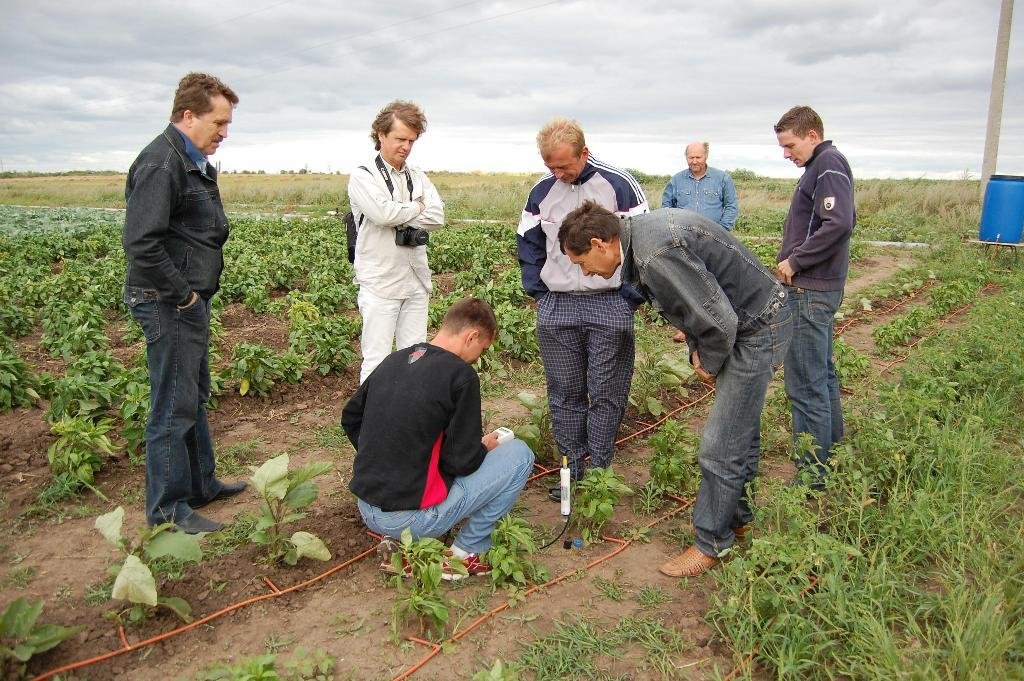
Concerted thinking on common problems of water scarcity [Российская Федерация]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Anatoly Zeyliger
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: David Streiff
Жить рядом – думать об общей воде (Russian)
approaches_2426 - Российская Федерация
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Moscow State University of Environmental Engineeri (Moscow State University of Environmental Engineeri) - Российская Федерация1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
27/02/2009
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП

Drip irrigation [Российская Федерация]
Drip irrigation systems gradually apply water into the zone around the stem of the irrigated plant.
- Составитель: Anatoly Zeyliger
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Testing and disseminating of a water-saving technology like drip irrigation
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Aims / objectives: The objective of the Rural Development Programme (RDP) is to assist farmers who have to deal with difficult environmental conditions (drought, steep slopes) in applying sustainable farming practices either at the implementation phase or for maintenance. The programme is carried out to: 1) improve the socio-economic conditions of rural areas; 2) prevent land abandonment, and 3) prevent on-site and off-site damage caused by land degradation and erosion. To achieve these objectives, the RDP identifies different lines of action: 1) compensation for difficult natural conditions; 2) combating erosion; 3) reducing farming intensity; and 4) promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Methods: The main method used in RDP is to provide farming subsidies for farming practices following a cross-compliance principle. Each line of action implies a combination of conservation measures that are subsidised, but only when applied in combination. Hence, single conservation measures outside of these lines of action are not subsidised.
Stages of implementation: Two years of testing with following phase of result dissemination.
Role of stakeholders: The level of subsidy is based on estimated implementation and maintenance costs and possible loss of productivity caused by the conservation measures. These values were obtained after consultation with various stakeholder groups including farmer organisations with agricultural cooperatives. However, because of limited resources, not all farmers will receive subsidies for conservation measures. Priority is given to: 1) farmers who have 50% of their land within the Nature 2000 network, a European-wide network of protected areas for the preservation of habitats and threatened species; 2) farmers with >50% of their land in unfavourable zones; and 3) farmers who did not receive subsidy in previous RDPs.
Other important information: Furthermore, areas with slopes of more than 20% are not subsidised in this programme since it is recommended that no agriculture should take place. Instead, reforestation of these areas is subsidised. RDPs are developed for a period of seven years. At the end of this period, a new RDP is defined and priorities and levels of subsidies may be changed. The present RDP is valid for the period 2007-2013
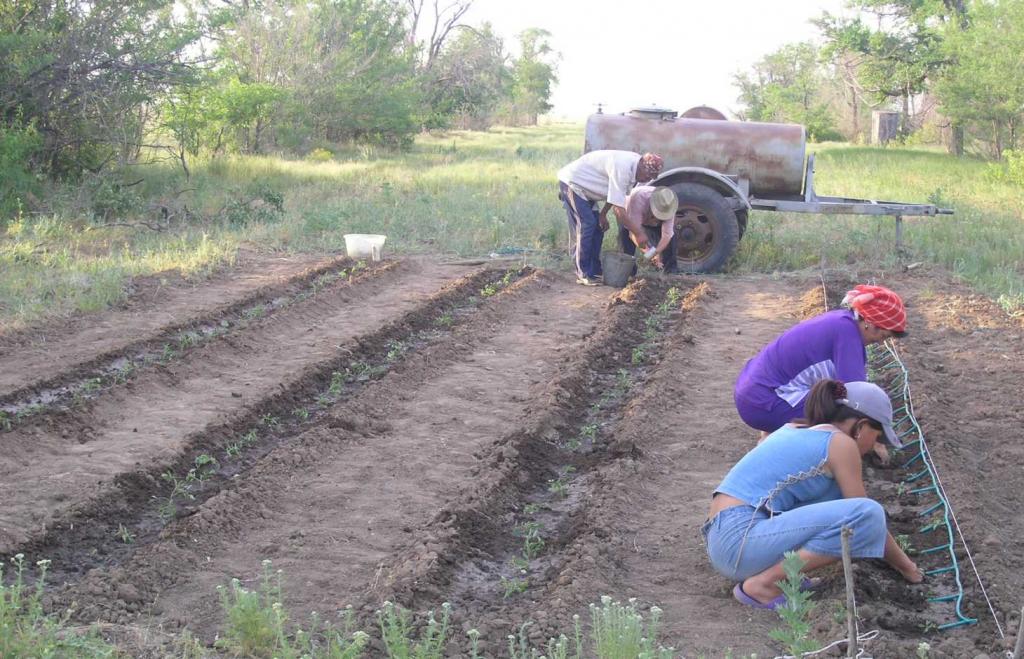
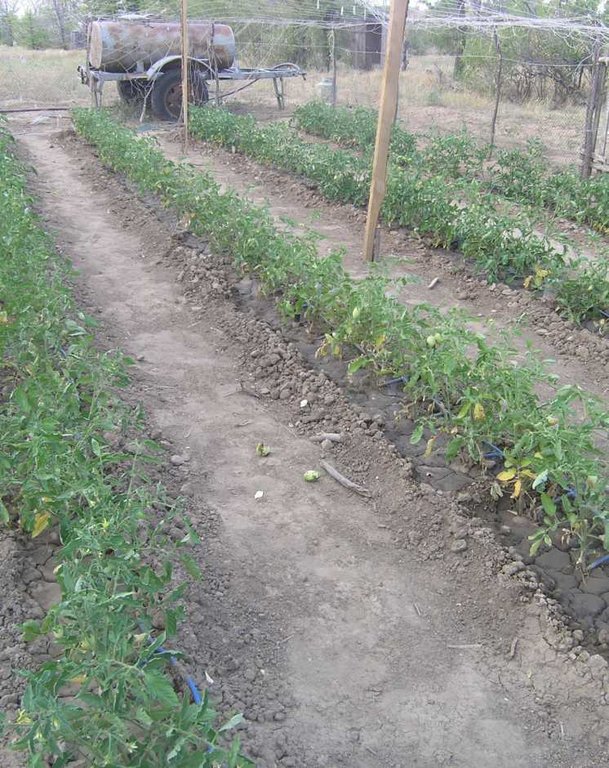
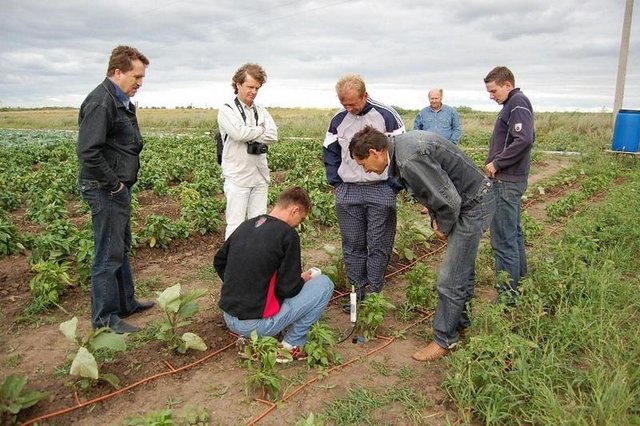
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Российская Федерация
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Russia
Более точная привязка места:
Pallasovsky district, Volgograd region
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
2002
Год окончания (Если Подход больше не применяется):
2011
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused on SLM only
To consider the common problems of water scarcity at villages remote from water sources. To provide the best examples of water usage and initiate implementation of water-saving technologies.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main problem to be addressed by this approach is the conflicts over the common use of water supplied to the villages. In this dry area, water is scarce and has to be brought from remote rivers, lakes and artificial water storage facilities through irrigation channels. In the dry season, when water demand exceeds availability, there is a pivotal problem of poor water availability for all villagers. During the most difficult period, water even has to be transported to the villagers’ houses by car.
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Социальные/ культурные/ религиозные нормы и ценности
- затрудняют
People do not know much about water-saving technologies. Whatever they learn about it, they are convinced that it is very complicated or too costly.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Organization of training seminars, sharing ideas between farmers
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- затрудняют
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Testing of drip irrigation on their subsidiary plots, participation in monitoring activities, training and dissemination.
Owing to simple installation and control of drip irrigation, it is promising that disadvantaged people grow vegetables and fruits for their own consumption in order to improve their income and to save water for domestic use.
- организации местных сообществ
Collective farmers are involved in approach for future implementation of it at vegetable plantation
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
Agronomists as well as reseachers were involved in this approach by development scheme of applications, advising people.
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
Administration of the region was informed about DESIRE project activities. It supports the activities by giving advice, introduction to useful people.
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | интерактивное | SLM specialists - introducing the technology to people Planners - introducing the technology to people ready for testing it |
| планирование | интерактивное | SLM specialists - planning of test implementation Land users - agreement to test the technology |
| выполнение | внешняя поддержка | SLM specialists – implementation of schemes development Land users – preparation of experimental plots |
| мониторинг/ оценка | внешняя поддержка | Land users - simple monitoring of drip irrigation system performance |
| Research | внешняя поддержка | Land users – reporting of water used for irrigation, workload and harvested yield |
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
Within the DESIRE project field trip several meetings with stakeholders were performed. Different variant were discussed. Local land users mentioned the technology of drip irigation and ask help of expert in implementation and training.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Method was chosen as it is saving water resources and labour time, is suitable for the local conditions and not complicated to implement.
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Укажите, кто проходил обучение:
- землепользователи
Тип обучения:
- опытные участки
- общие собрания
Рассматриваемые темы:
drip irrigation technology, knowledge about varying quantities for plants during the growing season according to the hydrological cycle, etc.
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- на полях землепользователей
Описание/ комментарий:
Name of method used for advisory service: Drip irrigation technology; Key elements: Water cycle: elaborated and explained to stakeholders during an initial stakeholder workshop as well as during field visits, Water-saving technologies: explained to stakeholders during stakeholder workshops. They were based on conceptual approaches and data gathered during field monitoring
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The government cannot provide special services in order to ensure its continuation; however, farmer-to-farmer dissemination is working.
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, умеренно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Укажите тип поддержки:
- повышение компетенций/ обучение
Подробнее:
The local administration organized some demonstration and training activities for local users.
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
Bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through measurements; indicators: through farm visits and sampling of soils for chemical parameters (for example to control for ecological farming practices)
Technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Comparison of water consumption using drip irrigation and furrow irrigation. The very high water efficiency as well as the minimal rate of water used for crop growing by drip irrigation was clearly demonstrated.
Economic / production aspects were monitored through measurements; indicators: by comparing production between years
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were several changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Some changes were made as a result of bio-physical monitoring of plant development according to water quantities, fertilizer application, etc.
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- технология
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
The implementation of drip irrigation technology under local conditions was performed by a team from the Moscow State University of Environmental Engineering under the framework of the EU-DESIRE project.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 2000-10000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (EU research project DESIRE): 100.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
Если да, укажите тип(-ы) поддержки, кто ее предоставил и условия предоставления:
Agricultural activities are subsidised by government
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- оборудование
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| техника | профинансированы полностью | |
| инвентарь/ инструменты | профинансированы полностью | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- в обмен на другие материальные ресурсы
Комментарии:
Materials (pipes for irrigation system, water tank) for the implementation of the experimental plots were supplied to land users. Some of the land users’ activities, like monitoring of soil water capacity, were paid with small amounts of cash. Other work was implemented voluntarily.
As this drip irrigation is in a testing phase, the materials for the irrigation system were financed by the project and not by the land users.
Labour was also paid in cash or sometime it was voluntarely.
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
decreased water use
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
It enables people with low income to avoid having to buy vegetables in the market by growing them for their own use and for sale.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Land users share their knowledge and experience with each other. Where this occurs, drip irrigation disseminates amongst the stakeholders.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Possibilities to grow vegetables, to increase their income and to diversify their food.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The practice allows people to produce food on their subsidiary plots.
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост продуктивности
by using this technology people can increase food production.
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
People want to save water, but also to improve their well-being
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- да
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| increasing the well-being of people (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Table of land users become more rich by vegetable, some vegetables can be sold on the market) |
| Labour time saving (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Giving people more time for others activities) |
| water saving (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Implementation of water saving technologies) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Increasing the well-being of people: food availability for land users becomes enriched in terms of vegetables and some vegetables can be sold on the market (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Dissemination of these opportunities to other people) |
| Reduction of labour input (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Giving people more time for other activities) |
| Combating land degradation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: sharing this knowledge with other users) |
| Sharing water-saving knowledge with other users (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Implementation of water-saving technologies and dissemination of these skills to neighbours.) |
| Concerted thinking by stakeholders on common problems of water scarcity in villages remote from water sources (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Provide best-practice examples of water usage and initiate implementation of water-saving technologies ) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Relatively high starting implementation costs |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Zeiliguer, A., G. Sokolova, V. Semeonv, O. Ermolaeva. Results of field experimentations at 2008 to grow tomatoes under drip irrigation at Pallasovsky District of Volgograd Region. Proceeding of conference at MSUEE. 2008, p. 45-56
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Drip irrigation [Российская Федерация]
Drip irrigation systems gradually apply water into the zone around the stem of the irrigated plant.
- Составитель: Anatoly Zeyliger
Модули
Нет модулей