Jatropha curcas hedge [Эфиопия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Simon Bach
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Fabian Ottiger
Agulo Keter
technologies_1524 - Эфиопия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Ayele Habtamu
+251 92 592 0594
Haramaya University
Haramaya University, P.O. Box 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
Эфиопия
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Haramaya University (HU) - Эфиопия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
30/04/2011
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Gully rehabilitation and hill stabilization with Jatropha hedges.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
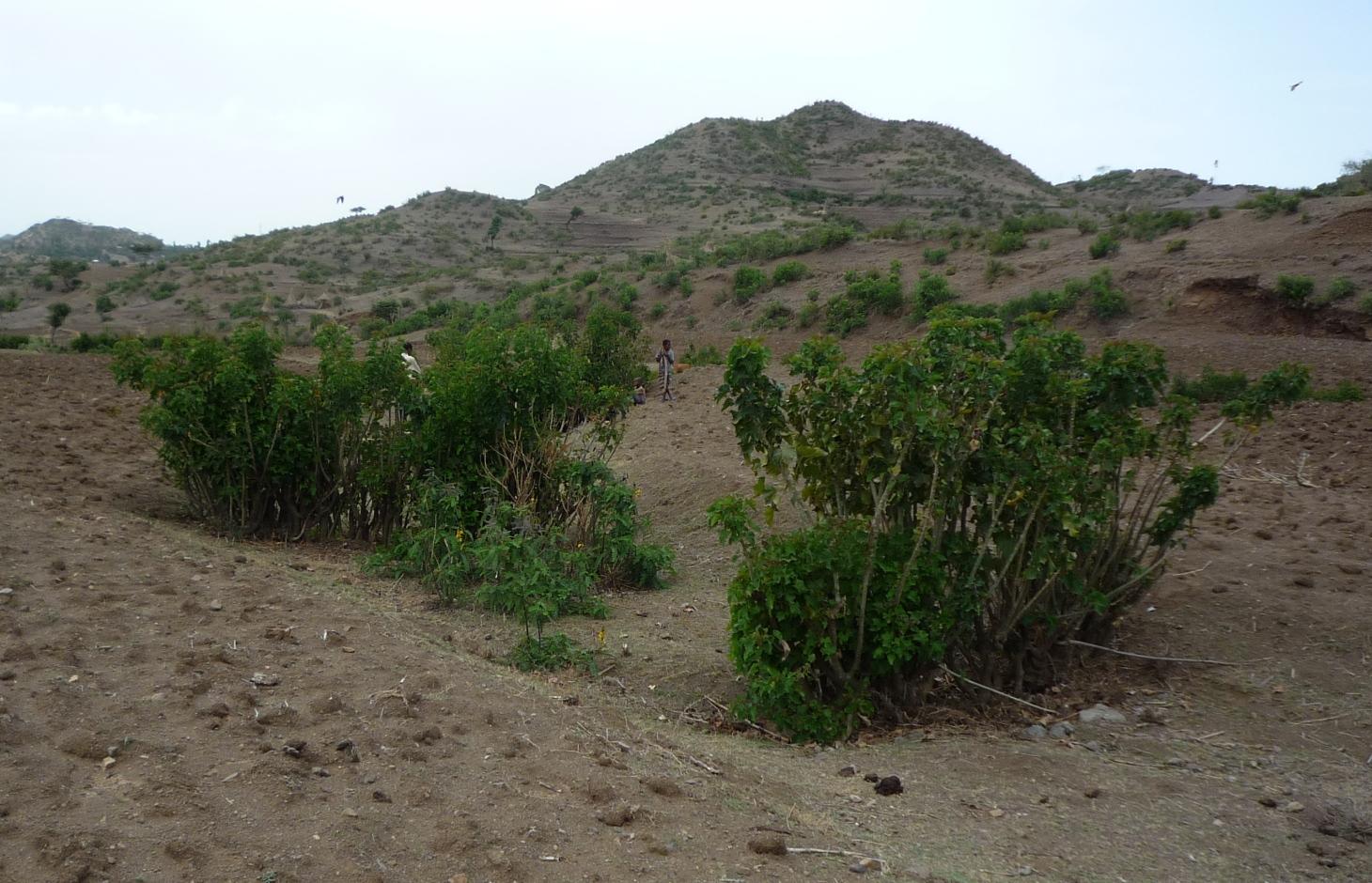
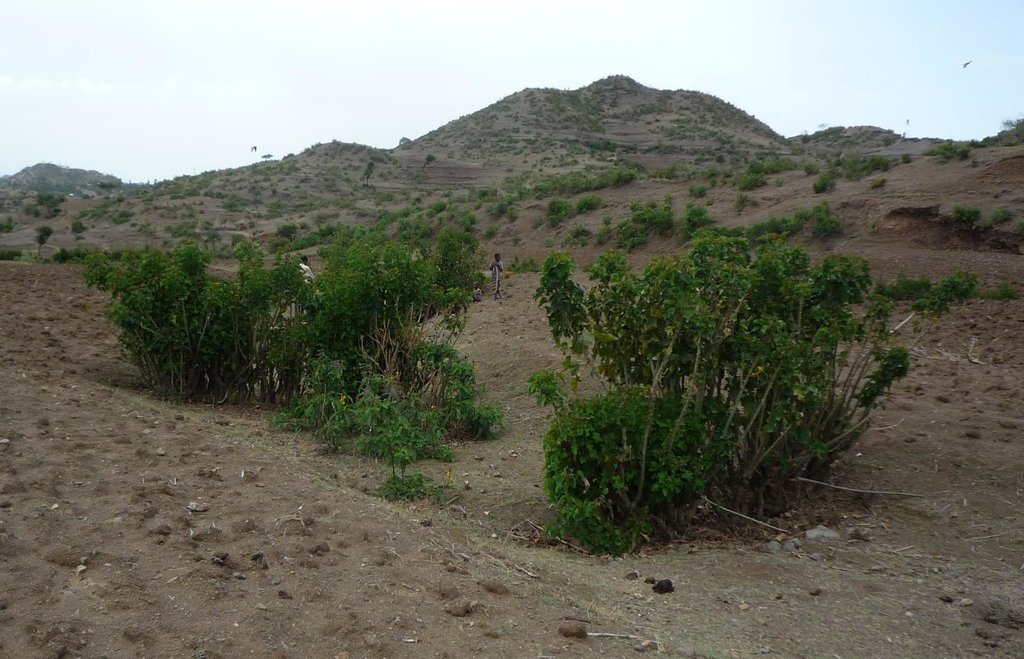
In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Эфиопия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
Более точная привязка места:
Bati
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- 10-50 лет назад
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Farmers are using Jatropha curcas since approximately 30 years in the research area in Bati mostly for fencing. Innovative farmers started using the plant for stabilizing existing physical structures (stone walls, terraces, gully check dams) or using it as a complete substitute for these physical structures.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
Major food crop: Sorghum
Major other crop: Corn

Смешанное землепользование (пашня/ пастбища/ лес), включая агролесоводство
- Лесо-пастбищное хозяйство
Основные виды продукции/ услуг:
Major food product: Cattle, goat, sheep, camel
Major other product: Chicken
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Type of grazing system comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues. Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Пояснения:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September
Поголовье скота на единицу площади (если применимо):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Size of the case study watershed.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров

инженерные мероприятия
- И1: Террасирование
- И6: Стенки, барьеры, заборы, изгороди
Пояснения:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (60% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
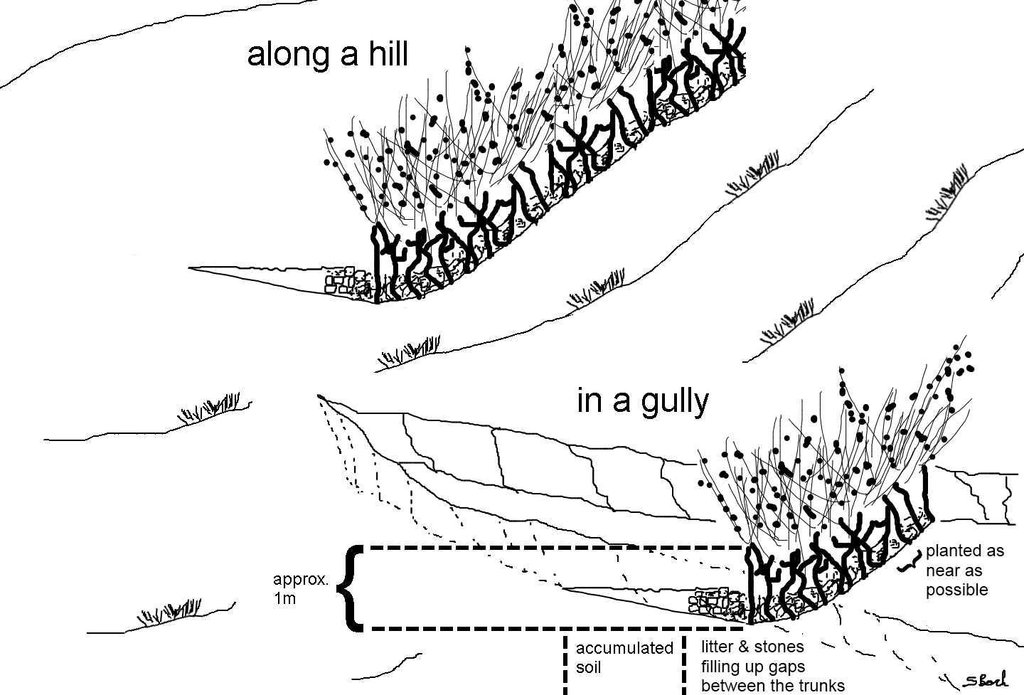
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
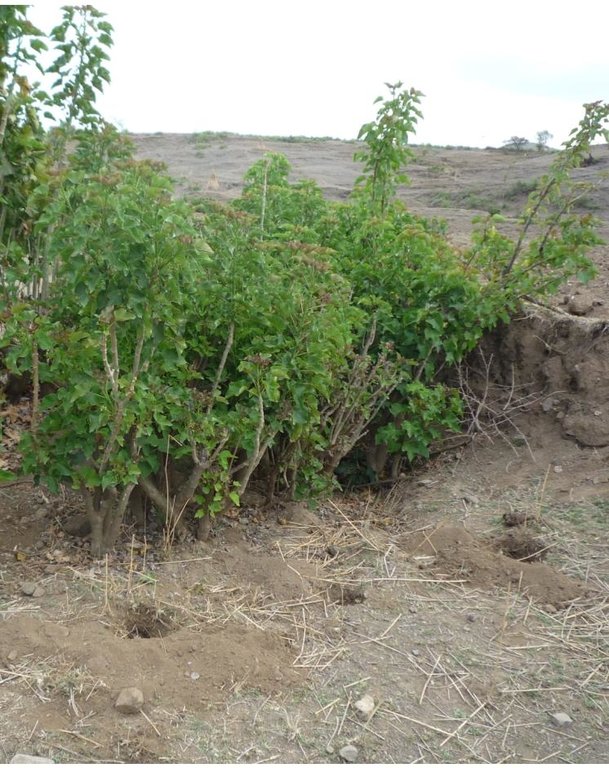
Jatropha hedges as they can be found in the region of Bati. Often the plant is used for gully rehabilitation. For that purpose it is planted (mostly by cuttings) with a minimal interval between each plant to create a barrier-like hedge. The gaps are filled up with litter or stones.
Approximately 1 m of soil can be collected by the trunk - above that height it is too thin. The Jatropha seed can create additional income besides the purpose of soil and water conservation. Often, the plant is used in combination with traditional technologies (terraces, stone walls) and planted on top or in front of these traditional structures to improve their stability.
Location: South of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 05.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Planting takes place rather randomly in places of needs.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10 per m
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~20m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Vegetative measure: filling material
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha curcas
Other species: Stones, shrubs, sticks - things that can be found and utilized to fill up gaps between each plant.
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Ethiopian Birr
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
16,82
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
1.00
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | One time initial sawing of Jatropha seeds (30 years ago). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Initial. Wet season. |
| 2. | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | dry season |
| 3. | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | dry season |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Seeding | person day | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools for cutting | 500m | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds | kg | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 33,0 | |||||
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of Jatropha seeds (5 person days needed). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Off farming season(Okt.) |
| 2. | Filling up the gaps with litter (5 person days needed). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | If necessary |
| 3. | Pruning of the Jatropha hedges (15 person days needed). | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Yearly before wet season. |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15,0 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools | Person days | 15,0 | 0,333333333 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Wood | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Строительные материалы | Stone | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 30,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: saw, axe
Total costs of a hectare are calculated for a hedge of 100 m length every 20 m (500 m total hedge) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
751-1000 mm ranked 1
501-750 mm ranked 2
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Thermal climate class: tropics
LGP shorter than 90 days.
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1), shallow (ranked 2)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
недостаточны/ отсутствуют
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Ground water table is unknown.
Availability of surface water: Only during rainy season
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- обеспеченный
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Комментарий/ пояснения:
gullies are transformed to fields
риск потери продуктивности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
improving soil moisture
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
управление землями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
производство электроэнергии
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
Доступность и качество воды
доступность питьевой воды
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
new fields lead to higher productivity
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
экономическое неравенство
Комментарий/ пояснения:
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
объем работ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
additional space for new fields
местное самоуправление
институты госуправления
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
positive examples for other land users
положение социально и экономически уязвимых групп населения
Комментарий/ пояснения:
up -downstream problems may be solved
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
количество воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased soil moisture
сбор воды/ водоудержание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
уровень грунтовых/ подземных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased infiltration
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas canopy
утрата почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased rooting
уплотнение почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased rooting
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas biomass
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
разнообразие фауны
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
полезные виды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
разнообразие местообитаний
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
new habitat for rodents etc.
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
последствия наводнений
Комментарий/ пояснения:
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
little effect by additional plants
риск пожаров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
скорость ветра
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
Другие экологические последствия
Increased competition
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Over water and sunlight
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
доступность воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
possibility of spring development
надежность и постоянство водотоков
Комментарий/ пояснения:
if a spring can develop
подтопление ниже по течению
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
отложение наносов ниже по течению
Комментарий/ пояснения:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
загрязнение подземных/ речных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increased infiltration
отложения, переносимые ветром
ущерб прилегающим полям
Комментарий/ пояснения:
due to gully rehabilitation
ущерб объектам инфраструктуры общего/ частного пользования
Комментарий/ пояснения:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | хорошо |
| местные ураганы | хорошо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | не известно |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | хорошо |
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо отрицательное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Пояснения:
Establishment needs a little time, although not very much. Maintenance work is very little needed and can be done if needed or in off-farming season. Establishment and mainentance costs are none or very little.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 90-100%
Пояснения:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local technology spread from farmer to farmer.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Completely based on farmer's initiative.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A lot of farmer are adopting (or already have adopted) Jatropha curcas as a SWC technology in the region.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Soil and water conservation are very important. Also the conservation of soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create farmer's awareness that SWC is very important for a sustainable land management. |
|
In combination, Jatropha curcas can also be used to stabilize traditional stone structuress (terraces, dams). These physical structures are not consideret very stable and need a lot of work to establish and maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further research to improve physical structures, Jatropha curcas structures as well as their combination. |
|
The roots bind the soil and holding it together and help collecting additional soil that otherwise would be washed out. The root and the plant also help to slow down flowing water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research on how tolerant is the plant on flooding etc. |
|
Jatropha curcas is also a very good life fence that animals do not browse through because the leaves are poisonous. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
|
The seeds can be sold. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Creating and improving markets, infrastructures and technologies that need Jatropca curcas oil or biofuel. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Very low labor and money input for establishment and maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the technology as simple as it is today. |
|
Easy to atopt in a wide range of environments (Jatroha curcas is a rather tolerant plant). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Additional research to improve knowledge of Jatropha curcas. |
|
Selling of the seeds is an additional income. If the seeds are crushed to oil it can substitute for example lamp oil that has to be bought. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve market situation and find technologies suitable to use Jatropha curcas oil or biofuel. |
|
The plant can be used in a wide range of rehabilitation purposes (gully rehabilitation, hill stabilization, improvment of micro climate etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create and maintain awareness of the farmers. |
|
If plantet on bare land only, the plant does not compete with food production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sensitize the farmers that food is more important than gaining an extra income so they do not give up their fields for Jatropha seed production. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| If children eat the seeds they get sick. | Rise awareness that the plant is poisonous. |
| Plant competes for soil moisture. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Plant competes for sun light. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Jatropha curcas is an alien plant although it is used for more than 30 years in the region. | Research on the long term effects of Jatropha curcas in specific areas. |
| If the plant should reach maximum yields inputs have to be increased as well and it has to be planted on fertile soil (food competition). | Make shure people only use it as fence or as a SWC plant on bare land. |
| To avoid shading the plant is often pruned every year and the yield is therefore very small (economically irrelevant). | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade to maximize yield. |
| The plant is poisonous. People have to take care and children have to be sensitized. But acording to the farmers eating the leaves or the seeds leads to stomach ache and is not too dangerous. | Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
| Farmers plant and use Jatropha curcas quite randomly and without any specific approach. | The role of science: find the best practice. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей