Crimson clover as an overwintering cover crop for nitrogen supply [Eslovênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Tamara Korošec
- Editor: Gregor Kramberger
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Inkarnatka kot prezimni dosevek za oskrbo z dušikom
technologies_7507 - Eslovênia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Integration of cover crops into field crop rotation - Slovenia (EIP-AGRI)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - Eslovênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Crimson clover, overwintered as a cover crop, forms a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, capturing nitrogen and thus enriching the soil. This helps reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and aids in soil erosion control, weed suppression, and improved soil structure.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
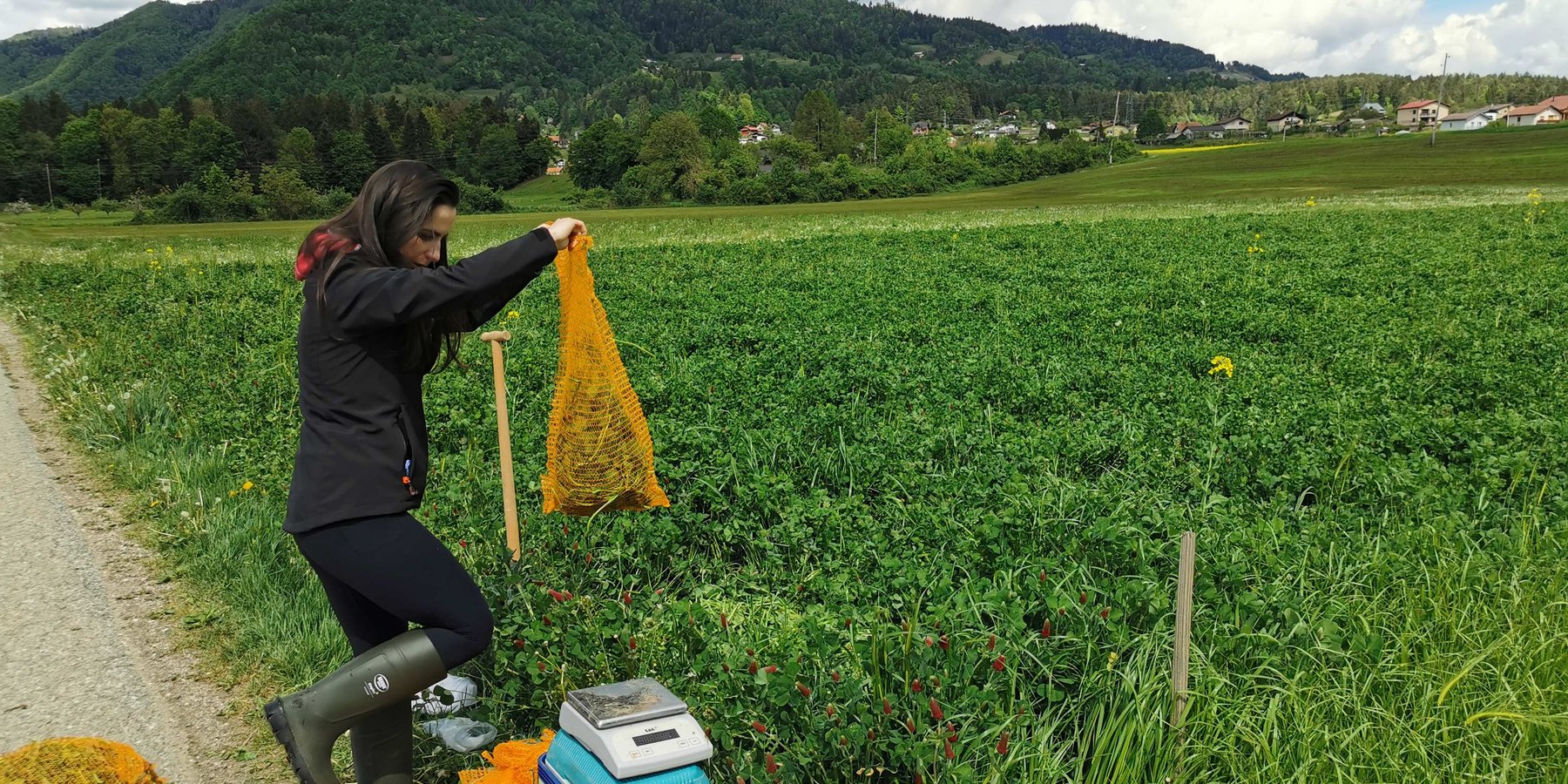
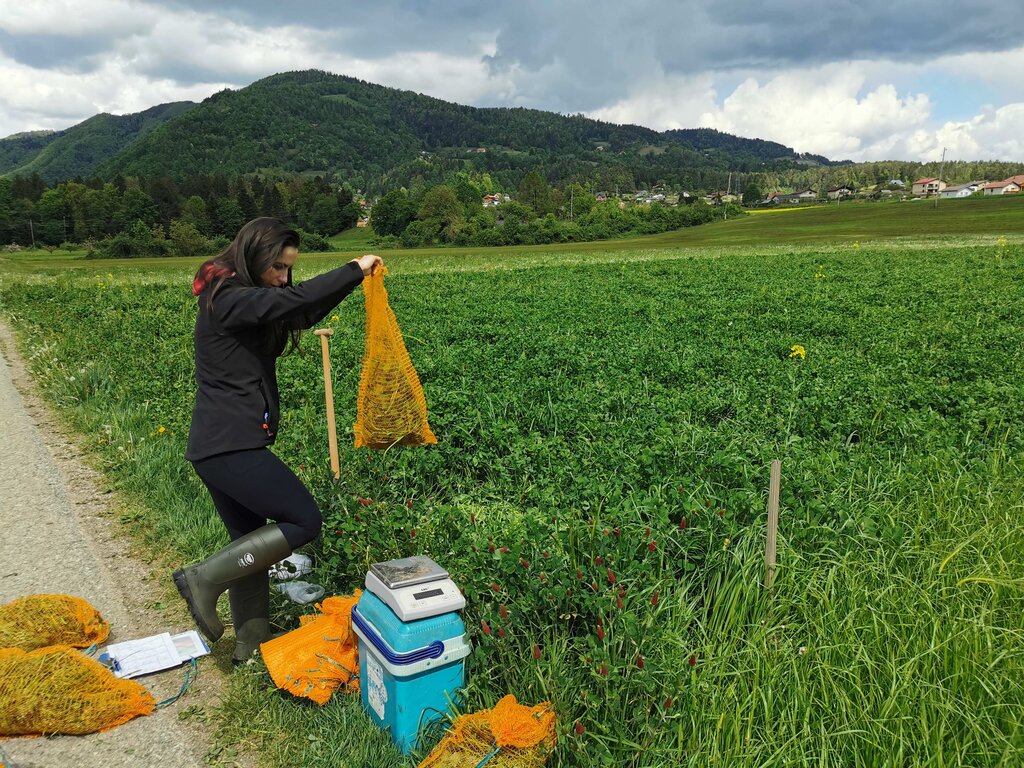
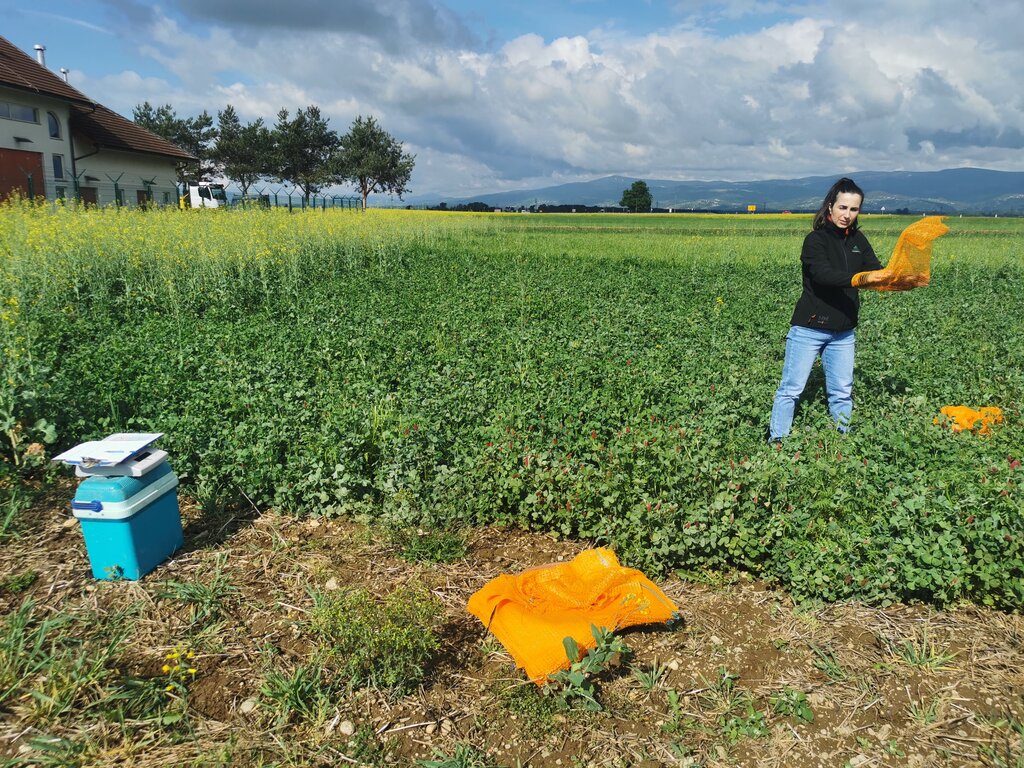
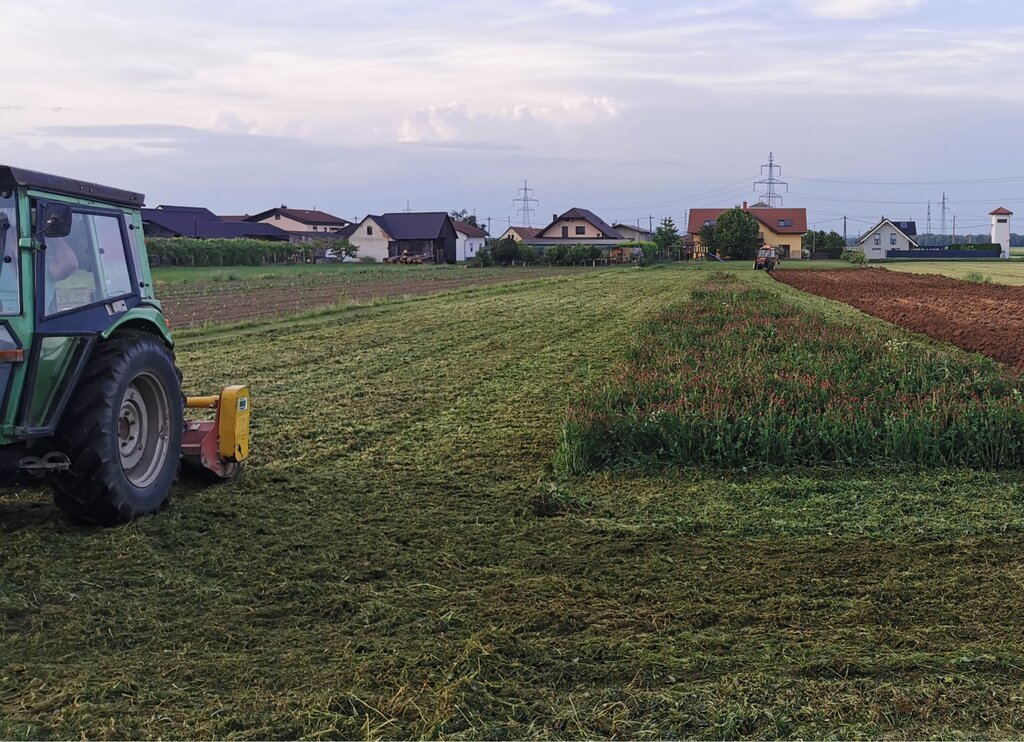
Crimson clover (Trifolium incarnatum) is a winter annual legume used as a cover crop for nitrogen fixation, erosion control, and soil improvement. It is well suited to mild winter climates and can be integrated into various farming systems. It can be sown alone or in mixtures after the main crop is harvested. It covers the soil from late summer until spring and can be used as fodder or for green manure.
Its key function is nitrogen fixation through the help of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Rhizobium). Through the winter it protects the soil from erosion, prevents nutrient leaching, and helps suppress weeds. The deep root system improves soil aeration and drainage. When terminated, it adds organic matter and nutrients to the soil, and its nectar-rich flowers attract pollinators and provide a habitat for beneficial predatory insects.
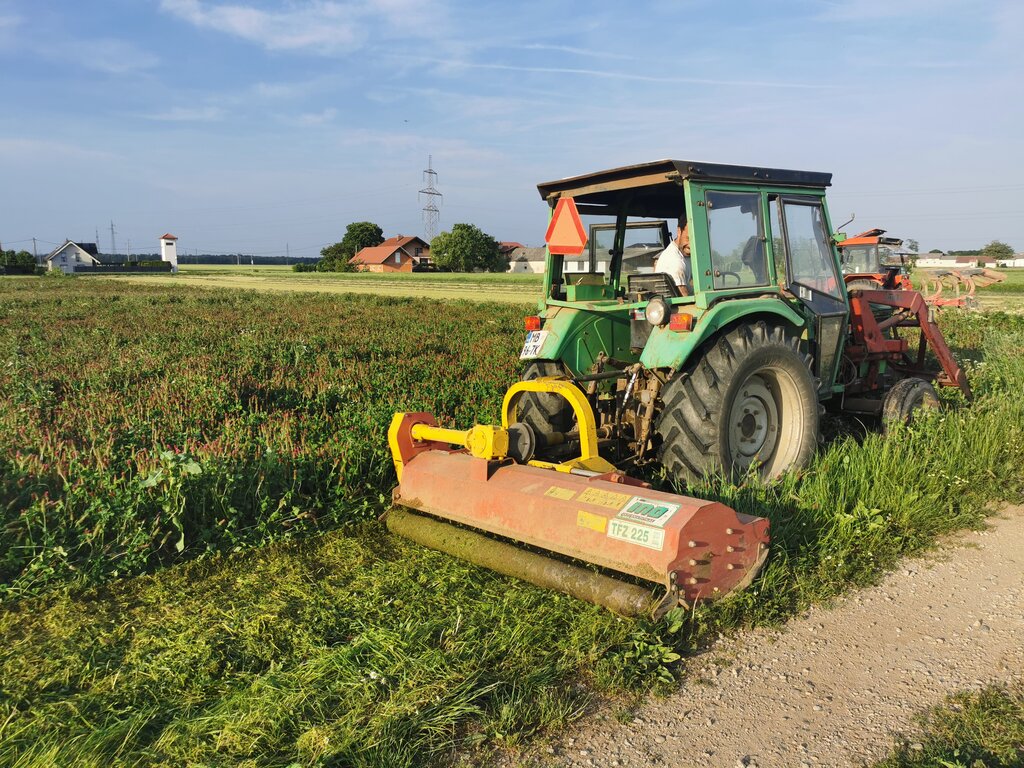
Crimson clover is often included in multi-year crop rotations. Activities include light tillage or no-till. Sowing usually takes place in late August to early September - or at least 6 to 8 weeks before the first frost. Fertilization with mineral nitrogen is not required, but phosphorus and potassium can help in establishment. Minimal maintenance is needed as these plants suppress weeds and reduce pests, but some fungal diseases may occur in wet conditions. Termination involves mowing or rolling at 50% bloom and then herbicides, or it can be incorporated as green manure.
Farmers value crimson clover for its multiple benefits including cost savings from reduced fertilizer use. Livestock farmers use it for forage. Some challenges may arise in colder climates, and when the soil is wet or compacted.
Under trials, the use of crimson clover as a cover crop to supply nitrogen was compared with a ryegrass cover crop and with fallow land, where no cover crops were used. The seeds were sown during two periods—early (August) and late (September)—and the cover crops were not further fertilized. The cover crops were terminated before sowing maize. The fallow area and the ryegrass area were fertilized according to the requirements of maize (215 kg N/ha) and soil analysis (for P and K). Half of the crimson clover area received no N fertilization, and the other half received only half of the required N. The maize crop was monitored by measuring soil, maize growth, grain yield, whole plant weight, and root weight. Crimson clover contributed between 61.6 and 78.6 kg of symbiotically fixed N ha⁻¹. The total soil amount of N accumulated by crimson clover was 100.7 kg N ha⁻¹, twice as much as under Italian ryegrass. The maize grain yields were significantly the lowest (10.9 t DM grain ha⁻¹) where crimson clover was sown early and the maize received no additional N. When crimson clover was used and maize was fertilized with half the N rate, grain yields were equivalent to those obtained on plots that received the full N rate (Italian ryegrass 13.5 t DM ha⁻¹, and the bare fallow control 13.4 t DM ha⁻¹).
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Eslovênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Podravje
Especificação adicional de localização:
Selnica ob Dravi, Cirkovce, Pragersko
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The technology is spread throughout arable land in Slovenia. The trial was conducted only on six farms in Podravje region .
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2024
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The European Innovation Partnership (EIP) projects for agricultural productivity and sustainability (EIP-AGRI) enable exchange of knowledge for agriculture, forestry, and rural areas. The technology was introduced on these farms through the EIP project: "Integration of Cover Crops in Crop Rotation – Possibilities for Replacing Nitrogen from Mineral Fertilizers in Fertilization of the Next Crop"
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
Sistema de cultivo anual:
Milho/sorgo/painço - leguminosa
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
5 year crop rotation: 3 different main crops in 5 years, plus cover crops after spring crops
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
Comentários:
Although primary cause of technology is natural nitrogen supply, the technology indirectly addressed also the soul erosion.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The technology of using crimson clover as a cover crop (variety 'Bolsena') to supply nitrogen was compared with the ryegrass cover crop (variety 'Turtetra') and fallow land, where no cover crops were used. Each plot covered area of 0.75 ha. The seeds were sown during two testing periods—early (August) and late (September)—and the cover crops were not further fertilized. The cover crops were terminated through mulching or ploughing before sowing the main crop, which was maize. The fallow area and the ryegrass area were fertilized according to the maize's requirements (215 kg N/ha) and soil analysis (phosphorus, P; potassium, K). Half of the area with crimson clover received no nitrogen fertilization, and the other half received only half of the required nitrogen (107 kg N/ha). The maize crop was monitored throughout the growing season by measuring soil nitrogen and assessing maize growth.
Autor:
Tamara Korošec
Data:
03/03/2025
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
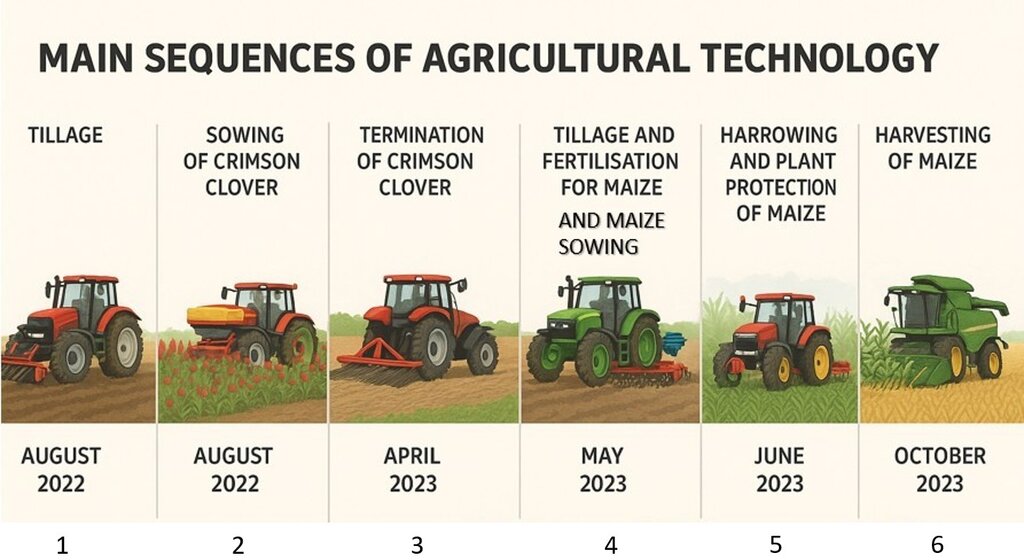
Main sequences of the technology: 1. tillage and seed bed preparation (disc cultivator or similar) for sowing cover crop (crimson clover) after the winter cereals harvest (August 2022); 2. sowing of crimson clover is usually combined with tillage, or done separately (August 2022); 3. mechanical termination of crimson clover (April 2023), 4. tillage, fertilisation, seed bed preparation and sowing of maize (may 2023), 5. harrowing and plant protection (herbicide) of maize (June 2023), 6. harvesting of maize (October 2023).
Autor:
Tamara Korošec (made with Chat GPT)
Data:
30/09/2025
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
ha
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
EUR
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
0,85
4.3 Atividades de implantação
Comentários:
None
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Comentários:
None
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stubble preparation (tillage) for crimson clover + sowing (stages 1 and 2 in diagram) | August (or September) |
| 2. | Mechanical cover crop termination and soil preparation before maize sowing (stage 3 in diagram) | end of April |
| 3. | Sowing of maize (stage 4 in diagram) | May |
| 4. | Fertilisation (part of stage 4 in diagram) | May, June |
| 5. | Hoeing and weed control (herbicide) (stage 5 in diagram) | May, June |
| 6. | Harvest (maize) (stage 6 in diagram) | October |
| 7. | Drying (maize) (part of stage 6 in diagram) | October |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | All labour costs | hour | 6,0 | 15,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Stubble preparation for crimson clover (tillage) | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Sowing of crimson clover | ha | 1,0 | 46,3 | 46,3 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Mechanical termination of the crimson clover | ha | 1,0 | 37,5 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tillage and seed bed preparation for maize | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Maize sowing | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Maize hoeing and weed control | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Maize harvesting | ha | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Crimson clover seed | ha | 28,0 | 3,5 | 98,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Maize seed | ha | 1,0 | 290,0 | 290,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicide | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Drying of maize grain | all harvest | 1,0 | 428,0 | 428,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 1589,8 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 1870,35 | |||||
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia:
1561,8
Comentários:
The above calculation is for combination of crimson clover cover crop and half the amount of nitrogen fertilizer (107 kg/ha) for maize production. This technology had similar grain production (13.7 t/ha) as full application of mineral nitrogen (215 kg/ha) with combination of fallow land or ryegrass as cover crop. The revenue for this technology from selling the grain was 2877 €/ha (0.21 €/kg). Crimson clover with no additional mineral fertilisation for maize had significantly lower yields (10.9 t/ha) and thus lower revenue per hectare (2289 €/ha; 0.21 €/kg of grain). For crops which need less nitrogen than corn, the additional mineral N fertilisation would not be necessary and so costs would be lower. Farmers get 180 € of basic subsidies per ha and further 148 € per ha for greening through the winter (EU CAP).
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Most important factors affecting the costs are the price of seeds and machinery hours.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
ARSO - Environmental Agency of Republic of Slovenia, archive data (last 10 years) for main station in Podravje region - Letališče Edvarda Rusjana Maribor
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Continental Climate (Central and Northeastern Slovenia). Meteo station Letališče Edvarada Rusjana Maribor:
Cold winters and hot summers. The average yearly temperature (last 10 years) is 11.5 degrees C.
Large temperature fluctuations between seasons. Average maximal temperature 16.7 degrees C. , the average minimal temperature is 6.4 degrees C. Absolute max. temperature (ave 10 years) was 34 degrees C, and the average absolute minimal temperature approximately -10 degrees.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
The test fields were on different soil types:
- Eutric alluvial soils pH 6,6-7,2
- Dystric brown soils on non calcareous sandy gravel sediments, pH4,6-5,5
- Eutric brown soils on alluvial-colluvial sediments and deluvium, pH 5,6-6,5
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
In Slovenia all drinking water is treated by chlorine. If we compare it to the rest of the world, we have good drinking water, but we never use it untreated.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Under the cover crop area soil biodiversity is high. Regarding overall habitat, the test areas are in intensive agricultural areas, that is why the habitat biodiversity which is otherwise high in Slovenia, is rated as moderate.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Especifique:
Land use rights in Slovenia are primarily based on modern statutory law, not traditional or customary law. The main frameworks are the Constitution of the Republic of Slovenia, the Law of Property Code (Stvarnopravni zakonik, SPZ), the Agricultural Land Act (Zakon o kmetijskih zemljiščih, ZKZ), and the Spatial Planning and Building Acts (Zakon o urejanju prostora, Gradbeni zakon, etc.).
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
215 kg/ha mineral nitrogen for 13.4 t of maize grain
Quantidade posterior à GST:
107 kg/ha mineral nitrogen for 13.7 t of maize grain
Comentários/especificar:
increased maize grain yields with less use of nitrogen fertiliser (positive impact)
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
201 €
Quantidade posterior à GST:
101 €
Comentários/especificar:
reduced expenses on mineral fertiliser for 100 kg of N per ha (positive impact)
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
improved water retention, filtration, drainage (positive impact)
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
water retention capacity improved (positive impact)
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
late summer to spring soil cover
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
lowered soil crusting, which is a positive impact
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
61-150 kg/ha
Comentários/especificar:
symbiotic nitrogen fixation with crimson clover 61 - 150 kg/ha N fixation (depending on the weather and soil conditions)
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
green manure from cover crops increases soil organic matter
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
diversified vegetation cover
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
increased soil microbial community, diversified crop rotation, benefits for pollinators
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
better drainage
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Lowered evaporation from soil, water retention capacity
Impactos de ciclones, temporais
Comentários/especificar:
protection against erosion due to heavy rain storms
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
On-site impacts included direct field measurements and expert judgements/ predictions on the basis of data from this and previous experiments.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
green cover filters the nutrients that go to the groundwater
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
Off-site impacts are predicted by expert judgements/ predictions on the basis of data from this and previous experiments.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | moderadamente |
| Temperatura sazonal | inverno | aumento | bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | não bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | inverno | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de granizo local | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | não bem |
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Infestação de insetos/vermes | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
They are mostly motivated by subsidies, so spontaneous adoption is a small percentage.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Lower costs for mineral fertilizers, subsidies for seeds |
| Good for soil health |
| Good for water absorption |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Climate change adaptation |
| Soil improvement - increase in organic matter, soil biodiversity, water capacity |
| Fixation of nitrogen form air, less mineral fertilisers |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Drought during the seeding of catch crop | earlier or later sowing - however it has an impact anyway |
| Additional work (compared to bare fallow) | combined machinery (soil preparation + sowing combined) |
| Risk of frost if the crimson clover is too big going into winter | sowing and mulching at right time |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Not applicable for all main crops - early spring crops do not get the same benefits as late spring/summer crops | for early spring crops other nitrogen fixings plants can be used. |
| Nitrogen runoff if no main crop follows after crimson clover destruction | always plant main crop right away |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
regular field visits and monitoring on 4 farms / fileds
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
4 farmers
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
consultation with colleagues from the Life science faculty (2)
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
previously prepared reports form the EIP project
Comentários:
The project was carried out for 2 years. The data were compiled during the whole time - regular monitoring, interviews, sampling...
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
GSELMAN, Anastazija, LISEC, Urška, KOROŠEC, Tamara, PODVRŠNIK, Miran. S prezimnimi metuljnicami do nadomeščanja dušika iz mineralnih gnojil = Winter legumes as a substitute for nitrogen from mineral fertilisers. V: ČEH, Tatjana (ur.), KAPUN, Stanko (ur.). 32. mednarodno znanstveno posvetovanje o prehrani domačih živali [tudi] Zadravčevi-Erjavčevi dnevi 2024 = 32nd International Scientific Symposium on Nutrition of Farm Animals [being] Zadravec-Erjavec Days 2024 : zbornik predavanj = proceedings : Murska Sobota, 14. in 15. november 2024, 14th and 15th November 2024. Murska Sobota: Kmetijsko gozdarska zbornica Slovenije, Kmetijsko gozdarski zavod, 2024. Str. 61-66, graf. prikazi. ISBN 978-961-96187-7-6. [COBISS.SI-ID 215866371]
Disponível de onde? Custos?
in various Slovenian libraries - in Slovene
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Website
URL:
https://dosevki.um.si/
7.4 Comentários gerais
Just a remark on question formulation: the instructions in section 6.1 appear a bit ambiguous when the response scale for some specific questions appears "reversed" in relation to the guideline parameter - such as "soil crusting" where a negative value is in fact a positive outcome.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos