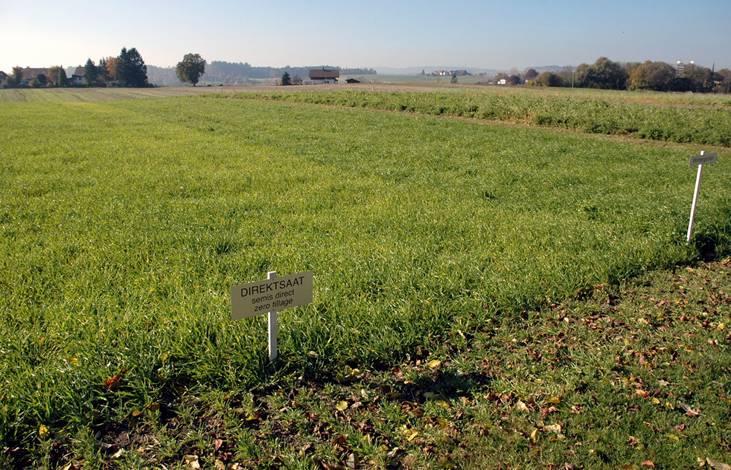
Subsidies for conservation agriculture [Швейцария]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Unknown User
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: David Streiff
Umstellungsverträge
approaches_2632 - Швейцария
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
Специалист по УЗП:
Wyler Roman
Швейцария
Специалист по УЗП:
Hofer Peter
+41 (0)31 970 53 37
Peter.hofer@vol.be.ch
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern LANAT
Rütti, 3052 Zollikofen
Швейцария
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern (LANAT) - Швейцария1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
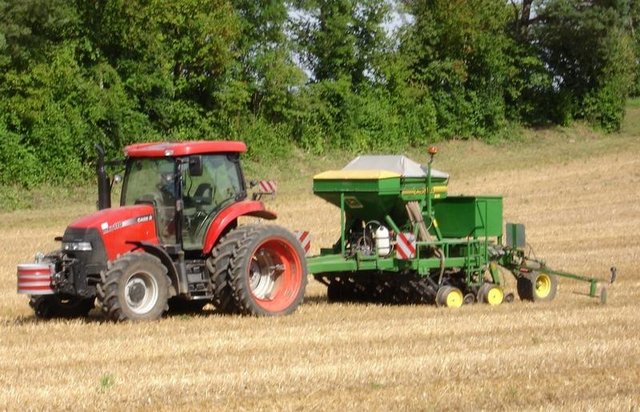

Direct seeding [Швейцария]
A cropping system which allows to plant the seeds directly into the soil without ploughing. The soil is covered with plant remainders.
- Составитель: Unknown User
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Land users commit to apply conservation agriculture on parts of their land for a period of 5 years. In return they get subsidies during this period.
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Aims / objectives: The Swiss environment protection law defines that soil fertility must be conserved on a long term basis. The cantons have to execute this national law. The way this is done differs from canton to canton. In this study the strategy of the canton of Berne is documented. It has three major goals: The prevention of soil erosion, the reduction of nitrate wash out and the prevention of soil compaction.
Methods: To reach these goals, farmers who accept to use conservation technologies can get additional subsidies for a period of 5 years. Furthermore they are supported by advisors. In this way land users are encouraged to change to soil conservation technologies, financial risk during the establishment phase is reduced due to the subsidies. The approach consist basically of a contract between land users and the office for soil conservation, in which land users commit to apply only soil conservation technologies on parts or on all their land during a period of 5 years. During that time direct seeding must be applied at least 2 times for main crops and for half of the catch crops. For the remaining crops ploughing is not allowed either. Technologies which reduce the reworking of the soil such as maize strip tillage ('Streifenfrässaat') or mulching need to be applied. In return land users get subsidies (during 5 years) which depend on the crop and the technology used. The highest subsidies are granted if direct seeding is used. The office for soil conservation is running a demonstration study comparing direct seeding to conventional agriculture. This helps land users to estimate the effects the new technology would have when applied in practice. If a specific farm receives the subsidies depends on whether in the running year there is still financial resources for the program. Resources have been limited by the government. Additionally it depends on where the farm is located. Farms that located in regions of major nitrate contamination, enhanced risk of eronsion or soil compaction or in regions with drinking water sources or polluted surface water are incorporated first. Land users can have their whole farm or single fields under contract. However a specific field can not be under contract for more than one period (5 years). As soon as a farmer gets a contract, details about which crop to plant where and when, with which technology are discussed by the farmer and an advisor.
Other important information: The goal is to find the best solution for every land user. Meetings of that kind take place on a regular basis. Besides supporting the farmer, advisors also check if conservation agriculture technologies are really being applied. After the 5 years under contract, it is the land users choice whether they want to continue using conservation technologies or not. Monitoring of the office for soil conservation shows that 85% keep on using conservation technologies. Its seems that the approach has a long term influence and subsidies are needed in the beginning only.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Швейцария
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Canton of Berne
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
1996
Комментарии:
It is possible to get subsidies in the whole canton of Berne. Cropland area in the canton is 539 km2, 2517 ha were under contract in the year 2006.
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused on SLM only
Spreading of conservation agriculture in areas with an enhanced risk for soil erosion and or washing out of nutritients. Good quality support so that farmers will not have lower crop yield due to the technology and therefore continue using conservation agriculture after 5 years without external support.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Water erosion under intense rainfall. Washing out of Nitrate to the ground water. Soil compaction.
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Социальные/ культурные/ религиозные нормы и ценности
- затрудняют
Ploughing is an important part of the tradition of agriculture. People are very critical towards no-tillage technologies, since they don't fit the common understanding of agriculture.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The people working in the project are farmers themselves. They can give on their practical experience. Furthermore a demonstration study can be visited
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
Most farmers have achinery for conventional agriculture. To change to conservation agriculture major investments need to be done or contractors need to be tasked. Furthermore crop yield can be lowered in the beginning.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: When changing to conservation agriculture farmers are supported financially for a period of 5 years.With this money the risk in case of crop failure ond the costs for a contractor are lowered.farmers can test a new techniquewithout major expenses or risks
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- затрудняют
If the owner of the farm changes, the new owner often returns to conventional agriculture.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: No solution inside the project
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation In Switzerland the number of farms is decreasing. New owners of land sometimes change back to conventional agriculture. It is possible however, that the new owner introduces conservation technologies.
другие
- затрудняют
In Switzerland there are subsidies to support farmers in hilly terrain. This encourages farmers plant crops on steeper slopes and therefore enhances the risk of erosion. This is not a constraint for the technology however.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Conservation agriculture helps to reduce erosion. However the project cannot change the fact, that these subsidies enhance the risk of erosion.
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Contracts are signed by the office for soil conservation and the head of the farm, who in general is male. The decision about which technology is applied is usually taken at the household level including both women and men.
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
The national government tasked the cantons with soil conservation. Therefore approaches differ from canton to canton.
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | нет | The project was introduced through the office for soil conservation |
| планирование | интерактивное | Landusers who wish to get subsidies have contact the office for soil conservation. It is the land users decision on which of their fields they want apply the technology. |
| выполнение | внешняя поддержка | Land user get subsidies for a period of 5 years, during which they have to apply soil conservation technologies. To actually use the technology they task a contractor or do the work on their own. |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | As there are discussions with the advisor on a regular basis, the implementation of the technology is monitored both by the farmer and the advisor. |
| Research | нет | There is a demonstration study where direct seeding and conventional agriculture is compared. |
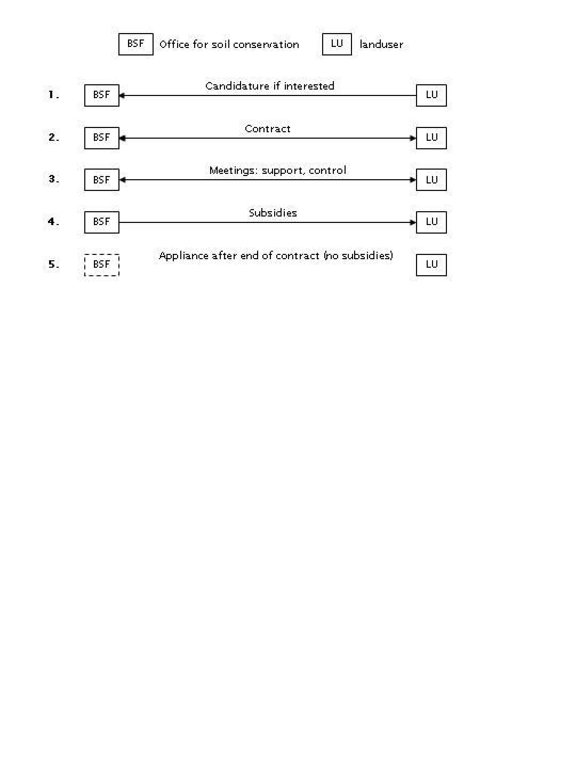
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
Описание:
Interactions between the office for soil conservation and land users during the progression of the project.
Автор:
Roman Wyler
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
The decisions were taken by the office for soil conservation. Since these people are working as farmers, too, land users perspective could be included.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. To get the subsidies criteria from the contract need to be accepted. Besides this, land users can decide on their own how land is cultivated.
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Нет
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- на полях землепользователей
Описание/ комментарий:
nnual meetings between land user and advisor; Key elements: Technical support, Planning of crop rotation and technologies applied, Monitoring
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Following a study of the office for soil conservation most land users continue to use conservation technologies after the end of the contract.
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, немного
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Подробнее:
The office for soil conservation was involved in Swiss no-till, which is a platform to exchange knowledge.
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: advisory meetings
technical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: advisory meetings
economic / production aspects were None monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: farmer himself
area treated aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: only the area under contract is known
no. of land users involved aspects were None monitored by 0 through None; indicators: only the number of land users under contract is known
survey aspects were None monitored by land users through None; indicators: afther the first two years there was an evalution of the project. Farmers were asked for their opini
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- технология
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
Research is not part of the actual project. However the advisors are involved in research projects through other activities. Therefore new knowledge is usually incorporated in the advisory meetings.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 100 000-1 000 000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Kanton Bern): 100.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
Если да, укажите тип(-ы) поддержки, кто ее предоставил и условия предоставления:
Canton of Berne
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- сельскохозяйственные
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| семена | профинансированы частично | |
| удобрения | профинансированы частично | |
Комментарии:
There are subsidies per field under contract for a period of 5 years. During that time direct seeding must be applied at least 2 times for main crops and for half of the catch crops. For the remaining crops ploughing is not allowed either.
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
the advisory meetings help land users to better understand soil processes.
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Other cantons in Switzerland have started to subsidise conservation agriculture too.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
income is slightly enhanced in most cases.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост прибыли (доходности) и рентабельности
- материальное стимулирование/ субсидии
- экологическая сознательность
prevention of erosion
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- да
Если да, опишите как:
on a long term perspective conservation agriculture is rather cheaper. Only in the beginning it costs more.
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Not land user, but advisor of the project! |
| The structure of the project enables individual solutions. Still there are incentives for conservation agriculture. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Working together with the land users, searching for the best individual solution.) |
| After the end of the contract, there are no costs anymore. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: armers should be supported as good as possible, so that they are familiar with the technology and continue to apply it after the end of the contract.) |
| Advisors involved in the project all have an agricultural background, they are therefore familiar with the problems of farmers. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Working together with the farmers and trying adjust the program to their needs.) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Compared to the total number of farms the number of participants is rather small. | conditions for participation could be reduced in order to reach more people. This would however increase the costs. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Subsidies are expensive for the state. Since resources are limited there is already a waiting list for the farmers. | soil consvervation should get a higher importance in politics. This is not the case because most people don't even know that soil degradation is a problem. |
| f there is no possibility to rent the machines in the region, costs are very high, even if there are subsidies. | here it could be a possiblity to support contractors to buy the machines needed, so that land users could apply the technology at lower costs. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Amt für Landwirtschaft und Natur des Kantons Bern LANAT, Rütti, 3052 Zollikofen. Kanton Bern fördert Ressourcen schonenden Ackerbau.AGRARForschung 14 (3): 128-133, 2007.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
http://www.vol.be.ch/site/lanat-3155-mbressourcen.pdf
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Direct seeding [Швейцария]
A cropping system which allows to plant the seeds directly into the soil without ploughing. The soil is covered with plant remainders.
- Составитель: Unknown User
Модули
Нет модулей