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afeganistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [Afeganistão]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- Compilador/a: Mohammad Arif
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
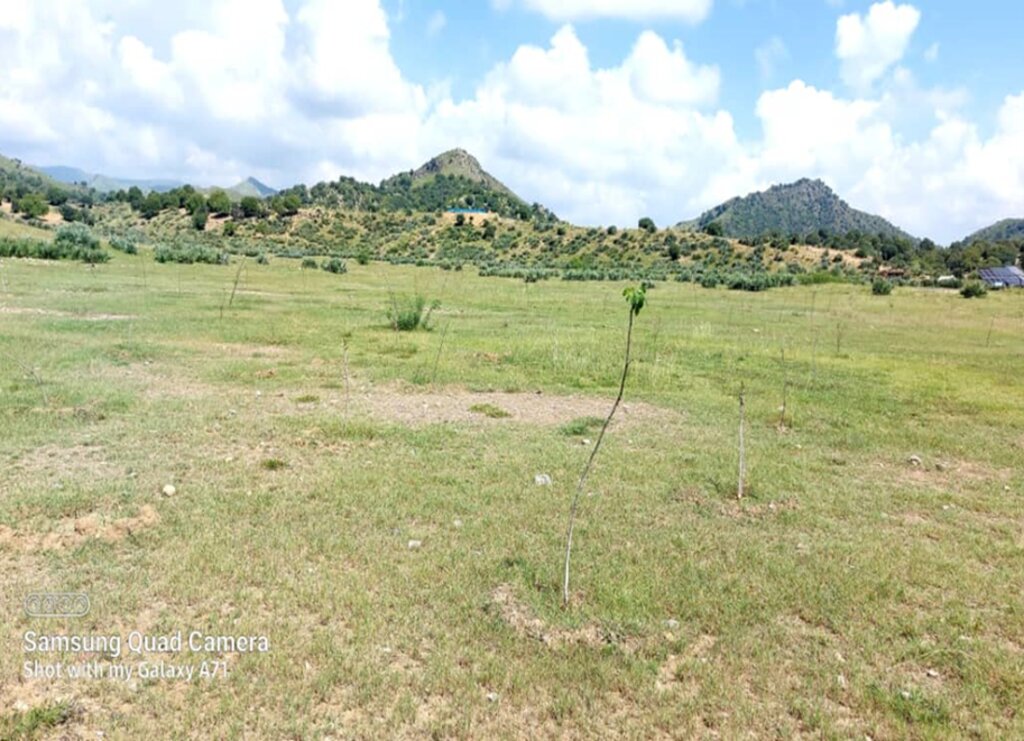
The learning site incorporates several key elements of the technology including a solar-powered water lifting system, three reservoirs and an adopted irrigation system. It features demonstration plots for various initiatives, such as tree planting (walnut, almond, pomegranate and mulberry, the cultivation of fodder (alfalfal Mazari palm) and and medicinal plants (e,g, cumin), and a nursery (walnut) established through the community’s own contributions.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
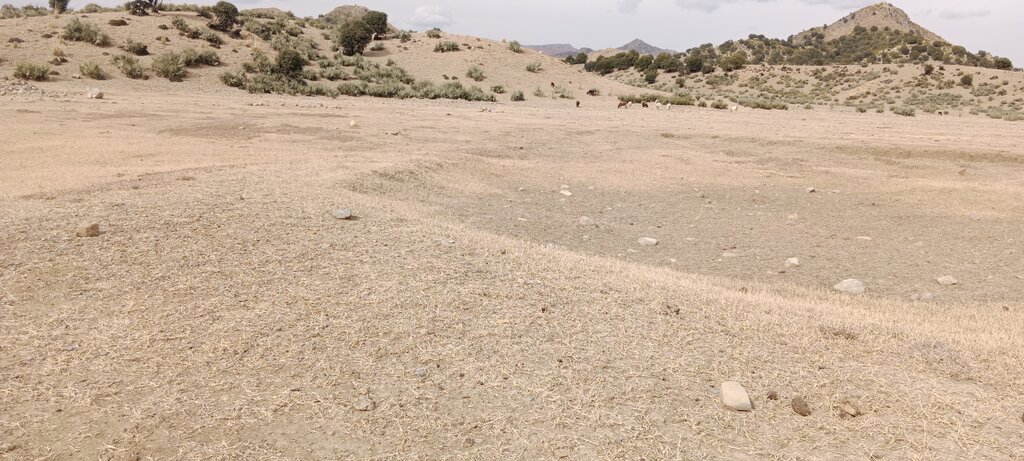
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging. The degradation of natural resources, particularly forests and rangelands, has significantly impacted local communities in Khost. Many residents rely on these resources for fuel, heating, and grazing livestock. However, challenges such as overgrazing, the uprooting of bushes and shrubs, and deforestation for fuel have led to considerable environmental degradation. The lack of proper management of these natural resources has resulted in consistent flooding, which erodes and pollutes agricultural lands. Additionally, local communities often do not recognize the value of these resources, leading to unsustainable land-use practices. Poverty, ongoing conflicts, political instability, and unemployment have driven residents to cut down trees for sale in local markets to support their livelihoods.
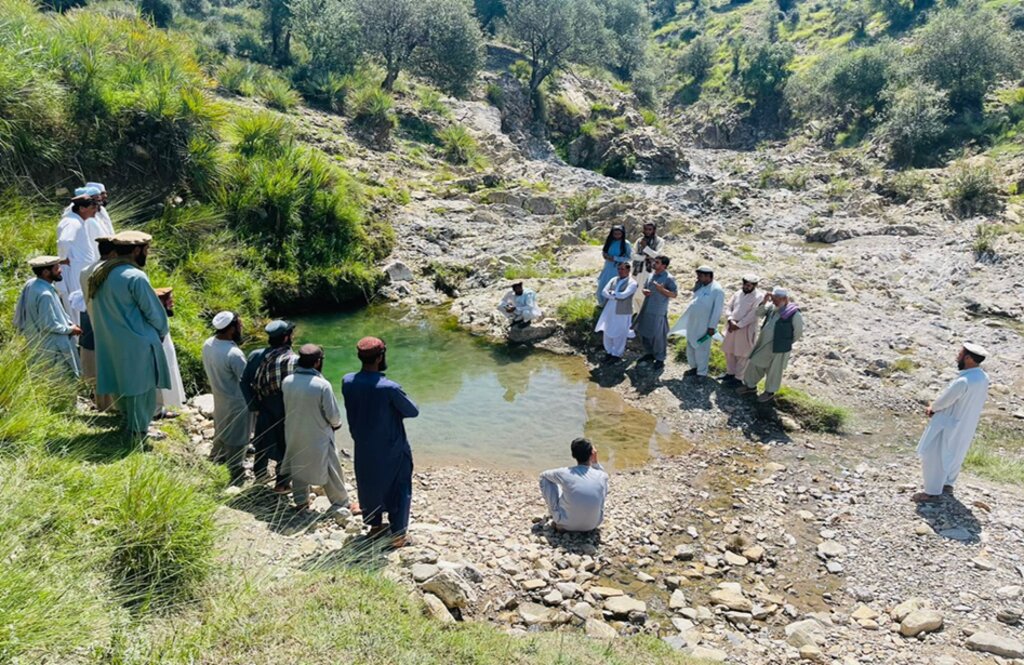
To address these challenges, we conducted a participatory assessment involving local communities and stakeholders, aiming to establish a learning site for sustainable land and forest management practices. Our assessment revealed that many local residents were unaware of sustainable practices or the ecological significance of these resources, contributing to ongoing environmental degradation.
After assessing the natural resources and community needs, we established a learning site for sustainable forest and rangeland management. Feasibility studies helped us identify available water sources, assess community interest, and select suitable land next to forests and rangelands. The site selected is easily accessible, located about 10 kilometers from the main road.
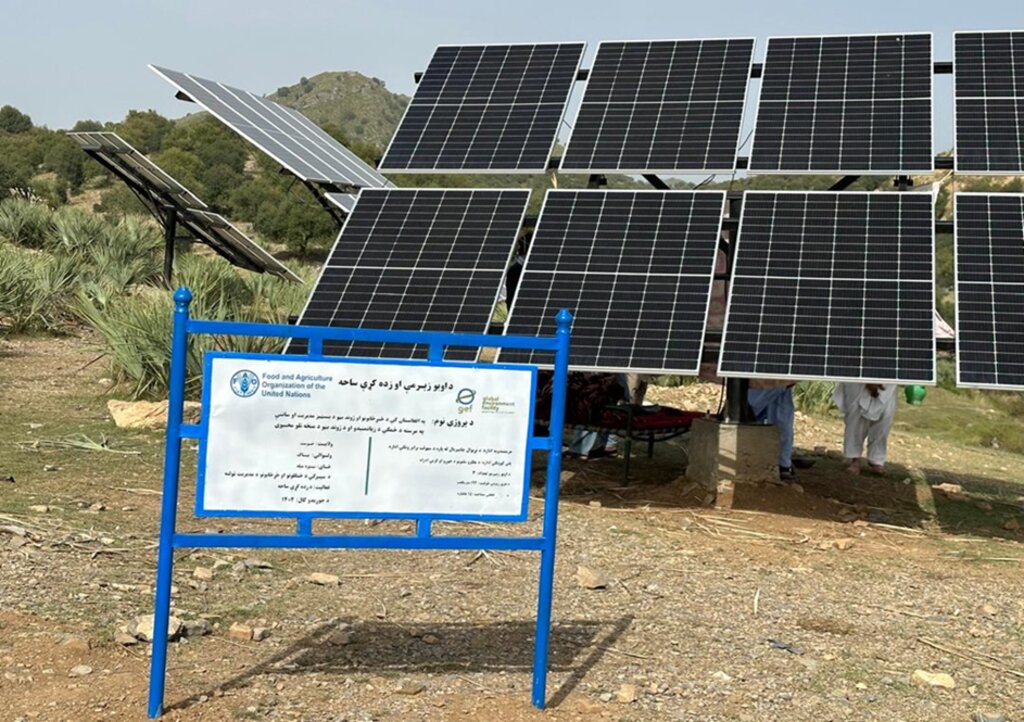
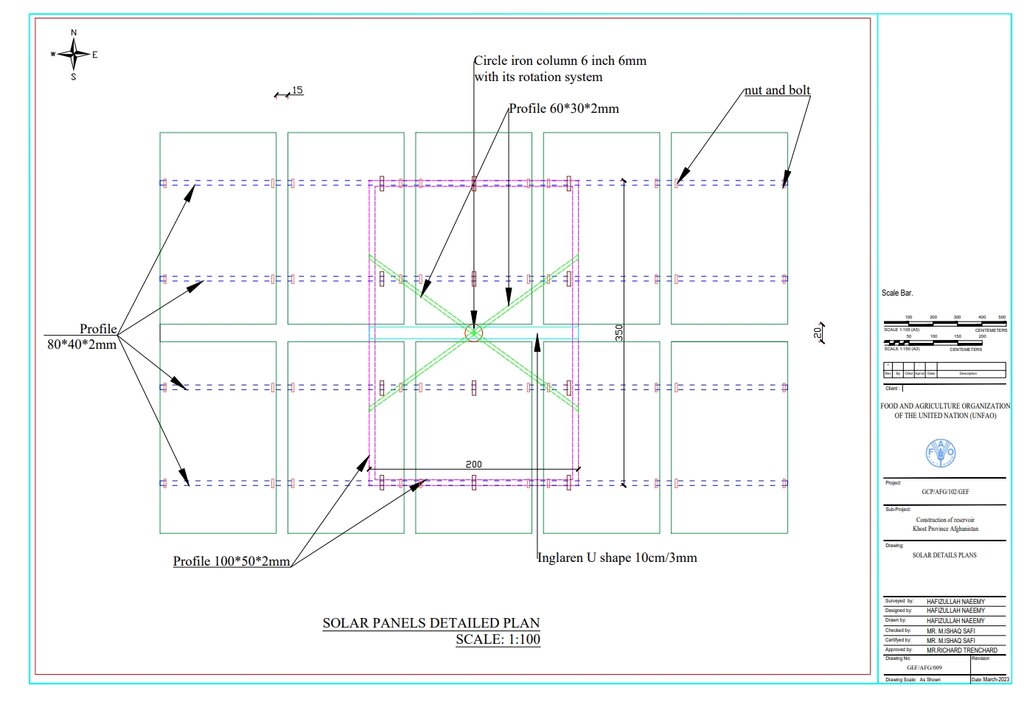
In the initial phase, we installed 26 solar panels on three metal stands, each with a capacity of 400 watts, positioned 200 meters from the water source. At the water source, we installed a 2-inch submersible pump to lift water to the learning site, which encompasses approximately 20 hectares of land across three small hills, each situated 300 meters apart.
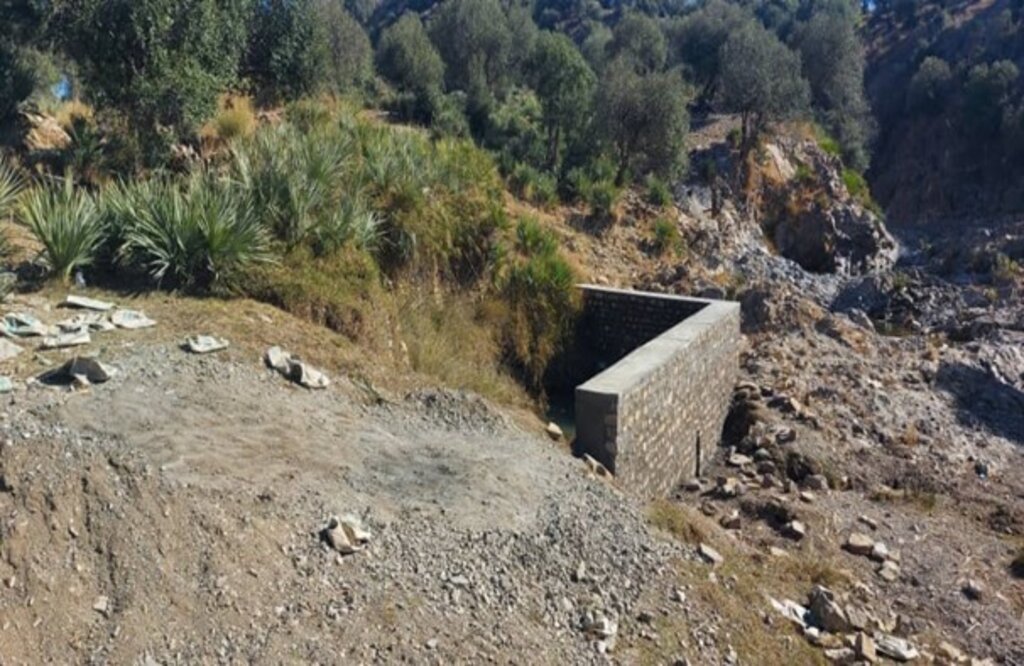
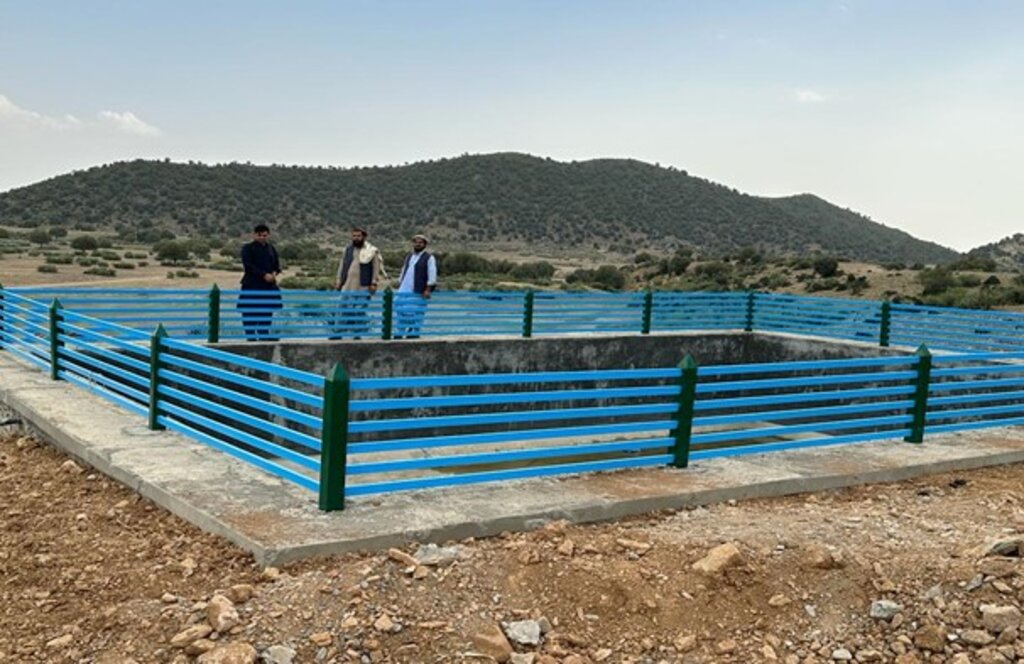
We constructed three reservoirs, each with a capacity of 192 cubic meters. The first reservoir is located 300 meters from the water source and is fed by the solar system. A pipe network system utilizing 2-inch pipes connects the water source to the first reservoir and the other two reservoirs. This system allows the reservoirs to supply water to lower fields or demonstration plots via gravity.
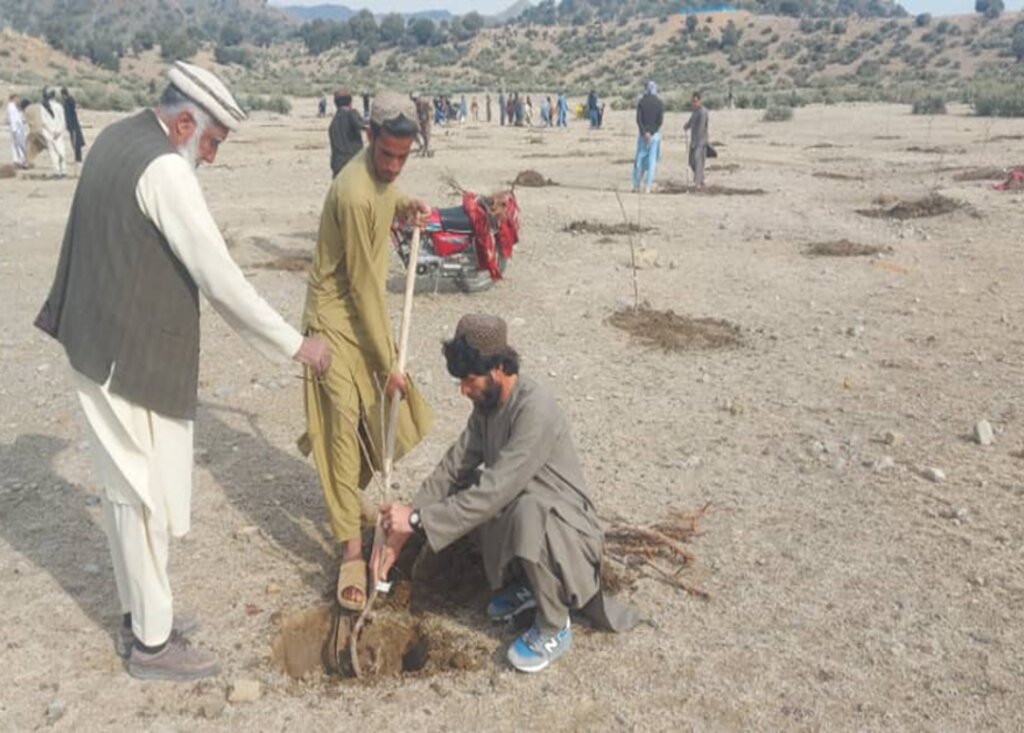
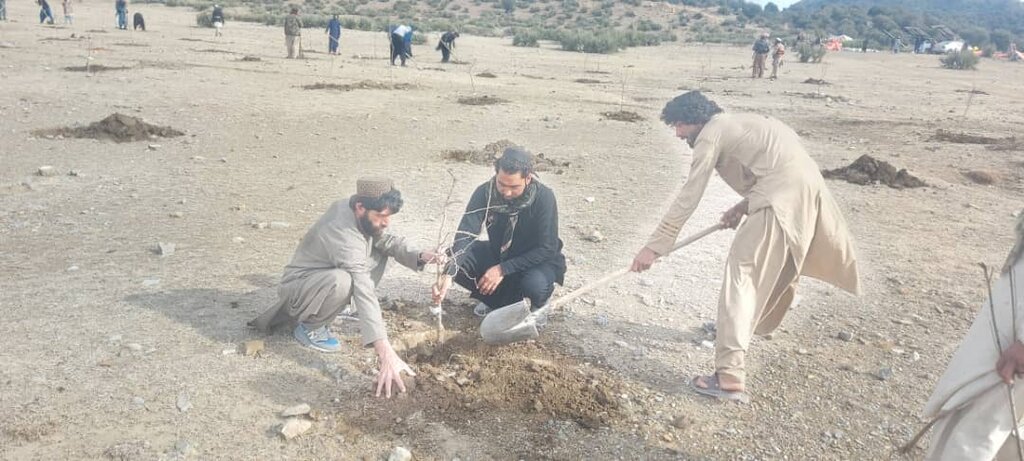
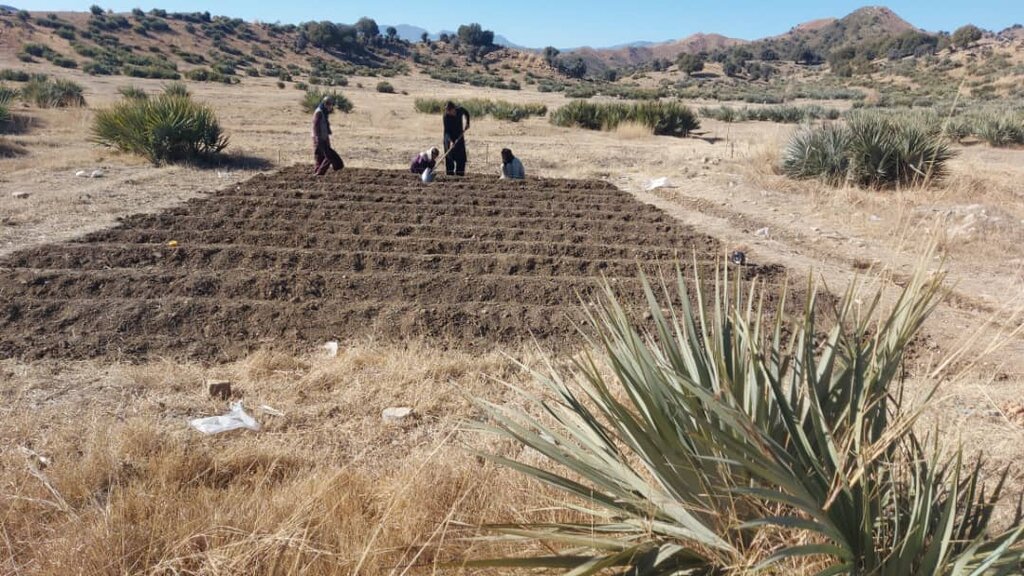
In the demonstration plots, a network of pipes was installed every 50 meters, with taps placed accordingly. We established a 20-hectare learning site focused on sustainable forest and rangeland management practices, featuring demonstration plots for reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant production, reseeding, and a forest nursery. The dimensions of these plots include 10 hectares for reforestation, 2 hectares for fodder production, 0.5 hectares for medicinal plants, and 0.1 hectares for the walnut nursery. A total of 3,000 forest species were planted in the reforestation plot, along with alfalfa and Mazari palm in the fodder plots, and black cumin in the medicinal plot.
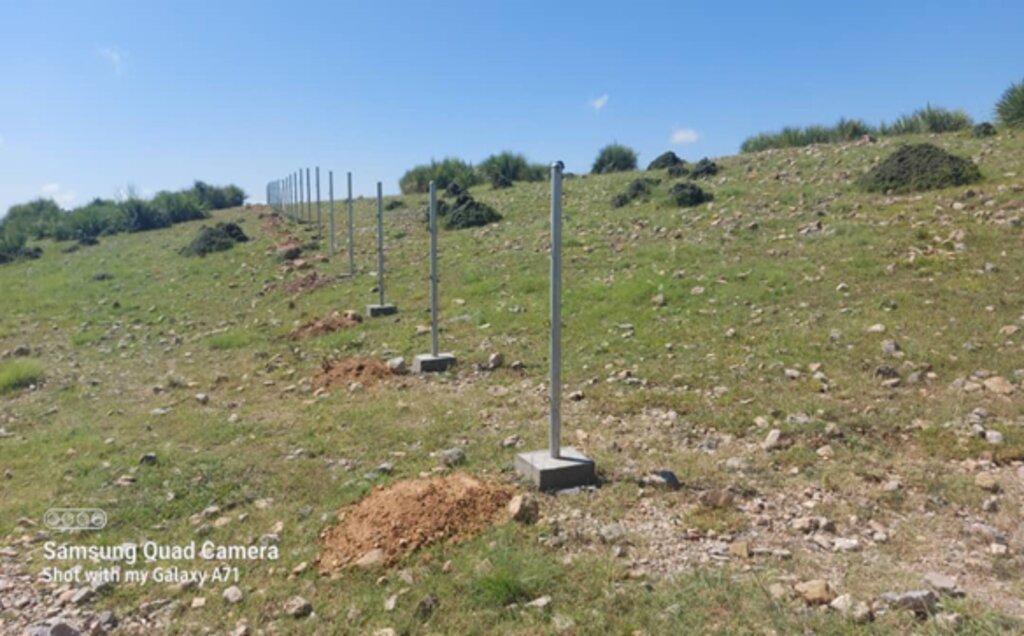
These plots are irrigated using flexible 1-inch pipes connected to the taps installed every 50 meters. Given Khost Province's favorable weather conditions, the plants require irrigation primarily from April to August; outside of this interval, the irrigation system provides sufficient water to sustain the site. The site were fenced with barbed wire for protection.
The technology is applied to communal land adjacent to forests and rangelands. It serves as an educational center for the local community, focusing on sustainable landscape restoration and management. A savings box was created, and a Forest and Rangeland Management Association was established. Social funds were set up, along with fencing and hiring guards for the maintenance of the technology.
Key infrastructure was established, including a solar-powered lifting system, constructed reservoirs, and a piping network for irrigation. Various forest species were planted in reforestation plots, while local seeds were planted in fodder and medicinal plots. Additionally, walnut seeds were sown in a nursery for diverse restoration practices. These efforts have revitalized the land. Barbed wire fencing was installed for protection, and the site is now fully operational as a learning site.
The introduction of this technology led to positive changes in the local community. They have successfully quarantined forest and rangeland, implemented rotational grazing, and collected local seeds and cuttings to plant on degraded lands and riverbanks. Community-based nurseries were also established to transplant seedlings into degraded forest areas, helping to revitalize natural resources.
The local community is optimistic about the technology, particularly the reservoir construction and solar-powered lifting systems that ensure water availability, as well as the restoration techniques employed. However, they expressed concerns about interference from neighbors, livestock grazing, floods that can clog pumps, and damage from hail and windstorms to solar panels.
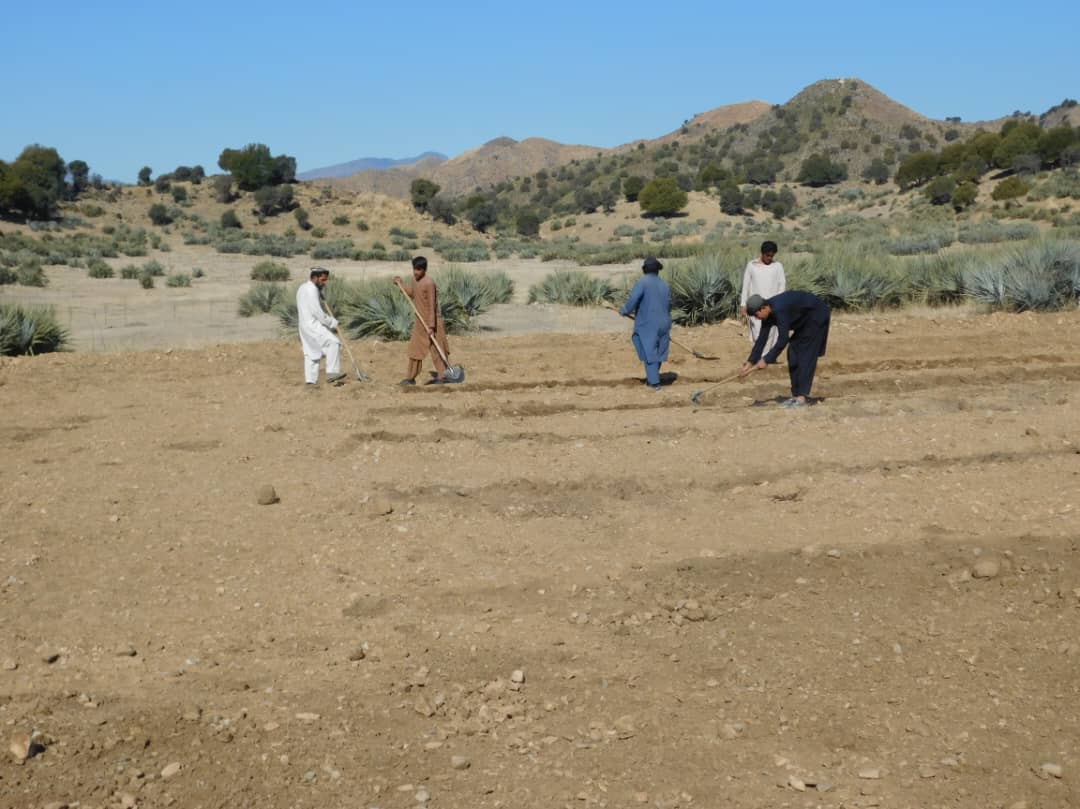
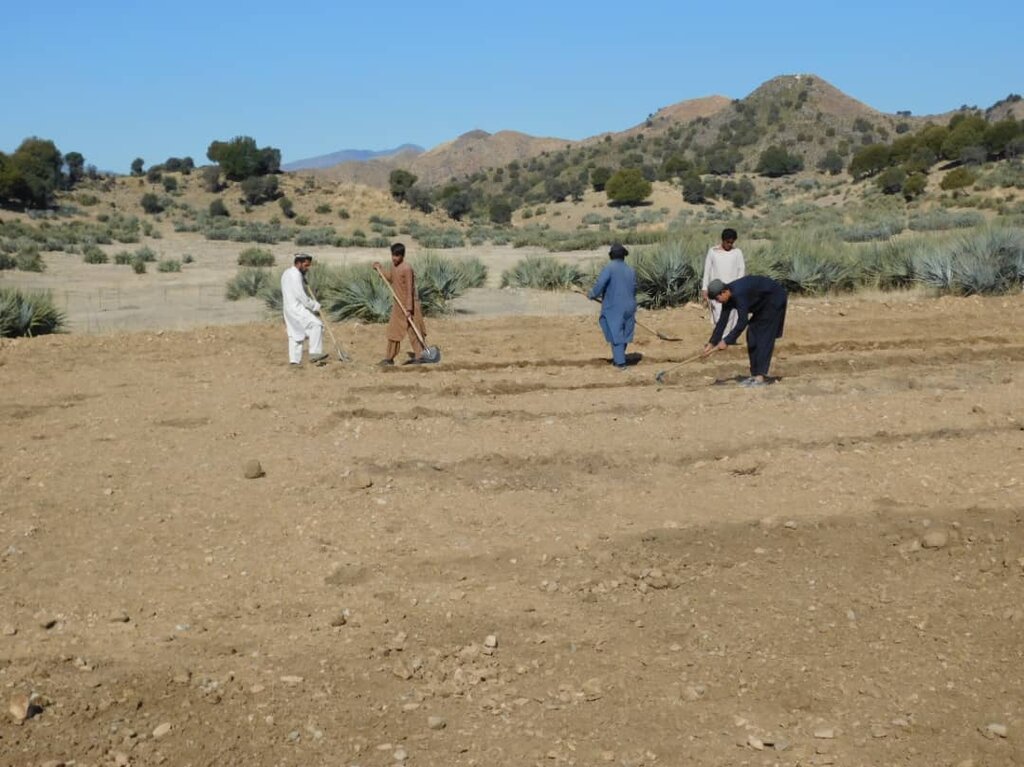
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The photo was taken with a low-quality smartphone.
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
N/A
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khost
Especificação adicional de localização:
Stara Mila, Sparkai village of Baak district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, approximately 20 km from the Baak main road, extending towards the Zazi Maidan district. It is classified as communal land
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2023
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
FAO- GEF-07 Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan (GEF7)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- serves as educational centre for the local community on sustainable landscape restoration and management
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Silvipecuária

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas, outros
- frutos secos (castanhas do Brasil, pistache, nozes, amêndoas, etc.)
- walnut, almond, pomegranate, mulberry
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Nomadismo
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
- caprinos
- ovelhas
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Não
Produtos e serviços:
- carne
- leite
Espécie:
gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
Contagem:
510

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
Florestas (semi)naturais/ bosques: Especificar o tipo de manejo:
- Retirada de madeira morta/podas
- Uso florestal não madeireiro
Tipo de floresta (semi)natural:
- sistemas montanhosos subtropicais vegetação natural
- wild olive, black thorn, hop bush, Mazari palm, cumin
As árvores especificadas acima são decíduas ou perenes?
- decíduas mistas/perene
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Outros produtos florestais
- Lazer/turismo
- Proteção contra desastres naturais
Comentários:
Due to poor management, the land has been overgrazed. To address this, we established a learning site focused on restoration through various interventions: reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant demonstration plots, and a 50-square-meter nursery for sapling production. The site is protected by fencing to prevent herders from grazing, allowing them to collect fodder instead. Some fodder is left in the field to produce seeds for natural regeneration.
Forest and Rangeland Management Association focuses on:
Local seed collection: Gathering native seeds to enhance biodiversity and ensure ecosystem resilience.
Ecotourism development: Encouraging visitors to explore the sites, fostering appreciation for local flora and fauna while supporting conservation efforts.
Regeneration of native species: Implementing strategies to restore and regenerate various native plant species, which play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance.
Fodder production for silage: Cultivating high-quality fodder crops that contribute to livestock nutrition and support sustainable agriculture.
Sapling production through nurseries: Establishing nurseries dedicated to growing saplings of native forest species as well as fruit and nut trees, which can be used for reforestation, habitat restoration efforts and generating income.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Nomadismo
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
- caprinos
- ovelhas
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Não
Produtos e serviços:
- carne
- leite
Espécie:
gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
Contagem:
510

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
Florestas (semi)naturais/ bosques: Especificar o tipo de manejo:
- Retirada de madeira morta/podas
Tipo de floresta (semi)natural:
- sistemas montanhosos subtropicais vegetação natural
- wild olive, Mazari palm, hop bush, black thorn and grasses
As árvores especificadas acima são decíduas ou perenes?
- decíduas mistas/perene
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Lazer/turismo
- Proteção contra desastres naturais
Comentários:
The area is a dry mountainous terrain with natural vegetation including wild olive, mazari palm, hopbush, and grasses. It supports nomadic and semi-nomadic pastoralism, primarily grazing goats, sheep, and cows.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Near the learning site, a gully and springs provide a year-round water source. We have installed a solar-powered lifting system and constructed three reservoirs to distribute water across 20 hectares, including the planted areas and demonstration plots. A network of pipes and taps with flexible hoses ensures efficient water distribution. This water source is exclusively for this site and does not affect neighboring villages or farmers.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de plantação florestal
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
- S10: medidas de economia de energia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M3: Disposição de acordo com o ambiente natural e humano
Comentários:
The whole area 20 hectares have been fenced with barbed wire, under the structure measures, reservoirs have been constructed and dug pits for plants.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
The local community relies on natural resources for their livelihoods, leading to deforestation, overgrazing, and the uprooting of shrubs and bushes for fuel. Severe runoff, droughts, and climate change have further contributed to environmental degradation.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
- Adaptar à degradação do solo
Comentários:
An educational center (learning site) has been established on degraded land to enhance the capacity of the local community and other stakeholders about best practices for landscape restoration.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
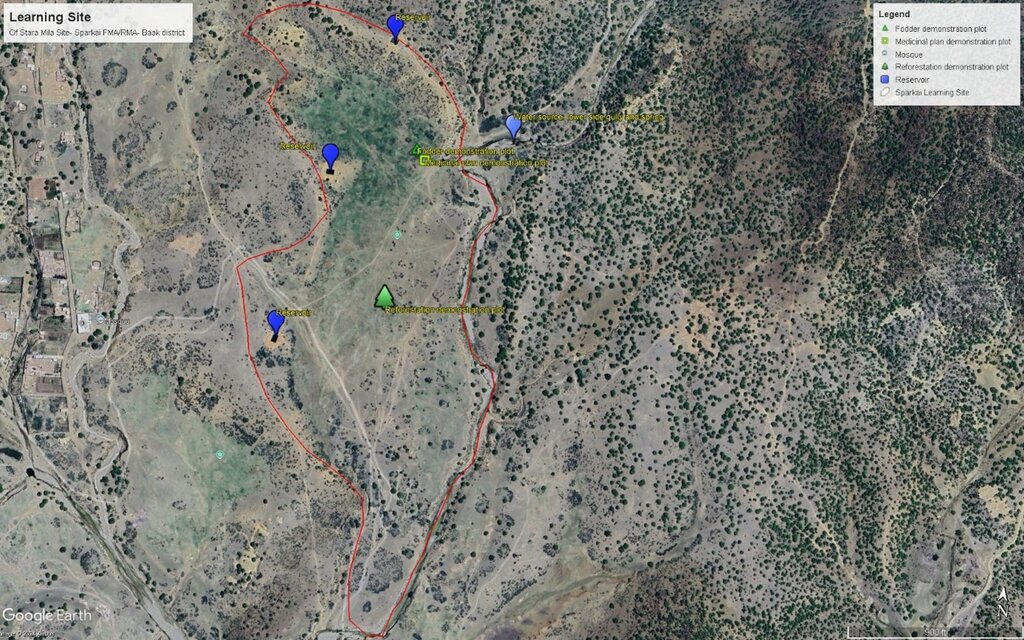
This GIS map highlights learning site elements. The blue pins indicate water source and reservoirs, while the green rectangular pins represent fodder demonstration plot. Yellow squire pin mark area dedicated to medicinal plants, and green tree-shaped pin indicate reforestation plot. Finally, the red track pin indicates location of barbed wire fencing. The site map has been prepared after the completion of intervention.
Autor:
Mohammad Omar Dost
Data:
17/09/2024
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
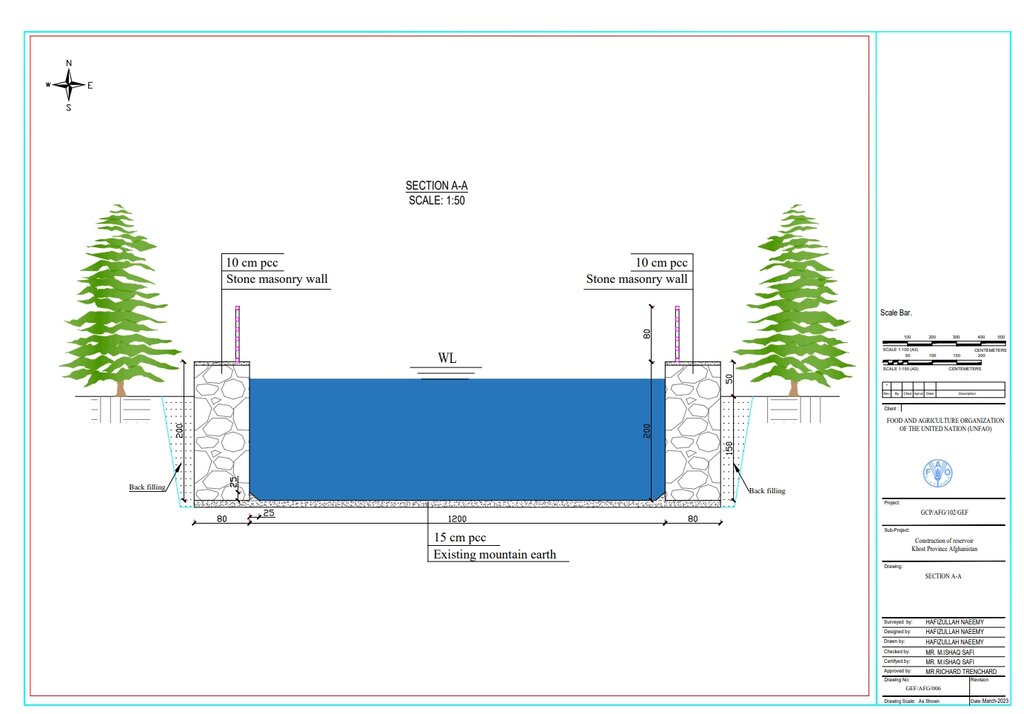
Each of the three reservoirs measures 2m x 8m x 12m with a water depth of 2m, holding a total capacity of 192 cubic meters.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Data:
18/01/2023
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
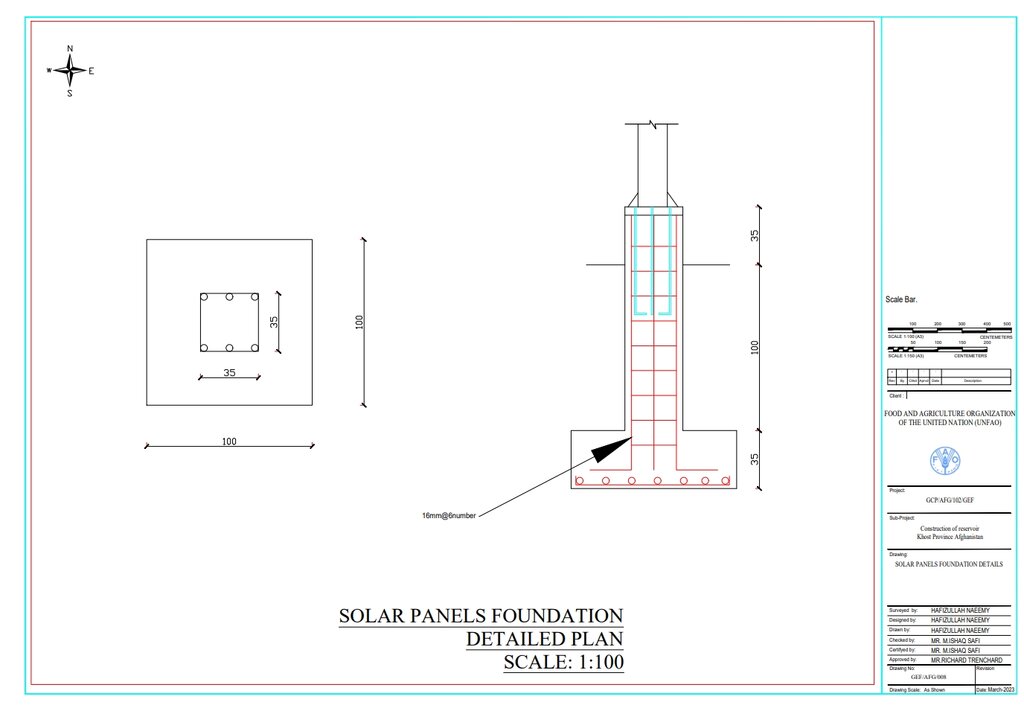
The solar panel stands, including their foundations, are 2 meters in height, with each panel measuring 1.2 meters high and 0.6 meters wide. The panels are installed at a 45° slope angle.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Data:
22/01/2023
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Detailed plan for solar panel installation: Three metal stands designed to support and rotate 26 solar panels, optimizing sunlight exposure throughout the day.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Data:
23/01/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
20 Hectares
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5 USD
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduction of survey, feasibility study, and site selection | 1st month |
| 2. | Finding of water source | 2nd month |
| 3. | Installation of solar power lifting system | 4rd month |
| 4. | Construction of reservoirs | 5th month |
| 5. | Installation of irrigation piping system | 12th-1st month of the year |
| 6. | Saplings delivered by supplier to the site from contracted nurseries | 1st-2th month |
| 7. | Planting of saplings | 2-3rdmonth |
| 8. | Preparation of two demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 9. | Planting of seeds for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 10. | Installation of barbed wire fencing for 20 hectares | 7-9th month |
| 11. | Ensurance of operation and maintenance of all systems | 24th month |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Installation of solar system and pipe installation | Person/day | 100,0 | 6,0 | 600,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Digging pits, plantation and irrigation of Plants | Person/day | 453,0 | 6,0 | 2718,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Excavation of foundation | Person/day | 80,0 | 5,0 | 400,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Preparing demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | Square meter | 25000,0 | 0,13 | 3250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Stone Masonry | Person/day | 136,0 | 6,0 | 816,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Plastering | Person/day | 72,0 | 5,0 | 360,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Plain cement concrete | Person/day | 57,0 | 5,0 | 285,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Plain cement concrete PCC M20 | Person/day | 390,0 | 5,0 | 1950,0 | |
| Equipamento | Entrance Gate | Number | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Equipamento | Solar panel 400W | Sheet | 26,0 | 140,0 | 3640,0 | |
| Equipamento | Rotating PV panel mount | Number | 3,0 | 350,0 | 1050,0 | |
| Equipamento | Submersible pump 2 inch (10PH-7500W) | Number | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Equipamento | DC-AC current inverter 7.5-11kw | Number | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Equipamento | Distribution board | Number | 1,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 | |
| Equipamento | Sign board | Number | 3,0 | 3,0 | 9,0 | |
| Equipamento | Sign board | Number | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Walnut | Sapling | 2000,0 | 0,56 | 1120,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Almond | Sapling | 500,0 | 0,67 | 335,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Mulberry | Sapling | 100,0 | 0,44 | 44,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Pomegranate | Sapling | 500,0 | 0,51 | 255,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Alfalfa seed | Kg | 50,0 | 2,72 | 136,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Black Cumin seed | Kg | 15,0 | 6,72 | 100,8 | |
| Material de construção | Tap | Number | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Material de construção | Flexon 1 inch rubberized pipes | Meter | 1250,0 | 2,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Material de construção | DC current wire | Meter | 100,0 | 2,0 | 200,0 | |
| Material de construção | AC current wire | Meter | 150,0 | 2,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material de construção | Polyethylene pipe 1.5 inch | Meter | 2000,0 | 2,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Polyethylene pipe 2 inch | Meter | 780,0 | 3,0 | 2340,0 | |
| Material de construção | Polyethylene pipe 3 inch | Meter | 300,0 | 5,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Outros | Delivery to the site | Lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Outros | Galvanized iron pipe 2 inch for pillar | Meter | 125,0 | 5,0 | 625,0 | |
| Outros | Galvanized iron pipe 1.5 inch for bracing | Number | 470,0 | 10,5 | 4935,0 | |
| Outros | Fence | Meter | 15,0 | 25,0 | 375,0 | |
| Outros | Double strand galvanized barbed wire for fencing | Meter | 4200,0 | 0,25 | 1050,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 36208,8 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 36208,8 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
FAO under GEF-7 project
Comentários:
The land users contributed primarily by digging pits for planting, preparing demonstration plots, and maintaining the system. Additionally, they hired guards to protect the area from disturbances. All other costs associated with the project were covered by the FAO GEF-7.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of sediment from reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Safeguarding the site such as solar system, and on-site interventions | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump and pipes | Regularly |
| 4. | Demonstration plots maintenance (pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding and Irrigation | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacing dead and dried plants | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing fencing | Year around |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour for cleaning the reservoir from sediment annually | Person/day | 15,0 | 5,0 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Hiring guards for safeguarding the site | Person/day | 12,0 | 100,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Fixing pump when needed | Lump sum | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Repairing pipes | Lump Sum | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Repairing solar panel when required | Lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Weed control | Person/day | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Integrated Pest Management | Lump sum | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Irrigation | Person/day | 8,0 | 50,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Saplings | Number | 1500,0 | 0,56 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Local Seed | Kg | 15,0 | 26,0 | 390,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Barbed wire | meter | 3000,0 | 0,14 | 420,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Replacing dead and dried plants | Lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 4830,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 4830,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Construction materials cost
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, with a gentle slope of approximately 45 degrees and an elevation of 1,279.49 meters above sea level. Surrounding mountains are covered with wild olive forests.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The water quality meets site requirements; however, seasonal fluctuations occur due to droughts. Floods in the lower gully, carry debris and sediments that can impact the source.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The land in question is communal and remains undivided, with no plans for future distribution. Most users have limited agricultural land downstream, typically no more than 0.5 hectares per household for crop cultivation. The learning site has been dedicated by the local community for future generations and educational purposes. Previously, this land was unused and primarily designated for grazing.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
Land use rights in traditional legal systems are generally straightforward, with each family in a village having equal access to natural resources.
Comentários:
Overall, this traditional approach emphasizes community and family roles in resource management, balancing individual rights with communal responsibilities
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
Due to three to four decades of political conflict, people lack access to essential services and infrastructure. This situation has been largely overlooked, with insufficient attention given to providing these services. Additionally, there has been a lack of budget allocation and support from the government and NGOs. As a result, communities continue to suffer from inadequate resources and infrastructure development.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
The local community is adopting rotational grazing and quarantine measures on rangeland, while also exploring silage-making and hay production techniques. Additionally, they are identifying alternative winter feed options for their animals.
Qualidade da floresta/do bosque
Comentários/especificar:
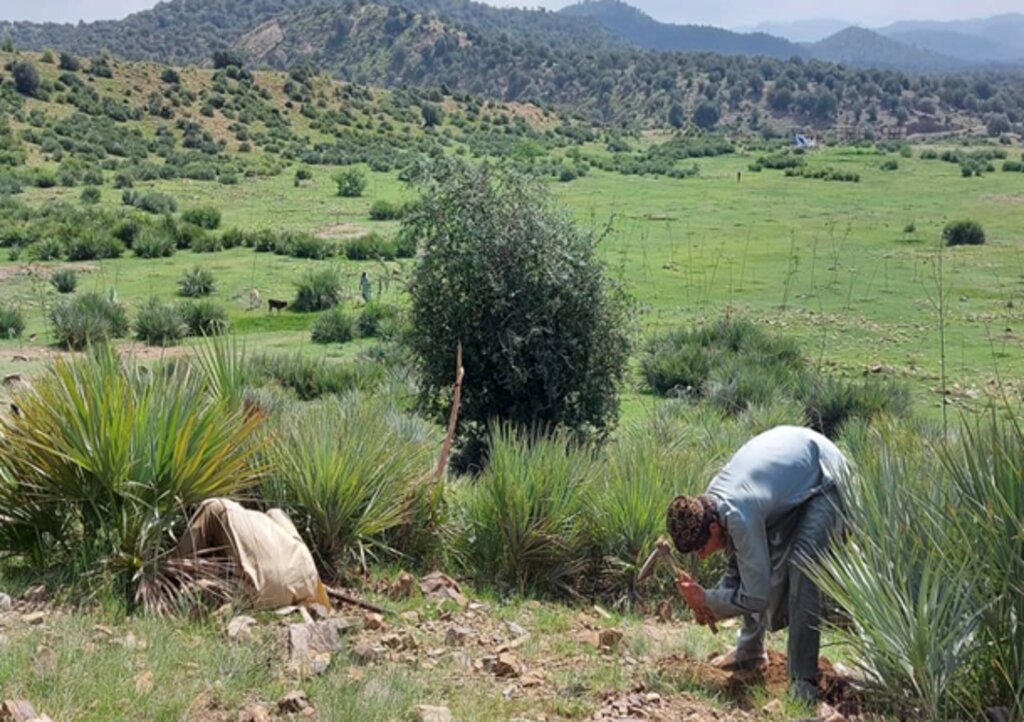
The local community has successfully quarantined all forest areas, effectively controlling illegal logging and managing grazing. As a result, the forest has been revitalized and is undergoing natural regeneration
Produção florestal não madeireira
Comentários/especificar:
The local community is utilizing Mazari palm for handcrafted products while also focusing on agroforestry. They have established fruit orchards and are collecting blackthorn, which they sell in the bazaar to support their livelihoods.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Previously, the community overgrazed the land and cut down trees for their livelihoods. However, after implementing quarantine measures and rotational grazing practices, the area is now showing signs of regeneration and has the potential to become a productive landscape in the future.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Following these practices, the local community has effectively managed more land under proper stewardship, including forest and rangeland quarantine and controlled grazing. They are now applying these methods in their vicinity, leading to the successful management of additional areas.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table and increasing availability for irrigation.
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
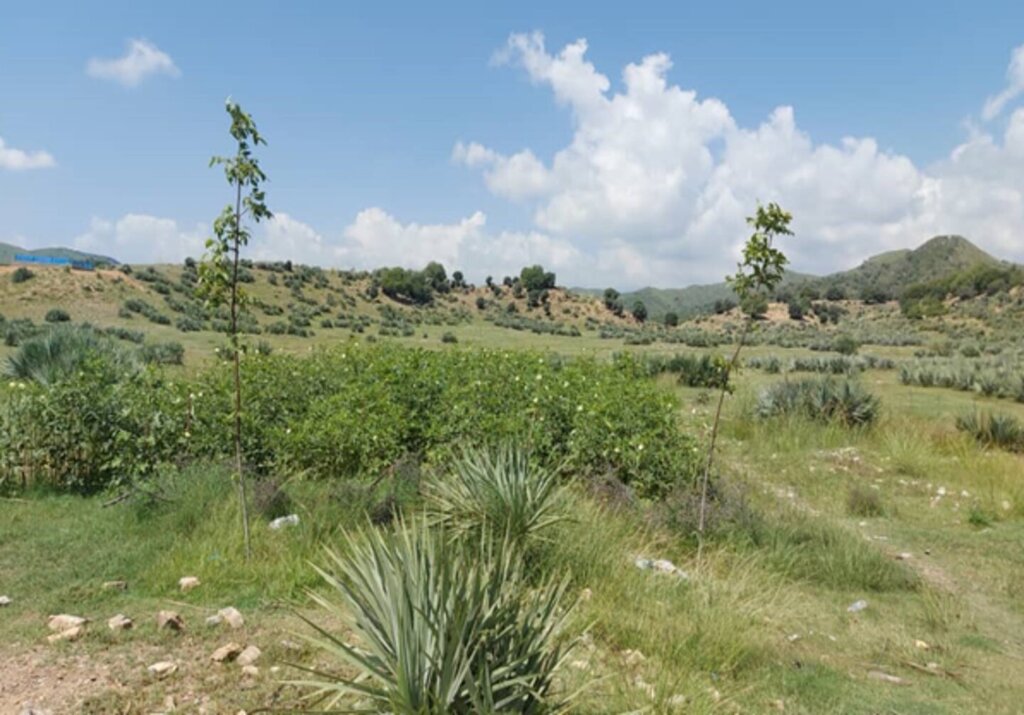
FAO and Forest and Rangeland Management Association have successfully revitalized this area, transforming it into a lush and green landscape. Many of the previously destroyed species regenerated, creating a thriving ecosystem. This site is now a focal point, surrounded by majestic mountains and rich forests, with water flowing from the upper watershed. It has become a popular destination for picnics and visits, where people can enjoy the soothing sounds of birds and the vibrant greenery of the surroundings.
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Through applying quarantine, rotational grazing, control grazing the vegetation covered increased.
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Biomass above the ground is increased
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
most of the seed regenerating and all the cut trees and bushes revegetated.
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Various migratory animals and birds have returned to the area due to the protection measures in place and the prohibition of human activities.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
Most of the riverbanks have been successfully revegetated through effective control measures, including water filtration during rain and floods. Local communities have also learned to plant cuttings along the riverbanks and shorelines, contributing to the restoration of these vital ecosystems.
Impactos da seca
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Healthy ecosystems like forests and wetlands act as carbon sinks, absorbing more CO2 through photosynthesis. Improved soil health and vegetation cover also enhance carbon storage, while restoring habitats promotes biodiversity, creating a more resilient ecosystem that sequesters carbon effectively.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table.
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | redução/diminuição | não bem em absoluto | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | não bem em absoluto | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | aumento | não bem em absoluto |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de neve local | não bem em absoluto |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | não bem em absoluto |
| Seca | não bem em absoluto |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação súbita | não bem em absoluto |
Comentários:
Before the implementation of the project land users faced severe challenges, including drought, high temperatures, water scarcity for irrigation, reduced yields, and a lack of winter feed alternatives for livestock.
Following the introduction of sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation, local communities adopted rotational grazing practices and protected forests from cutting, which had previously been their main source of income. As a result, vegetation cover improved, carbon stocks increased, and rainwater began to seep into the ground, recharging the water table, springs, canals, and Karezes. These efforts reulted in a more resilient and productive environment.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
The adoption of the technology in the specified area has primarily been spontaneous, significantly influenced by the support provided by the project. While a small percentage of land users may have received material incentives, the majority embraced the technology due to its demonstrated benefits and the project's educational efforts. This support helped to build trust and confidence among the land users, enabling them to implement the technology effectively in their practices. Overall, this highlights the importance of community engagement and capacity building in fostering sustainable land management practices.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| It is crucial for local communities to learn sustainable land and forest restoration techniques. These methods are not only accessible but also involve minimal operational costs. By empowering land users with this knowledge. |
| We can adopt sustainable land and forest management practices to revitalize our degraded land. This learning process is straightforward and easily applicable. |
| We have great opportunities and abundant resources to utilize. This area serves as a hub for scaling sustainable practices, allowing us to learn, observe, and implement solutions that will benefit future generations. |
| We can efficiently use surface water for irrigation instead of groundwater, helping to restore degraded land through these initiatives. |
| Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through effective carbon sequestration. |
| Learn regeneration techniques, rainwater harvesting, and grazing management methods like rotational grazing. Focus on producing fodder and medicinal plants, while understanding indigenous plants and shrubs for the future. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| This site is highly accessible, surrounded by dense forests and extensive rangelands that can be utilized sustainably. |
| Local community members, university students, and stakeholders can easily visit this site. |
| This site is an excellent destination for tourists to visit, enjoy, and learn about the importance of natural resources and their management techniques. |
| The local community can easily adopt these simple techniques to learn sustainable land and forest restoration practices. |
| The local community has hired guards to maintain the site effectively. They are gaining knowledge and enhancing their capacity for future interventions, contributing positively to development initiatives. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Insufficient maintenance and repair services for the technology. | Establishing strong linkages with service providers and maintenance support. This also facilitates nationwide technology transfer, enabling broader adoption and implementation of sustainable practices. |
| There is a lack of qualified professionals on-site to teach visitors the technical aspects of the technology. This gap hinders effective learning and limits the ability of visitors to fully understand and engage with the technology. | Hire on-farm officers to oversee and manage the learning site and provide information to visitors. |
| A check dam is required in the gully to store water for sustainability, especially during drought seasons when water availability decreases. | Construct a check dam in the lower section of the gully to store water for sustainability, allowing visitors to learn about water harvesting techniques. |
| There are currently no available resources for replacing the dead plants. | Establish nurseries for forest species to produce saplings that can replace dead and dried plants in the future. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| There are concerns about windstorms and hail potentially damaging the solar panels. | The local community should establish a social fund to cover repairs for any damage to solar panels caused by windstorms or hail, as well as to fund the installation of fencing around the solar panel stands. |
| Concerns have arisen regarding land disputes as the local community acts on land distribution amidst a growing population. | All villagers should receive a formal guaranteed letter, signed by the district governor, ensuring that no future actions will be taken to redistribute this site among the villagers. |
| There is a lack of essential water structures, such as percolation tanks and detention ponds, for effective rainwater harvesting. | Construct percolation tanks and detention ponds to harvest rainwater, which can be used to water livestock. Additionally, this initiative will provide an opportunity to learn and implement dryland farming techniques. |
| Too much water is wasted through flexible pipe basin irrigation methods. Additionally, required live hedges for fencing and windbreaks. | Install a drip irrigation system with an efficient piping layout and plant pine, poplar, and other trees alongside barbed wire to create a windbreak and a natural barrier for site protection. This will also provide an opportunity to learn various agricultural techniques. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
20
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
11
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
5
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
3
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
10/10/2024
Comentários:
The project was actively involved in all phases, from selection to implementation. Data was collected from local community volunteers, as well as SLM specialists and engineers.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
N/A
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
N/A
7.4 Comentários gerais
The questionnaire is well-structured, but some sections, particularly 6.2 and 6.3, need simplification. Additionally, the database should provide outputs during data processing, highlighting both best practices and common mistakes related to the technology. This will help us generate a comprehensive report that showcases effective practices and identifies areas for improvement.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [Afeganistão]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- Compilador/a: Mohammad Arif
Módulos
Não há módulos