Soil pH management [Великобритания]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Tandra Fraser
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2615 - Великобритания
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Tibbett Mark
m.tibbett@reading.ac.uk
University of Reading
Reading RG6 6UA
Великобритания
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
University of Reading (University of Reading) - Великобритания1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
03/05/2016
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
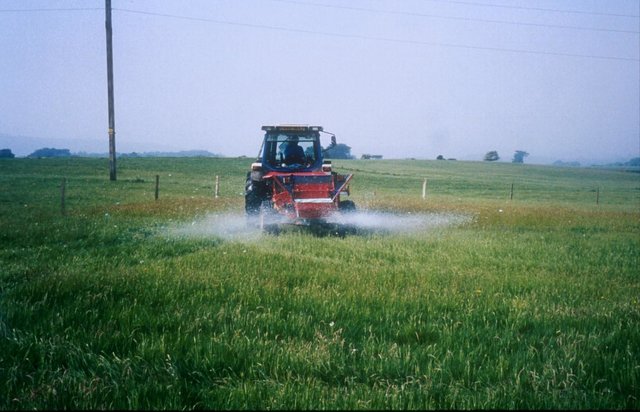

Soil pH management [Великобритания]
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to a semi-natural state
- Составитель: Tandra Fraser
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to low-intensity grazing land
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Aims / objectives: To convert the area from intensive pastureland to a semi-natural state with low intensity grazing through alteration of the soil pH. This change in land-use should have a positive effect on both above- and belowground biodiversity.
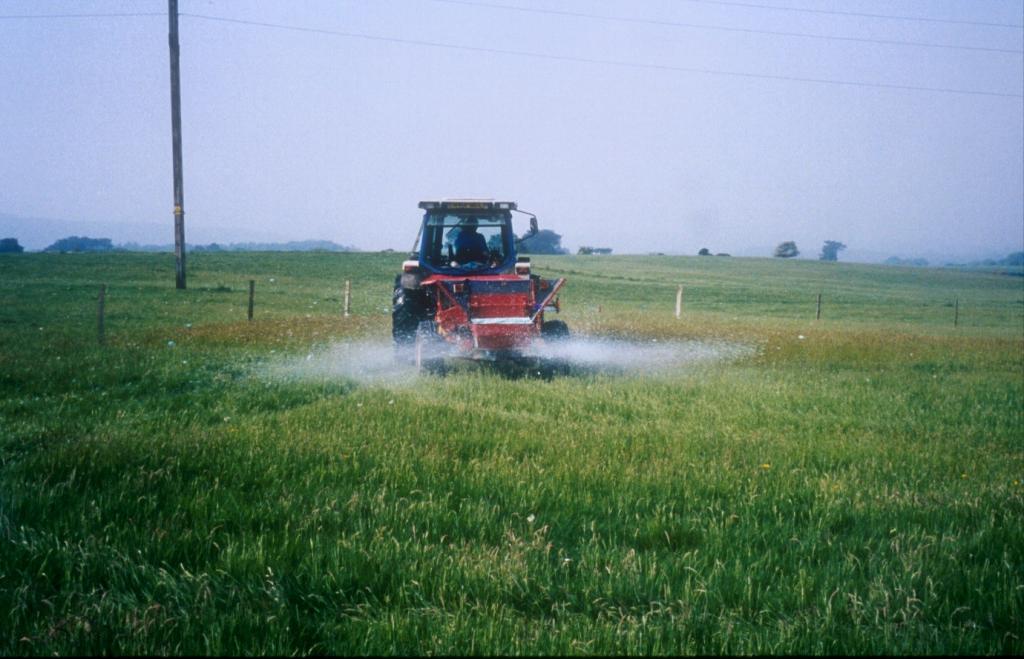
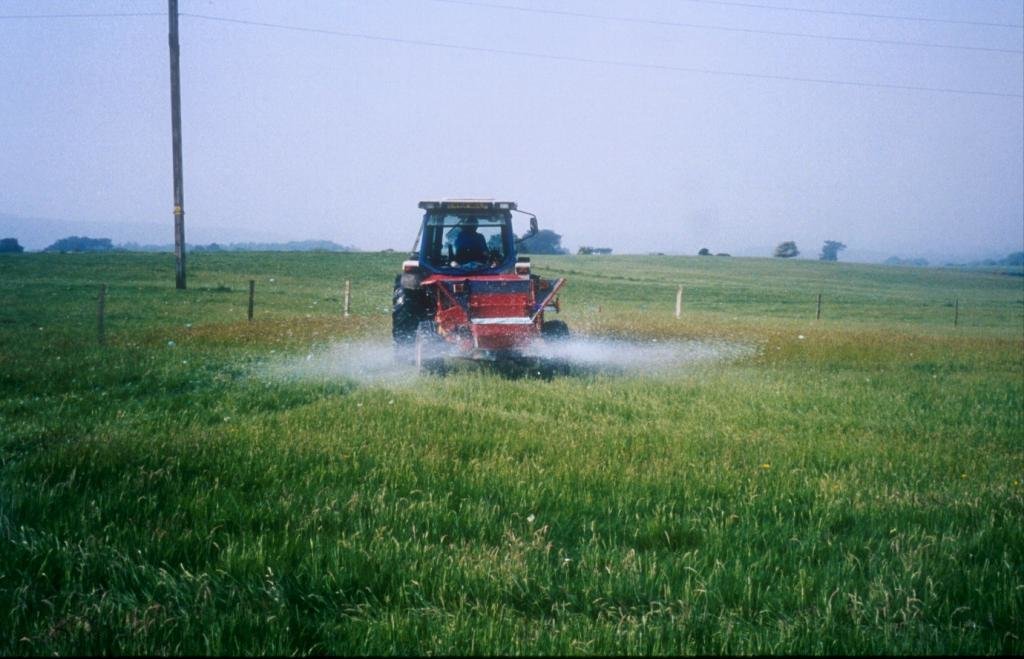
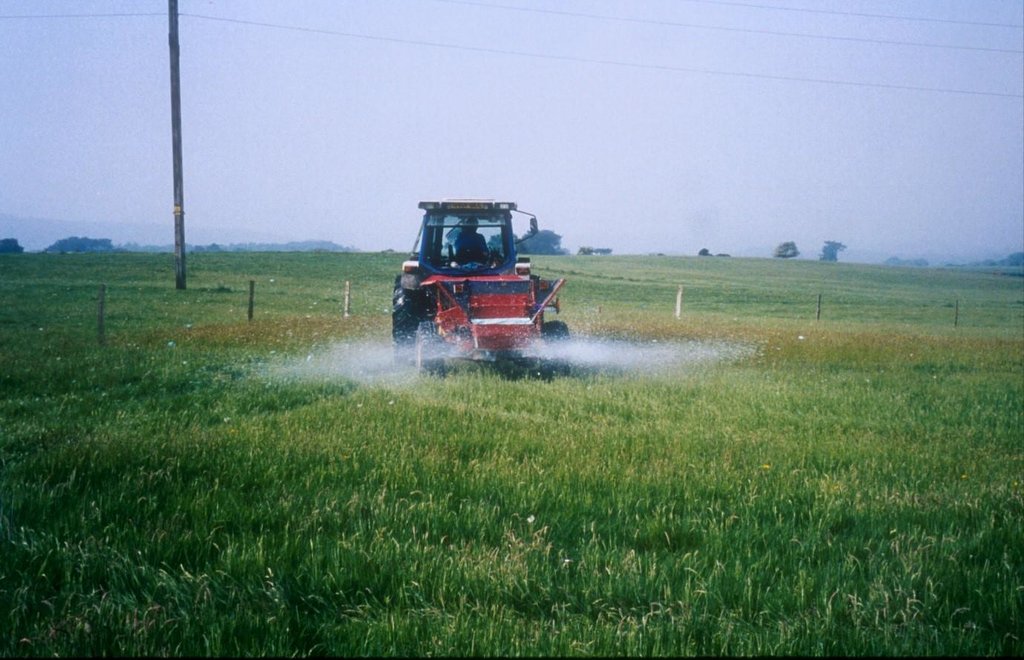
Methods: Plots were established on two adjacent farms owned by National Trust near Wareham, Dorset (Newlines Farm and Hartland Farm). A control and two sulphur amendments were compared on plots on ten fields (five from each farm) on 50 m x 50 m plots. Elemental sulphur (Brimestone 90TM) or ferrous sulphate (Mistrale “Wet Copperas” 50TM) were applied at equal rates of 2000 kg ha-1 in May 2000 and a second application of 1600 kg ha-1 in March 2001.
Stages of implementation: Treatments were applied in 2000 and 2001. Periodic monitoring has been conducted to monitor changes in plant diversity and soil chemical and biological properties.
Role of stakeholders: Stakesholders played an active role in identifying management options and implementing the technology. When the original plots were established, a charitable organisation was the primary stakeholder. For the intent of the current project, other stakeholders became involved, including parish council, landowners, and conservation organisations.
Other important information: Acidification treatments were applied to plots on the Isle of Purbeck that had previously been used for arable production and then high intensity grazing. The site is located on acidic fluvially-deposited soil and was in lowland heath until the middle of the 20th century at which time the land was tilled and treatments of rock phosphate, marl and chalk were added to increase soil pH and nutrient availability and improve the potential of the land for agricultural production.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Великобритания
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Dorset
Более точная привязка места:
Wareham
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
1999
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (soil, pH, below-ground biodiversity, low-intensity grazing)
To manage soil pH change and associated effects on above and below-ground diversity and function
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Management of soil pH and land use change to less intensive system
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Социальные/ культурные/ религиозные нормы и ценности
- затрудняют
Local confusion about land use change
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Public workshop explained reasons to stakeholders
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
Loss of earning as less intensive system is less productive
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Ecological benefits balance against economic losses
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- содействуют
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The land where the approach was implement was managed by National Trust UK who had a special interest in reclamation and conservation.
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
- общественные организации
- международные организации
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | внешняя поддержка | Land owners who acquired national support |
| планирование | внешняя поддержка | By specialist |
| выполнение | интерактивное | By land owner and specialist |
| мониторинг/ оценка | внешняя поддержка | By Specialist |
| Research | внешняя поддержка | By specialist |
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Укажите, кто проходил обучение:
- землепользователи
- местный персонал/консультанты
Тип обучения:
- обмен опытом между фермерами
- общие собрания
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- на полях землепользователей
- Public meetings
Описание/ комментарий:
Advisory service was not foreseen for this approach
Advisory service is totally inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; No additional government funding has been acquired.
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- нет
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
area treated aspects were regular monitored through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- экология
- технология
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
Research on the approach has been carried out by specialists at Bournemouth University and the University of Reading, UK.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 10000-100000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Department of Environment, Food & Rural Affairs): 50.0%; national non-government (National Trust): 30.0%; other (University): 20.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- сельскохозяйственные
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental S, Ferrous Sulphate | профинансированы полностью | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Conversion to low input system
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Other farms
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Enjoyment of traditional landscape
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- снижение объёма работ
- материальное стимулирование/ субсидии
- экологическая сознательность
- улучшение эстетической привлекательности
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- да
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Decreased spending on inputs where the only input in the system in dung from cattle grazing (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue grazing at a low enough density to allow adequate plant regrow) |
| Decreased labour required for management |
| Decreased compaction since regular use of tractors on site is no longer required (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Attempt to minimizing compaction by grazing livestock) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| The conversion in land use from a improved agriculture to a semi- natural low input grazing system should have a positive effect on above- and belowground biodiversity. |
| Considering that the Isle of Purbeck was historically a region of cultural importance, returning the system to a more natural state has important implications for the cultural and recreational value of the land. |
| Low input systems can increase resilience of the system to global change |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Fertilizer application rate too high for one application | Smaller, regular additions over several years |
| Decrease in economic returns | |
| Shrub encroachment (i.e. gorse; Alex europaeus) can be a problem when converting to low input pasture land in this region. | Grazing, mowing, and chemical herbicides are some options for slowing invasions. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Over time nutrients are being drawn down but exporting meat off the land with no inputs | Periodic applications of nutrients may be required to ensure long-term fertility of the system |
| Land use change and restoration are slow process and may result in economic losses on managed lands |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Re-creation of heathland on improved pasture using top soil removal and sulphur amendments: Edaphic drivers and impacts of ericoid mycorrhizas, Diaz, A., Green, I., Tibbett, M., 2008Heathland restoration on former agricultural land: Effects of artificial acidification on the availability and uptake of toxic metal cation, Green, I., Stockdale, J., Tibbett, M., Diaz, I., 2007Are sulphurous amendments an effective tool in the restoration of heathland and acidic grassland after four decades of rock phosphate fertlization, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2005The restoration of heathland and acid grassland at Hartland and Newline Farms, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2001
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Biological Conservation, 141:1628-1635, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006320708001353Water Air Soil Pollution, 178:287-295, http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11270-006-9197-8Restoration Ecology, 13:83-91, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00010.x/epdfFirst Year Report to National Trust, Purbeck
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Heathland restoration on former agricultural land: Effects of artificial acidification on the availability and uptake of toxic metal cation, Green, I., Stockdale, J., Tibbett, M., Diaz, I., 2007
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Water Air Soil Pollution, 178:287-295, http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11270-006-9197-8
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Are sulphurous amendments an effective tool in the restoration of heathland and acidic grassland after four decades of rock phosphate fertlization, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2005
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Restoration Ecology, 13:83-91, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-100X.2005.00010.x/epdf
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
The restoration of heathland and acid grassland at Hartland and Newline Farms, Tibbett, M., Diaz, A., 2001
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
First Year Report to National Trust, Purbeck
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Soil pH management [Великобритания]
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to a semi-natural state
- Составитель: Tandra Fraser
Модули
Нет модулей