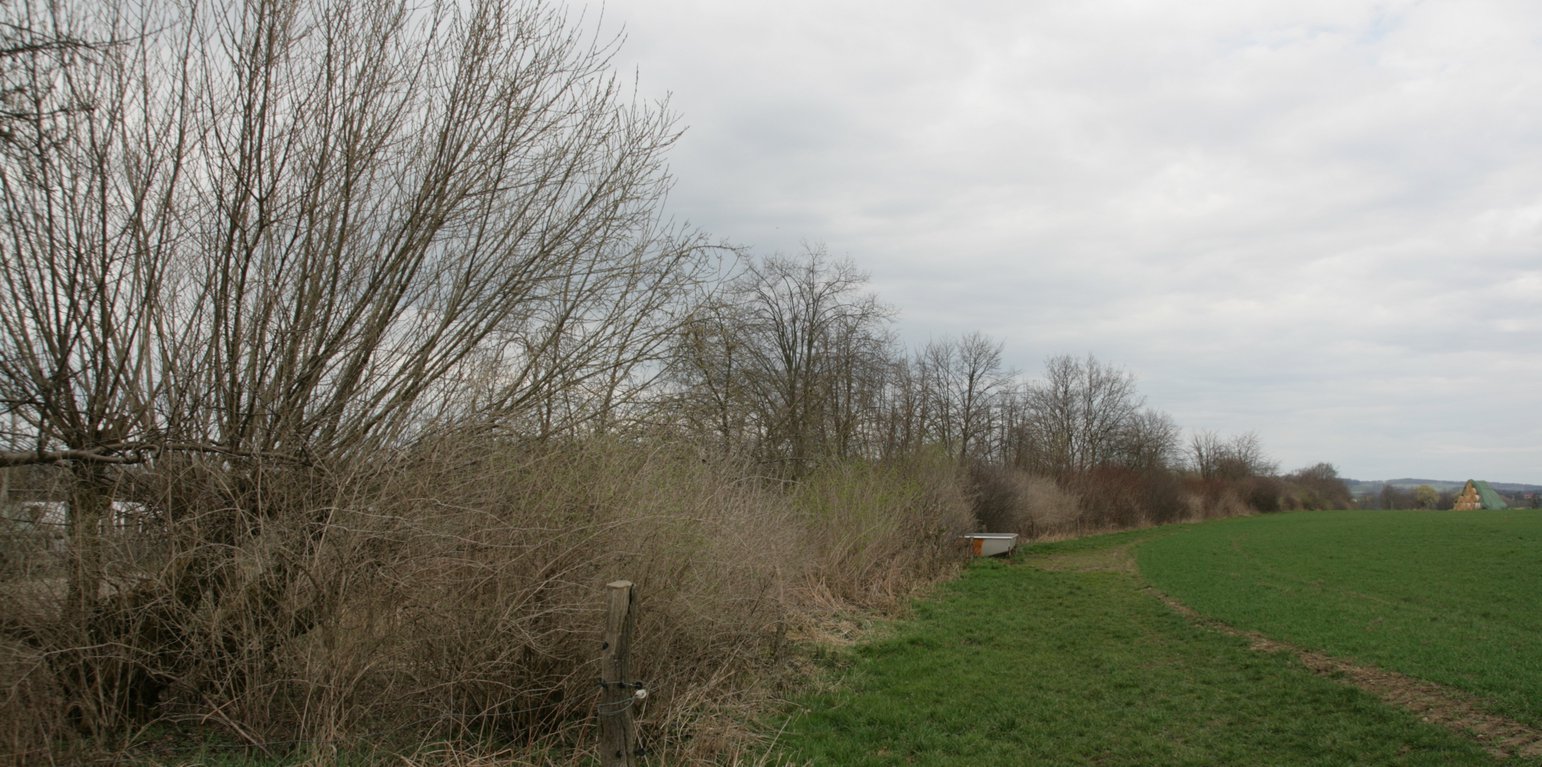




Hedges subdivide large fields and provide multiple other benefits. Improved soil structure, and deep and dense root systems in the hedgerow area result in slowing runoff from adjacent land, increasing infiltration rates and capturing sediment. These factors reduce water erosion and nutrient leaching. On steep slopes or embankments, deep roots can prevent wet soils from slipping. Additionally, hedges can acts as windbreaks and thus reduce wind erosion of light soils: simultaneously soil particles in the air are filtered out by hedges. Hedgerows provide a habitat for various wild animals for their food, reproduction, shelter and retreat. The hedge can act as a measure for natural pest control: for example as a habitat for raptors that control voles. A well-placed hedge may improve the microclimate of a field by reducing wind speed and increasing soil moisture in the wind-protected area.
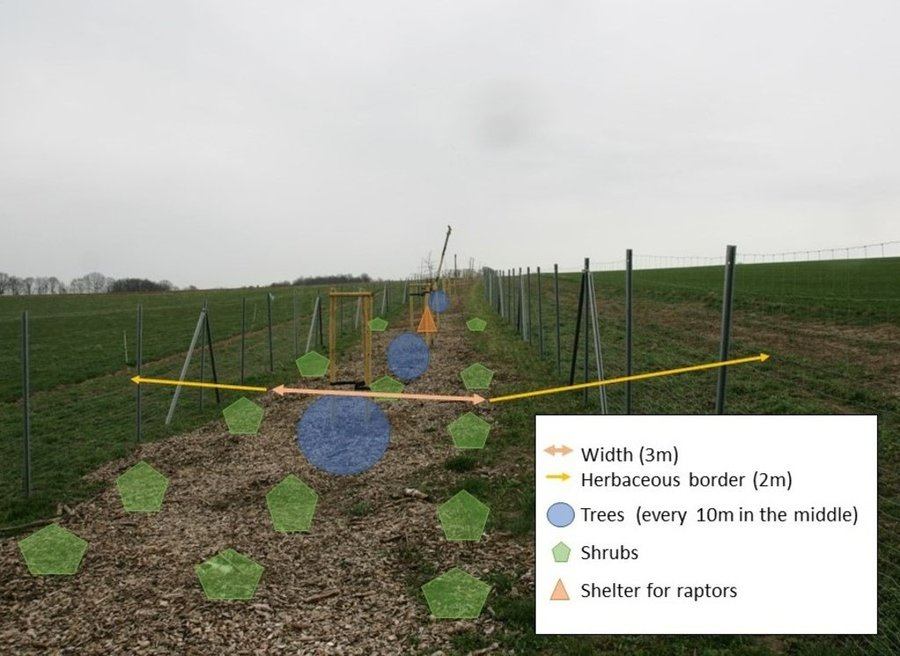
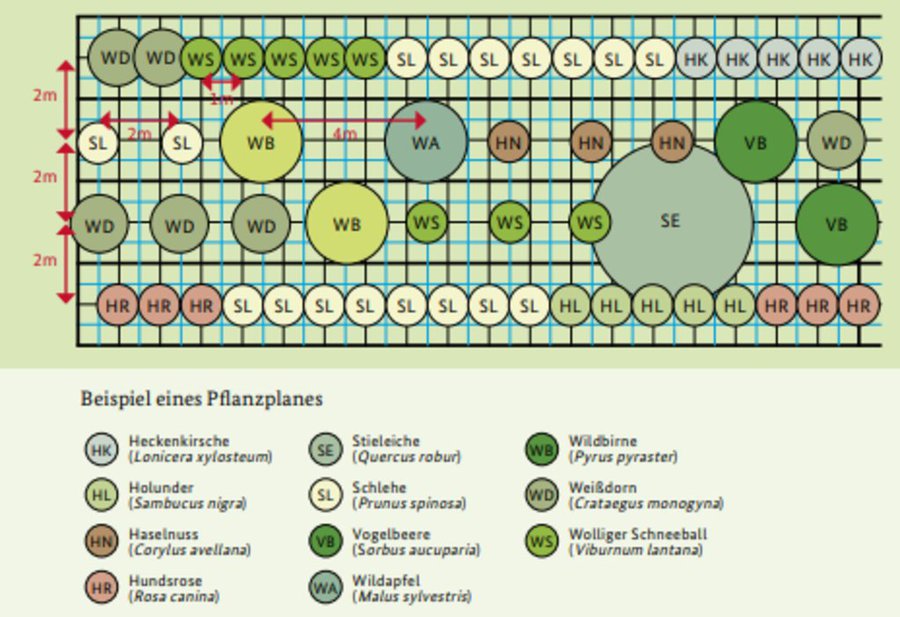
An effective hedge must be strategically sited and carefully established. The optimal hedge is a multi-row hedgerow (at least three rows) with a herbaceous border on both sides. The width of the hedge should be, ideally, 5-6 m (LfULG, 2014). Hedges are best planted parallel to the contour line, along the direction of cultivation, not on the headland, and should be sited a minimum of 20 m from the nearest road. Preparing a planting plan is very important for the establishment of a hedge. It should be based on native species (Kühne et al., 2018). Planting is usually done from October to November. Since a newly planted hedge requires regular costly watering (100 litres for trees, 20 litres for shrubs) spring planting is not advisable.
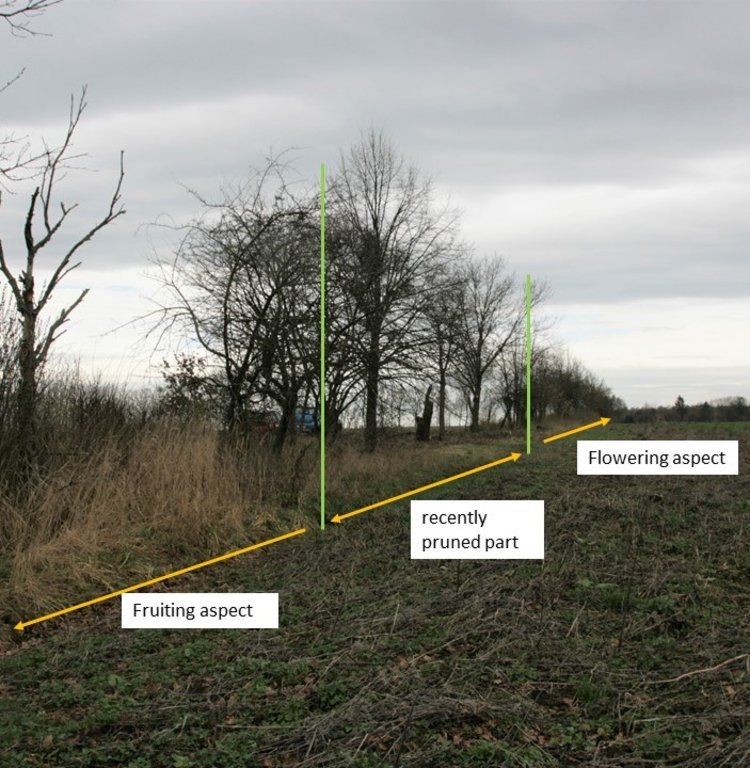
Maintenance pruning can be divided into hard pruning (every 10-15 years) and pruning for shape and maintenance (every year). Hedges that are not maintained will lack fruit, develop deadwood, or simply die back. Maintenance pruning should be done in February or March when there is no frost and before the plants sprout. A clean, smooth cut is important to prevent fungi or diseases from entering the plants. Hard pruning of hedges means cutting shrubs to a height of a few centimetres. As a general rule, a hedge should be divided into at least three sections, which should be hard pruned in succession. In this way, the hedge always retains a flowering and a fruiting element. Individual trees should be left as shelter/seed trees. The annual maintenance cuts should be used to shape the hedge, but also to remove broken or diseased branches (NABU Niedersachsen).
Hedgerows also have drawbacks for farmers and landowners. They take up cropland, which initially reduces yields. Once established, they cannot be easily removed, limiting management flexibility. It is uncertain whether hedges will be eligible for financial support or whether they will remain eligible after several years. For example, a hedge in Germany that is initially eligible for financial support must prove, after 10 years, that all the required species are still part of the hedge. If not, the money received from the subsidy must be repaid. Moreover, maintenance requires a lot of work, which needs to be compensated by subsidies (Thünen, 2021).
Местоположение: Pfaffendorf, Saxony, Германия
Число исследованных участков, где применяется Технология: 2-10 участков
Пространственное распространение Технологии: примененяется точечно/ на небольших участках
На постоянно охраняемой территории?: Нет
Продолжительность применения Технологии: 2003
Тип внедрения/ применения












Less input of pesticides from conventional agriculture.
In direct surrounding of the hedge.
Possible to sell berries and fruits from the hedge.
In direct surrounding of the hedge.
Considering the area of hedge.
In direct surrounding of the hedge.
In direct surrounding of the hedge.
It is important to use local planting/maintenance materials, e.g. regarding wood chips.
In direct surrounding of the hedge.
Impact decreases with distance from the hedge.
Impact decreases with distance from the hedge.
Impact decreases with distance from the hedge.