Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough [Танзания]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Alexandra Gavilano
elyeshero ne elyato (Haya tribe)
technologies_1157 - Танзания
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF для вывода на печать
- Полная аннотация в формате интернет-страницы
- Полная аннотация (неотформатированно)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 29 декабря 2016 г. (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 5 июня 2017 г. (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 28 июня 2018 г. (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 6 августа 2019 г. (public)
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
government:
Kagaruki Annagrace
Misseny District Council
Специалист по УЗП:
government:
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - ТанзанияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Италия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
28/08/2012
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Construction of indigenous water pond and a livestock watering trough along an underground water source.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
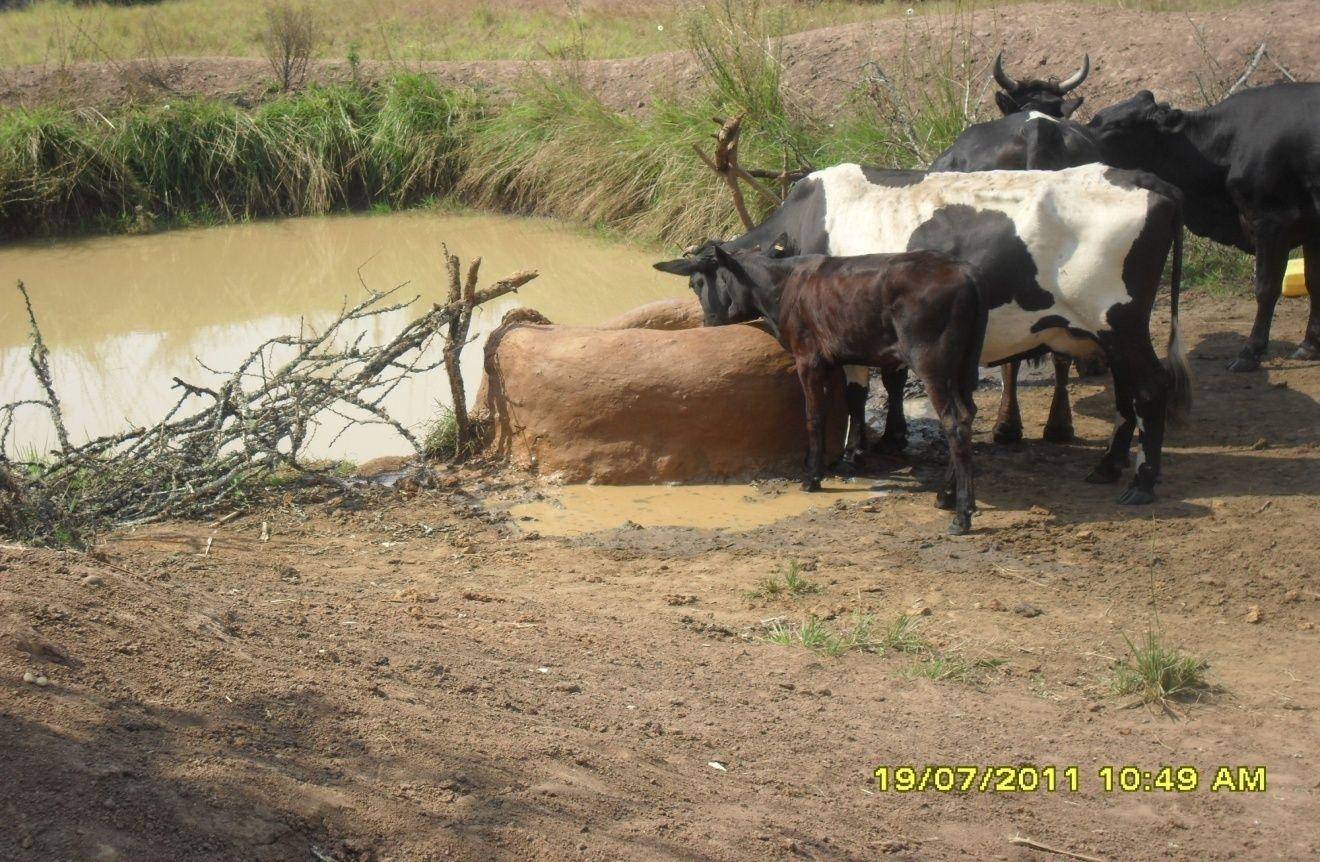
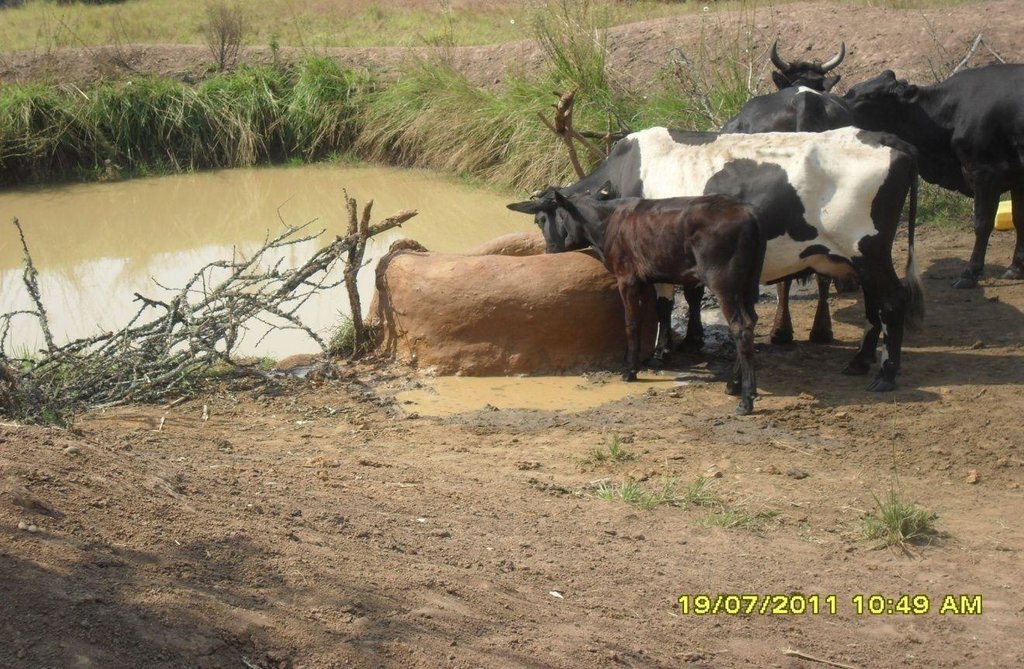
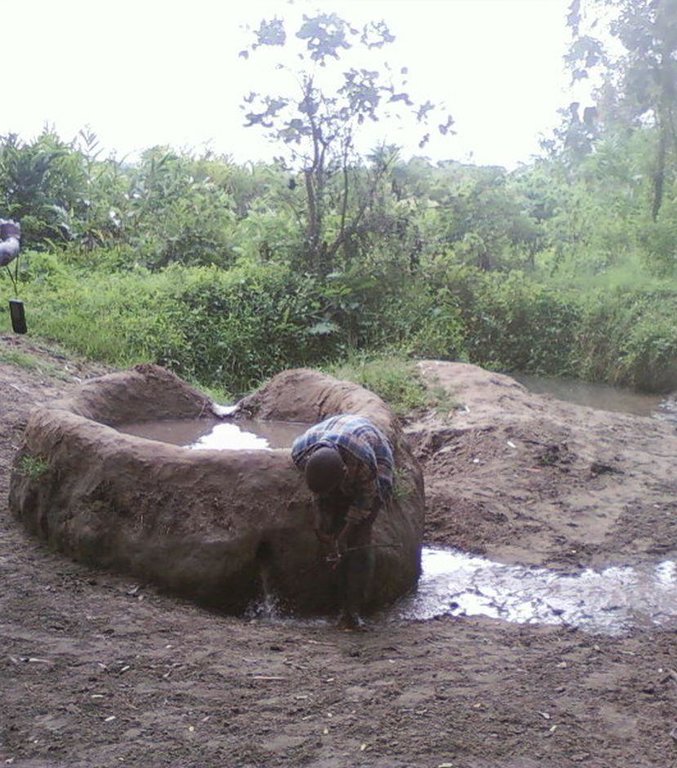
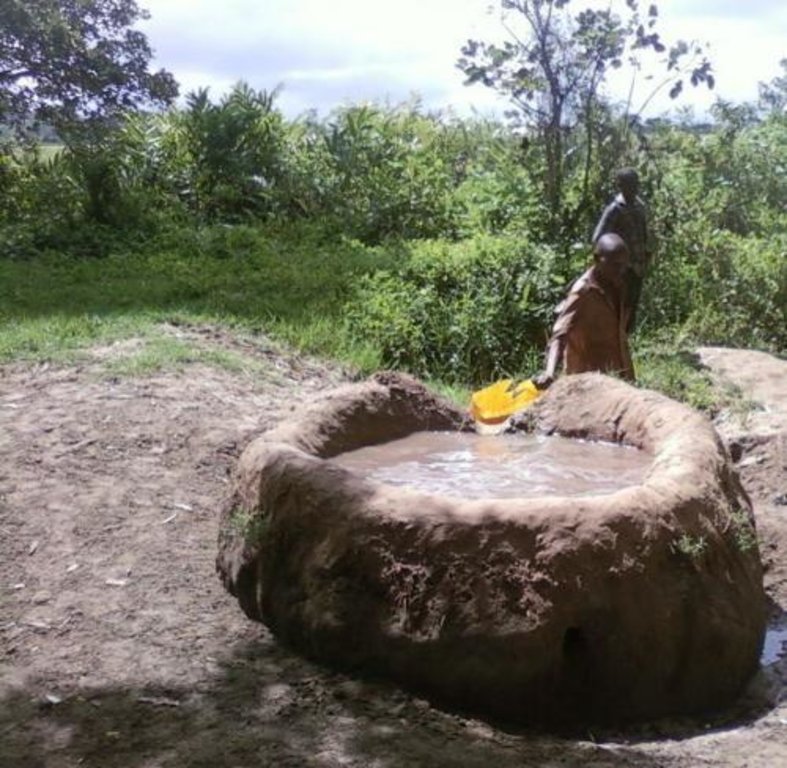
This technology is used during the dry seasons and where ground water level is high and there is natural water stream flowing from underground water source. Water pond is excavated along the naturally flowing water stream and is recharged by natural ground water. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available, groundwater table, slope and soil characteristic. Groundwater collection ponds described in this technology on average are 4m long, 3m wide and 1m deep of 12m3 (12 000 liter) capacity and the slope is moderate 5% to 8% and soil characteristics is clay loam with deep soil. Water troughs (Elyato by local name) are constructed adjacent to the water pond to allow livestock to access clean drinking water. The number of troughs per pond is usually 1 to 2. Materials used in construction of water trough include clay, red termite mound soil, grass and wooden poles. The number of ponds needed usually depends on the expected number of animals and are arranged at irregular intervals ranging from 10 to 20 meters apart. The average size of a water trough is 0.14 m3 and can cater for 5 cattle at a time. The Pond is stabilized by naturally growing grass on its banks. Common pond stabilizer species are Leodicatiar digitalia and Hyperrhenia rufa. Management of the natural water source is through preventive village/customary by-laws which prohibit tree and grass cutting around the water source. The dominant indicator tree species normally found are Erythrina abysinica, Ficus thorgii and Phoenix recrinata. The animal watering troughs are usually used in the dry period. Before watering the troughs are coated (smeared) with red termite mound soil (normally hand carried by herders) to provide a good taste which is attractive to animals. Water is transferred from the pond to the water trough manually using cans or buckets. Animals drink directly from the troughs. This water from the trough is rich in iron (Fe) from red termite mound soil. The troughs are constructed with outlets used to spill out water immediately after drinking in order to prevent their damage through excessive water saturation.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is preferred by livestock keepers as it provides for animals to drink clean and mineralized water and for health improvement. User fee payed to land owners also enable them to expand and diversify there income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment: Land clearing, excavation and shaping of water pond and construction of animal watering trough.
Maintenance: repair of water pond and water trough (de-siltation, grass slashing and gap refilling).
Inputs: labour, implements (machete, spade, hand hoe, sickle), clay, red termite mound soil, wooden poles, buckets, grass and tying rope. Average establishment cost for one pond and its water trough is 41.27 American dollars. Average annual maintenance and recurrent costs (filling and emptying of water trough) for one pond and its water trough stands at 458.76 dollars and labour is a core cost determinant factor.
Natural / human environment: Natural environment: Extensive grazing land. The technology is largely structural (excavation and shaping of water ponds and construction of water troughs) supported by the use of by-laws which prohibit destruction of the protective natural and indicative trees and grasses around. The technology is common in sub-humid climatic zone.
Social economic environment: Level of mechanization is handy tools with subsistence production systems on individual fields.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Танзания
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Tanzania
Более точная привязка места:
Missenyi District (Minziro)
Пояснения:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.11472, 31.655 ; -1,09972, 31.70194
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- более 50 лет назад (традиционная)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как часть традиционной системы землепользования (более 50 лет назад)
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
the technology has been in use for about 80 years ago
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пастбищные угодья
Пастбищные земли, экстенсивный выпас:
- Полукочевое/ отгонное животноводство
Основные породы скота и виды продукции:
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cattle, goats and sheeps

Смешанное землепользование (пашня/ пастбища/ лес), включая агролесоводство
- Агро-пастбищное хозяйство
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Eutrophication, siltation, water shortage, deforestation and wildfire outbreaks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Drying of the underground water source.
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September to DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
Поголовье скота на единицу площади (если применимо):
10-25 LU /km2
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
Пояснения:
The area is owned by individual farmer. The area is found adjacent to extensive grazing land. Water table is high and there is a permanent underground natural water flows.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения

инженерные мероприятия
- И11: Другие

управленческие мероприятия
- У7: Другие
Пояснения:
Specification of other structural measures: water collection pond and animal watering trough
Specification of other management measures: protect water source enclosure by naturally regenerating vegetation
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова

деградация водных ресурсов
- Взп: снижение качества поверхностных вод
Пояснения:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (cutting of natural tree and removal of grass along the natural water flow way), overgrazing (Compaction by trampling animals, rainfall runoff, siltation of water collection point and disapearence of vegatative cover.), discharges (point contamination of water) (spoilage and contamination of surface water by human and livestock feaces.), population pressure (Overstocking due to increase in the number of livestock), poverty / wealth (low capacity to invest in enviromental friendly energy sources), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Unavailable improved and reliable water ponds and animal watering troughs), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited knowledge on sustainable use of natural water sources), governance / institutional (limited enforcement of existing environmental regulatory systems.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (excavation and layout that contradict the natural environment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fire wood collection from the natural water source), industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, labour availability, war and conflicts
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
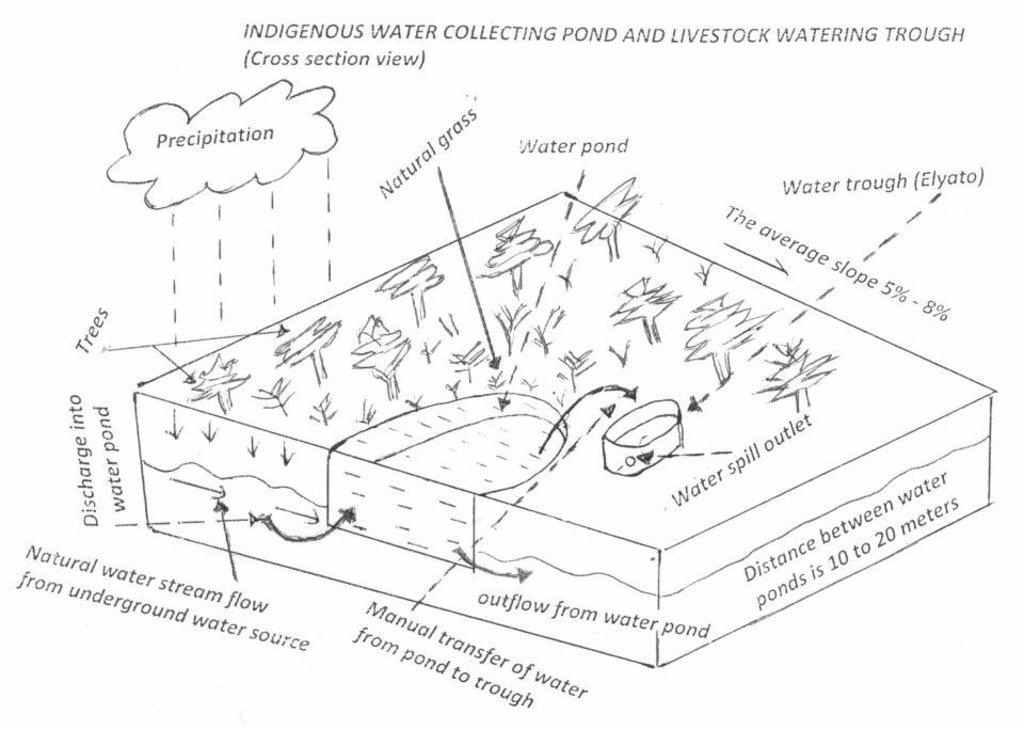
Water pond and water trough cross section view.
The water pond has an average internal capacity of size of 12m3 (4m length, 3m width and 1m depth).
Water troughs are constructed on the side of the water ponds. The water trough outside height is 0.2 - 0.4m above ground, inner depth is 0.5m, and diameter varies from 0.6 to 1m. It is made of cylindrical walls whose average width is 0.1m.
The average slope of the water catchment is 5% to 8%.
Location: Minziro village, Minziro ward, Missenyi division. Missenyi Dist, Kagera Reg, United Rep of Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (At least primary school leaver with the basic indigenous technical knowledge.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 10 to 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Structural measure: water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): mostry used clay soil and red termite mound soil.
Construction material (wood): for water pond and trough stabilization
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10.6m3
Catchment area: 4 acresm2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:4
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Tanzanian shillings
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
1600,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
3.13
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for pond excavation | Инженерные | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of pond | Инженерные | During dry period |
| 3. | Construction of water trough | Инженерные | During dry season |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | pond | person/day | 1,0 | 23,13 | 23,13 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | water trough | day | 1,0 | 3,13 | 3,13 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | pond | 1,0 | 12,51 | 12,51 | 100,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | wood | pcs | 2,0 | 1,24 | 2,48 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | earth | kg | 20,0 | 1,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 66,25 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiltation | Инженерные | During dry season |
| 2. | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | Инженерные | During dry season |
| 3. | Water trough repairing | Инженерные | dry season |
| 4. | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | Инженерные |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | maintenance | 1,0 | 444,38 | 444,38 | 100,0 | |
| Оборудование | tools | 1,0 | 6,88 | 6,88 | 100,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | wood | 1,0 | 3,75 | 3,75 | 100,0 | |
| Строительные материалы | earth | 1,0 | 3,75 | 3,75 | 100,0 | |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 458,76 | |||||
Пояснения:
The cost is calculated per one water pond and its one trough and as per 28 August 2012
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- влажная
- Умеренно-влажная
- полузасушливая
- засушливая
Thermal climate class: tropics. all months temperature is above 18
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
на поверхности
Доступность поверхностных вод:
хорошая
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода хорошего качества
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанное (самообеспечение/ товарное хозяйство
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: little involvement of women because at large/traditionally livestock rearing is done by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (the techology is used by rich and average livestock keepers who have the animal).
75% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (the village poors usually do not have the animals though most of them are cattle herders).
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- общинная/ поселковая
- индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
- индивидуальное
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство продуктов животноводства
разнообразие продукции
производство электроэнергии
Доступность и качество воды
доступность питьевой воды
Доходы и затраты
разнообразие источников дохода
экономическое неравенство
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
институты госуправления
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
количество воды
качество воды
сбор воды/ водоудержание
поверхностный сток
уровень грунтовых/ подземных вод
испарение
Почвы
влажность почв
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
разнообразие местообитаний
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
риск пожаров
скорость ветра
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
надежность и постоянство водотоков
подтопление ниже по течению
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
ущерб прилегающим полям
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | плохо |
| местные ураганы | хорошо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | плохо |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | не известно |
Пояснения:
Improving structure on the pond (use impermeable materials to prevent seepage, use concrete as a building material)
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
The technology requires low establishment and maintenance cost and benefit surpass the costs.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 10-50%
Пояснения:
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
All livestock keepers use the technology to water their animals voluntary and through self mobilization.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is cheap and requires low investment costs.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Income generation due to water use fee. How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve service to water users. . |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Reduce conflict between livestock keepers and domestic water users. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws reinforcement, Area enclosure and Demarcation |
|
Improve accessibility of water to animals (improved animal water intake) How can they be sustained / enhanced? sensitization on regular maintenance. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Not durable and requires frequent and regular maintenance | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| not durable | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| high labor demand to fill the troughs | Use simple leverage pump |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей