Soil productivity improvement and BXW control in epidemically affected banana zone [Танзания]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Ursula Gaemperli, David Streiff
technologies_1204 - Танзания
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Pesha
Kyerwa District Council
Танзания
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - ТанзанияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - ТанзанияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Kyerwa District Council - Танзания1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
25/07/2014
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Restoring banana production through temporal crop substitution and the use of SLM and recommended husbandry practices in controlling the deadly BXW disease.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
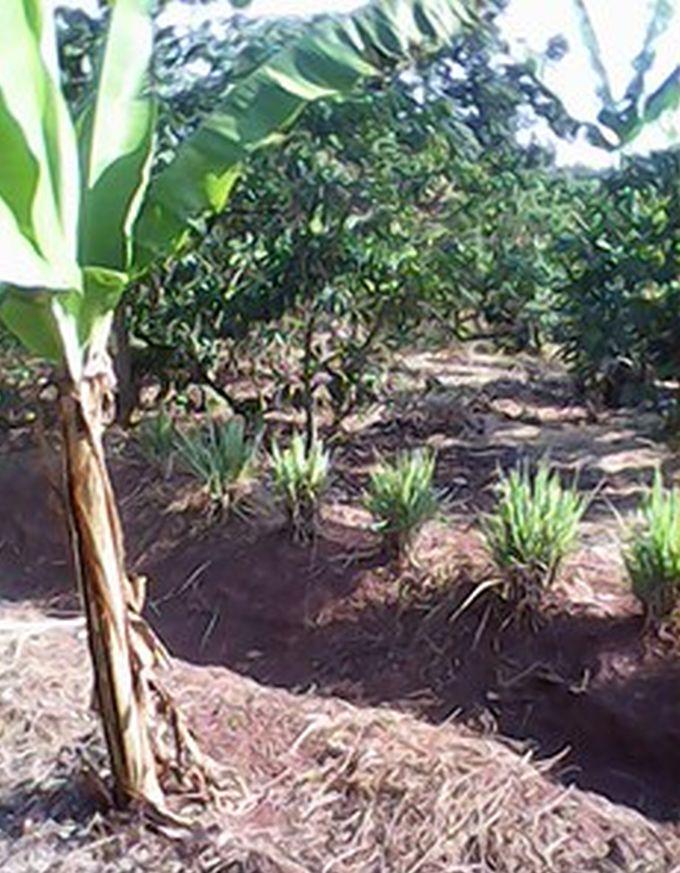
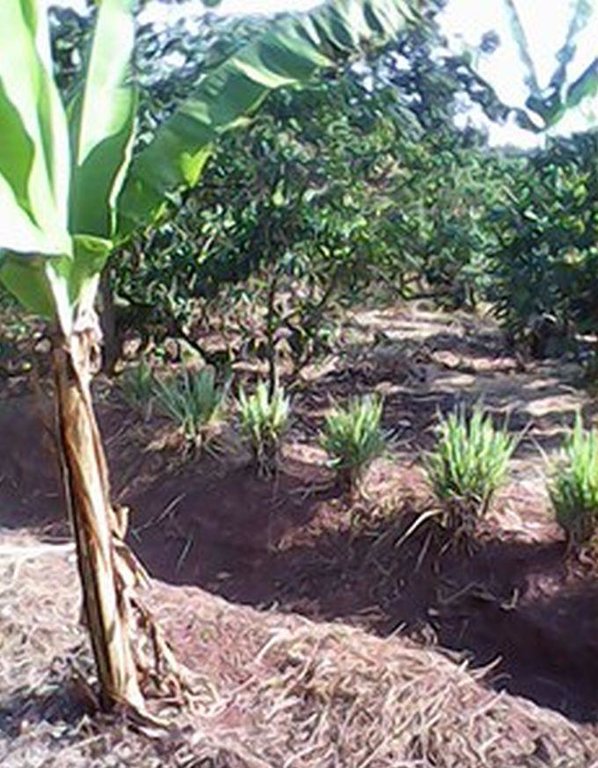
This conservation measure is used in BXW epidemically affected areas. Land users in affected areas are trained on the principle behind the diseases and means and ways to overcome it. Banana plants in seriously affected farms are uprooted and destroyed and non disease host crops usually maize and common beans are grown for starvation and destruction of BXW pathogen. The land is not used for banana production for a period of 6 months and instead substitute crops ensures food and income security to land users. Leguminous cover crops (beans) and crop residual management skills applied on the farm revitalize the soil health in terms of biomass, moisture and nutrient recycling. After 6 months, banana production is resumed where production is based on recommended husbandry practices combined with SLM conservation measures. The use of certified banana cultivars, optimal plant geometry and disease control cultural practices are some of the basic recommendation. Certified banana cultivars are planted at a space of 3m x 3m. The size of a hole used to plant banana is 0.9x0.9 m wide and 0.6 deep. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. 2 -3 tins of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The holes are left for microbial decay to take place and banana planting is done after 1 or 2 months. The tied Fanya chini water retention ditches are water harvesting and conserving structures constructed by digging trenches along the contour where dug soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. A-FRAME method is used to mark a contour line and on the other hand ARM OUTSTRETCHED LEVEL method determines how far apart the Fanya chini retention ditch should be. Unlike other retention ditches, the dug ditches are not continuous but instead are tied at regular interval with small cross–ties of 0.4-0.6m length. Ties intercept the ditch at right angle to form a series of narrow rectangular segments of infiltration ditches each of 5 meters long, 0.6m wide and 0.6m deep arranged in series within a contour line. Ties helps to prevent irregular flow of runoff and to ensure an evenly distribution of captured water. Fanya chini embankments are stabilized by planting crops on them the common crops are pigeon pea (space used between plant is stand is 1m x 1m), lemon grass (30cm x 30cm) or pineapples (60cm x 60cm). Mulching is done using grasses. The dominant grass species used is Hyperrenia rufa where a mulching depth of 15 cm is used.
Purpose of the Technology: PURPOSE: Improved food and fodder productivity, soil moisture and water holding capacity, nutrient recycling, and organic matter content, biomass cycle, crop tolerance to drought, income and food security, poverty reduction and health. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water, combating soil erosion by water runoff and biological degradation due the deadly BXW disease.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT: procurement and mobilization of working tools, uprooting and destruction of infected plants in affected fields, land tilling and harrowing, planting of alternative crops or creation of a productive disease free buffer zone, temporal harvesting of maize and beans, land preparation/ demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting, digging holes, manure application before planting, banana planting, demarcation of contour line for construction of Fanyachini contours with ties, digging and construction of Fanya chini contours with ties, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini bunds (using lemon grass, pineapples or pigeon pea), random planting of castor oil plants for future anchoring support of plants with heavy bunches and mulching application. MAINTENANCE: hand weeding to control noxious weeds combined with other pest and disease control (control of nematodes and weevils), de-suckering to leave the mother plant and two baby plants, de-trashing or trimming of unproductive leaves, regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector , recurrent manure application, removal of sediments and maintenance of Fanyachini bunds, harvest of bananas, maize, pineapples and pigeon pea. INPUTS USED: largely includes labour (strenuously varying from light, medium and heavy), tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock and A-frame), seedlings; improved or certified banana varieties, pineapples suckers, lemon grass and castor oil, seeds (beans, maize and pigeon pea), farm yard manure and mulching materials (preferably Hyperennial spps).
Natural / human environment: NATURAL ENV: The land use type is cropland with annual, perennial and some fruit tree crops. The technology involves a combination of agronomic, vegetative, structural and management conservation measures. Management measure involves all activities related to temporal shift to alternative crops for making the farm disease hot free and for staving and destroying the disease pathogen. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 days of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. A soil texture class is sandy loam with medium depth categories. HUMAN ENV: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market or commercial oriented). The average costs of inputs required is 3015.68 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Танзания
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Kagera Region Tanzania
Более точная привязка места:
Kyerwa District Council
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- более 50 лет назад (традиционная)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
This is one of the technologies tested and demonstrated under the support of the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project. Analysis and documentation of this technology is based on perspectives and experiences of field SLM specialist and FFS group members.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
major cash crop: Coffee and bananas
major food crop: Maize, beans, root crops and bananas
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land problems without land conservation are BXW disease, poor soil fertility, and moisture stress and soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): BXW disease.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Banana is the major food crop but in the recent years the crop was substituted by maize and beans due the out break of BXW.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Комплексная борьба с сельскохозяйственными вредителями и болезнями (включая органическое сельское хозяйство)
- crop substitution
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- 0,1-1 км2
Пояснения:
The area includes the totality of all farms of FFS members who applied the technology after being trained.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A1: Растительный/ почвенный покров
- A2: Органическое вещество/ почвенное плодородие

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения
- Р5: Другие

инженерные мероприятия
- И11: Другие

управленческие мероприятия
- У7: Другие
Пояснения:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Use of leguminous plants
Specification of other structural measures: Water retension ditches with fanya chini bunds and ties.
Specification of other management measures: Temporal substitution of a dominant crop by non disease host crops for pathogen distruction
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

биологическая деградация
- Бб: рост числа вредителей/болезней

деградация водных ресурсов
- Ва: почвенная засуха
Пояснения:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation on slopy land and nutrient mining without replenishment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor practices that encourage spread of BXW.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (No use of cross slope barriers.), change in temperature (Unproductive loos of green water due direct hit of of the soil by sunshine), change of seasonal rainfall (Due to climatic change and variability), poverty / wealth (Incapacity to invest in capital heavy conservation measures), labour availability (Rural to Urban migration of the enegetic youths), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (High input expenses.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Ignorance of SLM and shortage of field extension workers.), governance / institutional (Low capacity of rural based environmental/land committees)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Due unpredictable climatic change and variability), population pressure (Continuous land fragmentation)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
Пояснения:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Most of the concepts and principles were taught to field/agricultural advisers at the college.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (New innovations and change of mind set is crucial e.g. the use of A-frame, the principle behind BXW and cultural methods of controlling the disease.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyperania grass
Quantity/ density: 15 m3 /ha
Remarks: Across the slope
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure
Quantity/ density: 40ton/ha
Remarks: 3 tin applied to each banana plant.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: pegion peas
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pineapples
Grass species: lemmon grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 12
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70
Construction material (earth): Soil
Other type of management: Temporal substitution of the a diseased plant with other non-host plants for staving and complete wipe out of the disease causing pathogen. (BXW affected bananas substituted with maize and beans)
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
2.353
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | Управленческие | |
| 2. | Initial manure application (before banana planting) | Управленческие | |
| 3. | Initial banana seedlings (certified varieties) | Управленческие | |
| 4. | Initial mulching application | Управленческие | |
| 5. | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants in affected fields. | Агрономические | Before onstart of rain |
| 6. | Land tilling and harrowing. | Агрономические | Before onstart of rain |
| 7. | Planting of alternative crops (maize and beans) for starving and killing the pathogen. | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | After the first rains (usually September) |
| 8. | Demarcation of contour line using A-frame for construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | Инженерные | December |
| 9. | Digging and construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | Инженерные | December |
| 10. | Planting of lemon grass , pineapples and pigeon peas on bunds. | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | After constrution of fanya chini retension ditches with ties |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Planting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 5,0 | 2,353 | 11,77 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Demarcation of contour line | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,26857 | 15,88 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Digging and construction of Fanya | persons/day | 10,0 | 2,353 | 23,53 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | ha | 1,0 | 76,47 | 76,47 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Lemon grass and pidgeon seeds | kgs | 5,0 | 2,94 | 14,7 | |
| Посадочный материал | Pineapple seedlings | pieces | 513,0 | 0,0588304 | 30,18 | |
| Посадочный материал | Initial banana seedlings | pieces | 660,0 | 0,441181818 | 291,18 | |
| Посадочный материал | Maize and bean seeds | kgs | 81,0 | 0,947654 | 76,76 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Initial mulching application | bundles | 900,0 | 0,1764666 | 158,82 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Initial manure application | tons | 28,0 | 10,084 | 282,35 | |
| Другие | Labour: Land tilling and harrowing | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Planting of alternative crops | persons/day | 9,0 | 2,353 | 21,18 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 1054,58 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting and hole digging for planting bananas | Агрономические | Before onstart of rain |
| 2. | Manure application before planting Banana | Агрономические | Before onstart of rain |
| 3. | Banana planting | Агрономические | one to two months after manure application |
| 4. | Recurrent mulching application | Агрономические | once per season |
| 5. | Hand weeding to control noxious weeds, De-suckering, De-trashing and trimming | Агрономические | April and December |
| 6. | Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector | Агрономические | Routinely as need be |
| 7. | Recurrent manure application | Агрономические | September/October |
| 8. | Banana harvesting | Агрономические | Routinely after mature |
| 9. | Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas. | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | April |
| 10. | harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 11. | Removal of sediments and reshaping/maintenance of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | Инженерные | May |
| 12. | Weeding and thinning | Управленческие | (twice) first and second |
| 13. | Harvesting of maize and beans. | Управленческие | January/February |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting | persons/day | 35,0 | 2,353 | 82,36 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Manure application before planting Banana | persons/day | 33,0 | 2,353 | 77,65 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Banana planting | persons/day | 13,0 | 2,353 | 30,59 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Recurrent mulching applicatio | persons/day | 6,0 | 2,205 | 13,23 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Mulching material | bundles | 900,0 | 0,176464 | 158,82 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Compost/manure | tons | 16,0 | 13,235 | 211,76 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Labour: Maintenance of Fanya chini | persons/day | 3,0 | 2,353 | 7,06 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Labour: Weeding an thinning | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05916 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Labour: Harvesting of maize and beans | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05915 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Hand weeding to control noxious weeds | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Recurrent manure application | persons/day | 22,0 | 2,353 | 51,77 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Banana harvesting | persons/day | 16,5 | 2,353 | 38,82 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Labour: Harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 825,02 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattocks and forked wooden poles., Hand hoe, forked hole and machetes, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, spade, mattock and A-frame, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattock.
The above cost were calculated per unit of one land user's land (1.5 acres) where the technology was applied and estimate also done per hectare.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Manure is the most determinant factor
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature is 21°C
Average length of growing period is 210 days.
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil texture (topsoil): The average soil texture is sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Low use and application of mulching and cover crops
Soil fertility is low due to continue washout of the soil surface with rainfall runoff
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium because slope effect minimize the time required for water to infiltrate into the soil.
Soil water storage capacity is low because of low amount of humus and underused of mulching
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Only a few perennials and annual crops and minimal fauna diversity due to the washout of organic matter by rainfall runoff
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанное (самообеспечение/ товарное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
- обеспеченный
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the land users who are using the technology are running petty business and groceries (selling local brew).
Level of mechanization: Dominated by the use of small tools/implements.
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Количество до применения УЗП :
5 fingers
Количество после применения УЗП:
12 fingers
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased banana yield due to use of SLM and good husbandry practices
риск потери продуктивности
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Risk due to low moisture
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Caused by the use of mulching and manure
доходы хозяйства
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Income accrued from increased production and diversification to pineapples and lemon grass
объем работ
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Attributable to added tasks from use of SLM
Социальное и культурное воздействие
состояние здоровья
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Improved nutrition from e.g. introduction of pineapples
местное самоуправление
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Use of FFS have induced togetherness and group working spirit
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
SLM knowledge and skills gained through FFS trainings
положение социально и экономически уязвимых групп населения
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Indiscriminate participation of all genders, age and ethnicity
livelihood and human well-being
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Initially the technology has resulted to increased production, diversification to production of other income generating crops and dietary enrichment crops. The overall result is farmers capacity to meet education and health expenses
attraction to theiving
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Good looking banana bunches attract thieving
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Use of mulching and water retension ditches
Почвы
влажность почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Following use of mulching and manure
почвенный покров
Количество до применения УЗП :
40%
Количество после применения УЗП:
90%
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Improved soil coved caused by the use of grass mulching
утрата почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Controll of soil erosion attributable to use of mulching and construction of water retension ditches.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Use of luguminous plants, application of manure and mulching
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Use of manure
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Количество до применения УЗП :
40%
Количество после применения УЗП:
90%
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Biomass result from use of mulching and improved managment of crop residuals
разнообразие фауны
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased richness of soil fauna caused by the use of manure
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Количество до применения УЗП :
0%
Количество после применения УЗП:
95%
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Control of BXW
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
влияние засух
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased tolerance to drought and BXW infestation
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Managment of crop residues and manure
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Of the neighbouring Kashasha wetland
ущерб прилегающим полям
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
ущерб объектам инфраструктуры общего/ частного пользования
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | не известно |
| местные ураганы | не известно |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | плохо |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | хорошо |
Пояснения:
Retention ditches supported with ties to prevent flow of water and to encourage evenly distribution of water. The fanya chini bunds are stabilized by planting vegetation on them (pineapples, pigeon peas and lemon grass).
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Пояснения:
The high investment costs cause slight realization of rewards but in the long run very positive benefits are realized by land users.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- более 50%
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
42 households covering 77 percent of the stated area
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 10-50%
Пояснения:
42 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Supplied with banana suckers, farm yard manure and grass mulch.
42 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: land users who received suckers from neighbors but procured grass mulch and manure.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: most of the land users are impressed with the results attributable to the technology in terms of control of BXW, increased banana production, control of soil erosion and promising increase in income.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| The technology useful to the community and is easy to learn. |
| Encouraging results in terms of improved productivity and general performance of banana and other crops like coffee within the technology area attributable to use of technology. |
| The technology has made significant achievement in terms of decrease of BXW infestation. |
| Soil health has improved as the result of use of mulching materials, manure, leguminous plants and application water harvesting cross slope barriers. |
| There is positive change of mind set towards the use of SLM |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Good and attractive crops that consumers are willing to purchase at a high price have resulted to emergence of thieving. | Spread the technology and supply improved banana suckers to other farmers so that more farmers are engaged in banana production. Strengthen community police. |
| The technology initially is labour and capital intensive | Encourage group working spirit. |
| Unplanned Changes of service providers which may fall in the hands of untrustworthy service providers. | Pluralism in service delivery should be planned with doubly consciousness to take care of untrustworthy service providers. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей