Community efforts for improving drinking water quality
(Непал)
Piune paani ko gunastar sudhar ka lagi samudayik prayas
Описание
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
Aims / objectives: The People and Resource Dynamics in Mountain Watersheds of the Hindu Kush- Himalayas Project (PARDYP) implemented this approach with 30 drinking water user households at Barbot in the Jhikhu Khola watershed, Kavre Palanchok. The aim was to improve water quality and availability from an open spring source through participatory planning and implementation. The approach first identified local concerns and observed the sanitary situation of the catchment area. Meetings were held jointly with men and women users from different caste groups (Brahmin, Chhetri, Newar and Kami) to discuss the problems and issues and to identify viable solutions. The advantages and disadvantages of the various options were discussed, after which users selected the following three measures to improve the drinking water supply: 1) building a brick-cement walled structure around the main local spring, 2) establishing check dams across nearby rills and gullies, and 3) planting grass around the spring box and tree saplings within the catchment area. The aim was to prevent direct flow of surface water into the spring and reduce contamination and turbidity of the source. Understanding and support was gained by demonstrating the technology and running an awareness campaign.
Role of stakeholders: The project helped form a users committee made up of 11 women and 1 man and encouraged them to plant grass and tree seedlings across the entire catchment. The project regularly measured the quality of the water and shared the results with the users. Rules and regulations were developed to ensure equitable access to the spring and its sustainable use and management. A notice board with do’s and don’ts was placed near the spring. The users held monthly meetings and established a revolving fund for maintaining the structures. Spring users followed the rules and regulations by washing, cleaning, and bathing at separate sources. Livestock grazing was stopped in the nearby area and the area was regularly cleaned. Furthermore, users were encouraged to treat water for drinking using simple methods like SODIS and the low cost Safa filter to avoid microbiological contamination. They were made more aware of water quality, sanitation, and health issues.
Местоположение

Местоположение: Kavrepalanchowk district/ Jhikhu Kholawatershed, Непал
Географическая привязка выбранных участков
Дата ввода в действие: н/п
Дата завершения: 2005
Тип Подхода
-
традиционная/ местная система землепользования, используемая коренным населением
-
недавняя местная инициатива/ инновация
-
в рамках проекта/ программы
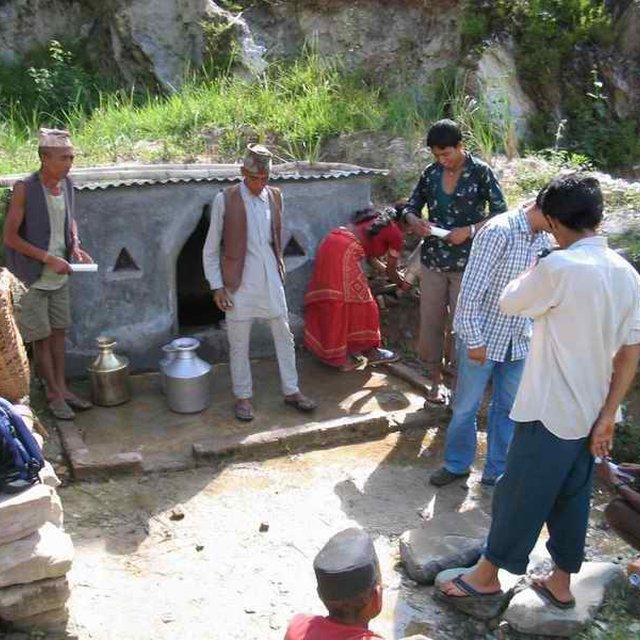

A meeting between project technicians and users to discuss problems and issues related to drinking water and to identify viable solutions. (PARDYP)
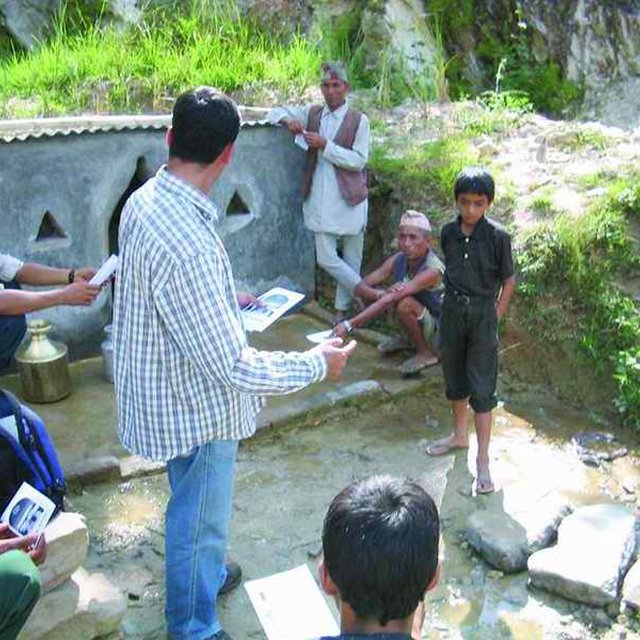

Sharing simple water quality treatment methods like SODIS and the low cost Safa filter with users. (B.S. Dongol)
Цели подхода и благоприятные условия для его реализации
Главные цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused on SLM only
- To explore and demonstrate appropriate water quality improving technologies and methods in a participatory way. - To increase awareness on water quality, water treatment, and health and hygiene. - To share knowledge gained on the water improvement options with farmers and other stakeholders
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Weak institutional collaboration to develop technological options for improving drinking water quality and availability and to raise awareness on health and hygiene and waterborne diseases.
Условия, содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода
-
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: mostly state owned land and some private land - which helped implementating the technology as there was no conflict.
Условия, затрудняющие применение Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода
-
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг: For the maintenance of the implemented technology
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Revolving fund collected by users
-
Институциональные условия: Weak institutional collaboration
Treatment through the SLM Approach: User group formed linking local community organisations
-
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки: Different water treatment methods
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness of structural and vegetative measures; direct water treatment methods including Safa filter, SODIS, chlorination
Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода, и их роли
| Какие заинтересованные стороны/ организации-исполнители участвовали в реализации Подхода? |
Перечислите заинтересованные стороны |
Опишите роли заинтересованных сторон |
| местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества |
Land users worked equally divided between men and women |
Improvement of drinking water quality and quantity was the major concern of all spring users. |
| общественные организации |
|
|
| государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений) |
|
|
| международные организации |
PARDYP/ICIMOD |
|
Ведущая организация
Concept designed by national specialist and implemented jointly with users
Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
нет
пассивное
внешняя поддержка
интерактивное
самоорганизация
инициирование/ мотивация
public meetings; meetings organised to identify problems and possible options to overcome them.
планирование
public meetings; organised regularly to identify implementing steps, and role and responsibility of different stakeholders in overcoming problems
выполнение
responsibility for major steps; the user group responsible for implementation and the project for technical support
мониторинг/ оценка
The quality of the water was measured in each season to monitor the impact of the technology. Detailed progress reports, results, and lessons learned were shared with district level institutions and authorities, water quality reports were shared with spring users at public meetings
Research
Water quality and availability recorded before and after technology implemented. Studies on access to water and confl icts among users
Схема реализации Подхода
PARDP project donors and implementing partners-- SDC: Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation IDRC: International Development Research Centre ICIMOD: International Centre for Integrated Mo
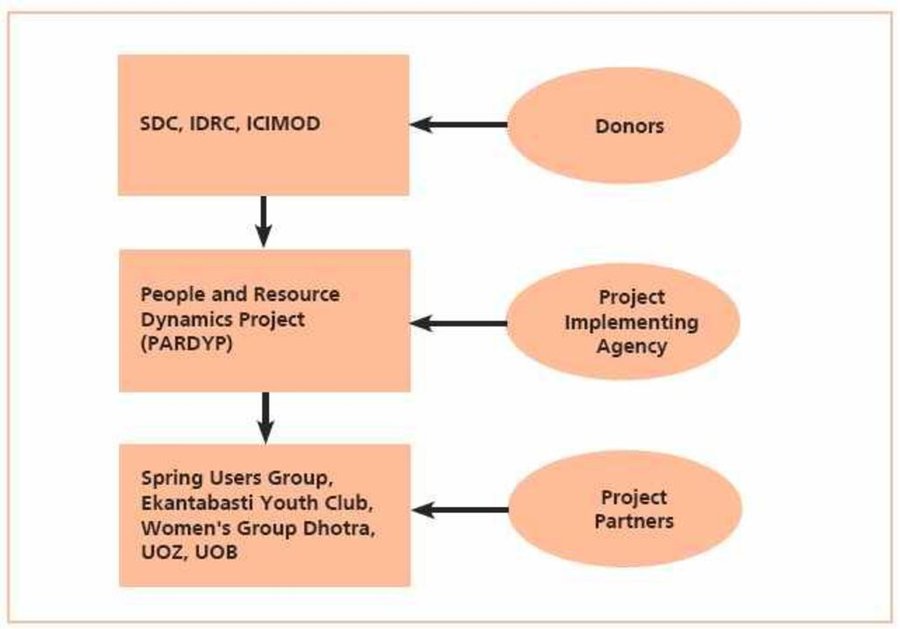
Автор: Madhav Dhakal
Принятие решений по выбору Технологии УЗП
Решения принимались
-
исключительно землепользователи (по собственной инициативе)
-
в основном землепользователи при поддержке специалистов по УЗП
-
все участники как часть процесса совместных действий
-
преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
-
исключительно специалисты по УЗП
-
политики/ руководители
Принятие решений было основано на
-
анализ подробно описанного опыта и знаний по УЗП (принятие решений на основе подтвержденных фактов)
-
результаты исследований
-
личный опыт и мнения (незадокументированные)
Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
Следующие мероприятия или работы являлись частью Подхода
-
Повышение компетенций/ обучение
-
Консультационные услуги
-
Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
-
Мониторинг и оценка
-
Научные исследования
Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Обучение было предоставлено следующим заинтересованным лицам
-
землепользователи
-
местный персонал/консультанты
Тип обучения
-
в ходе работы
-
обмен опытом между фермерами
-
опытные участки
-
общие собрания
-
курсы
Рассматриваемые темы
Concept of conservation measures, and methods of treating contaminated water using SODIS and safa filter.
Консультационные услуги
Консультационные услуги были предоставлены
-
на полях землепользователей
-
в постоянно функционирующих центрах
Name of method used for advisory service: Sharing information on water quality status, and raising awareness among users.; Key elements: catchment conservation, health hygiene, water treatment methods; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: awareness on health hygiene; catchment conservation activities and water treatment methods were shared during meetings.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
Институциональная поддержка
Какие институциональные структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы
-
нет
-
да, немного
-
да, умеренно
-
да, существенно
на уровне
-
местные
-
региональный
-
национальный
Опишите организацию, функции и ответственность, членство и т.д.
Тип поддержки
-
финансовая
-
повышение компетенций/ обучение
-
оборудование
Подробнее
Training on water quality treatment provided to local club
Мониторинг и оценка
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use and degradation, sanitary inspection, history of spring, available resources to trap water
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: seasonal water quality and discharge
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: number of spring users, household water requirements, users' issues
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: participation in conservation activities
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The project consulted with the local women's cooperative to solve a conflict over water quantity and access to spring source.
Научные исследования
Научные исследования проводились по следующим темам
-
социология
-
экономика / маркетинг
-
экология
-
технология
Access to drinking water, conflicts at water fetching times, water quality and quantity measurement, and effectiveness of water treatment methods.
Research was carried out on station
Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в долларах США
-
< 2000
-
2000-10000
-
10000-100000
-
100 000-1 000 000
-
> 1 000 000
Precise annual budget: н/п
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (users group): 10.0%
Землепользователям были оказаны/предоставлены следующие услуги или меры стимулирования
-
Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
-
Субсидии на отдельные затраты
-
Кредитование
-
Другие методы или инструменты стимулирования
Трудозатраты, вложенные землепользователями были
-
добровольный
-
в обмен на продукты
-
за денежное вознаграждение
-
в обмен на другие материальные ресурсы
Заём/кредит
-
Условия: н/п
-
Кредиторы: н/п
-
Заёмщики: н/п
Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
Влияние Подхода
Нет
Да, немного
Да, умеренно
Да, существенно
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
To build awareness on SLM and methods of improving drinking water quality. It also helped users to work in a group.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Similar approaches are being followed in other communities across Nepal.
Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
-
рост продуктивности
-
рост прибыли (доходности) и рентабельности
-
снижение деградации земель
-
снижение риска катастрофических погодных явлений
-
снижение объёма работ
-
материальное стимулирование/ субсидии
-
нормативно-правовое регулирование (штрафы)/ контроль
-
престиж, общественное давление/ солидарность
-
причастность к движению/ проекту/ группе/ сети
-
экологическая сознательность
-
традиции и верования, нравственные ценности
-
приобретение знаний и опыта в области УЗП
-
улучшение эстетической привлекательности
-
снижение остроты конфликтов
Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
Users are maintaining the implemented technology and also protecting the other nearby spring sources.
Заключительные положения и извлечённые уроки
Сильные стороны: по мнению землепользователей
-
Water users committee formed, revolving fund collected, and rules and regulations developed for the sustainable management of the drinking water system (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintain links with local community mobilisation groups for continuous guidance and support for the user group and for the proper use of the revolving fund.)
Сильные стороны: по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов
-
Users have become more aware of sanitation issues than before (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Awareness campaigns should be organized regularly covering more villages.)
-
Users have become more aware of 1) the quality of their drinking water, 2) its impact on their health, 3) water quality improvement options, and 4) the importance of soil and water conservation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Water quality testing campaigns should be continued and technical know how about different water quality treatment methods for improved health shared at regular meetings)
Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски: по мнению землепользователейвозможные пути преодоления
-
Water aviallability is still insufficient during dry period (March -May)
Other available nearrer sources should also be used, catchment protection activities should be continued.
Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски: по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистоввозможные пути преодоления
-
Conflicts are visible during the dry season due to insufficient quantity of water.
Good coordination among the group members should minimise conflicts- the strong and balanced role of users committee is vital for the equitable sharing of benefits.
Справочные материалы
Продолжительность применения Технологии: 19 января 2009 г.
Последнее обновление: 9 июля 2017 г.
Ответственные специалисты
-
Madhav Dhakal (mdhakal@icimod.org) - Специалист по УЗП
-
Provodoli Isabelle (himcat@icimod.org) - Специалист по УЗП
Полное описание в базе данных ВОКАТ
Документирование осуществлялось при участии
Организация
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцария
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал
Проект
Ключевые ссылки
-
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD: ICIMOD







