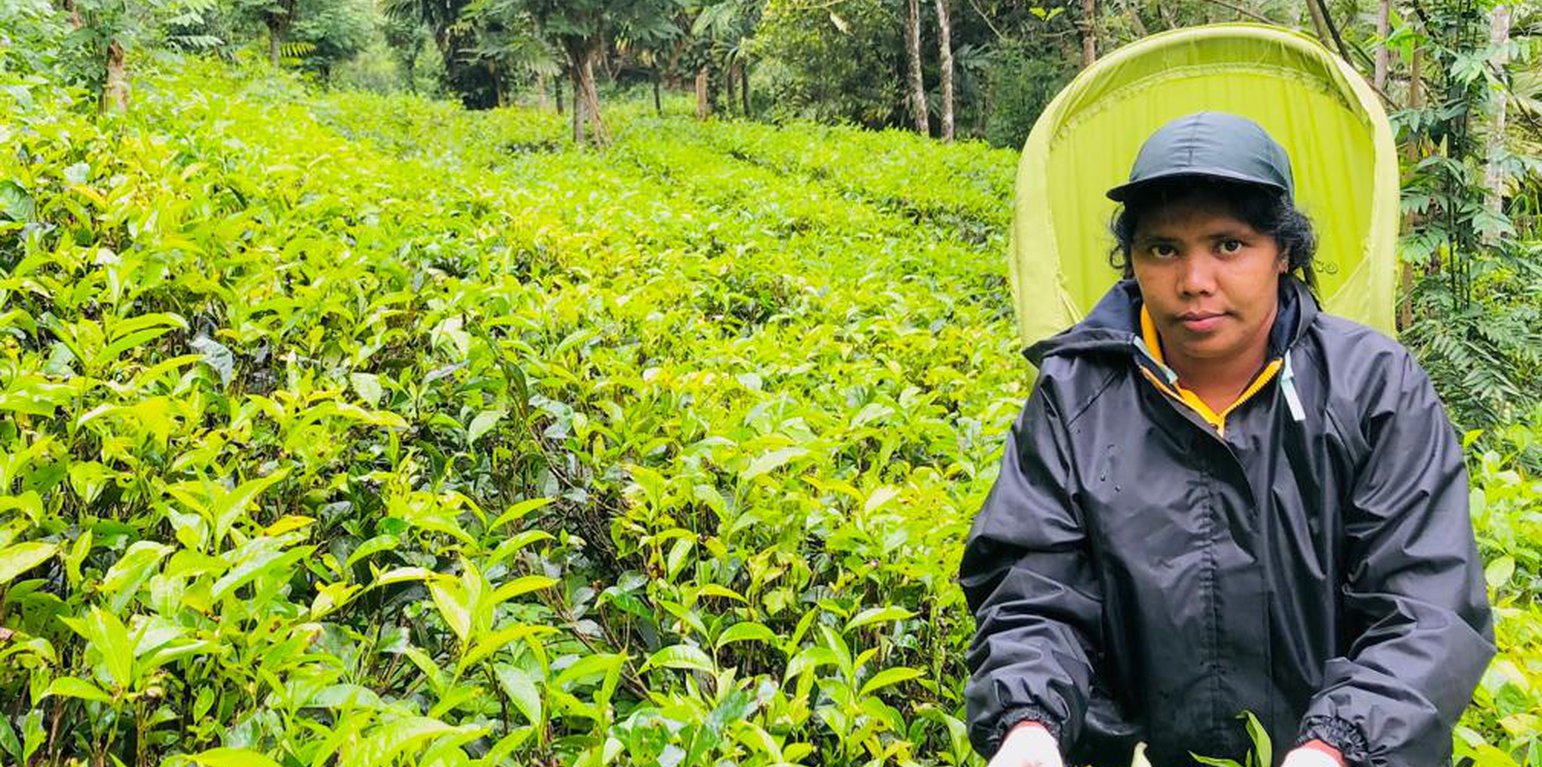




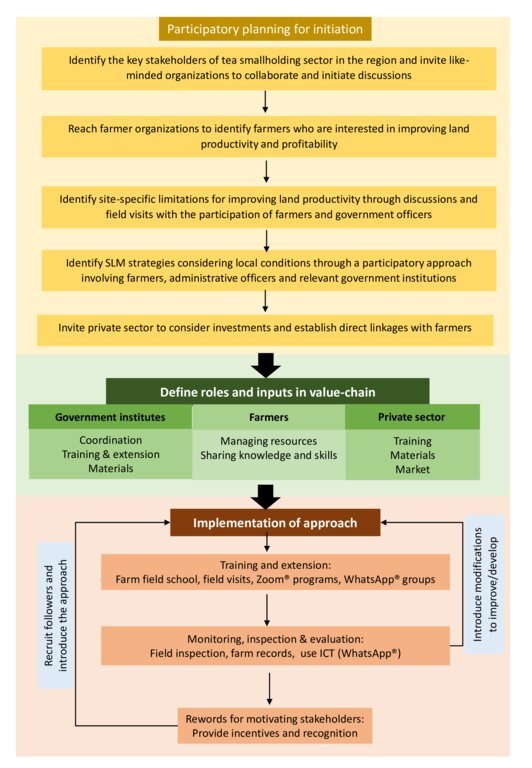
Due to unsustainable land management practices the monthly average green-leaf yield of tea smallholdings in Maligamale watershed in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka is as low as 1000 kg/hectare, whereas the potential is 2400 kg/hectare. Soil erosion, soil fertility decline, low plant density, and poor shade management are among the main reasons for low productivity. This causes reduced household incomes and farmers’ ability to invest in sustainable land management (SLM) practices. Inefficiencies in top-down extension methodology, lack of awareness and training on tea cultivation techniques, poor business practices, lack of access to services and poor perceptions about SLM have reduced profit margins of tea smallholdings. Hence, the aim/ objectives of the approach are to increase the land productivity in tea smallholdings and increase farmer’s incomes and gain environmental benefits through proper implementation of SLM practices. To address this, the Rehabilitation of Degraded Agricultural Land Project (RDALP) introduced a participatory approach together with Tea Smallholdings Development Authority (TSHDA), Department of Agrarian Development and other relevant government institutions, the private sector and farming community. The approach considered methods for strengthening linkages between stakeholder groups, providing training and resources for SLM practices, enhancing market orientation, using ICT for knowledge sharing, monitoring and evaluation, improving perceptions of farming community on agriculture and enhancing food-security of the households.
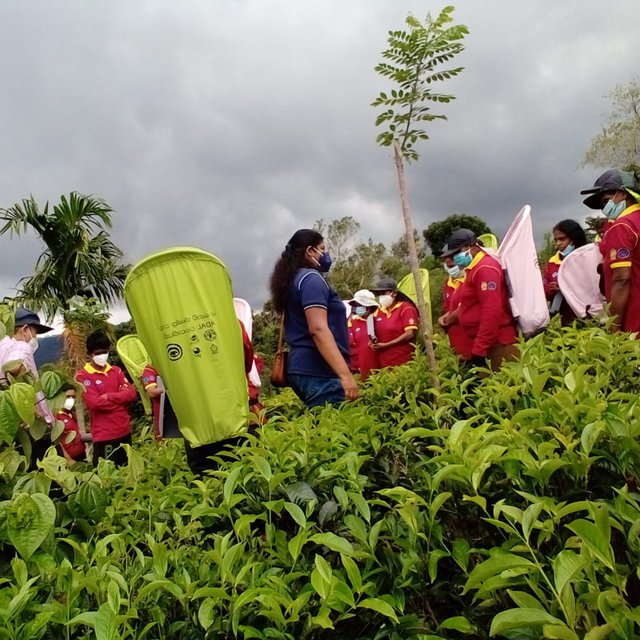
Firstly, tea smallholders who volunteered to learn about SLM were linked with the experts to collectively develop a participatory land restoration proposal. Site specific limitations for productivity improvement, recommendations, roles of different stakeholders, and training and material needs were identified in the proposal. The existing institutional setup was used for coordination of activities. The experts from government institutes provided training on SLM through farmer field schools, field demonstrations and ICT tools. More specifically, farmers were educated on soil conservation and soil fertility management practices: these included producing organic fertilizers using locally available resources, building live fences with green-manure crops and edible crops, intercropping using export agriculture crops, in-filling, selective weeding, developing and maintaining nurseries, using machinery for cutting pits and harvesting, using safety measures during field operations, and shade tree management. In addition, farmers have been encouraged to share good-practices, keep records and practice soil test-based decision making for nutrient management. Farmers and officers effectively used WhatsApp®, Zoom® and Facebook® for knowledge sharing and for monitoring and evaluating progress. Dissemination of knowledge using ICT and performance-based rewarding helped to recruit more farmers as followers. The TSHDA supported with extension service and regular monitoring of progress. With the support of government institutes, farmers were linked with private sector companies to promote market orientation. Export agriculture crops such as peppers, vanilla, areca nut and cloves were successfully incorporated into tea smallholding landscape, allowing farmers to earn an extra income. The partners from the private sector provided planting materials and extension services to transfer necessary knowledge and skills to the farmers. Machinery was provided to farmer organizations for the members to share.
Improving profitability of farming, improving hygiene and safety of farmers, and reducing time spent on agronomic practices have uplifted the living-status of famers and increased their willingness to invest in SLM. These characters could attract youth to the sector.
Местоположение: Pambadeniya village, Kandy District- Central Province, Шри-Ланка
Дата ввода в действие: 2017
Дата завершения: н/п
Тип Подхода

| Какие заинтересованные стороны/ организации-исполнители участвовали в реализации Подхода? | Перечислите заинтересованные стороны | Опишите роли заинтересованных сторон |
| местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества | Men and women farmers are involved in tea cultivation | They involved in practicing SLM technologies as the technologies were not gender biased. But the operation of mechanical weeder and auger for infilling are mainly done by male farmers. |
| организации местных сообществ | Farmer organizations | Support coordination of activities with farmers Support Farmer Field Schools Maintain common equipment and rent for members and non-members to support SLM practices |
| эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству | Tea Smallholding Development Authority, Department of Agrarian Development, Department of Export Agriculture, Department of Agriculture | Provide tea plants for infilling, promote inter-cropping and provide technical guidance to farmers Serve as resource-persons in Farmer Field Schools and in WhatsApp® groups |
| ученые-исследователи | University of Uva Wellassa, Sri Lanka | Study the effectiveness of knowledge dissemination approach and effectiveness of some SLM technologies |
| частный сектор | Several private sector companies are involved (Bio Food (Pvt) Ltd, Adamjee Lukmanjee (Pvt) Ltd) | Buying products, providing planting materials and continuing extension services to transfer necessary knowledge and skills to the farmers who are linked with them |
| местные власти | Local government institutes are involved in the process (Tea Smallholdings Development Authority (TSHDA), Department of Agrarian Development, Department of Agriculture, Department of Export Agriculture, Divisional Secretariat office- Doluwa | Capacity building, advisory services on fertilizer usage, land management, crop selection etc. |
| государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений) | Ministry of Environment | Helps to raise awareness among private and government sector stakeholders and within communities about SLM approaches and technologies, Project coordination and partial financial support |
| международные организации | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations | Project coordination, partial financial support and capacity building |
Before implementing the approach the level of productivity of tea lands that belong to the farmers who participated in the project were in class ‘C’ and below. In this scale of productivity lands were classified from A to D where A is the best and D is the worst. After implementation of the approach most of the fields upgraded to ‘A’ and ‘B’ performance levels. An interview conducted with a farmer revealed that the average green-leaf tea yield before and after participating in the approach were 1000 kg/ha/month and 2400 kg/ha/month, respectively.
Решения принимались
Принятие решений было основано на
Soil conservation practices, intercropping in tea lands, organic fertilizer preparation (compost tea, vermi- compost), burying of pruned plant parts, infilling, documentation, improving tea buds quality and quantity, handling of machines for cutting pits and tea plucking
Tea plucking machines, grass cutting machines and machine for cutting pits in tea lands
Tea buds collecting buckets
Tea plants for infilling, liming materials to correct soil pH, soil testing service
Трудозатраты, вложенные землепользователями были
н/п
Application of organic fertilizers such as compost tea, vermi-compost enhance the market value and some farmers ventured into organic tea production
Participatory approach in all stages of the project and farmer field schools encouraged the farmers and officers for evidence-based decision making. This also helped to recruit followers for the approach.
Approach helps to maintain better environment within the community as it introduced practices that improved safety and hygiene of the farmers while being more efficient. Farmers have been maintaining the SLM technologies
Approach used existing institutional set-up and farmer organizations to coordinate the activities. Therefore, it was cost effective and helped to strengthen the collaborations between stakeholders
Introducing private sector collaborations and improving market orientation of farmers helped to attract financial support to maintain sustainability of the approach
Approach improved the knowledge and capacity of practitioners. Although only about 25 farmers attended farmer field school the number of farmers who joined WhatsApp group is high as 70. Farmers are sharing knowledge and experiences and were able to improve land productivity through the approach
The knowledge and capacities of other stakeholders were improved similarly. Several officers were trained on SLM practices and technologies, use of ICT for extension, etc
Approach helps to strengthen the collaboration between institutes and stakeholders
Improving communication through the project supported the stakeholders to build healthy relationships.
Approach helps to earn income in different ways. It is not limited for tea. They can earn money by selling the harvest from intercropping such as vanilla, pepper cultivation, managing nurseries, etc.
Women engagement is high as the new agronomic measures help to reduce time spent on field practices
Usage of ICT knowledge, improving hygiene and safety of farmers, increased their willingness to invest on SLM and these characters could attract youth to the sector
Increased family improved food security of the practitioners. In addition, the approach promoted intercropping tea with export agricultural crops/ fruit crops and the use of edible crops in fencing. These also increased food supply. Since the mechanization and safety kits helped to reduce time spent on field work the farmers, especially women, were able to invest more time in their home garden and increase the provision of nutritious food to the household
Linkages developed through government entities increased market access. Further some farmers ventured into organic tea production using SLM practices and training provided through the approach. This helped them to reach a niche market
Improving soil fertility status has improved the resilience of tea stand for drought. Therefore, the effect of climate change on the income was only slightly affected. Further the SLM techniques they practiced helped them to rely less on inorganic fertilizers and therefore, the farmers were less affected by the fertilizer shortage in the market that happened due to changes in government policies. Using ICT tools for communication helped the farmers to share knowledge and coordinate activities even under COVID19 pandemic situation. They have got used to distant learning methods with this and now able to seek support from experts without having to travel
Farmer organizations were given some machinery for weeding and land preparation like activities. The members from the farmer organizations, who were trained to use the machinery, provided their service to the farmers for a payment from which a fraction is given to the farmer organization for maintaining the equipment. In addition, some farmers started nursery management as a business
Approach has converted the most of non- productive lands to productive levels with the support of external bodies. Lands needs low external inputs as farmers produce required fertilizers by themselves in their own land by using natural organic materials. The crop diversification helps to reduce risk of crop losses and increase various income pathways to farmer. As well as approach helps access to markets. And there is a trend of farmers who succeed with approach to share their knowledge and experience with others. The ICT knowledge provided by the approach is much useful in that aspect. So, land users can sustain what has been implemented through the approach.