Gravity Irrigation for enhancing Community-Based Restoration efforts in the degraded forests of Paktya [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Mohammad Wazir Ahmadzai
- Editores: Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal, Mohammad Mustafa Sahebzada, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi, Megha bajaj
Obu Zakhira
technologies_7481 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in AfghanistanNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afeganistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
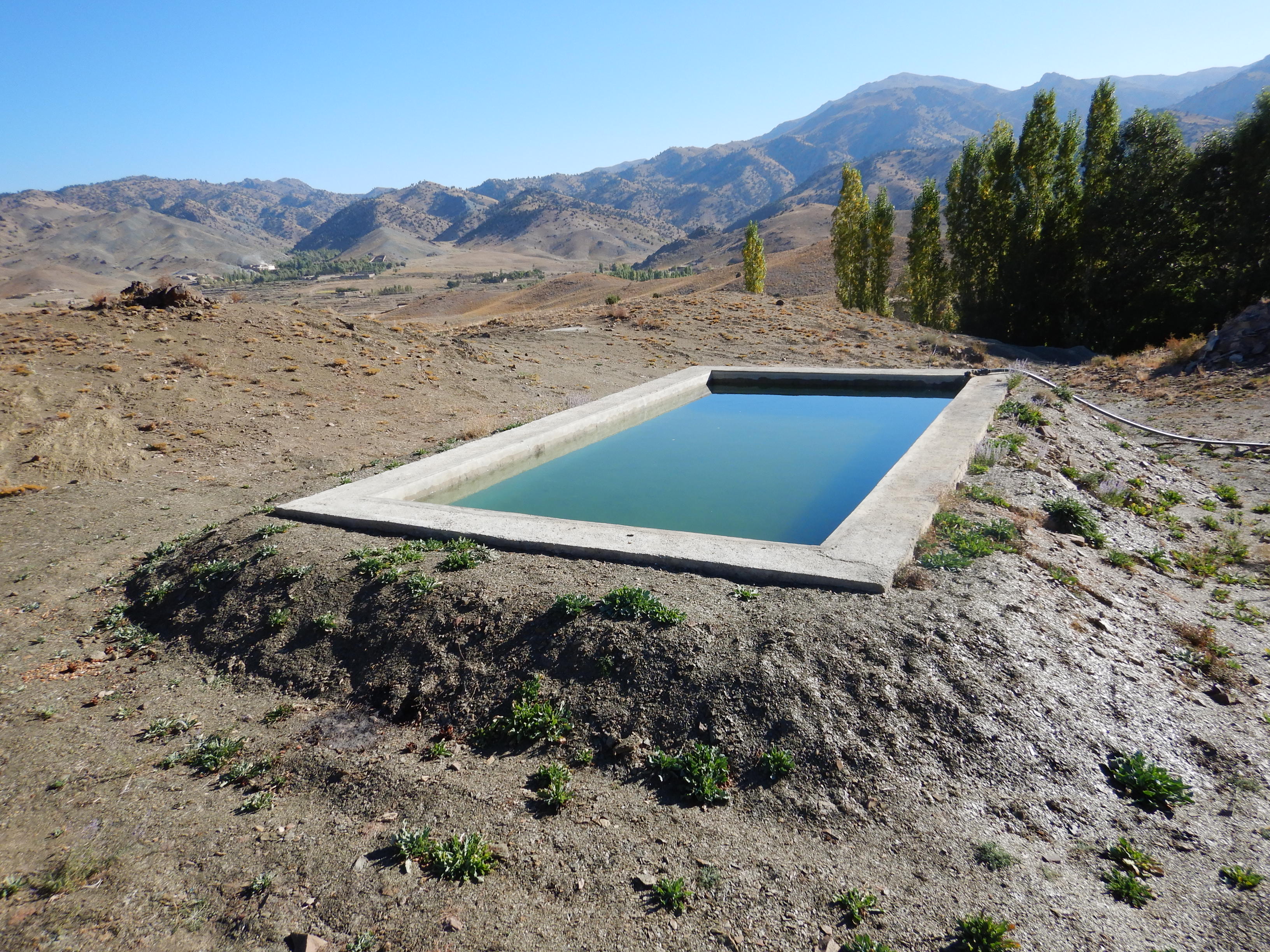
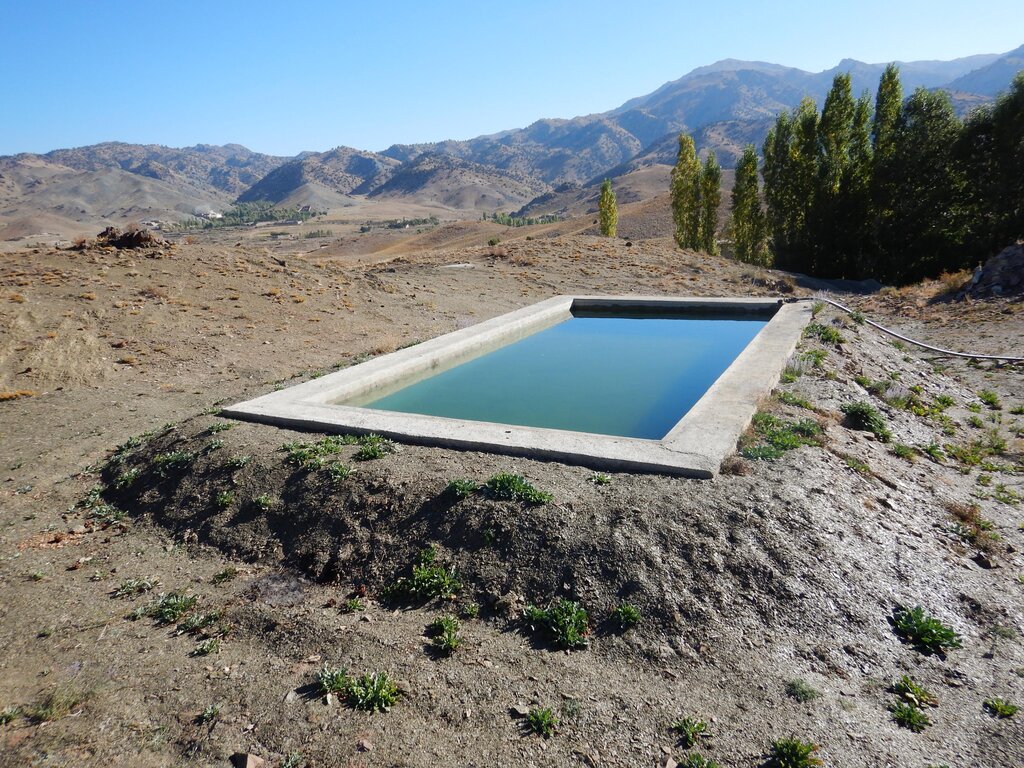
Using a gravity-irrigation system, spring water is diverted to fill reservoirs and then distributed to fields for the restoration of degraded forest areas, with the active involvement of local communities and a focus on the sustainable use of water resources (spring water).
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Paktya province in Afghanistan, known for its mountainous terrain and rich forests of pine nuts deodar, cedar, and conifers, faces severe challenges. Most water in the province comes from rivers, springs, and tube wells, with high mountains acting as natural reservoirs. Unfortunately, many traditional water sources have been destroyed over decades of conflict and natural drought, forcing farmers to rely on costly tube wells for irrigation.
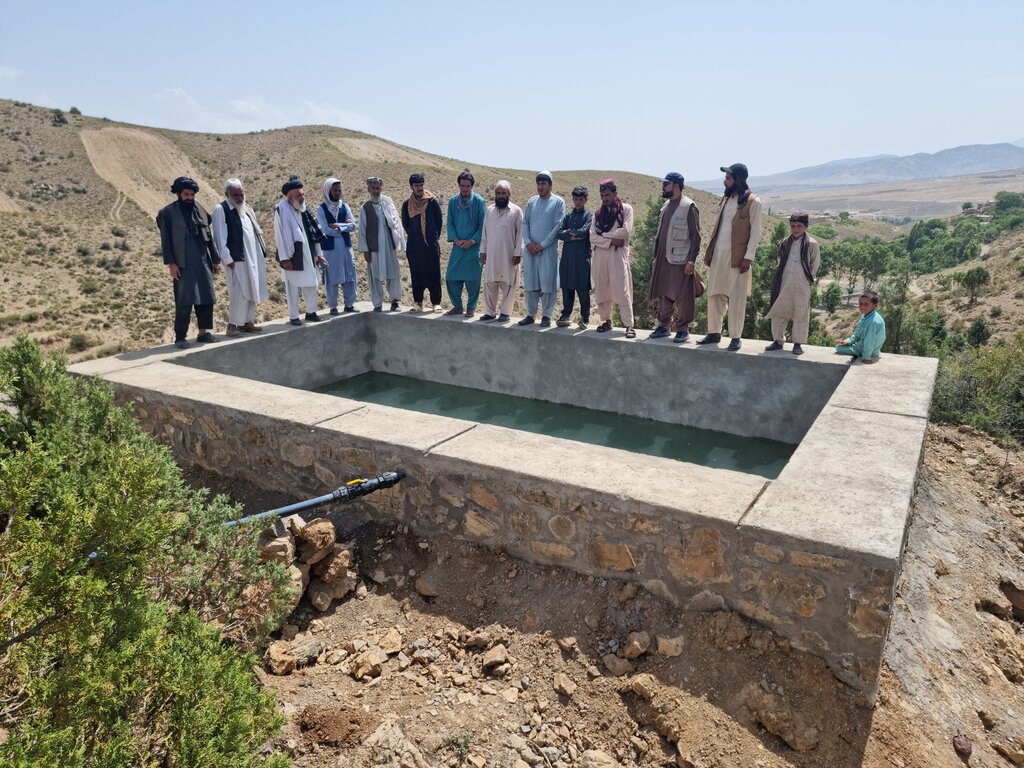
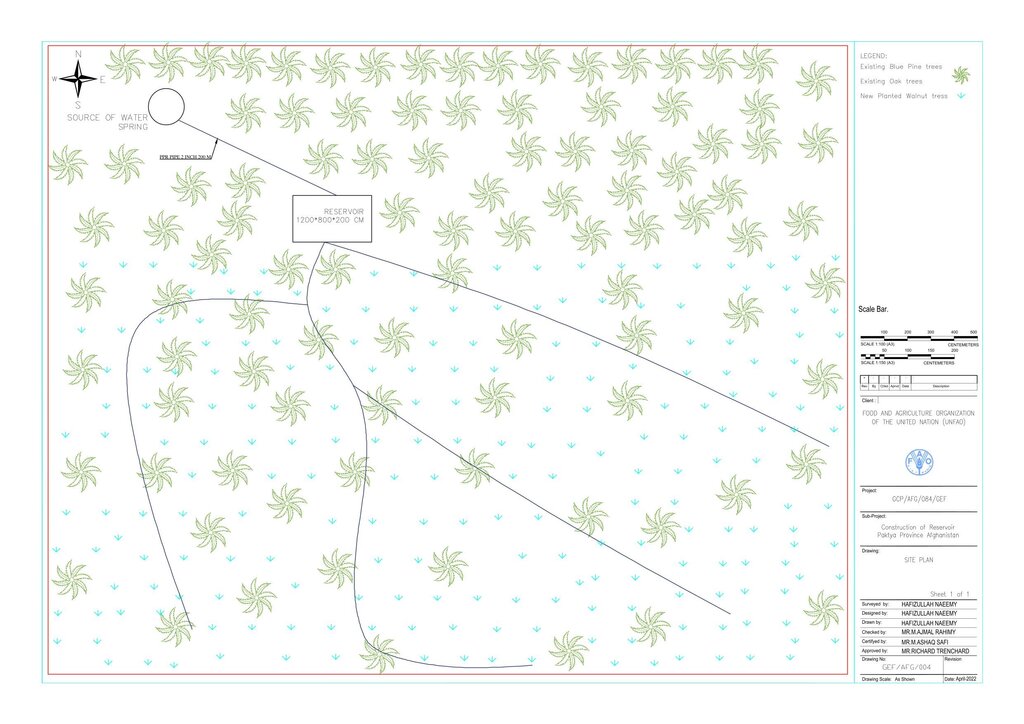
To support sustainable water management in the mountainous areas of Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam districts, 60 water reservoirs with a total storage capacity of 6,000 m³ were constructed. The volume of individual reservoirs varies depending on the availability and flow of upstream spring water ranging from 36 m³ to 192 m³.
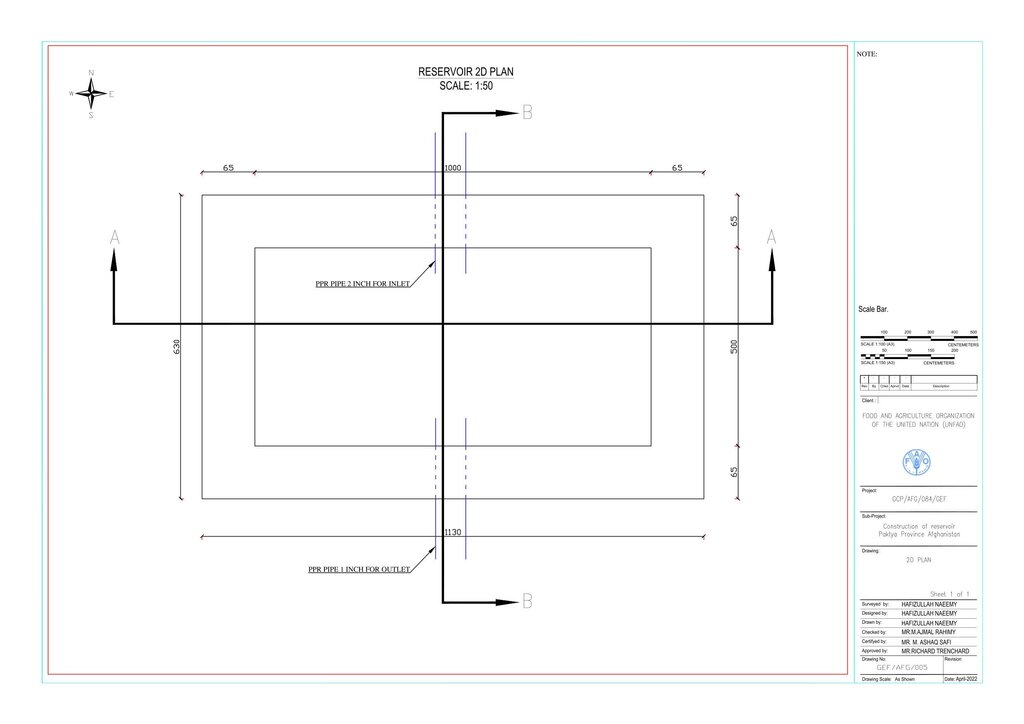
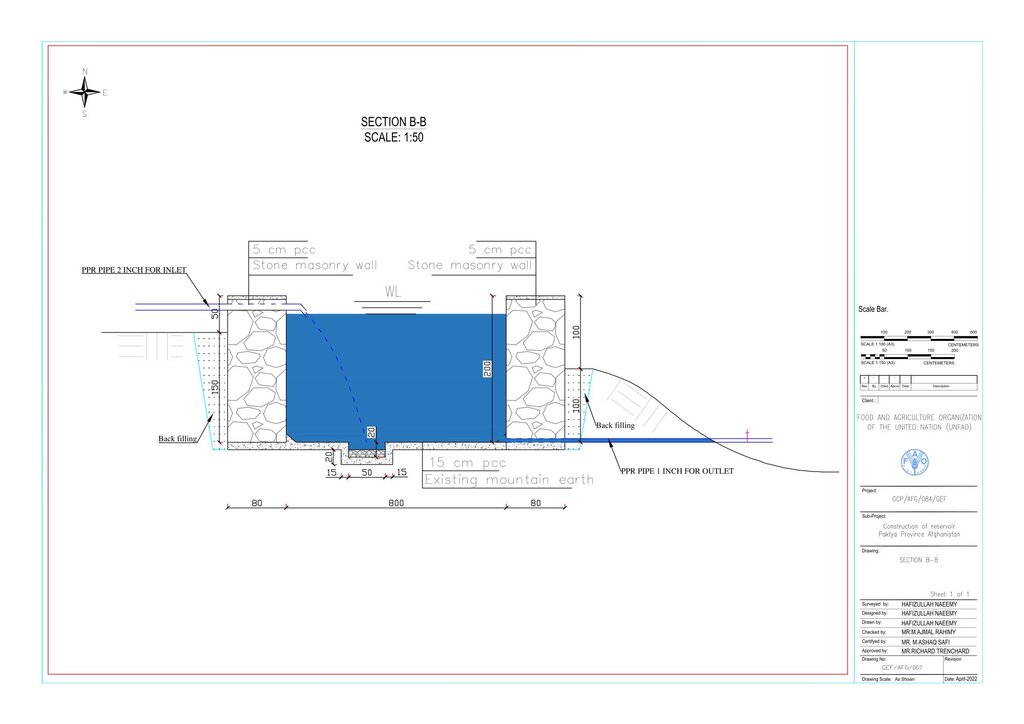
Water is diverted from a small intake near the source and delivered to the reservoir inlet through a 2-inch Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe. For irrigation of the restored areas, the outlets from the reservoirs are connected to 1-inch PVC pipes for distributing water to various plantation sites.
This technology is applied in a natural environment and is designed to support environmental sustainability by recharging the groundwater table, as water is harvested into reservoirs, it can infiltrate through the side walls and bottom. This percolation process contributes to the natural hydrological cycle, harvesting surplus water (water evaporate or percolating into atmosphere or soil) into reservoirs for irrigation of planted saplings, and extending existing forest boundaries.
The system enables the local community to sustainably manage and utilize spring water for gravity-based irrigation of restored areas, while also supporting the expansion of forested land through sapling plantation.
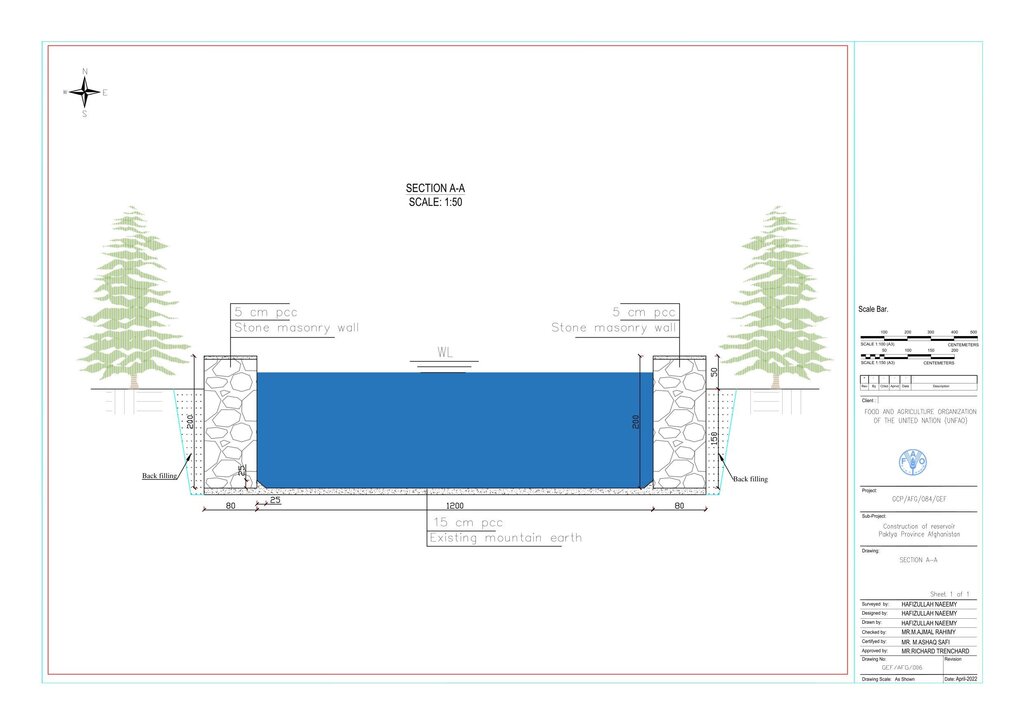
Before constructing the reservoirs, a feasibility survey of the water source (the spring) was conducted to verify the perennial availability of water and to determine the optimal distance between the spring and the designated reforestation sites. The preliminary selection of reservoir locations was based on key criteria including the year-round reliability of the water source, the size of the target reforestation area, and the discharge capacity of the spring. Excavation of the rocky mountain earth was carried out using a hand excavator as per the specified requirements as per technical drawing and approved design. The stone masonry work was completed using random rubble coursed stone with a cement-sand mortar mix (1:2, Type A). As per the design, Plain Cement Concrete (PCC M20) was applied to the top of the stone masonry and on all floors of the reservoirs. A 20 mm thick plastering was carried out on the internal walls using cement-sand mix (1:2). The external walls were backfilled to a height of 1.5 meters.
The benefits of this gravity-fed irrigation technique include increased reforestation rates, reduced water loss due to evaporation and runoff, achieved by using closed piping systems instead of open channels, and improved water use efficiency. These improvements have led to higher sapling survival rates and better growth. Overall, the socio-economic and environmental conditions of rural populations have been improved. Additionally, the implementation of the gravity irrigation system has reduced the cost of restoring degraded forests.
As a low-cost, environmentally friendly technology, it allows for the efficient harvesting of spring water for irrigation, supports sapling planting for carbon sequestration, and helps mitigate the severe impacts of climate change.
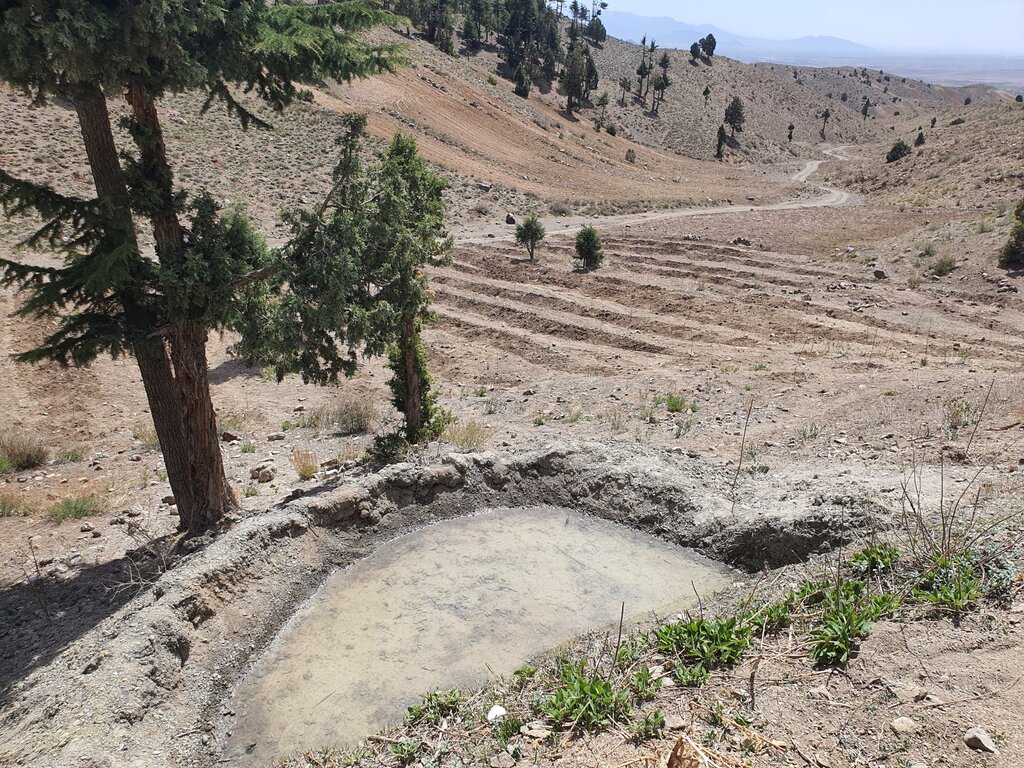
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Paktya
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ahamd Aba and Sayed Karam district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Sim
Comentários:
The technology being applied in various location of forest areas, while in the map only two points highlighted in Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam district of Paktya
However, 46 water reservoirs constructed in Sayed Karam, while 14 water reservoirs constructed in Ahmad Ab
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Atenuar a mudanças climáticas e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Floresta/bosques
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
Plantação de árvores, florestamento: Especificar a origem e composição das espécies:
- Monocultura de variedade local
Tipo de plantação de árvores, florestamento:
- plantação de floresta seca subtropical - Pinus spp.
Tipo de árvore:
- Espécies de pinho
As árvores especificadas acima são decíduas ou perenes?
- decíduas mistas/perene
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
Comentários:
With the implementation of the technology, degraded land has been restored to forested areas through reforestation.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de plantação florestal
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical drawing: indicated the details of the dimension of water reservoirs
Autor:
Hafizullah Neemy
Data:
30/03/2022
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical drawing
Autor:
Hafizullah Neemy
Data:
23/03/2022
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical drawing
Autor:
Hafizullah Neemy
Data:
30/03/2022
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Drawing
Autor:
Hafizullah Neemy
Data:
30/03/2022
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation to build reservoirs | When construction work is possible |
| 2. | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | After construction the reservoir |
| 3. | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | When construction work is possible |
| 4. | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | When construction work is possible |
| 5. | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | When construction work is possible |
| 6. | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | After construction work |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Excavation to build the reservoris | M3 | 62,0 | 10,0 | 620,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | M3 | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | M3 | 6,0 | 14,0 | 84,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | M3 | 42,0 | 14,0 | 588,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | Man-days | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | Man-days | 8,0 | 5,0 | 40,0 | |
| Equipamento | Shovel | PC | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| Equipamento | Hammer | PC | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | |
| Equipamento | Excavator (taking by rent for excavation) | Cubic meter cost | 192,0 | 10,0 | 1920,0 | |
| Material de construção | Cement | Package | 75,0 | 6,0 | 450,0 | |
| Material de construção | Stone | Cubic meters | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| Material de construção | Polyethelen pipe 1 inch | Meter | 500,0 | 0,8 | 400,0 | |
| Material de construção | Polyethelen pipe 2 inch | Meter | 200,0 | 1,0 | 200,0 | |
| Material de construção | Elbow joint | Piece | 3,0 | 1,0 | 3,0 | |
| Material de construção | Valves | Piece | 4,0 | 4,0 | 16,0 | |
| Material de construção | Sand | Cumbic meter | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | |
| Outros | Transportation | LS | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 5835,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 5835,0 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of pipes to outlet and inlet area of water reservoir | Spring season |
| 2. | Maintenance of reservoir for clearing and unclogging the inlet area | As per requirement |
| 3. | Replacement and installation of valves and elbow joints to prevent water clogging in the pipes | During non-function |
| 4. | The embankment constructed to accumulate the water and put the pipes inside to water for diverting to the reservoir | Spring season |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour for repairing of pipes at outlet and valves | Person | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labour for clearing and unclogging | Person | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Valves | PC | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Elbow joint | Pc | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 170,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 170,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The distance between the spring and reservoir can affect the total cost of technology
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
553,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The construction site is situated at an elevation of 2500-3000 meters above sea level, with a terrain slope ranging from 15% to 20%. Photo related to field skitch, indicated that the area of reforestation is around the reservoir.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
As the water from spring harvesting through pipes and accumulated in reservoirs can reduced the evaporation and stored for 2 or 3 days in reservoirs that can excess the water quantity for irrigation purposes.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
All age group excluding children
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
- Média escala
Comentários:
The small-scale covered the reforestation areas about 10 ha for irrigation, while the medium scale covered about 20 ha for irrigation purposes.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The water reservoirs were constructed on communal land for use by the local community, allowing shared access for irrigating reforested areas. Access and use are managed through a community-agreed contribution system.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
The establishment of woodlots and other forest can increase the fuel wood for heating the house and cooking, fodder for livestock and fruit for home consumption. The established woodlots consist of a mix of fruit and non-fruit tree species.
Produção florestal não madeireira
Comentários/especificar:
The non-wood forest productions increased with increasing the area of production through gravity irrigation systems enhanced the community-based efforts in degraded forest.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The production areas of NTFPs have expanded due to the annual planting of saplings in degraded forest areas, supported by water reservoirs that provide irrigation and enable the extension of existing forest boundaries.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The irrigation water availability has improved due to efficient management of the spring water. As the spring water gradually decreases from June to December months which considered as dry period, while January to March months is the wettest period that water is excessive and can be harvested for the following dry period.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
As the construction of water reservoirs can significantly improve the water availability during the year both in the wettest period and followed by dry period, by storing the water can balance the demand for the irrigation water.
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Households living in rural areas rely on income from non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and agricultural production, resulting in a diversification of their income sources.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
the workload for the irrigation of reforestation areas reduced with application of technology because the number of days for irrigation done manually reduced and also the cost of irrigation.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Vegetation Cover
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation cover has improved each year due to ongoing tree planting and the protection of designated areas through quarantine measures.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Acumulação de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Impactos da seca
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Microclima
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | muito bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | primavera | aumento | muito bem |
Comentários:
The forest function for the regulating of climate, rainfall and snowfall. By increasing the forest cover that can help in regulating the annual rainfall.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mudança climática/extremo
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
The technology adapted well to reduce the severe impacts of the water on the plant growth and development during water scarity situation in summer.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The technology is cost-effective for irrigating afforested areas and is easy to use and conducive to implementation. |
| The workload for irrigating the afforested area has been reduced, resulting in fewer man-days required for irrigation. |
| The harvesting of water from ground spring allows to expand the forest area through plantation of saplings, otherwise it not possible. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The sustainable management of ground water spring contributed to the expansion of restoration efforts in the community level. |
| By implementation of technology at specific point, the soil vegetation cover improved from 10 to 15 percent. |
| The biodiversity enhanced with restoration of degraded forest area, through plantation of native species, regeneration of native bushes, grasses. |
| The unproductive soil converted into productive soil through plantation of bio energy plants to produce fuel wood, fodder and fruit. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital for construction of water reservoir. | Government should provide subsidy for construction of reservoir. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Communities' willingness and technical knowledge for the resource management depends on the component of the project . | Providing supporting from the government side for establishment and technical knowledge. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Sixty field visits were conducted to assess the constructed water systems.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Four land users interviewed using SLM technology questionnaire.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Two SLM specialists were interviewed to gather their insights on aspects of the project.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos