Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) [Португалия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Celeste Coelho
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Fabian Ottiger
Zona de Intervenção Florestal (Portuguese)
approaches_2588 - Португалия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - Португалия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
10/02/2009
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
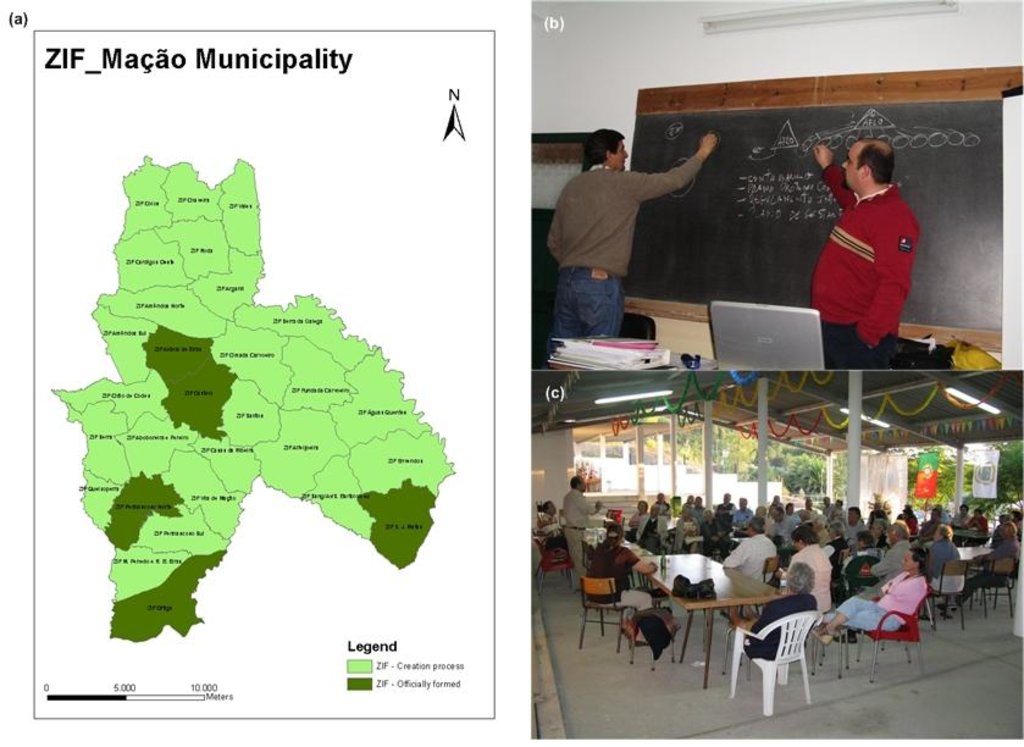
Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) is a territorial unit, where the main land use is forestry. This approach assembles and organizes small forest holders and defines a joint intervention for forest management and protection. Defined by law in 2005, and revised in 2009, each ZIF of private forest has to include at least a contiguous area of 750 ha, 50 landowners and 100 forest plots, and has to be managed by a single body, defined by ZIF members.
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Aims / objectives: The ZIF overall objective is to promote the efficient management of forest and to mitigate current constraints of forest intervention (e.g. land size and tenure). Other objectives are to develop structural measures for fire prevention, to integrate local and central administration actions and to implement the national and regional forest management policy at the local level. The final purpose of ZIF areas is to improve productivity in rural forest areas, contributing to rural development
Methods: The idea emerged after the catastrophic wildfires of 2003 and was developed and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, City Council, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries. The ZIF approach was legislated by Law 127/2005, and revised under Law 15/2009. Each ZIF assembles small properties, which will be jointly managed by a single entity, which can be a non-profit-making and voluntary organization or some other group of people approved by the forest owners. Each ZIF will have a Forest Management Plan (PGF), where the forestry operations and activities for ZIF area are defined accordingly to the guidelines of the Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning (PROF), and a Specific Plan to Forest Protection (PEIF), which includes actions to protect forest against biotic and abiotic risks. The management entity should have a team with qualifications and experience in forestry and with technical ability to design these plans.
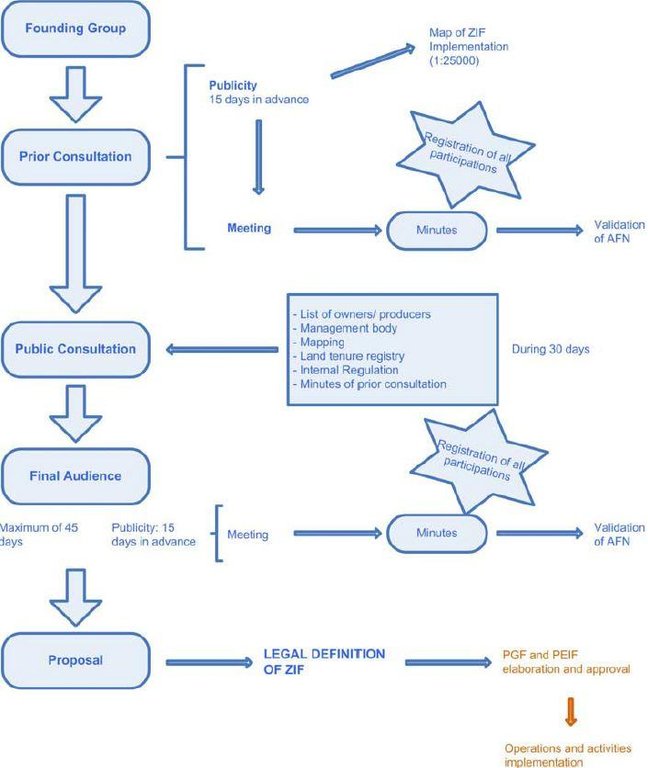
Stages of implementation: The legal constitution of ZIF includes six mandatory steps, namely the constitution of the founding group (group of landowners with at least 5% of a continuous area inside the ZIF), the prior consultation meeting, the public consultation, the final audience meeting, the proposal submission to the National Forest Authority (AFN) and legal publication of each ZIF (already done). After these procedures, the PGF and PEIF of each ZIF will be designed by the management entity and evaluated and approved by AFN. The implementation activities can then be implemented by the management entity or by individual landowners following the rules described on the plans. PEIF validity is five years and PGF validity is 25 years (still in preparation). [See figure below].
Role of stakeholders: The founding group is mainly composed of forest owners and producers and is the starting point for creating a ZIF. The management entity administers the ZIF in order to achieve their main purposes and the aims defined on the plans. AFN will support and monitor ZIF activities. ZIF non-supporting landowners are obliged to have a PGF for their land, as well as to accomplish the PEIF of the ZIF.
Other important information: The landowners inside the ZIF who are non-supporters do not have a clear role. Based on PROF - Plano Regional de Ordenamento Florestal (Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning), for ownerships of > 25 ha, the owners are obliged to have a PGF - Plano de Gestão Florestal (Plan for Forestry Management) for their property.
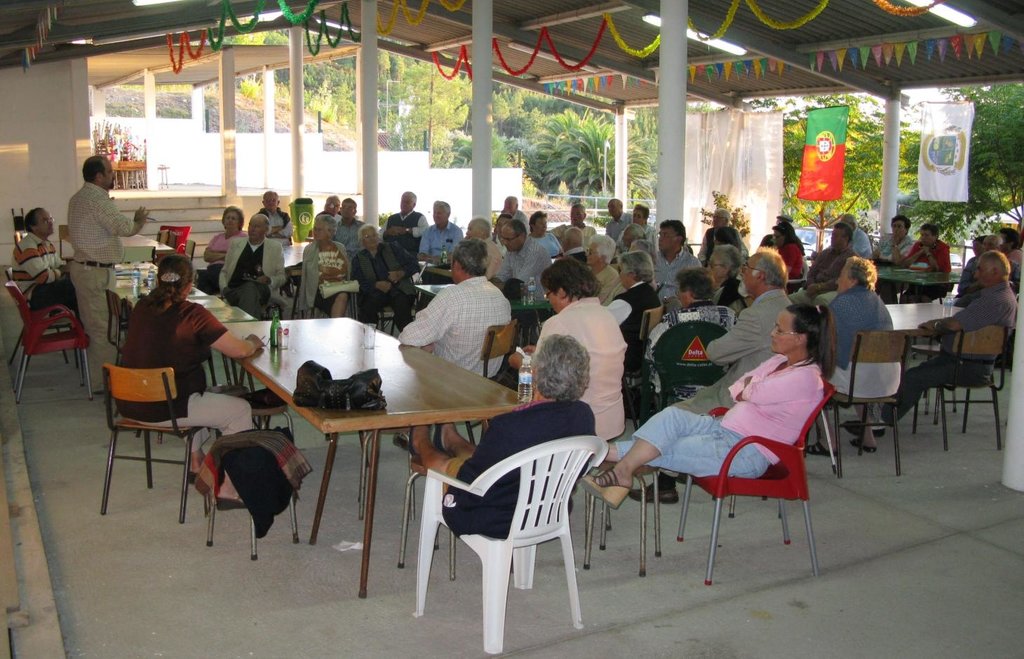
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Португалия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Santarém
Более точная привязка места:
Mação
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
2003
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (The main objective is to increase land management and profitability)
- To promote the sustainable management of forest; - To coordinate the protection of forest and natural areas; - To reduce the conditions to fire ignition and spread; - To coordinate the recovery of forest and natural areas affected by forest fires; - To give territorial coherence and effectiveness to the action of local administration and others actors.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - lack of forest planning and management, forest fires, land structure and tenure, land abandonment, rural depopulation and ageing.
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Социальные/ культурные/ религиозные нормы и ценности
- затрудняют
Social resistance to this approach. Landowners fear to lose tenure rights. Difficult to reach and find owners due to inheritance and out-migration. Rural depopulation occurred in the last decades.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Financial support, creation of new job opportunities in rural areas.
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
High implementation cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Governmental incentives
Институциональные условия
- затрудняют
Scepticism about the practical effects of this approach. Very high costs for implementation and lack of private investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: ZIF pilot areas will motivate implementation and investment into other ZIFs.
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- затрудняют
Land structure and tenure (private holdings)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Minimum area to constitute a ZIF is 750 ha
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation The ZIF join small properties and their management is undertaken as a single property, guide by a forest management plan. This entity can be a non-profit and voluntary organization or an other group of people approved by the forest owners and/or producers.
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Gender: mixed, Age: 50 years old
The majority of forest owners are usually pensioners, with low incomes
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
AFLOMAÇÃO technicians
- частный сектор
Private organizations
- местные власти
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
Municipality
Если участвовало несколько заинтересованных сторон, назовите ведущую организацию:
Based on an initial idea from Mação local specialists; the national ZIF legislation emerged in 2005 and was revised in 2009
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | интерактивное | Balance alternatives and take decision to test the agave forestry information sessions about ZIF approach; informal contacts, door-to-door approaches and formal agreement of the landowners to become ZIF members. |
| планирование | пассивное | information sessions to present the ZIF plans (PGF and PEIF). |
| выполнение | интерактивное | management activities can be made by the land owners or by the ZIF management entity. Regular meetings with ZIF members |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | not defined yet |
| Research | интерактивное | on-farm research, good practice demonstration and collaboration with research projects. |
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
Описание:
Legal process related with the ZIF constitution (blue)
Elaboration and approval of the ZIF plans (orange)
Implementation of the plans (orange)
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
Users’ perceptions and expectations were also considered.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by SLM specialists alone (top-down)
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
- opinion leaders
Рассматриваемые темы:
information sessions and individual contacts with opinion leaders
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Описание/ комментарий:
Name of method used for advisory service: Information sessions; Key elements: ZIF process, Explaining rational of ZIF for specific municipality and its conditions like depopulation, forest fires, etc, Elaboration of the ZIF plans; The extension system is well set up to ensure follow-up activities
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, существенно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Подробнее:
City council supports the forest association activities.
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Комментарии:
There were None changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: (* The monitoring procedures are not structured yet)
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- социология
- экономика / маркетинг
- экология
- forestry, politics
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
The approach includes technical and local knowledge. The idea was prepared and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries and legislated by the Law n. º 127/2005, 5 August.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- > 1 000 000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Permanent Forest Fund): 100.0%; local community / land user(s) (ZIF implementation activities: National Strategic Reference Framework (60%), Land users (40%))
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- оборудование
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| Printer, toners, map production | профинансированы полностью | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
Landowners can work on their properties or can be substituted by the ZIF management entity. Some activities, such as the implementation of the Primary Strips Network System for Fuel Management can be supported by the municipality services.
1-technical, fully financed (FFP).2- preparation of PGF,partly financed. 3-implementation,partly financed.
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Reduction of the number and likelihood of forest fires.
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
It is expected that the increase in land productivity through the implemented technologies will help to improve the socio-economic situation of these rural groups.
Сумел ли Подход разрешить правовые проблемы землевладения/ землепользования, препятствующие использованию технологий УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The initial social resistance to the approach will diminish through the existence of a successful ZIF.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
It is expected that the implementation of this approach will contribute to the improvement of rural socio-economic conditions through productivity increase, creation of employment and promotion of local products.
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- нормативно-правовое регулирование (штрафы)/ контроль
- причастность к движению/ проекту/ группе/ сети
- aesthetic
- forest fires
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- нет
Если нет или нет уверенности, объясните почему:
The forest owners do not have the financial capacity to apply and support these activities by themselves.
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Social conscience (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: through awareness campaigns and information sessions provided at national and local level.) |
| Prevention of forest fires (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: the increase of forest management will contribute to the decrease of large forest fires. The implementation of integrated and global measures to fire prevention will be suitable within the ZIF approach.) |
| Restoration of burnt areas (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The use of forest species to enable the protection and recovery of degraded soils or soils with high erosion risk has a very positive influence on the rehabilitation of burnt areas. However, many of these species are not economically attractive at short or medium term. The management of the land using ZIF model will allow the definition of the most affected areas for an urgent intervention.) |
| Increase productivity (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: present land tenure and structure of forest holdings constitute a bottleneck for forest productivity. The integrated management of the ZIF will allow a better management and use of the land, increasing the exploitation of timber and non-timber products and also increasing the resilience to wildfires.) |
| Improve forest management (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: promotion of the planting of more fire-resilient species which are better adapted to the local conditions. AFN should: (i) provide information about the guidelines; (ii) develop new policies and tools, which are more suitable to the local level; (iii) support and implement public awareness campaigns about forest values and services, and (iv) provide financial support to ZIF constitution and implementation activities.) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Unattractive investment (low public support and lack of private support) | the need to review and reform the existing QREN or provide others means of support. Incentives to private initiative or donors should be found. |
| Highly bureaucratic nature of the ZIF approach | simplification of the bureaucratic process |
| Rather complex process: unclear role for the non-adherent landowners within the ZIF; ZIF has to follow many laws and plans; control and monitoring activities still not defined | clarification and simplification of the bureaucratic process of the ZIF |
| Costs related to the approach | major financial support from the government needs to be provided. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Decree- Law 127/2005, 5 August. Official Gazette n. 150 - I series A.: 4521-4527Decree-Law 15/2009, 14 January. Official Gazette n. 9 - I series: 254-267AFN (2011). Caracterização das Zonas de Intervenção Florestal. Lisboa, Autoridade Florestal Nacional: 54
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей