Agro-forestry [Индия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Unknown User
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Fabian Ottiger
Kaadu, Vilai, Thottam (Tamil)
technologies_1083 - Индия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
27/02/2003
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
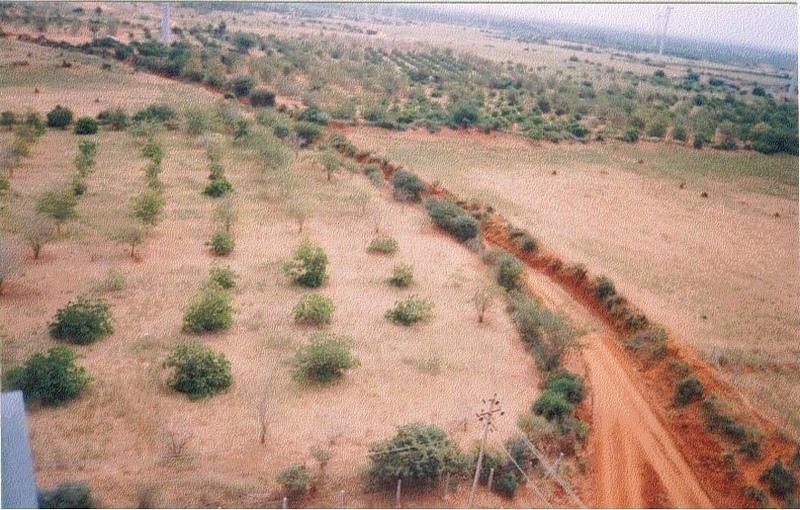
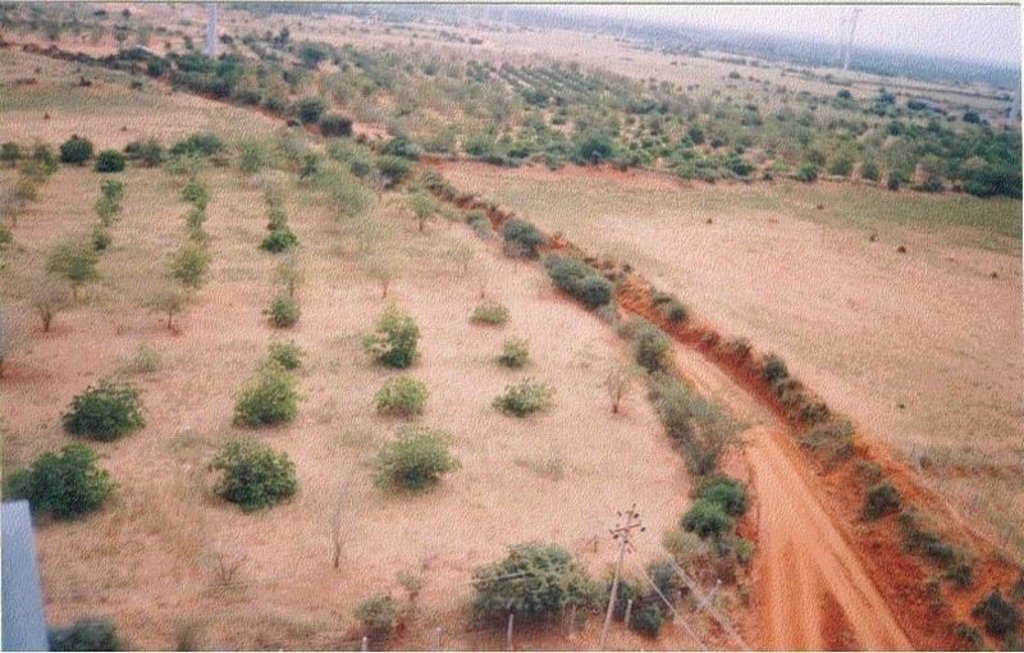
Development of degraded lands through plantation of productive tree species for long term benefit (conservation and economic) and cultivation of intercrop for short term benefit.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
The technology can be described as a combination of tree cultivation ( mainly horticulture species) along with intercrop of pulse crops on degraded private lands, supported by in-situ measures for soil and water conservation. The supportive technology required is provision of water for protective irrigation during establishment phase.
Purpose of the Technology: the technology serves the folowing purposes 1. Short and long term economic benefits to land owners 2. Employment generation leading to reduced migration 3. Conservation of soil and water through vegetative and mechanical measures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: 1. Community organisation, formation of Village Development Association, Identification and training of beneficiaries 2. Delineation of micro-watersheds and plantation blocks. 3. Establishment of farmers's nurseries 4. Land preparation, sinking bore-well, plantation and inter-cropping 5. Watch and ward.
Natural / human environment: The environment is semi-arid, drought prone and subject to wind erosion. Soil depth is good.
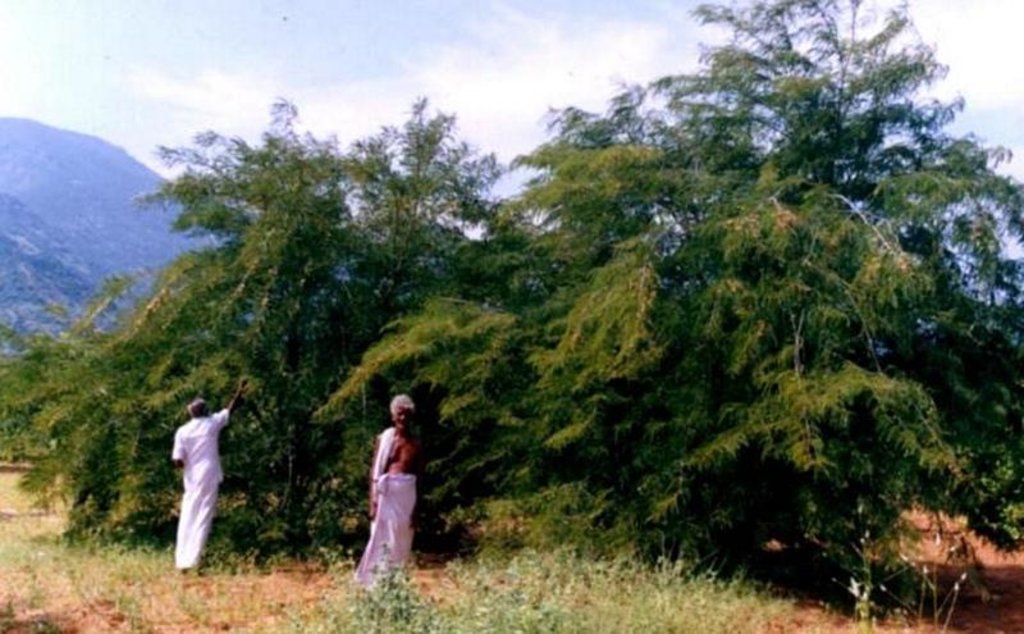
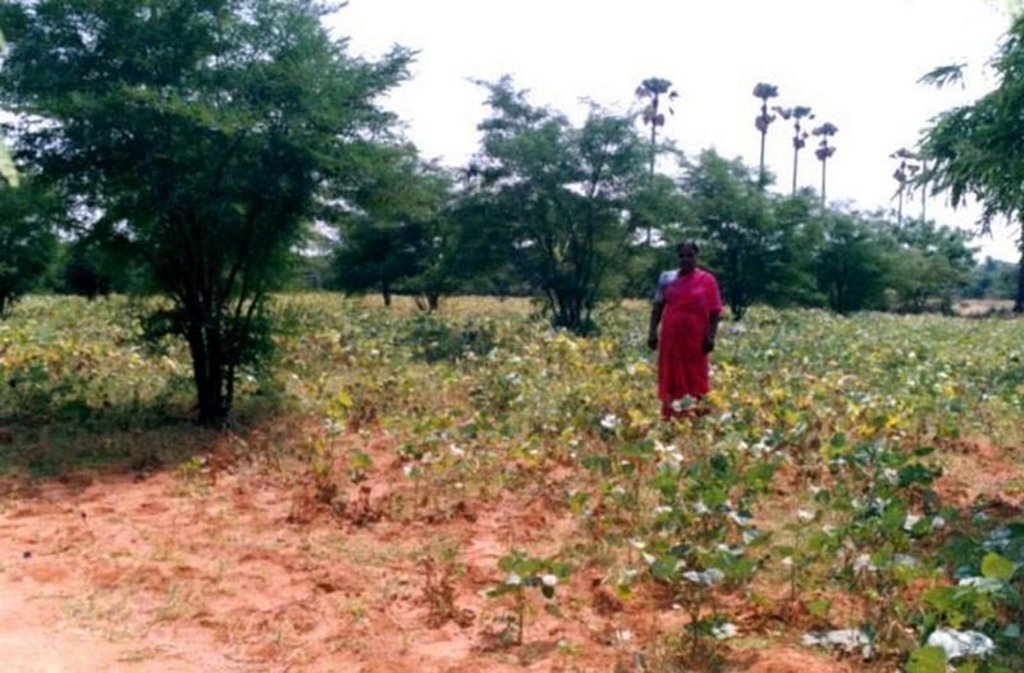
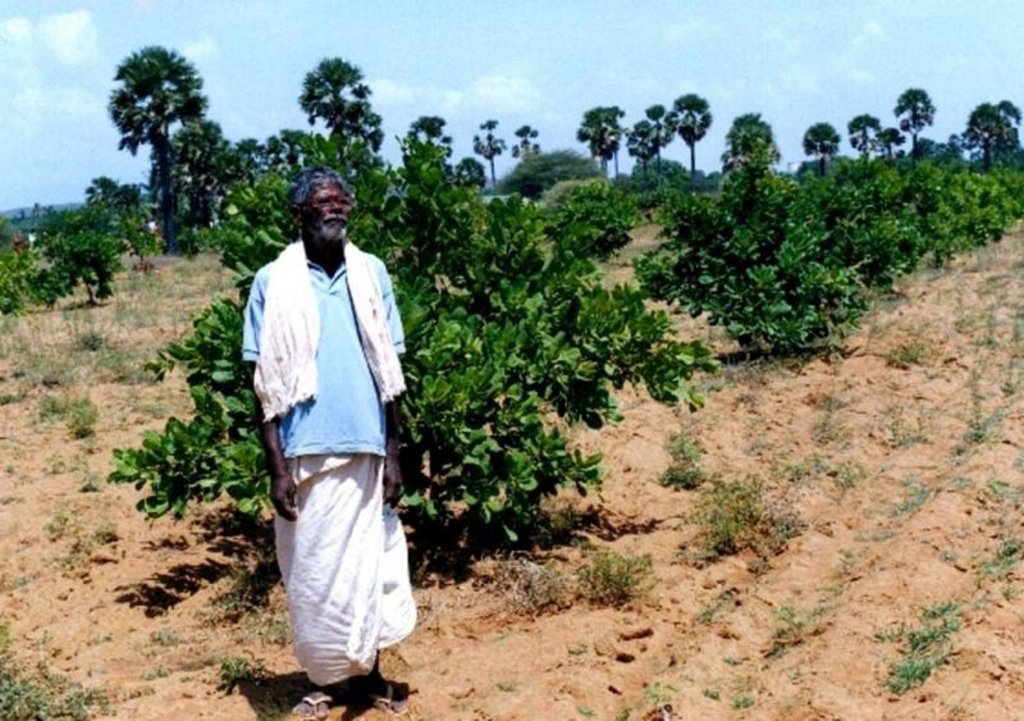
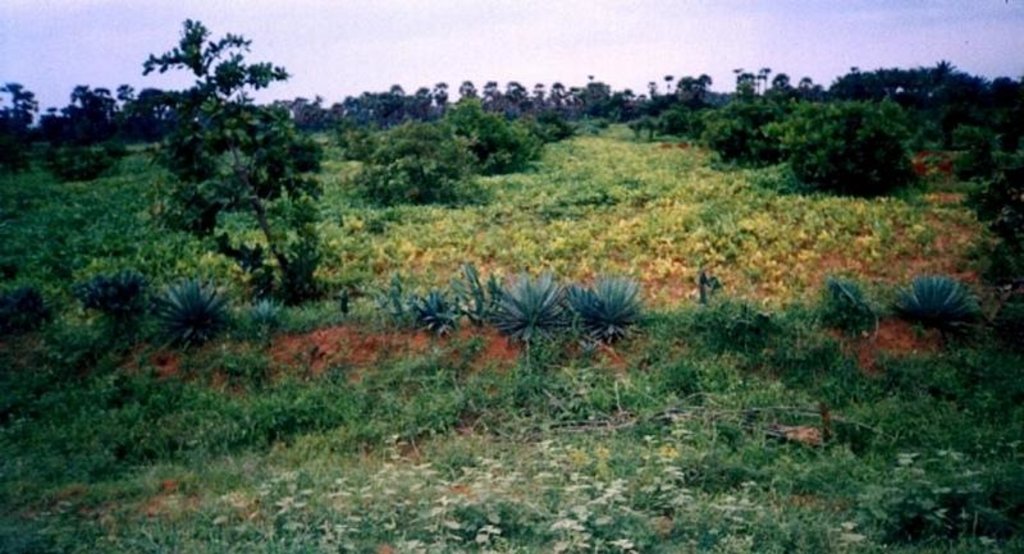
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Индия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Tamilnadu
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- более 50 лет назад (традиционная)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The technology evolved out farmers suggestions and project experiences while implementing the shelter programme to combat wind erosion.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Смешанное землепользование (пашня/ пастбища/ лес), включая агролесоводство
- Агролесоводство
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Uncontrolled grazing on un-cultivated lands, abandonment of fields by poor farmers due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Crop lands are not economocal to cultivate due to recurrent crop failure as a result of drought. This has lead to abandonment of fields and increase in numbers of small livestock which are left free to graze.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The area is single cropped and hence only one food crop is taken per year.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jan
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- агролесоводство
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.83 km2.
The area is predominantly degraded land affected by wind erosion. The annual rainfall is <600 mm, however distribution is erratic resulting in drought conditions. People are mostly small farmers engaged in rainfed agriculture, however large areas have been abandoned due to frequent crop failure. The technology has been applied in a gross area of over 300 sq.km.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
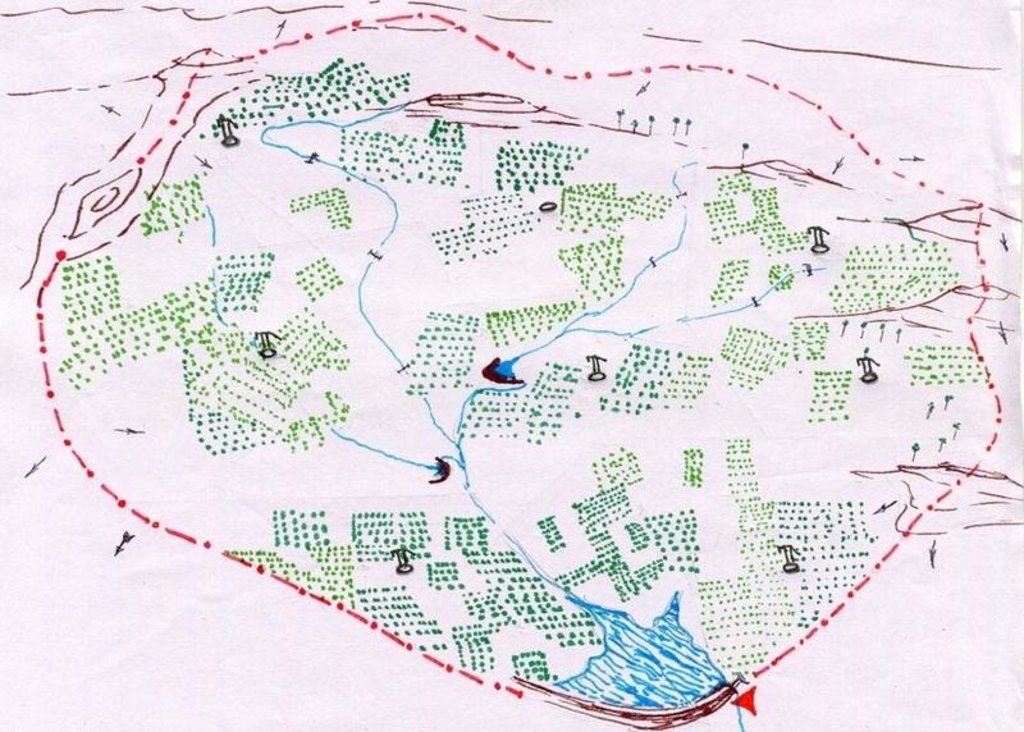
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Technical Drawing Agro-forestry
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: trees + legume crops
Quantity/ density: 125 trees/
Remarks: Block plantation/ intercorp
Mulching
Material/ species: soil mulch
Quantity/ density: 125 basins
Remarks: 1 m. diameter basin per tree
Agronomic measure: vegetative hedges
Material/ species: agace, euphorbia sp.
Quantity/ density: 15 cm. Spa
Remarks: Along field boundries
Pits
Remarks: 125 pits/ha., 9 m. spacing. 45*45*45 cm for local species & 60*60*60 cm for grafts.
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: disc ploughing before pitting in first year, tiller ploughing annually at sowing of intercorp..
Trees/ shrubs species: Azadirachta indica, Albizia lebeck
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Anacardium occidentale, Tamarandus indicus, Emblica officianalis, Mangifera incica
Other species: Phaseolus mungo, Arachis hypogea
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
Change of land use type: open grazing, cropping to agro-forestry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: open access to protected
Layout change according to natural and human environment: borewell blocks formed as per human environment but within watershed boundary.
Control / change of species composition: scrub clearance followed by plantation of agro-horticulture species.
Other type of management: VDA established - to manage all activities at village level
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Indian Rupee
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
48,85
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
1.00
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | May - Nov |
| 2. | Planting in pits | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Oct -Dec, onset of monsoon |
| 3. | Life watering | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | immediately after plantation |
| 4. | Planting of vegetative hedges | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Oct - Dec |
| 5. | Sowing of intercrop (broadcasting, dibbling) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Premonsoon-groundnut, monsoon-legumes |
| 6. | Application of FYM to intercrop | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | September during tiller ploughing |
| 7. | Selection of village as per criteria | Управленческие | Mar/Apr, dry season |
| 8. | Rapport building, awareness generation | Управленческие | |
| 9. | VDA formation | Управленческие | April / May |
| 10. | Development of watershed plan including agroforestry | Управленческие | May / June |
| 11. | Trainings for VDA, farmers, nursery etc. | Управленческие | Jun - Aug |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | scrub clearance | Агрономические | Sept/Oct,dry season / once before planting |
| 2. | deep ploughing | Агрономические | Oct/Nov,onset of monsoon / once before planting |
| 3. | pitting | Агрономические | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 4. | manuring | Агрономические | Oct/Nov / once before planting |
| 5. | filling pits, planting, forming basins | Агрономические | Nov / once before planting |
| 6. | life watering | Агрономические | Nov / after planting |
| 7. | tiller ploughing & sowing | Агрономические | Oct/Nov / annually after onset of monsoon |
| 8. | maintenance of tree basins | Агрономические | Oct / after annual tiller ploughing |
| 9. | Periodical watering | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | dry months 1st year /weekly |
| 10. | Weed removal | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Nov / Dec /once during annual crop |
| 11. | Application of pesticides | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Dec - Feb /as necessary |
| 12. | Pruning | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Nov /annually |
| 13. | Casualty replacement | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Nov /One year after plantation |
| 14. | Monitoring by VDA | Управленческие | - / monthly |
| 15. | Hand pump maintenance | Управленческие | / as required |
| 16. | Protection against animals | Управленческие | Year one / full time |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
Пояснения:
- The costs were calculated for establishment of one block (average area 12.5 ha.) of horticulture plantation with project support. The agriculture component was implemented by farmer with project support for seeds during first monsoon and tiller ploughing during second monsoon.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
- Establishment of the technology requires high labor input, specially for watering and watch & ward, which adds significantly to the cost. - Presence of hard pan necessiates deep ploughing with machinery. - Horticulture tree species were selected over forest species.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
680 mm, however the rainfall over the past few years has been < 500 mm.
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Since past few years arid conditions prevail in the area
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms: Plateau/plains (level lands lying between hill slopes of Western mountain range & East coast of south India.)
Slopes on average: Flat (level land with some gullies passing through (originating in upper hilly area))
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1) and deep (ranked 2, patches of deep soil)
Soil texture: Medium (sandy loam)
Soil fertility: Medium (loss of top soil due to erosion)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (originally low before agro-forestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration level: Medium (presence of hardpan below six inch depth. However, no waterlogging is observed due to runoff.)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (has improved due to deep ploughing post treatment)
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
- средний
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
11% of the land users are rich and own 18% of the land (large holdings > 2 ha.).
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (holdings of 1 to 2 ha.).
39% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (holdings < 1 ha.).
Off-farm income specification: Off farm sources are; poor - rolling beedis (locally made cigarettes), daily wage labor in fields and brick kilns. Average / rich; Business, livestock.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (ranked 1, pitting, planting, watering, cultivating, watch and ward), mechanised (ranked 2, deep ploughing, tiller ploughing, drilling borewell) and animal traction (ranked 3, ploughing)
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо отрицательное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо отрицательное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Пояснения:
99% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
284 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are purchasing seedlings for plantation on their fields in small patches around existing water sources - Farmers who did not participate initially are now expressing a desire to treat their lands under the project.
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Review reports.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Project Implementation Plan. 2001.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Participatory Impact Evaluation. 2001.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей